1
/
of
10
PayPal, credit cards. Download editable-PDF & invoice in 1 second!
GB 4789.5-2012 English PDF
GB 4789.5-2012 English PDF
Regular price
$85.00 USD
Regular price
Sale price
$85.00 USD
Unit price
/
per
Shipping calculated at checkout.
Couldn't load pickup availability
Delivery: 3 seconds. Download true-PDF + Invoice.
Get QUOTATION in 1-minute: Click GB 4789.5-2012
Historical versions: GB 4789.5-2012
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll if blank)
GB 4789.5-2012: National food safety standard -- Microbiological examination of food hygiene -- Examination of shigella
GB 4789.5‐2012
NATIONAL STANDARD
OF THE PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
National Food Safety Standard Microbiological
Examination of Food Hygiene - Examination of
Shigella
ISSUED ON. MAY 17, 2012
IMPLEMENTED ON. JULY 17, 2012
Issued by. Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China
GB
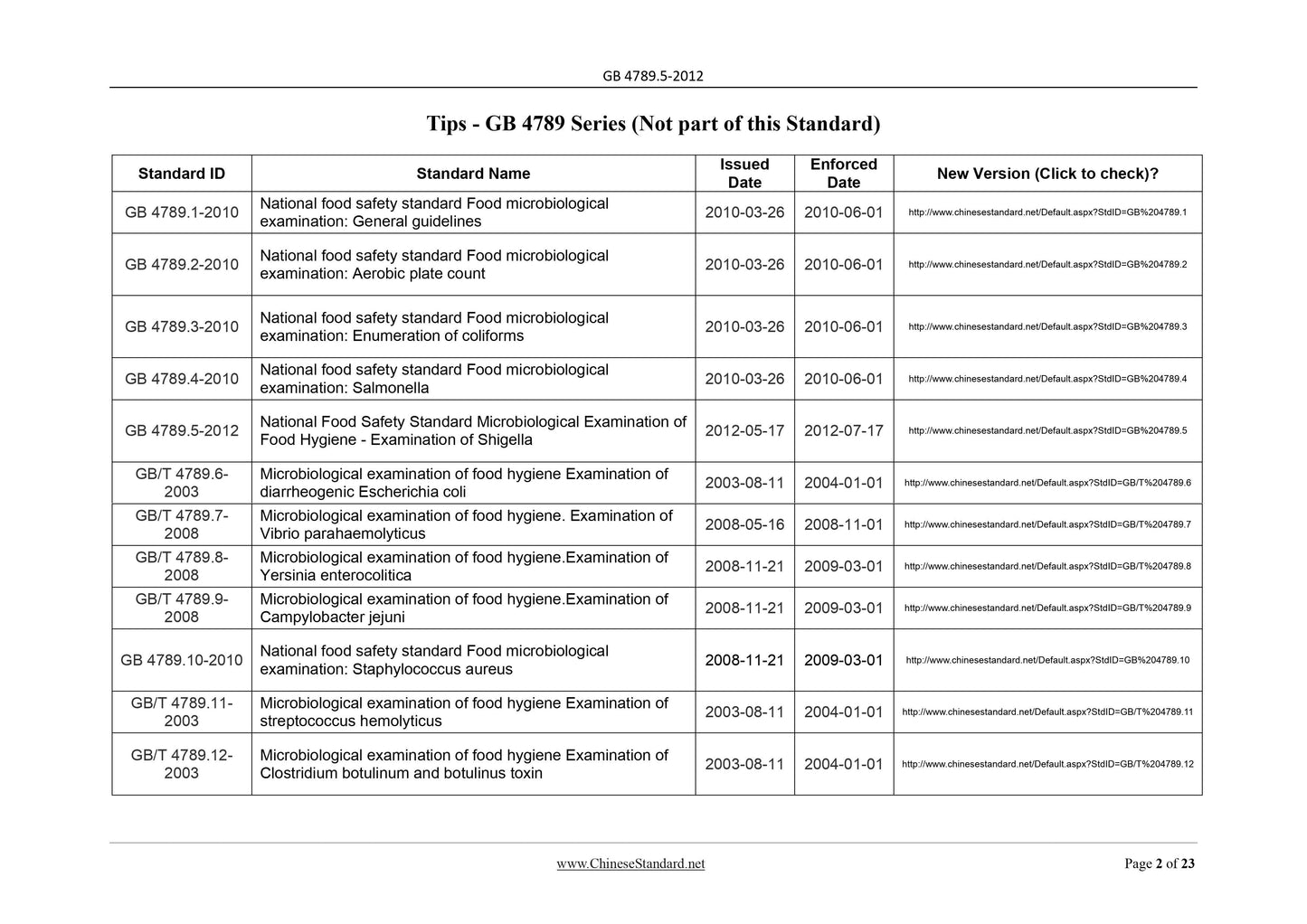
Tips - GB 4789 Series (Not part of this Standard)
Standard ID Standard Name Issued Date
Enforced
Date New Version (Click to check)?
GB/T 4789.6-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene Examination of
GB/T 4789.7-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene. Examination of
GB/T 4789.8-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene.Examination of
GB/T 4789.9-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene.Examination of
GB/T 4789.11-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene Examination of
GB/T 4789.12-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene Examination of
GB/T 4789.14-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene Examination of
GB/T 4789.16-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene Identification of
GB/T 4789.17-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene Examination of
GB/T 4789.19-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene Examination of
GB/T 4789.20-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene Examination of
GB/T 4789.21-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene Examination of
GB/T 4789.22-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene Examination of
GB/T 4789.23-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene Examination of
GB/T 4789.24-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene Examination of
GB/T 4789.25-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene Examination of
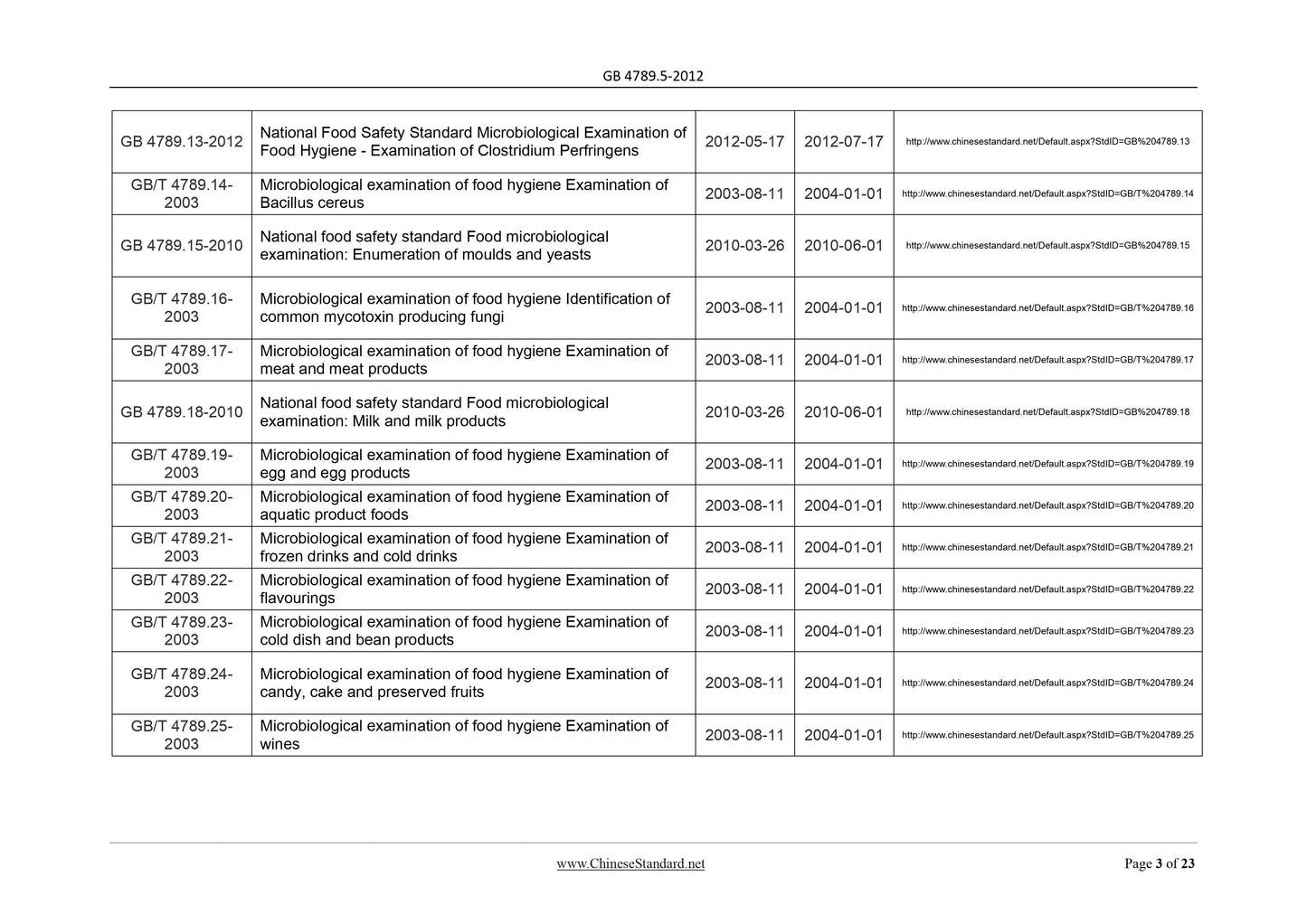
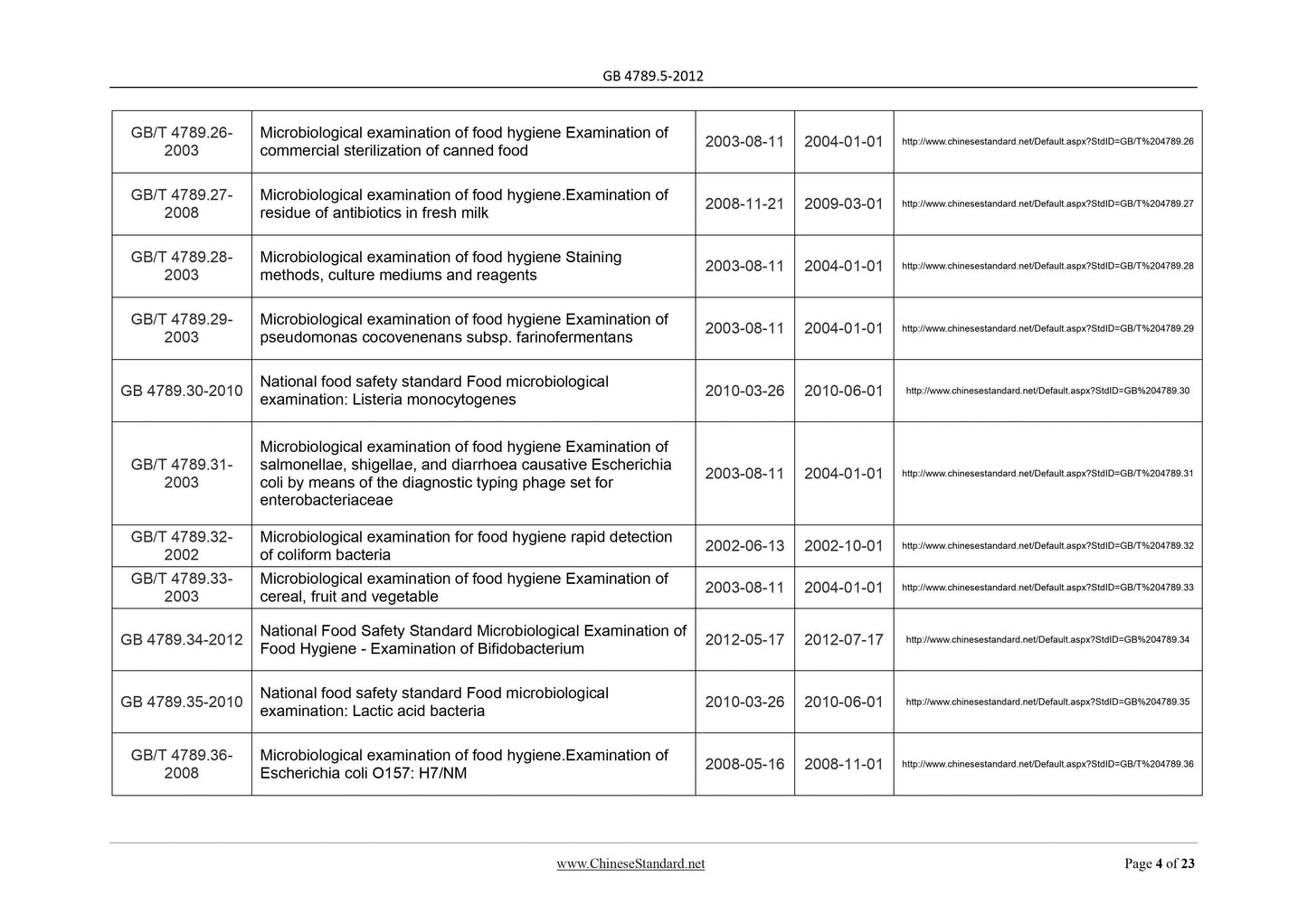
GB/T 4789.26-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene Examination of
GB/T 4789.27-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene.Examination of
GB/T 4789.28-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene Staining
GB/T 4789.29-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene Examination of
GB/T 4789.31-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene Examination of
salmonellae, shigellae, and diarrhoea causative Escherichia
coli by means of the diagnostic typing phage set for
enterobacteriaceae
GB/T 4789.32-
Microbiological examination for food hygiene rapid detection
GB/T 4789.33-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene Examination of
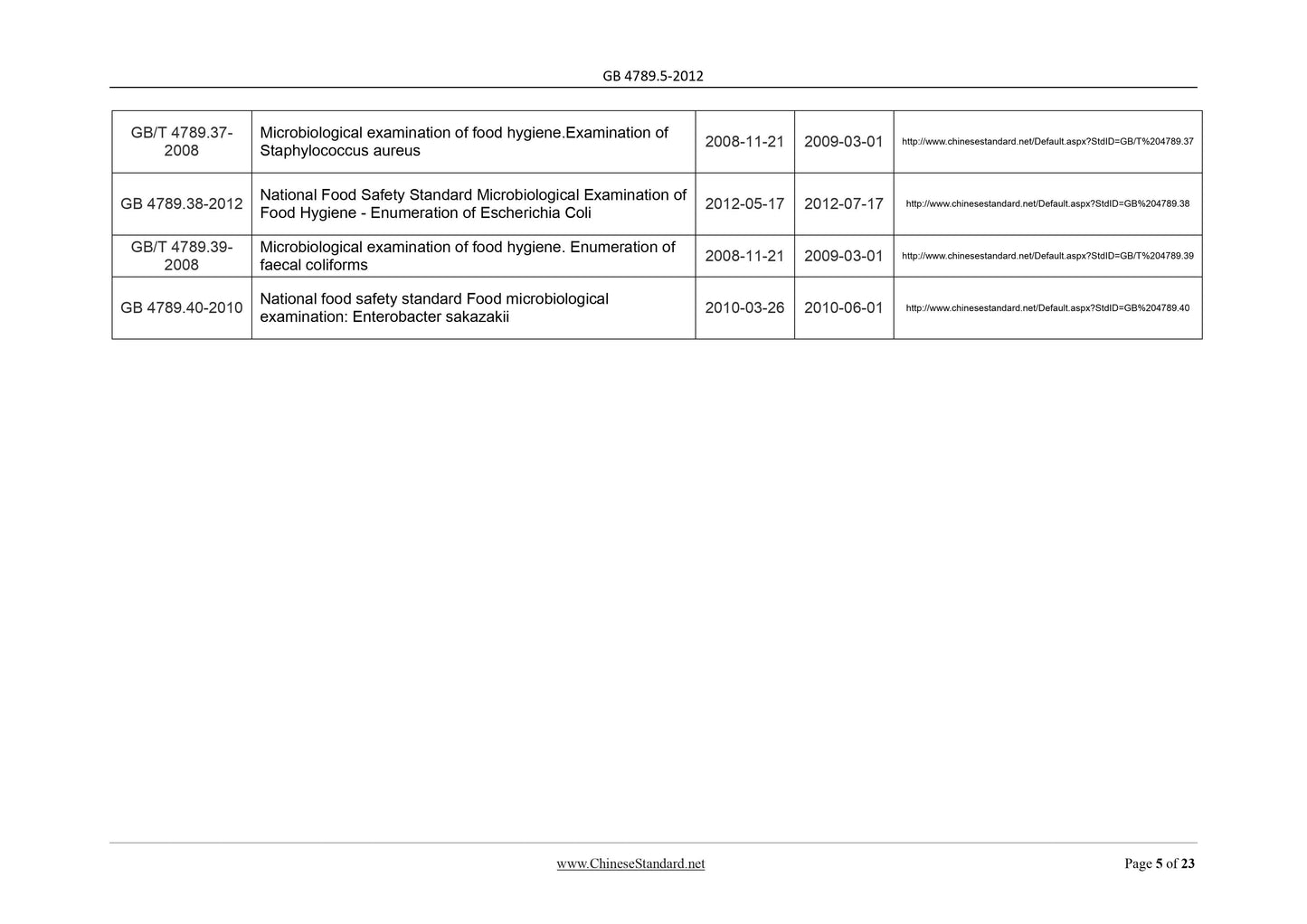
GB/T 4789.36-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene.Examination of
GB/T 4789.37-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene.Examination of
GB/T 4789.39-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene. Enumeration of
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 7
1 Scope ... 8
2 Devices and Materials ... 8
3 Culture Medium and Reagents... 8
4 Examination Procedures ... 9
5 Operational Procedures ... 10
Appendix A ... 15
Foreword
This Standard replaces GB/T 4789.5-2003 "Microbiological Examination of Food Hygiene -
Examination of Shigella".
Compared with GB/T 4789.5-2003, main changes in this Standard are as follows.
- The standard name was modified;
- Culture mediums and reagents were modified;
- Enrichment part, biochemical test and additional biochemical test part in the
operational procedures were modified;
- Table 2 was modified;
- Table 4 was modified.
National Food Safety Standard Microbiological Examination
of Food Hygiene - Examination of Shigella
1 Scope
This Standard specifies the methods to examine the Shigella in foods.
This Standard is applicable to the examination of Shigella in foods.
2 Devices and Materials
In addition to the conventional sterilization and cultivation devices in the microbiological
laboratory, other devices and materials needed for the examination are as follows.
a) Thermostatic incubator. 36ºC±1ºC;
b) Refrigerator. 2ºC~5ºC;
c) Membrane filter system;
d) Anaerobic cultivation device. 41.5ºC±1ºC;
e) Electronic balance. sensibility of 0.1g;
f) Microscope. 10x~100x;
g) Homogenizer;
h) Oscillator;
i) Sterile pipette. 1mL (with 0.01mL scale), 10mL (with 0.1mL scale) or micro-pipettor and
sucker head;
j) Aseptic homogenizing cup or aseptic homogenizing bag. capacity of 500mL;
k) Sterile culture dish. diameter of 90 mm;
l) PH meter or pH colorimetric tube or precise pH test paper;
m) Full automatic microorganism biochemical identification system.
3 Culture Medium and Reagents
3.1 Enriched Shigella broth - novobiocin. see A.1 in Appendix A.
3.2 MAC agar. see A.2 in Appendix A.
3.3 XLD agar. see A.3 in Appendix A.
3.4 Shigella chromogenic medium.
3.5 TSI agar. see A.4 in Appendix A.
3.6 Nutrient agar slant. see A.5 in Appendix A.
3.7 Semi-solid agar. see A.6 in Appendix A.
3.8 Ammonium dextrose medium. see A.7 in Appendix A.
3.9 Urea agar. see A.8 in Appendix A.
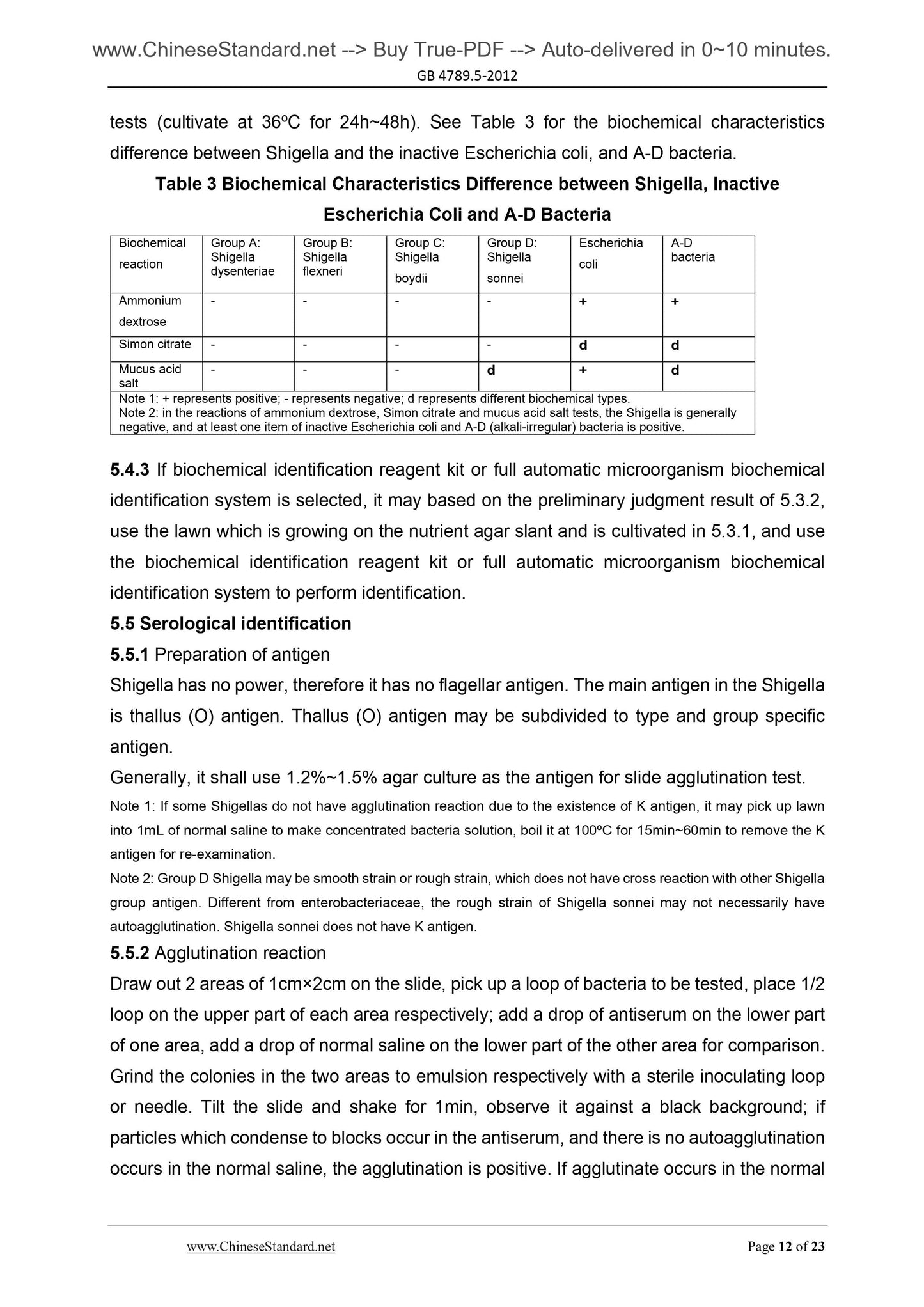
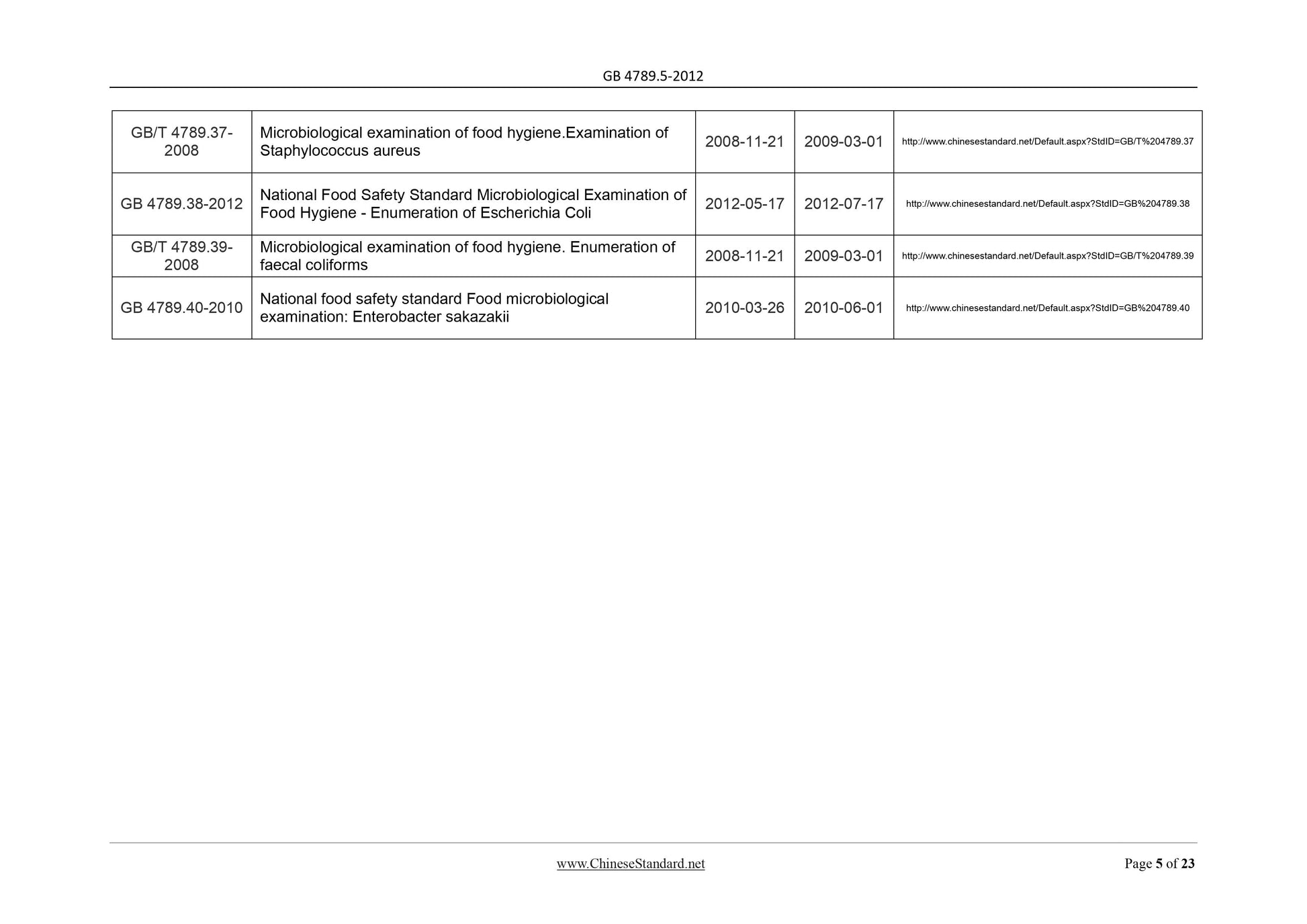
tests (cultivate at 36ºC for 24h~48h). See Table 3 for the biochemical characteristics
difference between Shigella and the inactive Escherichia coli, and A-D bacteria.
Table 3 Biochemical Characteristics Difference between Shigella, Inactive
Escherichia Coli and A-D Bacteria
Biochemical
reaction
Group A.
Shigella
dysenteriae
Group B.
Shigella
flexneri
Group C.
Shigella
boydii
Group D.
Shigella
sonnei
Escherichia
coli
A-D
bacteria
Ammonium
dextrose
- - - - + +
Simon citrate - - - - d d
Mucus acid
salt
- - - d + d
Note 1. + represents positive; - represents negative; d represents different biochemical types.
Note 2. in the reactions of ammonium dextrose, Simon citrate and mucus acid salt tests, the Shigella is generally
negative, and at least one item of inactive Escherichia coli and A-D (alkali-irregular) bacteria is positive.
5.4.3 If biochemical identification reagent kit or full automatic microorganism biochemical
identification system is selected, it may based on the preliminary judgment result of 5.3.2,
use the lawn which is growing on the nutrient agar slant and is cultivated in 5.3.1, and use
the biochemical identification reagent kit or full automatic microorganism biochemical
identification system to perform identification.
5.5 Serological identification
5.5.1 Preparation of antigen
Shigella has no power, therefore it has no flagellar antigen. The main antigen in the Shigella
is thallus (O) antigen. Thallus (O) antigen may be subdivided to type and group specific
antigen.
Generally, it shall use 1.2%~1.5% agar culture as the antigen for slide agglutination test.
Note 1. If some Shigellas do not have agglutination reaction due to the existence of K antigen, it may pick up lawn
into 1mL of normal saline to make concentrated bacteria solution, boil it at 100ºC for 15min~60min to remove the K
antigen for re-examination.
Note 2. Group D Shigella may be smooth strain or rough strain, which does not have cross reaction with other Shigella
group antigen. Different from enterobacteriaceae, the rough strain of Shigella sonnei may not necessarily have
autoagglutination. Shigella sonnei does not have K antigen.
5.5.2 Agglutination reaction
Draw out 2 areas of 1cm×2cm on the slide, pick up a loop of bacteria to be tested, place 1/2
loop on the upper part of each area respectively; add a drop of antiserum on the lower part
of one area, add a drop of normal saline on the lower part of the other area for comparison.
Grind the colonies in the two areas to emulsion respectively with a sterile inoculating loop
or needle. Tilt the slide and sh...
Get QUOTATION in 1-minute: Click GB 4789.5-2012
Historical versions: GB 4789.5-2012
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll if blank)
GB 4789.5-2012: National food safety standard -- Microbiological examination of food hygiene -- Examination of shigella
GB 4789.5‐2012
NATIONAL STANDARD
OF THE PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
National Food Safety Standard Microbiological
Examination of Food Hygiene - Examination of
Shigella
ISSUED ON. MAY 17, 2012
IMPLEMENTED ON. JULY 17, 2012
Issued by. Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China
GB
Tips - GB 4789 Series (Not part of this Standard)
Standard ID Standard Name Issued Date
Enforced
Date New Version (Click to check)?
GB/T 4789.6-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene Examination of
GB/T 4789.7-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene. Examination of
GB/T 4789.8-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene.Examination of
GB/T 4789.9-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene.Examination of
GB/T 4789.11-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene Examination of
GB/T 4789.12-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene Examination of
GB/T 4789.14-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene Examination of
GB/T 4789.16-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene Identification of
GB/T 4789.17-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene Examination of
GB/T 4789.19-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene Examination of
GB/T 4789.20-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene Examination of
GB/T 4789.21-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene Examination of
GB/T 4789.22-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene Examination of
GB/T 4789.23-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene Examination of
GB/T 4789.24-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene Examination of
GB/T 4789.25-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene Examination of
GB/T 4789.26-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene Examination of
GB/T 4789.27-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene.Examination of
GB/T 4789.28-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene Staining
GB/T 4789.29-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene Examination of
GB/T 4789.31-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene Examination of
salmonellae, shigellae, and diarrhoea causative Escherichia
coli by means of the diagnostic typing phage set for
enterobacteriaceae
GB/T 4789.32-
Microbiological examination for food hygiene rapid detection
GB/T 4789.33-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene Examination of
GB/T 4789.36-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene.Examination of
GB/T 4789.37-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene.Examination of
GB/T 4789.39-
Microbiological examination of food hygiene. Enumeration of
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 7
1 Scope ... 8
2 Devices and Materials ... 8
3 Culture Medium and Reagents... 8
4 Examination Procedures ... 9
5 Operational Procedures ... 10
Appendix A ... 15
Foreword
This Standard replaces GB/T 4789.5-2003 "Microbiological Examination of Food Hygiene -
Examination of Shigella".
Compared with GB/T 4789.5-2003, main changes in this Standard are as follows.
- The standard name was modified;
- Culture mediums and reagents were modified;
- Enrichment part, biochemical test and additional biochemical test part in the
operational procedures were modified;
- Table 2 was modified;
- Table 4 was modified.
National Food Safety Standard Microbiological Examination
of Food Hygiene - Examination of Shigella
1 Scope
This Standard specifies the methods to examine the Shigella in foods.
This Standard is applicable to the examination of Shigella in foods.
2 Devices and Materials
In addition to the conventional sterilization and cultivation devices in the microbiological
laboratory, other devices and materials needed for the examination are as follows.
a) Thermostatic incubator. 36ºC±1ºC;
b) Refrigerator. 2ºC~5ºC;
c) Membrane filter system;
d) Anaerobic cultivation device. 41.5ºC±1ºC;
e) Electronic balance. sensibility of 0.1g;
f) Microscope. 10x~100x;
g) Homogenizer;
h) Oscillator;
i) Sterile pipette. 1mL (with 0.01mL scale), 10mL (with 0.1mL scale) or micro-pipettor and
sucker head;
j) Aseptic homogenizing cup or aseptic homogenizing bag. capacity of 500mL;
k) Sterile culture dish. diameter of 90 mm;
l) PH meter or pH colorimetric tube or precise pH test paper;
m) Full automatic microorganism biochemical identification system.
3 Culture Medium and Reagents
3.1 Enriched Shigella broth - novobiocin. see A.1 in Appendix A.
3.2 MAC agar. see A.2 in Appendix A.
3.3 XLD agar. see A.3 in Appendix A.
3.4 Shigella chromogenic medium.
3.5 TSI agar. see A.4 in Appendix A.
3.6 Nutrient agar slant. see A.5 in Appendix A.
3.7 Semi-solid agar. see A.6 in Appendix A.
3.8 Ammonium dextrose medium. see A.7 in Appendix A.
3.9 Urea agar. see A.8 in Appendix A.
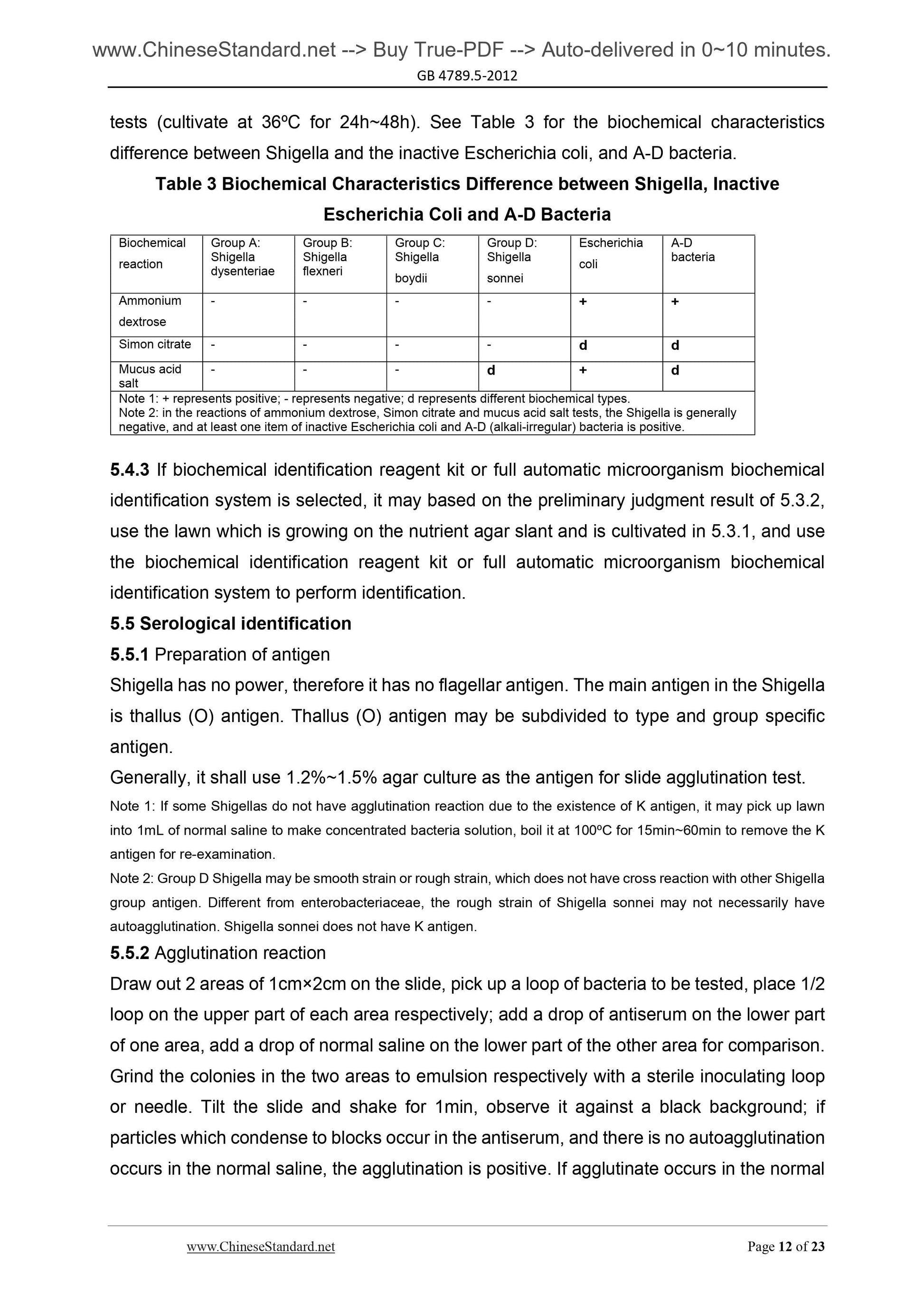
tests (cultivate at 36ºC for 24h~48h). See Table 3 for the biochemical characteristics
difference between Shigella and the inactive Escherichia coli, and A-D bacteria.
Table 3 Biochemical Characteristics Difference between Shigella, Inactive
Escherichia Coli and A-D Bacteria
Biochemical
reaction
Group A.
Shigella
dysenteriae
Group B.
Shigella
flexneri
Group C.
Shigella
boydii
Group D.
Shigella
sonnei
Escherichia
coli
A-D
bacteria
Ammonium
dextrose
- - - - + +
Simon citrate - - - - d d
Mucus acid
salt
- - - d + d
Note 1. + represents positive; - represents negative; d represents different biochemical types.
Note 2. in the reactions of ammonium dextrose, Simon citrate and mucus acid salt tests, the Shigella is generally
negative, and at least one item of inactive Escherichia coli and A-D (alkali-irregular) bacteria is positive.
5.4.3 If biochemical identification reagent kit or full automatic microorganism biochemical
identification system is selected, it may based on the preliminary judgment result of 5.3.2,
use the lawn which is growing on the nutrient agar slant and is cultivated in 5.3.1, and use
the biochemical identification reagent kit or full automatic microorganism biochemical
identification system to perform identification.
5.5 Serological identification
5.5.1 Preparation of antigen
Shigella has no power, therefore it has no flagellar antigen. The main antigen in the Shigella
is thallus (O) antigen. Thallus (O) antigen may be subdivided to type and group specific
antigen.
Generally, it shall use 1.2%~1.5% agar culture as the antigen for slide agglutination test.
Note 1. If some Shigellas do not have agglutination reaction due to the existence of K antigen, it may pick up lawn
into 1mL of normal saline to make concentrated bacteria solution, boil it at 100ºC for 15min~60min to remove the K
antigen for re-examination.
Note 2. Group D Shigella may be smooth strain or rough strain, which does not have cross reaction with other Shigella
group antigen. Different from enterobacteriaceae, the rough strain of Shigella sonnei may not necessarily have
autoagglutination. Shigella sonnei does not have K antigen.
5.5.2 Agglutination reaction
Draw out 2 areas of 1cm×2cm on the slide, pick up a loop of bacteria to be tested, place 1/2
loop on the upper part of each area respectively; add a drop of antiserum on the lower part
of one area, add a drop of normal saline on the lower part of the other area for comparison.
Grind the colonies in the two areas to emulsion respectively with a sterile inoculating loop
or needle. Tilt the slide and sh...
Share