1
/
of
8
PayPal, credit cards. Download editable-PDF and invoice in 1 second!
GB/T 12326-2008 English PDF (GBT12326-2008)
GB/T 12326-2008 English PDF (GBT12326-2008)
Regular price
$85.00 USD
Regular price
Sale price
$85.00 USD
Unit price
/
per
Shipping calculated at checkout.
Couldn't load pickup availability
Delivery: 3 seconds. Download true-PDF + Invoice.
Get QUOTATION in 1-minute: Click GB/T 12326-2008
Historical versions: GB/T 12326-2008
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll if blank)
GB/T 12326-2008: Power quality -- Voltage fluctuation and flicker
GB/T 12326-2008
GB
NATIONAL STANDARD
OF THE PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 27.100
F 020
Replacing GB 12326-2000
Power quality - Voltage fluctuation and flicker
ISSUED ON. JUNE 18, 2008
IMPLEMENTED ON. MAY 1, 2009
Issued by. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and
Quarantine;
Standardization Administration Committee.
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
1 Scope ... 5
2 Normative references ... 5
3 Terms and definitions ... 5
4 Limits of voltage fluctuation ... 7
5 Limits of flicker ... 7
6 Measurement and estimation of voltage fluctuation ... 9
7 Flicker measurement and calculation ... 11
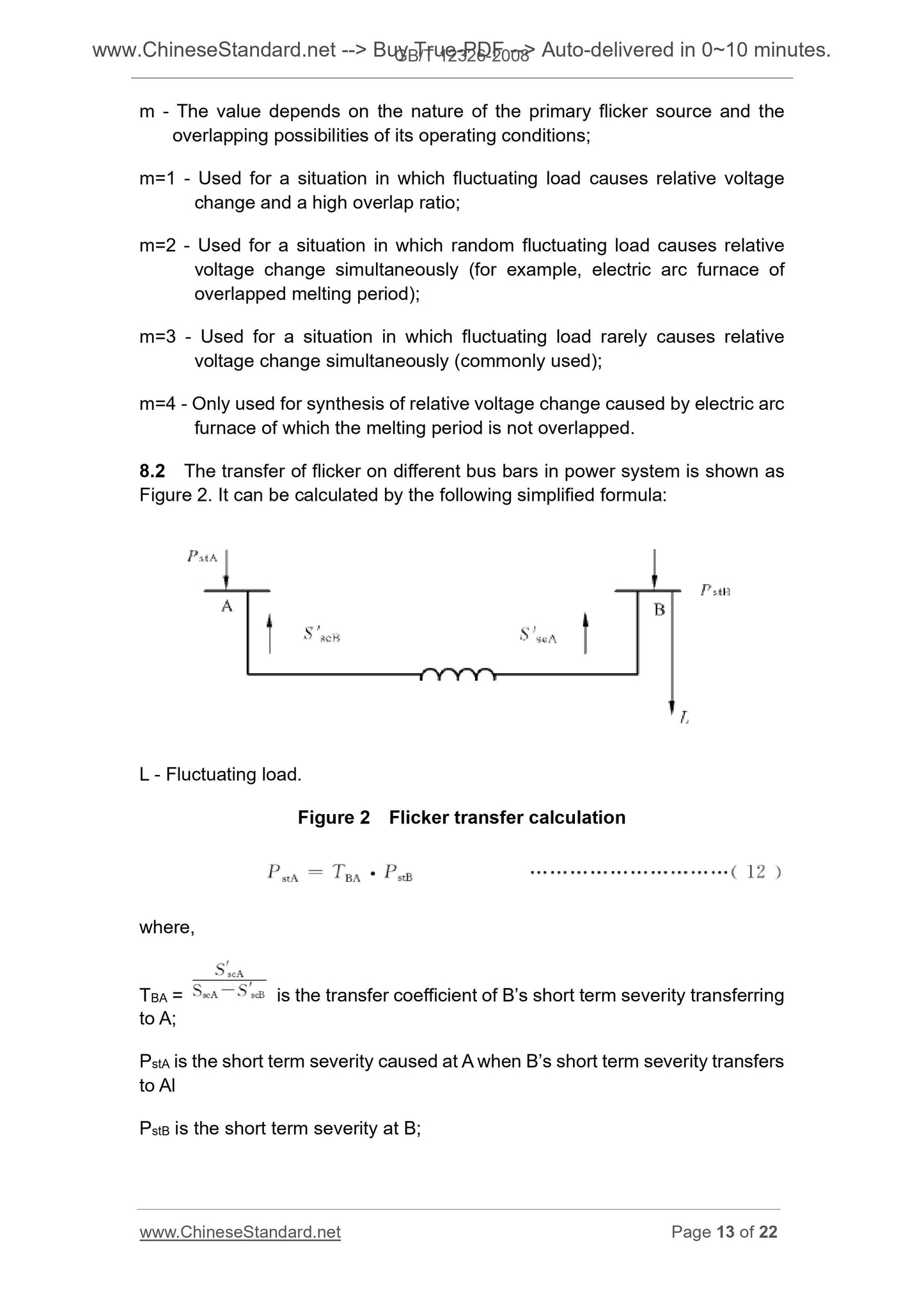
8 Superposition and transfer of flicker ... 12
Annex A (Normative) Flicker measurement and calculation formulas ... 15
Annex B (Informative) Estimation method for total supply capacity StHV of high
voltage (HV) ... 19
Annex C (Informative) Estimation method for flicker of electric arc ... 20
Annex D (Informative) Statistical method of flicker qualification rate ... 21
Bibliography ... 22
Foreword
This Standard replaces GB 12326-2000 Power quality--Voltage fluctuation and
flicker.
Compared with GB 12326-2000, the main contents of this modification are as
follows.
- adjusted the limits of flicker, used the long-term flicker value Plt as the limit
for flicker, a certain degree of relaxation than the original flicker limit. For
flicker caused by a single fluctuating load, according to the actual situation,
it was still divided into three levels, but there was a certain simplification,
and put forward a clear management requirements for excessive user;
- adjusted the criterion of the voltage fluctuation limit. For voltage
fluctuation of low voltage fluctuation frequency or regular periodic voltage
fluctuation, the current limit was still used as the criterion; for irregular
voltage fluctuations, it specified the maximum value of the voltage
fluctuation as criterion and adjusted the previous limit. This enhanced the
voltage fluctuation measurement and judged whether the operability was
qualified;
- adjusted the flicker’s measurement duration, value method. The flicker of
the common connection point of the power system used one week (168 h)
to measure. The flicker caused by a single fluctuating load used one day
(24 h) to measure. They all took the maximum value as criterion for
qualification;
- simplified flicker estimation method; deleted the sine wave which was not
commonly used, triangular wave voltage fluctuation Pst = 1 curve analysis
method, the simulation method which was difficult to implement and flicker
time analysis in the previous standard;
- simplified flicker analysis examples and evaluation methods involved in
Annex C of the previous standard; used a more concise way to list various
arc furnace flicker evaluation coefficients;
- expanded the application scope of voltage fluctuations and flicker limits
to extra high voltage (EHV) system, regardless of the flicker transmission
of EHV to the next voltage level; unified the flicker transfer coefficient to
0.8, the recommended value;
- added statistical method of flicker passing rate, so as to facilitate the
assessment of flicker conditions.
Power quality - Voltage fluctuation and flicker
1 Scope
This Standard specifies the limits and test, calculation and evaluation methods
of voltage fluctuation and flicker.
This Standard is applicable to the rapid change of the voltage of the common
connection point caused by the fluctuating load under the normal operation
mode of the AC 50Hz power system and the occasion where people may
obviously feel the light flicker.
2 Normative references
The following standards contain the provisions which, through reference in this
Standard, constitute the provisions of this Standard. For dated references,
subsequent amendments (excluding corrections) or revisions do not apply to
this Standard. However, the parties who enter into agreement based on this
Standard are encouraged to investigate whether the latest versions of these
documents are applicable. For undated reference documents, the latest
versions apply to this Standard.
GB/T 156-2007 Standard voltage (IEC 60038.2002, MOD)
GB 17625.2 Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) - Limits - Limitation of
voltage changes, voltage fluctuations and flicker in public low-voltage supply
systems, for equipment with rated current ≤ 16 A (GB 17625.2-2007, IEC
61000-3-3.2005, IDT)
GB/Z 17625.3 Electromagnetic compatibility--Limits--Limitation of voltage
fluctuations and flicker in low-voltage power supply systems for equipment
with rated current greater than 16A (GB/Z 17625.3-2000, idt IEC 61000-3-
5.1994)
IEC 61000-4-15.1996 Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) - Testing and
measurement techniques - Flicker meter - Functional and design
specifications
3 Terms and definitions
For the purposes of this document, the following terms and definitions apply.
Each user, according to the ratio between its agreed capacity Si (Si = Pi /cos φi)
and the total capacity, shall determine the flicker limits of this user after
considering the factors such as the effect of the last level on the next level flicker
transfer (the transmission of next level to the last level is generally ignored).
The flicker limits of single user can be calculated as follows.
First, calculate the total flicker limits G generated by all loads connected to PCC
point.
where,
LP - Long term severity Plt limit of PCC corresponding voltage level;
LH - Long term severity Plt limit of last voltage level;
T - The flicker transfer coefficient of the last voltage level to the next voltage
level, 0.8 as recommended. The flicker transfer of EHV system to the next level
voltage system shall not be considered. The flicker limits of each voltage levels
are shown in Table 2.
The flicker limit of single user Ei is.
where,
F - Simultaneous coefficient of fluctuating load of which the typical value F =
0.2 ~ 0.3 (but it must meets Si/F ≤ St); the determination method for PCC’s total
capacity StHV of HV system is shown in Annex B.
5.2.4 The third level regulation. For the single fluctuating load user which does
not comply with the regulations of the second level, if it still exceeds its flicker
limits after treatment, it shall relax the limit appropriately, based on PCC point
actual flicker conditions and development forecast of grid. However, the flicker
value of PCC point must comply with the provisions of 5.1.
6 Measurement and estimation of voltage fluctuation
The voltage fluctuation can be described by R.M.S. voltage shape U(t). The
relative voltage change d and rate of occurrence of voltage changes r are
indicators to measure the voltage fluctuation size and speed.
where,
ΔSi - Three-phase load changes.
For phase single-phase load.
where,
ΔSi - Phase single-phase load.
NOTE In absence of short-circuit capacity of normal smaller way, the system short-circuit
capacity designed to take can be calculated by the maximum short circuit capacity of the
system during production multiplied by 0.7, the coefficient.
7 Flicker measurement and calculation
Flicker is the cumulative effect of voltage fluctuations over a period of time. It
reflects the light perception caused by the instability of the illumination. It is
mainly measured by short term severity Pst and long term severity Plt. The
calculation method of short term...
Get QUOTATION in 1-minute: Click GB/T 12326-2008
Historical versions: GB/T 12326-2008
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll if blank)
GB/T 12326-2008: Power quality -- Voltage fluctuation and flicker
GB/T 12326-2008
GB
NATIONAL STANDARD
OF THE PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 27.100
F 020
Replacing GB 12326-2000
Power quality - Voltage fluctuation and flicker
ISSUED ON. JUNE 18, 2008
IMPLEMENTED ON. MAY 1, 2009
Issued by. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and
Quarantine;
Standardization Administration Committee.
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
1 Scope ... 5
2 Normative references ... 5
3 Terms and definitions ... 5
4 Limits of voltage fluctuation ... 7
5 Limits of flicker ... 7
6 Measurement and estimation of voltage fluctuation ... 9
7 Flicker measurement and calculation ... 11
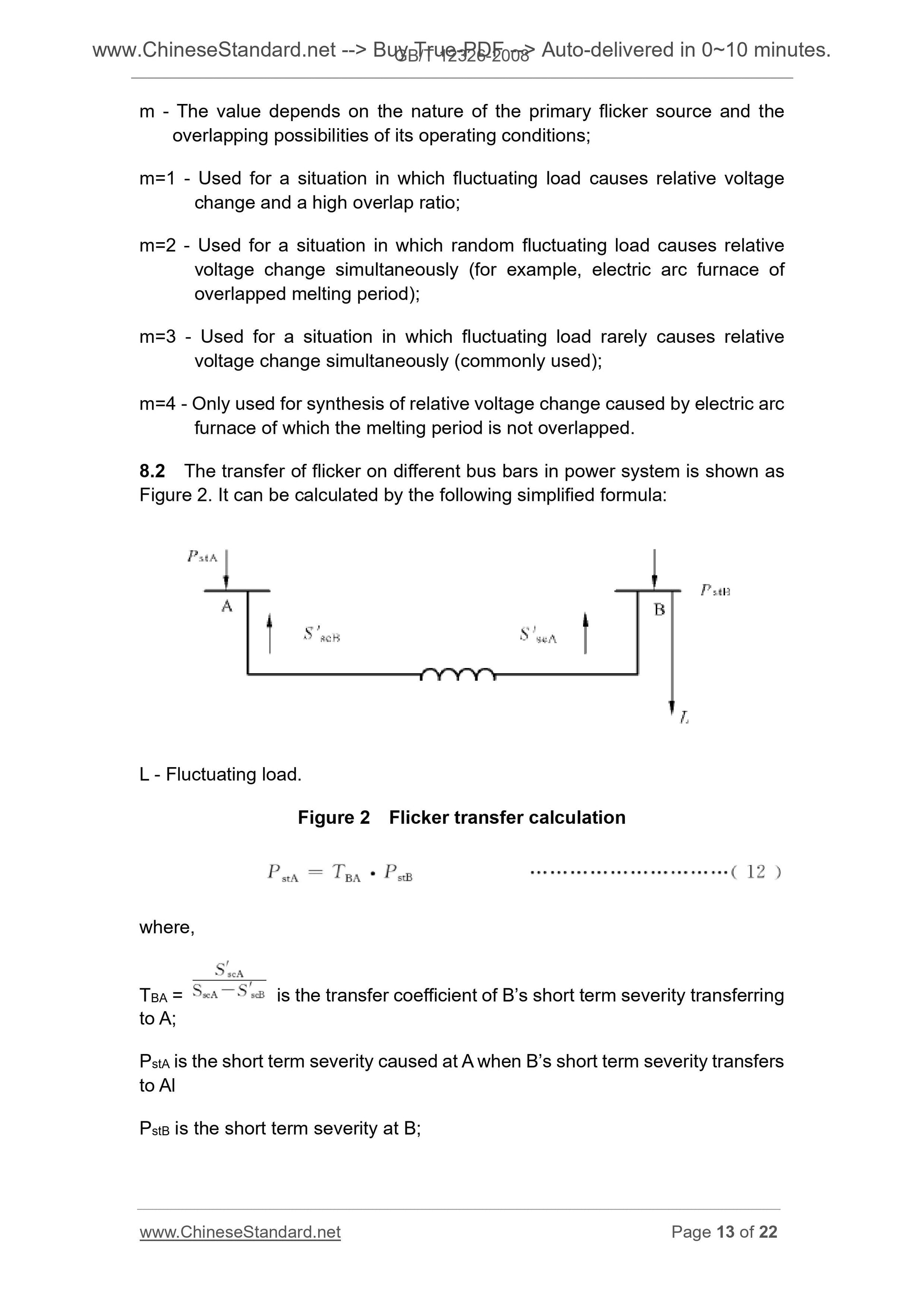
8 Superposition and transfer of flicker ... 12
Annex A (Normative) Flicker measurement and calculation formulas ... 15
Annex B (Informative) Estimation method for total supply capacity StHV of high
voltage (HV) ... 19
Annex C (Informative) Estimation method for flicker of electric arc ... 20
Annex D (Informative) Statistical method of flicker qualification rate ... 21
Bibliography ... 22
Foreword
This Standard replaces GB 12326-2000 Power quality--Voltage fluctuation and
flicker.
Compared with GB 12326-2000, the main contents of this modification are as
follows.
- adjusted the limits of flicker, used the long-term flicker value Plt as the limit
for flicker, a certain degree of relaxation than the original flicker limit. For
flicker caused by a single fluctuating load, according to the actual situation,
it was still divided into three levels, but there was a certain simplification,
and put forward a clear management requirements for excessive user;
- adjusted the criterion of the voltage fluctuation limit. For voltage
fluctuation of low voltage fluctuation frequency or regular periodic voltage
fluctuation, the current limit was still used as the criterion; for irregular
voltage fluctuations, it specified the maximum value of the voltage
fluctuation as criterion and adjusted the previous limit. This enhanced the
voltage fluctuation measurement and judged whether the operability was
qualified;
- adjusted the flicker’s measurement duration, value method. The flicker of
the common connection point of the power system used one week (168 h)
to measure. The flicker caused by a single fluctuating load used one day
(24 h) to measure. They all took the maximum value as criterion for
qualification;
- simplified flicker estimation method; deleted the sine wave which was not
commonly used, triangular wave voltage fluctuation Pst = 1 curve analysis
method, the simulation method which was difficult to implement and flicker
time analysis in the previous standard;
- simplified flicker analysis examples and evaluation methods involved in
Annex C of the previous standard; used a more concise way to list various
arc furnace flicker evaluation coefficients;
- expanded the application scope of voltage fluctuations and flicker limits
to extra high voltage (EHV) system, regardless of the flicker transmission
of EHV to the next voltage level; unified the flicker transfer coefficient to
0.8, the recommended value;
- added statistical method of flicker passing rate, so as to facilitate the
assessment of flicker conditions.
Power quality - Voltage fluctuation and flicker
1 Scope
This Standard specifies the limits and test, calculation and evaluation methods
of voltage fluctuation and flicker.
This Standard is applicable to the rapid change of the voltage of the common
connection point caused by the fluctuating load under the normal operation
mode of the AC 50Hz power system and the occasion where people may
obviously feel the light flicker.
2 Normative references
The following standards contain the provisions which, through reference in this
Standard, constitute the provisions of this Standard. For dated references,
subsequent amendments (excluding corrections) or revisions do not apply to
this Standard. However, the parties who enter into agreement based on this
Standard are encouraged to investigate whether the latest versions of these
documents are applicable. For undated reference documents, the latest
versions apply to this Standard.
GB/T 156-2007 Standard voltage (IEC 60038.2002, MOD)
GB 17625.2 Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) - Limits - Limitation of
voltage changes, voltage fluctuations and flicker in public low-voltage supply
systems, for equipment with rated current ≤ 16 A (GB 17625.2-2007, IEC
61000-3-3.2005, IDT)
GB/Z 17625.3 Electromagnetic compatibility--Limits--Limitation of voltage
fluctuations and flicker in low-voltage power supply systems for equipment
with rated current greater than 16A (GB/Z 17625.3-2000, idt IEC 61000-3-
5.1994)
IEC 61000-4-15.1996 Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) - Testing and
measurement techniques - Flicker meter - Functional and design
specifications
3 Terms and definitions
For the purposes of this document, the following terms and definitions apply.
Each user, according to the ratio between its agreed capacity Si (Si = Pi /cos φi)
and the total capacity, shall determine the flicker limits of this user after
considering the factors such as the effect of the last level on the next level flicker
transfer (the transmission of next level to the last level is generally ignored).
The flicker limits of single user can be calculated as follows.
First, calculate the total flicker limits G generated by all loads connected to PCC
point.
where,
LP - Long term severity Plt limit of PCC corresponding voltage level;
LH - Long term severity Plt limit of last voltage level;
T - The flicker transfer coefficient of the last voltage level to the next voltage
level, 0.8 as recommended. The flicker transfer of EHV system to the next level
voltage system shall not be considered. The flicker limits of each voltage levels
are shown in Table 2.
The flicker limit of single user Ei is.
where,
F - Simultaneous coefficient of fluctuating load of which the typical value F =
0.2 ~ 0.3 (but it must meets Si/F ≤ St); the determination method for PCC’s total
capacity StHV of HV system is shown in Annex B.
5.2.4 The third level regulation. For the single fluctuating load user which does
not comply with the regulations of the second level, if it still exceeds its flicker
limits after treatment, it shall relax the limit appropriately, based on PCC point
actual flicker conditions and development forecast of grid. However, the flicker
value of PCC point must comply with the provisions of 5.1.
6 Measurement and estimation of voltage fluctuation
The voltage fluctuation can be described by R.M.S. voltage shape U(t). The
relative voltage change d and rate of occurrence of voltage changes r are
indicators to measure the voltage fluctuation size and speed.
where,
ΔSi - Three-phase load changes.
For phase single-phase load.
where,
ΔSi - Phase single-phase load.
NOTE In absence of short-circuit capacity of normal smaller way, the system short-circuit
capacity designed to take can be calculated by the maximum short circuit capacity of the
system during production multiplied by 0.7, the coefficient.
7 Flicker measurement and calculation
Flicker is the cumulative effect of voltage fluctuations over a period of time. It
reflects the light perception caused by the instability of the illumination. It is
mainly measured by short term severity Pst and long term severity Plt. The
calculation method of short term...
Share