1
/
of
10
PayPal, credit cards. Download editable-PDF & invoice in 1 second!
GB 27953-2020 English PDF
GB 27953-2020 English PDF
Regular price
$155.00 USD
Regular price
Sale price
$155.00 USD
Unit price
/
per
Shipping calculated at checkout.
Couldn't load pickup availability
Delivery: 3 seconds. Download true-PDF + Invoice.
Get QUOTATION in 1-minute: Click GB 27953-2020
Historical versions: GB 27953-2020
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll if blank)
GB 27953-2020: General requirements on disinfectant for infectious focus
GB 27953-2020
NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE
PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 11.080
C 50
Replacing GB 27953-2011
General Requirements on Disinfectant for Infectious
Focus
ISSUED ON: APRIL 09, 2020
IMPLEMENTED ON: NOVEMBER 01, 2020
Issued by: State Administration for Market Regulation;
Standardization Administration of PRC.
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
1 Scope ... 5
2 Normative References ... 5
3 Terms and Definitions ... 5
4 Raw Material Requirements ... 6
5 Technical Requirements ... 6
6 Inspection Methods ... 7
7 Use Methods ... 7
8 Label and Instruction Manual ... 18
Foreword
All the technical contents in this Standard are mandatory.
This Standard was drafted as per the rules specified in GB/T 1.1-2009.
This Standard replaced GB 27953-2011 Hygienic Requirements of Disinfectant for
Infectious Focus. Compared with GB 29753-2011, this Standard has the major
technical changes as follows:
--- Add the normative references (see Clause 2 of this Edition);
--- Add terms and definitions of “concurrent disinfection”, “terminal disinfection” (see
Clause 3 of this Edition);
--- Add requirements of raw materials (see Clause 4 of this Edition);
--- Add the range of killing pathogenic microorganisms (see 7.1.1.1, 7.1.1.3, 7.1.1.4,
7.1.1.5, 7.1.1.6 of this Edition);
--- Add the selection requirements for disinfectants for contaminants of pathogens
of blood-borne infectious disease and special infectious disease (7.1.1.5, 7.1.1.6
of this Edition);
--- Include the label instruction manual requirements and precautions into Clause 8;
modify the precautions (see 8.1, 8.2 of this Edition);
--- Delete Appendix A; modify the dosage of the disinfectant; after adding the
treatment method of the prion contaminant, include it into the text (see 7.2 of this
Edition; Appendix A of 2011 Edition);
--- Delete the disinfection contents of drinking water, fruits and vegetables, hands
and skin (see 5.2.3, 5.2.4, 5.2.6 of 2011 Edition).
This Standard was proposed by and under the jurisdiction of National Health
Commission of PRC.
Drafting organizations of this Standard: Hebei Provincial Center for Disease Control
and Prevention; National Institute of Environmental Health, China CDC; the PLA
Center for Disease Control and Prevention; Jiangsu Provincial Health Supervision
Institute; Shandong Center for Disease Control and Prevention; Shanghai Municipal
Center for Disease Control and Prevention; and Zhejiang Provincial Center for Disease
Control and Prevention.
Chief Drafting staffs of this Standard: Chen Suliang, Han Yanshu, Zhang Liubo, Sun
Yinqi, Ban Haiqun, Cui Yujie, Sun Keqin, Wang Qian, Zhang Haixia, Wang Jinyan, Yao
Chushui, Li Xinwu, Gu Jian, Cui Shuyu, Zhu Renyi, Hu Guoqing, and Sun Huihui.
The historical edition replaced by this Standard is as follows:
--- GB 17953-2011.
General Requirements on Disinfectant for
Infectious Focus
1 Scope
This Standard specifies the raw material requirements, technical requirements,
inspection methods, use methods, labels and instruction manual for disinfectants used
for disinfection of epidemic disease of infectious focus.
This Standard applies to disinfectants that disinfect the epidemic source of infectious
diseases or the environment contaminated by infectious pathogens.
2 Normative References
The following documents are essential to the application of this document. For the
dated documents, only the versions with the dates indicated are applicable to this
document; for the undated documents, only the latest version (including all the
amendments) are applicable to this document.
GB 19193 General Principle on Disinfection for Infectious Focus
WS/T 367 Regulation of Disinfection Technique in Healthcare Settings
Technical Standard for Disinfection (2002 Edition) [Ministry of Health (WFJF [2002]
No.282)]
Hygienic Standard for Factories Producing Disinfectants (2009 Edition) [Ministry
of Health (WJDF [2009] No.53)]
3 Terms and Definitions
For the purpose of this Document, the following terms and definitions apply.
3.1 Infectious focus
The place where the source of infection exists or existed; or the scope of the source of
infection may spread the pathogen.
3.2 Disinfection for infectious focus
Disinfection (2002 Edition), national standards and related regulations. After taking
effective protective measures, it shall not cause harm to users' health.
6 Inspection Methods
6.1 Physical and chemical indicators
It shall be tested according to the method specified in Technical Standard for
Disinfection (2002 Edition) and/or relevant standard.
6.2 Killing microorganism effect
It shall be tested according to the method specified in Technical Standard for
Disinfection (2002 Edition) and/or relevant standard. The test methods for the target
microorganism of the infectious disease can refer to the relevant standards or test
technical specifications.
6.3 Toxicology test
It shall be tested according to the method specified in Technical Standard for
Disinfection (2002 Edition) and/or relevant standard.
7 Use Methods
7.1 Selection of commonly-used disinfectant
7.1.1 Determine the commonly used disinfectants according to the types and
resistance of contaminated pathogens
7.1.1.1 Prion contaminants: select chlorine disinfectant or sodium hydroxide, combined
with pressure steam for sterilization method.
7.1.1.2 Spore contaminants (such as Bacillus anthracis, Clostridium tetani, etc.):
Select disinfectants containing chlorine, peroxides, bromine and formaldehyde, etc.
7.1.1.3 Mycobacteria (such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycobacterium leprae),
hydrophilic viruses (such as poliovirus, norovirus, adenovirus, rotavirus, hepatitis A
virus, hepatitis E virus and pathogens that cause hand, foot and mouth disease),
mycoplasma, chlamydia, rickettsiae and other pathogen contaminants: Select
disinfectants containing chlorine, bromine, peroxides, aldehydes and iodine, etc.
7.1.1.4 Bacterial propagules (such as Vibrio cholerae, Shigella shigae,
Corynebacterium diphtheriae, Salmonella typhi and Paratyphoid, Brucella, Neisseria
gonorrhoeae, etc.), Nonlipid-coated viruses (such as influenza virus, measles virus,
Hantavirus, etc.) and the contaminants of pathogens such as spirochetes: select
disinfectants containing chlorine, bromine, peroxides, aldehydes, iodine, alcohols,
guanidines, quaternary ammonium salts, etc.
7.1.1.5 For contaminants of pathogens (such as hepatitis B virus, hepatitis C virus,
hepatitis D virus, human immunodeficiency virus, etc.) that are susceptible to organic
matter and cause serious diseases, high-level disinfectants shall be used, such as
disinfectants containing chlorine, bromine and peroxide, etc.
7.1.1.6 For contaminants of pathogens of special infectious diseases (such as SARS-
Coronavirus, MERS-Coronavirus, Ebola virus, highly pathogenic avian influenza virus,
H7N9 avian influenza virus, Yersinia pestis and rabies virus), it shall be carried out
according to the relevant guideline formulated by the country.
7.1.1.7 For contaminants of unidentified pathogens, determine the applicable
disinfectant according to 7.1.1.2.
7.1.2 Commonly-used disinfectants determined according to the disinfection
objects contaminated by pathogens
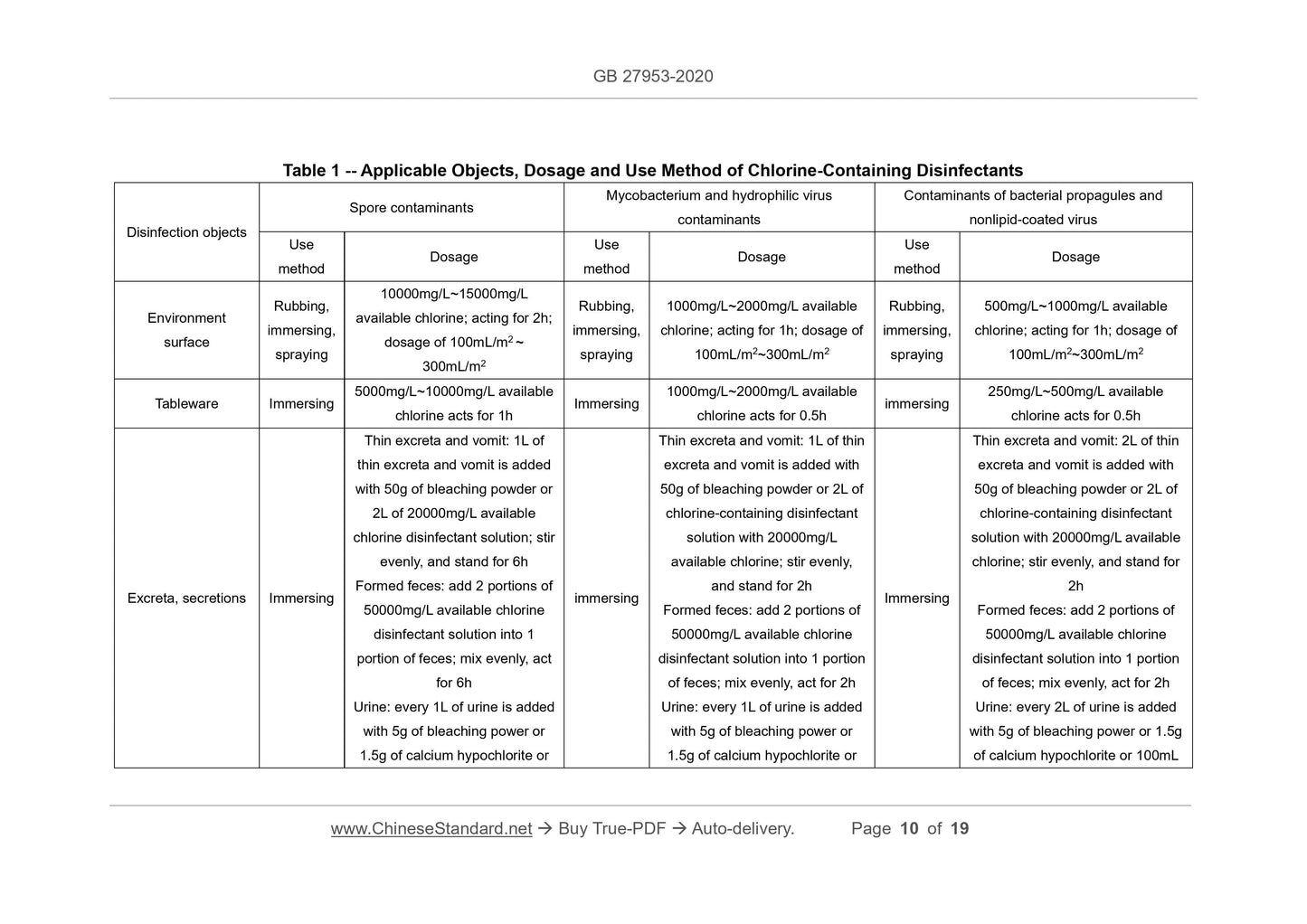
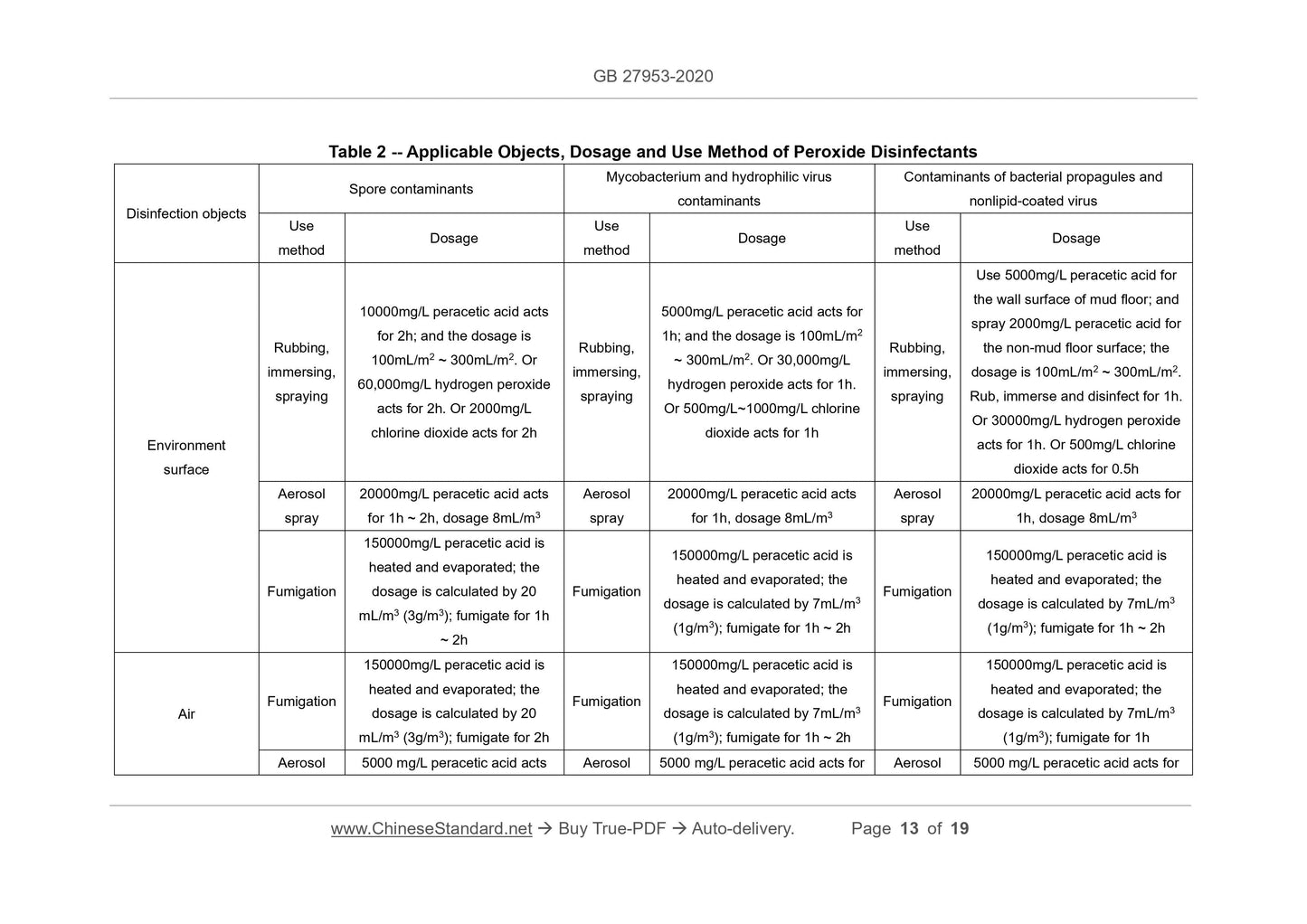
7.1.2.1 Commonly-used surface disinfectants: chlorine-containing, bromine-containing
and peroxide disinfectants, etc.
7.1.2.2 Commonly-used air disinfectants: peroxide disinfectants (such as per...
Get QUOTATION in 1-minute: Click GB 27953-2020
Historical versions: GB 27953-2020
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll if blank)
GB 27953-2020: General requirements on disinfectant for infectious focus
GB 27953-2020
NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE
PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 11.080
C 50
Replacing GB 27953-2011
General Requirements on Disinfectant for Infectious
Focus
ISSUED ON: APRIL 09, 2020
IMPLEMENTED ON: NOVEMBER 01, 2020
Issued by: State Administration for Market Regulation;
Standardization Administration of PRC.
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
1 Scope ... 5
2 Normative References ... 5
3 Terms and Definitions ... 5
4 Raw Material Requirements ... 6
5 Technical Requirements ... 6
6 Inspection Methods ... 7
7 Use Methods ... 7
8 Label and Instruction Manual ... 18
Foreword
All the technical contents in this Standard are mandatory.
This Standard was drafted as per the rules specified in GB/T 1.1-2009.
This Standard replaced GB 27953-2011 Hygienic Requirements of Disinfectant for
Infectious Focus. Compared with GB 29753-2011, this Standard has the major
technical changes as follows:
--- Add the normative references (see Clause 2 of this Edition);
--- Add terms and definitions of “concurrent disinfection”, “terminal disinfection” (see
Clause 3 of this Edition);
--- Add requirements of raw materials (see Clause 4 of this Edition);
--- Add the range of killing pathogenic microorganisms (see 7.1.1.1, 7.1.1.3, 7.1.1.4,
7.1.1.5, 7.1.1.6 of this Edition);
--- Add the selection requirements for disinfectants for contaminants of pathogens
of blood-borne infectious disease and special infectious disease (7.1.1.5, 7.1.1.6
of this Edition);
--- Include the label instruction manual requirements and precautions into Clause 8;
modify the precautions (see 8.1, 8.2 of this Edition);
--- Delete Appendix A; modify the dosage of the disinfectant; after adding the
treatment method of the prion contaminant, include it into the text (see 7.2 of this
Edition; Appendix A of 2011 Edition);
--- Delete the disinfection contents of drinking water, fruits and vegetables, hands
and skin (see 5.2.3, 5.2.4, 5.2.6 of 2011 Edition).
This Standard was proposed by and under the jurisdiction of National Health
Commission of PRC.
Drafting organizations of this Standard: Hebei Provincial Center for Disease Control
and Prevention; National Institute of Environmental Health, China CDC; the PLA
Center for Disease Control and Prevention; Jiangsu Provincial Health Supervision
Institute; Shandong Center for Disease Control and Prevention; Shanghai Municipal
Center for Disease Control and Prevention; and Zhejiang Provincial Center for Disease
Control and Prevention.
Chief Drafting staffs of this Standard: Chen Suliang, Han Yanshu, Zhang Liubo, Sun
Yinqi, Ban Haiqun, Cui Yujie, Sun Keqin, Wang Qian, Zhang Haixia, Wang Jinyan, Yao
Chushui, Li Xinwu, Gu Jian, Cui Shuyu, Zhu Renyi, Hu Guoqing, and Sun Huihui.
The historical edition replaced by this Standard is as follows:
--- GB 17953-2011.
General Requirements on Disinfectant for
Infectious Focus
1 Scope
This Standard specifies the raw material requirements, technical requirements,
inspection methods, use methods, labels and instruction manual for disinfectants used
for disinfection of epidemic disease of infectious focus.
This Standard applies to disinfectants that disinfect the epidemic source of infectious
diseases or the environment contaminated by infectious pathogens.
2 Normative References
The following documents are essential to the application of this document. For the
dated documents, only the versions with the dates indicated are applicable to this
document; for the undated documents, only the latest version (including all the
amendments) are applicable to this document.
GB 19193 General Principle on Disinfection for Infectious Focus
WS/T 367 Regulation of Disinfection Technique in Healthcare Settings
Technical Standard for Disinfection (2002 Edition) [Ministry of Health (WFJF [2002]
No.282)]
Hygienic Standard for Factories Producing Disinfectants (2009 Edition) [Ministry
of Health (WJDF [2009] No.53)]
3 Terms and Definitions
For the purpose of this Document, the following terms and definitions apply.
3.1 Infectious focus
The place where the source of infection exists or existed; or the scope of the source of
infection may spread the pathogen.
3.2 Disinfection for infectious focus
Disinfection (2002 Edition), national standards and related regulations. After taking
effective protective measures, it shall not cause harm to users' health.
6 Inspection Methods
6.1 Physical and chemical indicators
It shall be tested according to the method specified in Technical Standard for
Disinfection (2002 Edition) and/or relevant standard.
6.2 Killing microorganism effect
It shall be tested according to the method specified in Technical Standard for
Disinfection (2002 Edition) and/or relevant standard. The test methods for the target
microorganism of the infectious disease can refer to the relevant standards or test
technical specifications.
6.3 Toxicology test
It shall be tested according to the method specified in Technical Standard for
Disinfection (2002 Edition) and/or relevant standard.
7 Use Methods
7.1 Selection of commonly-used disinfectant
7.1.1 Determine the commonly used disinfectants according to the types and
resistance of contaminated pathogens
7.1.1.1 Prion contaminants: select chlorine disinfectant or sodium hydroxide, combined
with pressure steam for sterilization method.
7.1.1.2 Spore contaminants (such as Bacillus anthracis, Clostridium tetani, etc.):
Select disinfectants containing chlorine, peroxides, bromine and formaldehyde, etc.
7.1.1.3 Mycobacteria (such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycobacterium leprae),
hydrophilic viruses (such as poliovirus, norovirus, adenovirus, rotavirus, hepatitis A
virus, hepatitis E virus and pathogens that cause hand, foot and mouth disease),
mycoplasma, chlamydia, rickettsiae and other pathogen contaminants: Select
disinfectants containing chlorine, bromine, peroxides, aldehydes and iodine, etc.
7.1.1.4 Bacterial propagules (such as Vibrio cholerae, Shigella shigae,
Corynebacterium diphtheriae, Salmonella typhi and Paratyphoid, Brucella, Neisseria
gonorrhoeae, etc.), Nonlipid-coated viruses (such as influenza virus, measles virus,
Hantavirus, etc.) and the contaminants of pathogens such as spirochetes: select
disinfectants containing chlorine, bromine, peroxides, aldehydes, iodine, alcohols,
guanidines, quaternary ammonium salts, etc.
7.1.1.5 For contaminants of pathogens (such as hepatitis B virus, hepatitis C virus,
hepatitis D virus, human immunodeficiency virus, etc.) that are susceptible to organic
matter and cause serious diseases, high-level disinfectants shall be used, such as
disinfectants containing chlorine, bromine and peroxide, etc.
7.1.1.6 For contaminants of pathogens of special infectious diseases (such as SARS-
Coronavirus, MERS-Coronavirus, Ebola virus, highly pathogenic avian influenza virus,
H7N9 avian influenza virus, Yersinia pestis and rabies virus), it shall be carried out
according to the relevant guideline formulated by the country.
7.1.1.7 For contaminants of unidentified pathogens, determine the applicable
disinfectant according to 7.1.1.2.
7.1.2 Commonly-used disinfectants determined according to the disinfection
objects contaminated by pathogens
7.1.2.1 Commonly-used surface disinfectants: chlorine-containing, bromine-containing
and peroxide disinfectants, etc.
7.1.2.2 Commonly-used air disinfectants: peroxide disinfectants (such as per...
Share