1
/
of
7
www.ChineseStandard.us -- Field Test Asia Pte. Ltd.
GB/T 14849.4-2014 English PDF (GB/T14849.4-2014)
GB/T 14849.4-2014 English PDF (GB/T14849.4-2014)
Regular price
$130.00
Regular price
Sale price
$130.00
Unit price
/
per
Shipping calculated at checkout.
Couldn't load pickup availability
GB/T 14849.4-2014: Methods for chemical analysis of silicon metal - Part 4: Determination of impurity contents - Inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometric method
Delivery: 9 seconds. Download (& Email) true-PDF + Invoice.
Get Quotation: Click GB/T 14849.4-2014 (Self-service in 1-minute)
Historical versions (Master-website): GB/T 14849.4-2014
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll-down if blank)
GB/T 14849.4-2014
NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE
PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 77.120.10
H 12
Partially replacing GB/T 14849.4-2008
Methods for chemical analysis of silicon metal - Part
4: Determination of impurity contents - Inductively
coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometric
method
ISSUED ON: DECEMBER 05, 2014
IMPLEMENTED ON: AUGUST 01, 2015
Issued by: General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and
Quarantine of PRC;
Standardization Administration of PRC.
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
1 Scope ... 5
2 Normative references ... 5
3 Summary of method ... 6
4 Reagents ... 6
5 Instruments ... 7
6 Specimen ... 7
7 Analytical procedures ... 8
8 Calculation of analytical results ... 10
9 Precision ... 11
10 Quality assurance and control ... 12
11 Test report ... 12
Appendix A (Informative) Preparation of standard stock solutions ... 13
Appendix B (Informative) Instrument’s working conditions ... 17
Methods for chemical analysis of silicon metal - Part
4: Determination of impurity contents - Inductively
coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometric
method
1 Scope
This part of GB/T 14849 specifies the determination methods of iron, aluminum,
calcium, manganese, titanium, nickel, copper, chromium, vanadium,
magnesium, cobalt, phosphorus, potassium, sodium, lead, zinc, boron in
industrial silicon.
This part applies to the determination of iron, aluminum, calcium, manganese,
titanium, nickel, copper, chromium, vanadium, magnesium, cobalt, phosphorus,
potassium, sodium, lead, zinc, boron in industrial silicon. The measurement
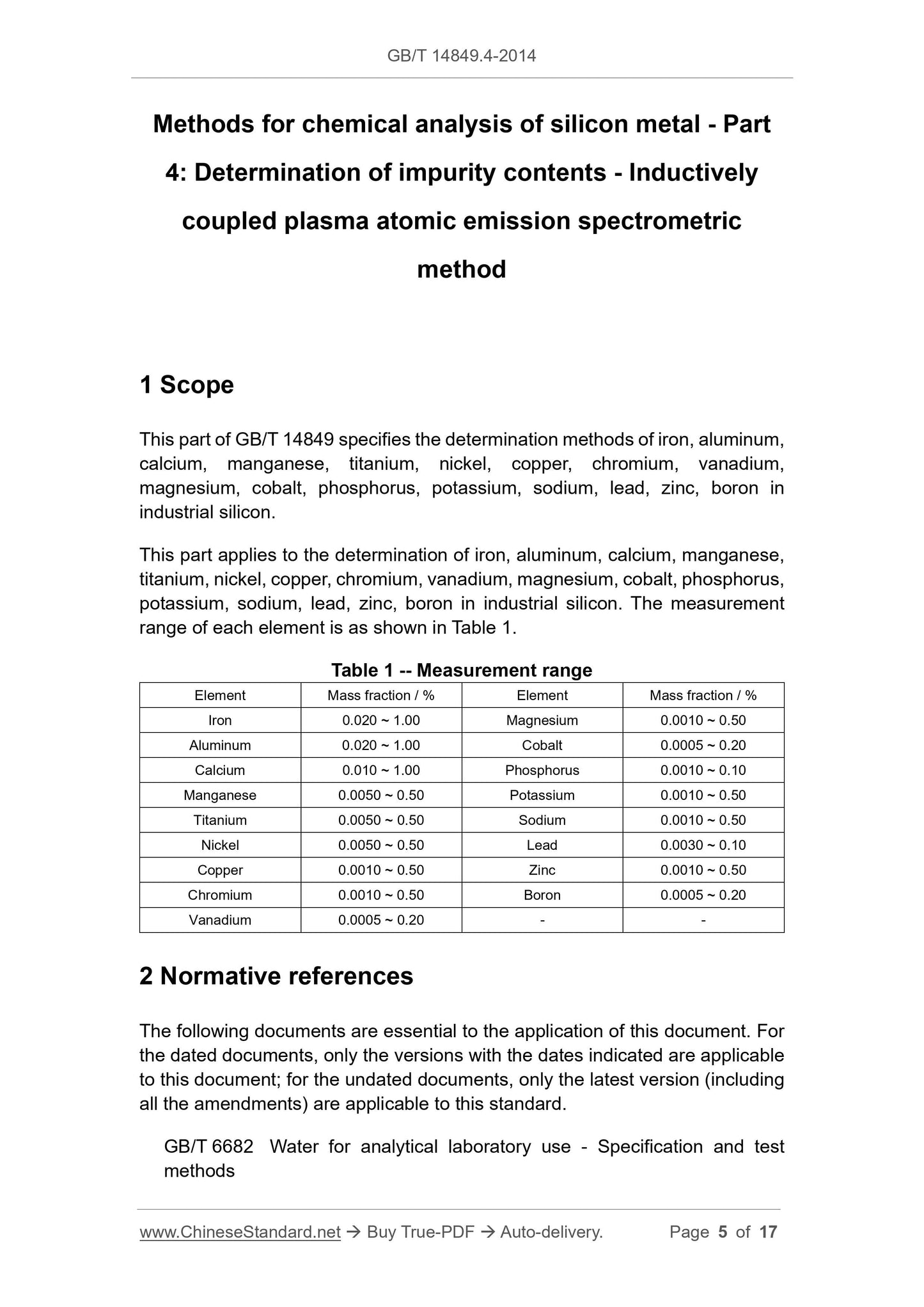
range of each element is as shown in Table 1.
Table 1 -- Measurement range
Element Mass fraction / % Element Mass fraction / %
Iron 0.020 ~ 1.00 Magnesium 0.0010 ~ 0.50
Aluminum 0.020 ~ 1.00 Cobalt 0.0005 ~ 0.20
Calcium 0.010 ~ 1.00 Phosphorus 0.0010 ~ 0.10
Manganese 0.0050 ~ 0.50 Potassium 0.0010 ~ 0.50
Titanium 0.0050 ~ 0.50 Sodium 0.0010 ~ 0.50
Nickel 0.0050 ~ 0.50 Lead 0.0030 ~ 0.10
Copper 0.0010 ~ 0.50 Zinc 0.0010 ~ 0.50
Chromium 0.0010 ~ 0.50 Boron 0.0005 ~ 0.20
Vanadium 0.0005 ~ 0.20 - -
2 Normative references
The following documents are essential to the application of this document. For
the dated documents, only the versions with the dates indicated are applicable
to this document; for the undated documents, only the latest version (including
all the amendments) are applicable to this standard.
GB/T 6682 Water for analytical laboratory use - Specification and test
methods
4.16 Metal copper (Cu ≥ 99.99%).
4.17 Potassium dichromate (base reagent or excellent grade pure).
4.18 Vanadium pentoxide (V2O5 ≥ 99.99%).
4.19 Metal magnesium (Mg ≥ 99.99%).
4.20 Metal cobalt (Co ≥ 99.99%).
4.21 Potassium dihydrogen phosphate (base reagent).
4.22 Potassium chloride (spectral pure).
4.23 Sodium chloride (spectral pure).
4.24 Metal lead (Pb ≥ 99.99%).
4.25 Metal zinc (Zn ≥ 99.99%).
4.26 Boric acid (Excellent grade pure).
4.27 Standard stock solution: For the preparation of standard storage solutions
for each analytical element, see Appendix A. It may also use a certified series
of national standard materials (solutions).
4.28 Standard solution A: Dilute the standard stock solution (4.5) to 100 μg/mL
and maintain a consistent acidity (dilute it before use) with the standard stock
solution.
4.29 Standard solution B: Dilute the standard stock solution (4.6) to 10 μg/mL
and maintain a consistent acidity (dilute it before use) with the standard stock
solution.
5 Instruments
Inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer.
Light source: Plasma source, using power of 750 W ~ 1750 W.
See Appendix B for the working conditions of the instrument.
6 Specimen
The specimen shall pass through a 0.149 mm standard sieve.
Follow the requirements of Table 2 to weigh the sample (7.1) in a 250 mL Teflon
beaker. Use a small amount of water to wet it. Add 5 mL ~ 10 mL of hydrofluoric
acid (4.2). Add nitric acid (4.3) to the sample to completely dissolve it. Add 5 mL
of hydrochloric acid (4.4). Continue heating to dissolve the sample completely.
Evaporate it to 0.5 mL. Remove and cool it. Then add 5 mL of hydrochloric acid
(4.4). Heat to evaporate it to 0.5 mL. Remove it. Use a small amount of water
to rinse the dish wall. Add 5 mL of hydrochloric acid (4.4). Heat to completely
dissolve the residue. Cool it to room temperature. Use water to transfer it into a
volumetric flask of the corresponding volume in Table 2. Dilute it to the mark.
Shake it uniformly.
7.4.3 Determination of B content
Follow the requirements of Table 2 to weigh the sample (7.1) in a 100 mL
platinum dish or 250 mL Teflon beaker. Use a small amount of water to wet it.
Add 5 mL ~ 10 mL of hydrofluoric acid (4.2). Add nitric acid (4.3) slowly dropwise
until the sample is completely dissolved. Add another 1 mL. After the violent
reaction is stopped, heat it to near dry (control heating temperature below
140 °C). Remove and cool it. Add 10 mL of hydrochloric acid (4.5). Heat in a
water bath to completely dissolve the residue. Cool it to room temperature.
Transfer it into a volumetric flask of the corresponding volume in Table 2. Duse
water to dilute it to the mark. Shake it uniformly.
Note 1: When measuring low levels of easily contaminated elements, use high
purity acid and quartz sub-boiling distilled water; use clean analytical vessels.
Note 2: In the determination of phosphorus, potassium, sodium, boron, it shall
prepare the standard solution separately.
Note 3: In the determination of boron, it is recommended to use a hydrofluoric
acid-resistant atomization system using an inductively coupled plasma atomic
emission spectrometer.
Note 4: For the determination of boron, the volumetric flask is made of PFA (it
should choose BLAUBRAND volumetric measuring device with certificate).
7.5 Preparation of series standard solution
7.5.1 Add a suitable amount of standard solution B (4.29) to a set of 100 mL
volumetric flask. The medium and acidity are the same as the sample solution.
Use water to dilute it to the mark. Shake it uniformly. Use the specimen in which
no standard solution is added as the blank solution. The content of the element
to be determined shall be within the range of the plotted working curve. The
amount of the series standard solution is determined by the accuracy
requirements. Take at least 6 points.
7.5.2 According to the designation of the sample, it may also select the
Appendix A
(Informative)
Preparation of standard stock solutions
A.1 Iron standard stock solution (1.0 mg/mL)
Accurately weigh 1.0000 g of metal iron (4.10) in a beaker. Add 40 mL of
hydrochloric acid (4.4). Heat to dissolve it completely. Remove to cool it down.
Transfer it into a 1000 mL volumetric flask. Add another 30 mL of hydrochloric
acid (4.4). Use water to dilute it to the mark. Shake it uniformly. 1 mL of this
solution contains 1.0 mg of iron.
A.2 Aluminum standard stock solution (1.0 mg/mL)
Accurately weigh 1.0000 g of metal aluminum (4.11) in a polytetrafluoroethylene
beaker. Add 20 mL of water and 3 g of sodium hydroxide (4.8). Completely
dissolve it. Use hydrochloric acid (4.4) to slowly neutralize it, until precipitation
occurs. Add another 20 mL. Heat to dissolve it. Cool it down. Transfer it into a
1000 mL volumetric flask. Use water to dilute it to the mark. Shake it uniformly.
1 mL of this solution contains 1.0 mg of aluminum.
A.3 Calcium standard stock solution (1.0 mg/mL)
Accurately weigh 2.4971 g of calcium carbonate (4.12) which was pre-baked at
105 °C. Place it in a beaker. Cover the dish. Add 10 mL of water. Add
hydrochloric acid (4.4) dropwise to completely dissolve it. Then add 20 mL of
hydrochloric acid (4.4). Boil off the carbon dioxide. Remove to cool it down.
Transfer it into a 1000 mL volumetric flask. Use water to dilute it to the mark.
Shake it uniformly. 1 mL of this solution contains 1.0 mg of calcium.
A.4 Manganese standard stock solution (1.0 mg/mL)
Accurately weigh 1.0000 g of metal manganese (4.13) in a 400 mL beaker.
Cover the watch glass. Add 40 mL of hydrochloric acid (4.4). Slowly heat to
dissolve is completely. Remove to cool it down. Transfer it into a 1000 mL
volumetric flask. Use water to dilute it to the mark. Shake it uniformly. 1 mL of
this solution contains 1.0 mg of manganese.
A.5 Titanium standard stock solution (1.0 mg/mL)
Accurately weigh 1.0000 g of titanium metal (4.14) in platinum crucible. Add a
little water. Slowly add hydrofluoric acid (4.2) dropwise to dissolve the sample
completely. Add nitric acid (4.3) dropwise to completely oxidize low-valent
titanium. Add 10 mL of sulfuric acid (4.6). Shake it uniformly. Heat it for
A.11 Cobalt standard stock solution (1.0 mg/mL)
Accurately weigh 1.0000 g of metallic cobalt (4.20). Place it in a 400 mL beaker.
Add 60 mL of hydrochloric acid (4.4) and 10 mL of nitric acid (4.3). Cover the
watch glass. Dissolve it completely at low temperature. Transfer the solution
into a 1000 mL volumetric flask. Add 40 mL of hydrochloric acid (4.4). Use water
to dilute it to the mark. Mix it uniformly. 1 mL of this solution contains 1.0 mg of
cobalt.
A.12 Phosphorus standard stock solution (1.0 mg/mL)
Accurately weigh 4.3936 g of reference potassium dihydrogen phosphate (4.21)
which was dried to constant weight at 110 °C in a 400 mL beaker. Add 200 mL
of water. Dissolve it completely and transfer it into a 1000 mL volumetric flask.
Use water to dilute it to the mark. Mix it uniformly. 1 mL of this solution contains
1.0 mg of phosphorus.
A.13 Potassium standard stock solution (1.0 mg/mL)
Accurately weigh 1.9067 g potassium chloride (4.22) (previously burned to
constant weight at 500 °C ~ 600 °C) in a 400 mL beaker. Add 20 mL of
hydrochloric acid (4.4) to dissolve it slightly. After cooling, transfer the solution
to a 1000 mL volumetric flask. Use water to dilute it to the mark. Mix it uniformly.
1 mL of this solution contains 1.0 mg of potassium.
A.14 Sodium standard stock solution (1.0 mg/mL)
Accurately weigh 2.5409 g of sodium chloride (4.23) (previously burned to
constant weight at 500 °C ~ 600 °C) in a 400 mL beaker. Add 20 mL of
hydrochloric acid (4.4) to dissolve it slightly. After cooling, transfer the solution
into a 1000 mL PFA volumetric flask. Use water to dilute it to the mark. Mix it
uniformly. 1 mL of this solution contains 1.0 mg of sodium.
A.15 Lead standard stock solution (1.0 mg/mL)
Accurately weigh 1.0000 g of lead (4.24). Place it in a 400 mL beaker. Add 40
mL of nitric acid (4.3). Cover the watch glass. Slowly heat to completely dissolve
it. Drive off the nitrogen oxides. Cool it down. Transfer the solution into a 1000
mL volumetric flask. Use water to dilute it to the mark. Mix it uniformly. 1 mL of
this solution contains1.0 mg of lead.
A.16 Zinc standard stock solution (1.0 mg/mL)
Accurately weigh 1.0000 g of zinc (4.25). Place it in a 400 mL beaker. Add 40
mL of hydrochloric acid (4.4). Cover the watch glass. Slowly heat to completely
dissolve it. Cool it down. Transfer the solution into a 1000 mL volumetric flask.
Use water to dilute it to the mark. Mix it uniformly. 1 mL of this solution contains
GB/T 14849.4-2014
NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE
PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 77.120.10
H 12
Partially replacing GB/T 14849.4-2008
Methods for chemical analysis of silicon metal - Part
4: Determination of impurity contents - Inductively
coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometric
method
ISSUED ON: DECEMBER 05, 2014
IMPLEMENTED ON: AUGUST 01, 2015
Issued by: General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and
Quarantine of PRC;
Standardization Administration of PRC.
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
1 Scope ... 5
2 Normative references ... 5
3 Summary of method ... 6
4 Reagents ... 6
5 Instruments ... 7
6 Specimen ... 7
7 Analytical procedures ... 8
8 Calculation of analytical results ... 10
9 Precision ... 11
10 Quality assurance and control ... 12
11 Test report ... 12
Appendix A (Informative) Preparation of standard stock solutions ... 13
Appendix B (Informative) Instrument’s working conditions ... 17
Methods for chemical analysis of silicon metal - Part
4: Determination of impurity contents - Inductively
coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometric
method
1 Scope
This part of GB/T 14849 specifies the determination methods of iron, aluminum,
calcium, manganese, titanium, nickel, copper, chromium, vanadium,
magnesium, cobalt, phosphorus, potassium, sodium, lead, zinc, boron in
industrial silicon.
This part applies to the determination of iron, aluminum, calcium, manganese,
titanium, nickel, copper, chromium, vanadium, magnesium, cobalt, phosphorus,
potassium, sodium, lead, zinc, boron in industrial silicon. The measurement
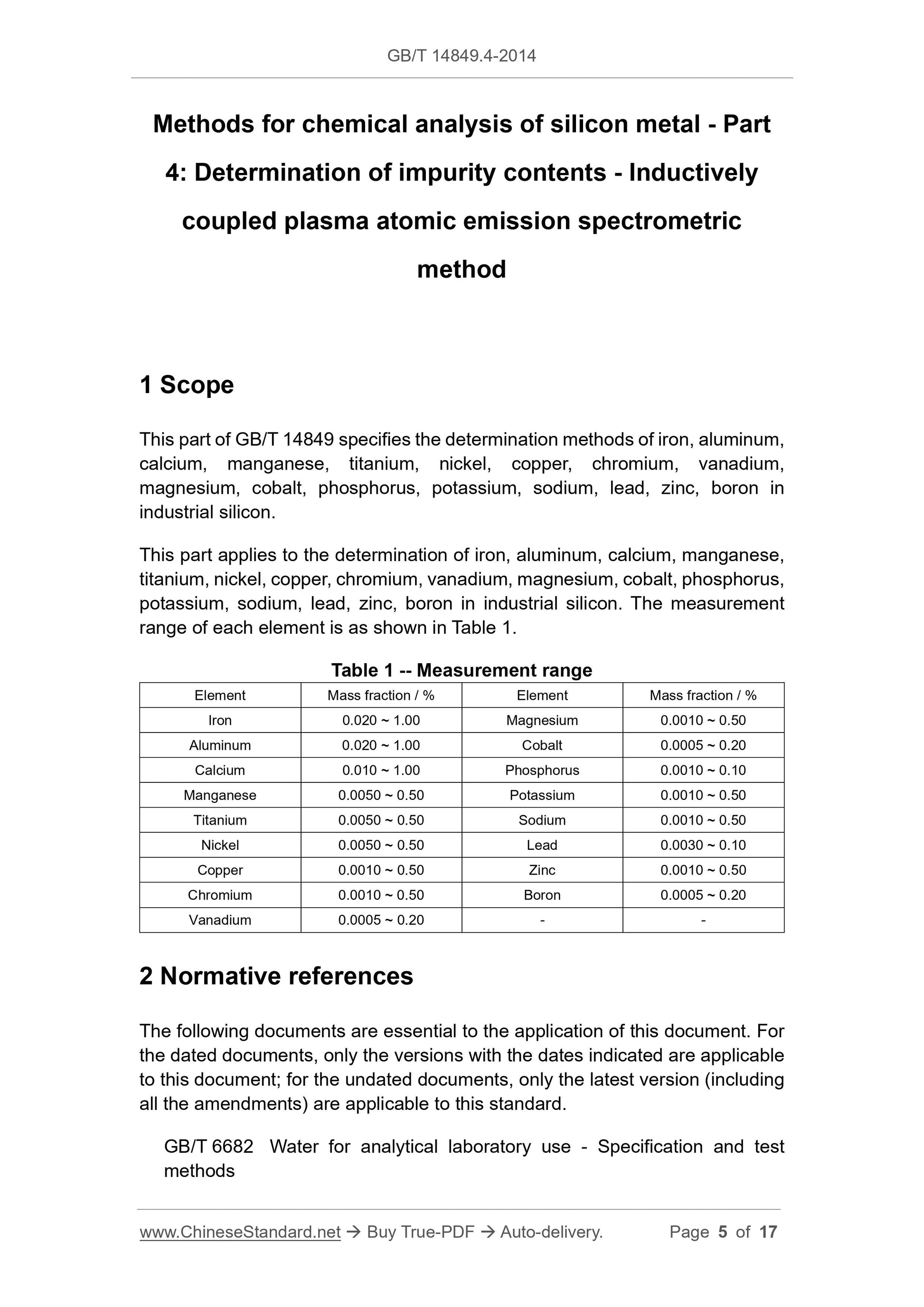
range of each element is as shown in Table 1.
Table 1 -- Measurement range
Element Mass fraction / % Element Mass fraction / %
Iron 0.020 ~ 1.00 Magnesium 0.0010 ~ 0.50
Aluminum 0.020 ~ 1.00 Cobalt 0.0005 ~ 0.20
Calcium 0.010 ~ 1.00 Phosphorus 0.0010 ~ 0.10
Manganese 0.0050 ~ 0.50 Potassium 0.0010 ~ 0.50
Titanium 0.0050 ~ 0.50 Sodium 0.0010 ~ 0.50
Nickel 0.0050 ~ 0.50 Lead 0.0030 ~ 0.10
Copper 0.0010 ~ 0.50 Zinc 0.0010 ~ 0.50
Chromium 0.0010 ~ 0.50 Boron 0.0005 ~ 0.20
Vanadium 0.0005 ~ 0.20 - -
2 Normative references
The following documents are essential to the application of this document. For
the dated documents, only the versions with the dates indicated are applicable
to this document; for the undated documents, only the latest version (including
all the amendments) are applicable to this standard.
GB/T 6682 Water for analytical laboratory use - Specification and test
methods
4.16 Metal copper (Cu ≥ 99.99%).
4.17 Potassium dichromate (base reagent or excellent grade pure).
4.18 Vanadium pentoxide (V2O5 ≥ 99.99%).
4.19 Metal magnesi...
Delivery: 9 seconds. Download (& Email) true-PDF + Invoice.
Get Quotation: Click GB/T 14849.4-2014 (Self-service in 1-minute)
Historical versions (Master-website): GB/T 14849.4-2014
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll-down if blank)
GB/T 14849.4-2014
NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE
PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 77.120.10
H 12
Partially replacing GB/T 14849.4-2008
Methods for chemical analysis of silicon metal - Part
4: Determination of impurity contents - Inductively
coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometric
method
ISSUED ON: DECEMBER 05, 2014
IMPLEMENTED ON: AUGUST 01, 2015
Issued by: General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and
Quarantine of PRC;
Standardization Administration of PRC.
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
1 Scope ... 5
2 Normative references ... 5
3 Summary of method ... 6
4 Reagents ... 6
5 Instruments ... 7
6 Specimen ... 7
7 Analytical procedures ... 8
8 Calculation of analytical results ... 10
9 Precision ... 11
10 Quality assurance and control ... 12
11 Test report ... 12
Appendix A (Informative) Preparation of standard stock solutions ... 13
Appendix B (Informative) Instrument’s working conditions ... 17
Methods for chemical analysis of silicon metal - Part
4: Determination of impurity contents - Inductively
coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometric
method
1 Scope
This part of GB/T 14849 specifies the determination methods of iron, aluminum,
calcium, manganese, titanium, nickel, copper, chromium, vanadium,
magnesium, cobalt, phosphorus, potassium, sodium, lead, zinc, boron in
industrial silicon.
This part applies to the determination of iron, aluminum, calcium, manganese,
titanium, nickel, copper, chromium, vanadium, magnesium, cobalt, phosphorus,
potassium, sodium, lead, zinc, boron in industrial silicon. The measurement
range of each element is as shown in Table 1.
Table 1 -- Measurement range
Element Mass fraction / % Element Mass fraction / %
Iron 0.020 ~ 1.00 Magnesium 0.0010 ~ 0.50
Aluminum 0.020 ~ 1.00 Cobalt 0.0005 ~ 0.20
Calcium 0.010 ~ 1.00 Phosphorus 0.0010 ~ 0.10
Manganese 0.0050 ~ 0.50 Potassium 0.0010 ~ 0.50
Titanium 0.0050 ~ 0.50 Sodium 0.0010 ~ 0.50
Nickel 0.0050 ~ 0.50 Lead 0.0030 ~ 0.10
Copper 0.0010 ~ 0.50 Zinc 0.0010 ~ 0.50
Chromium 0.0010 ~ 0.50 Boron 0.0005 ~ 0.20
Vanadium 0.0005 ~ 0.20 - -
2 Normative references
The following documents are essential to the application of this document. For
the dated documents, only the versions with the dates indicated are applicable
to this document; for the undated documents, only the latest version (including
all the amendments) are applicable to this standard.
GB/T 6682 Water for analytical laboratory use - Specification and test
methods
4.16 Metal copper (Cu ≥ 99.99%).
4.17 Potassium dichromate (base reagent or excellent grade pure).
4.18 Vanadium pentoxide (V2O5 ≥ 99.99%).
4.19 Metal magnesium (Mg ≥ 99.99%).
4.20 Metal cobalt (Co ≥ 99.99%).
4.21 Potassium dihydrogen phosphate (base reagent).
4.22 Potassium chloride (spectral pure).
4.23 Sodium chloride (spectral pure).
4.24 Metal lead (Pb ≥ 99.99%).
4.25 Metal zinc (Zn ≥ 99.99%).
4.26 Boric acid (Excellent grade pure).
4.27 Standard stock solution: For the preparation of standard storage solutions
for each analytical element, see Appendix A. It may also use a certified series
of national standard materials (solutions).
4.28 Standard solution A: Dilute the standard stock solution (4.5) to 100 μg/mL
and maintain a consistent acidity (dilute it before use) with the standard stock
solution.
4.29 Standard solution B: Dilute the standard stock solution (4.6) to 10 μg/mL
and maintain a consistent acidity (dilute it before use) with the standard stock
solution.
5 Instruments
Inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer.
Light source: Plasma source, using power of 750 W ~ 1750 W.
See Appendix B for the working conditions of the instrument.
6 Specimen
The specimen shall pass through a 0.149 mm standard sieve.
Follow the requirements of Table 2 to weigh the sample (7.1) in a 250 mL Teflon
beaker. Use a small amount of water to wet it. Add 5 mL ~ 10 mL of hydrofluoric
acid (4.2). Add nitric acid (4.3) to the sample to completely dissolve it. Add 5 mL
of hydrochloric acid (4.4). Continue heating to dissolve the sample completely.
Evaporate it to 0.5 mL. Remove and cool it. Then add 5 mL of hydrochloric acid
(4.4). Heat to evaporate it to 0.5 mL. Remove it. Use a small amount of water
to rinse the dish wall. Add 5 mL of hydrochloric acid (4.4). Heat to completely
dissolve the residue. Cool it to room temperature. Use water to transfer it into a
volumetric flask of the corresponding volume in Table 2. Dilute it to the mark.
Shake it uniformly.
7.4.3 Determination of B content
Follow the requirements of Table 2 to weigh the sample (7.1) in a 100 mL
platinum dish or 250 mL Teflon beaker. Use a small amount of water to wet it.
Add 5 mL ~ 10 mL of hydrofluoric acid (4.2). Add nitric acid (4.3) slowly dropwise
until the sample is completely dissolved. Add another 1 mL. After the violent
reaction is stopped, heat it to near dry (control heating temperature below
140 °C). Remove and cool it. Add 10 mL of hydrochloric acid (4.5). Heat in a
water bath to completely dissolve the residue. Cool it to room temperature.
Transfer it into a volumetric flask of the corresponding volume in Table 2. Duse
water to dilute it to the mark. Shake it uniformly.
Note 1: When measuring low levels of easily contaminated elements, use high
purity acid and quartz sub-boiling distilled water; use clean analytical vessels.
Note 2: In the determination of phosphorus, potassium, sodium, boron, it shall
prepare the standard solution separately.
Note 3: In the determination of boron, it is recommended to use a hydrofluoric
acid-resistant atomization system using an inductively coupled plasma atomic
emission spectrometer.
Note 4: For the determination of boron, the volumetric flask is made of PFA (it
should choose BLAUBRAND volumetric measuring device with certificate).
7.5 Preparation of series standard solution
7.5.1 Add a suitable amount of standard solution B (4.29) to a set of 100 mL
volumetric flask. The medium and acidity are the same as the sample solution.
Use water to dilute it to the mark. Shake it uniformly. Use the specimen in which
no standard solution is added as the blank solution. The content of the element
to be determined shall be within the range of the plotted working curve. The
amount of the series standard solution is determined by the accuracy
requirements. Take at least 6 points.
7.5.2 According to the designation of the sample, it may also select the
Appendix A
(Informative)
Preparation of standard stock solutions
A.1 Iron standard stock solution (1.0 mg/mL)
Accurately weigh 1.0000 g of metal iron (4.10) in a beaker. Add 40 mL of
hydrochloric acid (4.4). Heat to dissolve it completely. Remove to cool it down.
Transfer it into a 1000 mL volumetric flask. Add another 30 mL of hydrochloric
acid (4.4). Use water to dilute it to the mark. Shake it uniformly. 1 mL of this
solution contains 1.0 mg of iron.
A.2 Aluminum standard stock solution (1.0 mg/mL)
Accurately weigh 1.0000 g of metal aluminum (4.11) in a polytetrafluoroethylene
beaker. Add 20 mL of water and 3 g of sodium hydroxide (4.8). Completely
dissolve it. Use hydrochloric acid (4.4) to slowly neutralize it, until precipitation
occurs. Add another 20 mL. Heat to dissolve it. Cool it down. Transfer it into a
1000 mL volumetric flask. Use water to dilute it to the mark. Shake it uniformly.
1 mL of this solution contains 1.0 mg of aluminum.
A.3 Calcium standard stock solution (1.0 mg/mL)
Accurately weigh 2.4971 g of calcium carbonate (4.12) which was pre-baked at
105 °C. Place it in a beaker. Cover the dish. Add 10 mL of water. Add
hydrochloric acid (4.4) dropwise to completely dissolve it. Then add 20 mL of
hydrochloric acid (4.4). Boil off the carbon dioxide. Remove to cool it down.
Transfer it into a 1000 mL volumetric flask. Use water to dilute it to the mark.
Shake it uniformly. 1 mL of this solution contains 1.0 mg of calcium.
A.4 Manganese standard stock solution (1.0 mg/mL)
Accurately weigh 1.0000 g of metal manganese (4.13) in a 400 mL beaker.
Cover the watch glass. Add 40 mL of hydrochloric acid (4.4). Slowly heat to
dissolve is completely. Remove to cool it down. Transfer it into a 1000 mL
volumetric flask. Use water to dilute it to the mark. Shake it uniformly. 1 mL of
this solution contains 1.0 mg of manganese.
A.5 Titanium standard stock solution (1.0 mg/mL)
Accurately weigh 1.0000 g of titanium metal (4.14) in platinum crucible. Add a
little water. Slowly add hydrofluoric acid (4.2) dropwise to dissolve the sample
completely. Add nitric acid (4.3) dropwise to completely oxidize low-valent
titanium. Add 10 mL of sulfuric acid (4.6). Shake it uniformly. Heat it for
A.11 Cobalt standard stock solution (1.0 mg/mL)
Accurately weigh 1.0000 g of metallic cobalt (4.20). Place it in a 400 mL beaker.
Add 60 mL of hydrochloric acid (4.4) and 10 mL of nitric acid (4.3). Cover the
watch glass. Dissolve it completely at low temperature. Transfer the solution
into a 1000 mL volumetric flask. Add 40 mL of hydrochloric acid (4.4). Use water
to dilute it to the mark. Mix it uniformly. 1 mL of this solution contains 1.0 mg of
cobalt.
A.12 Phosphorus standard stock solution (1.0 mg/mL)
Accurately weigh 4.3936 g of reference potassium dihydrogen phosphate (4.21)
which was dried to constant weight at 110 °C in a 400 mL beaker. Add 200 mL
of water. Dissolve it completely and transfer it into a 1000 mL volumetric flask.
Use water to dilute it to the mark. Mix it uniformly. 1 mL of this solution contains
1.0 mg of phosphorus.
A.13 Potassium standard stock solution (1.0 mg/mL)
Accurately weigh 1.9067 g potassium chloride (4.22) (previously burned to
constant weight at 500 °C ~ 600 °C) in a 400 mL beaker. Add 20 mL of
hydrochloric acid (4.4) to dissolve it slightly. After cooling, transfer the solution
to a 1000 mL volumetric flask. Use water to dilute it to the mark. Mix it uniformly.
1 mL of this solution contains 1.0 mg of potassium.
A.14 Sodium standard stock solution (1.0 mg/mL)
Accurately weigh 2.5409 g of sodium chloride (4.23) (previously burned to
constant weight at 500 °C ~ 600 °C) in a 400 mL beaker. Add 20 mL of
hydrochloric acid (4.4) to dissolve it slightly. After cooling, transfer the solution
into a 1000 mL PFA volumetric flask. Use water to dilute it to the mark. Mix it
uniformly. 1 mL of this solution contains 1.0 mg of sodium.
A.15 Lead standard stock solution (1.0 mg/mL)
Accurately weigh 1.0000 g of lead (4.24). Place it in a 400 mL beaker. Add 40
mL of nitric acid (4.3). Cover the watch glass. Slowly heat to completely dissolve
it. Drive off the nitrogen oxides. Cool it down. Transfer the solution into a 1000
mL volumetric flask. Use water to dilute it to the mark. Mix it uniformly. 1 mL of
this solution contains1.0 mg of lead.
A.16 Zinc standard stock solution (1.0 mg/mL)
Accurately weigh 1.0000 g of zinc (4.25). Place it in a 400 mL beaker. Add 40
mL of hydrochloric acid (4.4). Cover the watch glass. Slowly heat to completely
dissolve it. Cool it down. Transfer the solution into a 1000 mL volumetric flask.
Use water to dilute it to the mark. Mix it uniformly. 1 mL of this solution contains
GB/T 14849.4-2014
NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE
PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 77.120.10
H 12
Partially replacing GB/T 14849.4-2008
Methods for chemical analysis of silicon metal - Part
4: Determination of impurity contents - Inductively
coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometric
method
ISSUED ON: DECEMBER 05, 2014
IMPLEMENTED ON: AUGUST 01, 2015
Issued by: General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and
Quarantine of PRC;
Standardization Administration of PRC.
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
1 Scope ... 5
2 Normative references ... 5
3 Summary of method ... 6
4 Reagents ... 6
5 Instruments ... 7
6 Specimen ... 7
7 Analytical procedures ... 8
8 Calculation of analytical results ... 10
9 Precision ... 11
10 Quality assurance and control ... 12
11 Test report ... 12
Appendix A (Informative) Preparation of standard stock solutions ... 13
Appendix B (Informative) Instrument’s working conditions ... 17
Methods for chemical analysis of silicon metal - Part
4: Determination of impurity contents - Inductively
coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometric
method
1 Scope
This part of GB/T 14849 specifies the determination methods of iron, aluminum,
calcium, manganese, titanium, nickel, copper, chromium, vanadium,
magnesium, cobalt, phosphorus, potassium, sodium, lead, zinc, boron in
industrial silicon.
This part applies to the determination of iron, aluminum, calcium, manganese,
titanium, nickel, copper, chromium, vanadium, magnesium, cobalt, phosphorus,
potassium, sodium, lead, zinc, boron in industrial silicon. The measurement
range of each element is as shown in Table 1.
Table 1 -- Measurement range
Element Mass fraction / % Element Mass fraction / %
Iron 0.020 ~ 1.00 Magnesium 0.0010 ~ 0.50
Aluminum 0.020 ~ 1.00 Cobalt 0.0005 ~ 0.20
Calcium 0.010 ~ 1.00 Phosphorus 0.0010 ~ 0.10
Manganese 0.0050 ~ 0.50 Potassium 0.0010 ~ 0.50
Titanium 0.0050 ~ 0.50 Sodium 0.0010 ~ 0.50
Nickel 0.0050 ~ 0.50 Lead 0.0030 ~ 0.10
Copper 0.0010 ~ 0.50 Zinc 0.0010 ~ 0.50
Chromium 0.0010 ~ 0.50 Boron 0.0005 ~ 0.20
Vanadium 0.0005 ~ 0.20 - -
2 Normative references
The following documents are essential to the application of this document. For
the dated documents, only the versions with the dates indicated are applicable
to this document; for the undated documents, only the latest version (including
all the amendments) are applicable to this standard.
GB/T 6682 Water for analytical laboratory use - Specification and test
methods
4.16 Metal copper (Cu ≥ 99.99%).
4.17 Potassium dichromate (base reagent or excellent grade pure).
4.18 Vanadium pentoxide (V2O5 ≥ 99.99%).
4.19 Metal magnesi...
Share