1
/
of
11
PayPal, credit cards. Download editable-PDF and invoice in 1 second!
GB/T 3077-2015 English PDF (GB/T3077-2015)
GB/T 3077-2015 English PDF (GB/T3077-2015)
Regular price
$85.00 USD
Regular price
Sale price
$85.00 USD
Unit price
/
per
Shipping calculated at checkout.
Couldn't load pickup availability
Delivery: 3 seconds. Download true-PDF + Invoice.
Get Quotation: Click GB/T 3077-2015 (Self-service in 1-minute)
Historical versions (Master-website): GB/T 3077-2015
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll-down if blank)
GB/T 3077-2015: Alloy Structure Steels
GB/T 3077-2015
Alloy structure steels
ICS 77.140.60
H40
National Standards of People's Republic of China
Replacing GB/T 3077-1999
Alloy structural steel
Issued on. 2015-12-10
2016-11-01 implementation
Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of People's Republic of China
Standardization Administration of China released
Table of Contents
Introduction Ⅲ
1 Scope 1
2 Normative references 1
3 Classification Code 2
4 order contents 3
5 size, shape, weight and tolerances 3
6 3 Technical requirements
6.1 Designation and chemical composition 3
6.2 Smelting 11
6.3 Delivery Status 11
6.4 Mechanical properties 11
6.5 hot forging 18
6.6 Low 18 times
6.7 Non-metallic inclusions 18
6.8 grain size 18
6.9 decarburization 18
6.10 Surface quality 19
6.11 special requirements 19
7 Test Method 20
20 8 Inspection Rules
8.1 inspection and acceptance 20
8.2 Batch Rule 20
8.3 the number of samples and sampling position 21
8.4 reinspection and decision rules 21
9 packaging, marking and certification 21
Appendix A (informative) This standard grades and standards similar foreign brands control 22
Foreword
This standard was drafted in accordance with GB/T 1.1-2009 given rules.
This standard replaces GB/T 3077-1999 "alloy structural steel."
This standard compared with GB/T 3077-1999, the main technical content amended as follows.
--- Modify the metallurgical quality classification according to the requirements (see Table 2, Table 4,6.7 and 68, 1999 edition Table 2, Table 4);
B --- boron content of the steel is adjusted to 0.0005% from the lower limit of 0.0008% (see Table 1);
--- Delete all with a letter grade of "A", but the same grade chemical composition is adjusted to the chemical composition of the original with the letters A grades (see Table 1, Table 1, 1999);
--- Increased 25MnB, 35MnB, 25CrMo, 50CrMo, 34CrNi2,15CrNiMo, 30CrNiMo, 30Cr2Ni2Mo,
30Cr2Ni4Mo, 34Cr2Ni2Mo, 35Cr2Ni4Mo, 40CrNi2Mo in 12 grades and technical requirements (see Tables 1 and 3, 1999 edition of Tables 1 and 3);
--- Adjust the steel sulfur and phosphorus content (Table 2, Table 2, 1999);
--- The surface defects and imperfections subdivided into defect (see 610, 1999 Version 6.6.);
--- Modify the surface quality of description and included in GB/T 28300 standard (see 610, 1999 edition 6.6.);
--- Modify the "nonmetallic inclusions" requirement (see 67, 1999. Version 6.9.);
--- Increased "grain size" requirement (see 6.8);
--- Modify the "special requirements" (see 611, 1999 edition 6.10.);
--- Increasing the numerical rounding requirements (see 7.2);
--- The standard grades and increased foreign standards similar grades table (see Appendix A).
This standard was proposed by the National Iron and Steel Association.
This standard by the National Steel Standardization Technical Committee (SAC/TC183) centralized.
This standard was drafted. Daye Special Steel Co., Ltd., Metallurgical Industry Information Standards Institute, Baoshan Iron and Steel Co., Ltd., Shijiazhuang Iron and Steel Co., Ltd., Fujian Sanming Iron and Steel (Group) Co., Ltd., Suzhou Su letter Special Steel Co., Ltd. Hubei tricyclic forging Co.,
Beijing Jiaotong University.
The main drafters of this standard. Huang Chenggang, Libo Peng, Luan Yan, Qiang Dai, Zhang Shuping, Mengrui Ying, Liu Jianfeng, not Lee Fang Hui Weijun, Liu Ping, stone in mind Bin, Sun Zhicheng, co-generation flat, Ding Hui.
This standard replaces the standards previously issued as follows.
--- GB/T 3077-1982, GB/T 3077-1988, GB/T 3077-1999.
Alloy structural steel
1 Scope
This standard specifies the classification of alloy steel and code, ordering the content, size, shape, weight and tolerance, technical requirements, test methods, inspection rules, packaging, marking and quality certification.
This standard applies to the nominal diameter or thickness of not more than 250mm of hot-rolled and forged alloy steel bars. Negotiated by both sides,
Also can supply nominal diameter or thickness greater than 250mm hot-rolled and forged alloy steel bars (hereinafter referred to as the bar).
The standards required grade and chemical composition are also applicable to steel ingot, billet and their products.
2 Normative references
The following documents for the application of this document is essential. For cited documents with dates, only the dated edition applies to this document. For undated references, the latest edition (including any amendments) applies to this document.
GB/T 222 chemical composition of finished steel tolerance
GB/T 223.4 steel and alloy - Determination of manganese content or visual titration potentiometric titration
GB/T 223.5 steel measuring soluble silicon and total silicon content reduced silicon molybdate salt spectrophotometric method
GB/T 223.9 steel and aluminum alloys - Determination of chromium content Azure S Spectrophotometry
Determination of GB/T 223.11 steel and alloy chromium content of visual titration or potentiometric titration
GB/T 223.13 Methods for chemical analysis of iron, steel and alloy The ammonium ferrous sulfate titration method for the determination of vanadium content
Spectrophotometric determination of titanium content GB/T 223.16 Methods for chemical analysis of iron, steel and alloy The chromotropic acid
GB/T 223.18 Methods for chemical analysis of iron, steel and alloy The sodium thiosulfate separation - determination of copper content Iodometry
GB/T 223.23 steel and alloy - Determination of nickel content dimethylglyoxime spectrophotometry
GB/T 223.26 steel and alloy - Determination of molybdenum content - Thiocyanate spectrophotometric
GB/T 223.43 steel and alloy of tungsten content - Gravimetric method and spectrophotometry
GB/T 223.49 Methods for chemical analysis of iron, steel and alloy Extraction separation - chlorophosphonazo mA Spectrophotometric determination of total rare earths
GB/T 223.59 Steel and Alloy Determination of phosphorus content by bismuth phosphomolybdate blue spectrophotometric method and antimony phosphomolybdate blue spectrophotometry
GB/T 223.60 Methods for chemical analysis of iron, steel and alloy perchloric acid dehydration gravimetric method for the determination of silicon content
GB/T 223.67 steel and alloy sulfur content - Methylene blue spectrophotometric method
GB/T 223.69 after carbon and alloy steel - Determination of the pipe furnace combustion gas volumetric method
GB/T 223.75 Determination of methanol distillation steel and alloy of boron content - Curcumin spectrophotometric
Determination of depth of decarburization GB/T 224 steel
GB/T 225 steel end quench hardenability test methods (Jominy test)
GB/T 226 steel macrostructure and defect etching test method
RT Test Method. Test Part 1 GB/T 228.1 metallic materials tensile
GB/T 229 metal Charpy pendulum impact test method
GB/T 231.1 metallic materials Brinell hardness test - Part 1. Test methods
GB/T 702 hot-rolled steel bars - Dimensions, shape, weight and tolerance
GB/T 908 forged steel bars size, shape, weight and tolerance
GB/T 1979 structure steel macrostructure and defect rating FIG.
General provisions GB/T 2101 steel acceptance, packaging, marking and quality certificate
GB/T 2975 Steel and Steel Products mechanical testing location and sample preparation
GB/T 4162 wrought steel rod ultrasonic testing method
GB/T 4336 carbon steel and low alloy steel spark source atomic emission spectrometry method (conventional method)
GB/T 6394 Determination of average grain size of metal
GB/T 6402 Steel Forgings Ultrasonic Testing Method
Low magnification GB/T 7736 steel defects Ultrasonic Inspection Act
GB/T 8170-2008 revised value represents about rules and limit values and judgment
GB/T 10561 Steel - Determination of content of nonmetallic inclusions - Micrographic method standards diagrams
GB/T 11261 steel oxygen content measured pulse heating inert gas fusion - infrared absorption method
GB/T 13298 metal microstructure inspection method
Microstructure GB/T 13299 Evaluation Method of Steel
GB/T 15711 Bars tower hairline acid leaching test methods
GB/T 17505 Steel and steel products General technical delivery requirements
GB/T 20066 Steel and iron - Sampling and determination of the chemical composition of the sample with a sample preparation method
GB/T 20123 Steel - Determination of total carbon and sulfur content of the high-frequency induction furnace combustion infrared absorption method (conventional method)
GB/T 20124 Steel - Determination of nitrogen content of inert gas fusion thermal conductivity method (conventional method)
GB/T 21834 in low-alloy steel multi-element distribution measurement metal position statistic distribution analysis
GB/T 28300 hot-rolled bars and wire rod surface quality class technical delivery conditions
Determination of YB/T 4306 steel and alloy nitrogen content of the inert gas fusion thermal conductivity method
YB/T 5293 Test methods for metallic materials upsetting
3 Classification Code
3.1 Bars by metallurgical quality is divided into the following three categories.
a) high quality steel;
b) high quality steel (grades after adding "A");
c) high-grade steel post (Grade plus "E").
Bars processing method by the use of 3.2 points following two categories.
a) the UP pressure working steel;
1) hot pressure processing UHP;
2) upsetting steel UF;
3) cold drawn blank UCD;
b) cutting steel UC.
3.3 according to the type of surface the bar divided into the following five categories.
a) pressure processing surface SPP;
b) pickling SA;
c) blasting (sand) the SS;
d) stripping SF;
e) polishing SP.
4 ordering content
According to the standard order contract or order should include the following.
a) the standard number;
b) the product name;
c) grades or Unified numbering;
d) control of residual elements (if required, see Table 2);
e) Delivery of weight (or number);
f) the size, shape and tolerance;
g) using the processing method (not indicated, by cutting steel);
h) heat treatment delivery or special surface state of delivery (if required, see 6.3.2 and 6.3.3);
i) hot forging (if required, see 6.5);
j) decarburization (if required, see 6.9);
k) special requirements (if required, see 6.11).
5 size, shape, weight and tolerance
5.1 hot-rolled steel bar size, shape, weight and tolerances shall comply with the relevant provisions of GB/T 702, the specific requirements should be specified in the contract.
5.2 forging steel bar size, shape, weight and tolerances shall comply with the relevant provisions of GB/T 908, the specific requirements should be specified in the contract.
5.3 Other dimensions of the bar size, shape, weight and tolerances should conform to appropriate standards or negotiated by both sides, the specific requirements specified in the contract.
6 Technical Requirements
6.1 Designation and chemical composition
6.1.1 grade steel, unified digital code and chemical composition (melting analysis) shall comply with the requirements in Table 1.
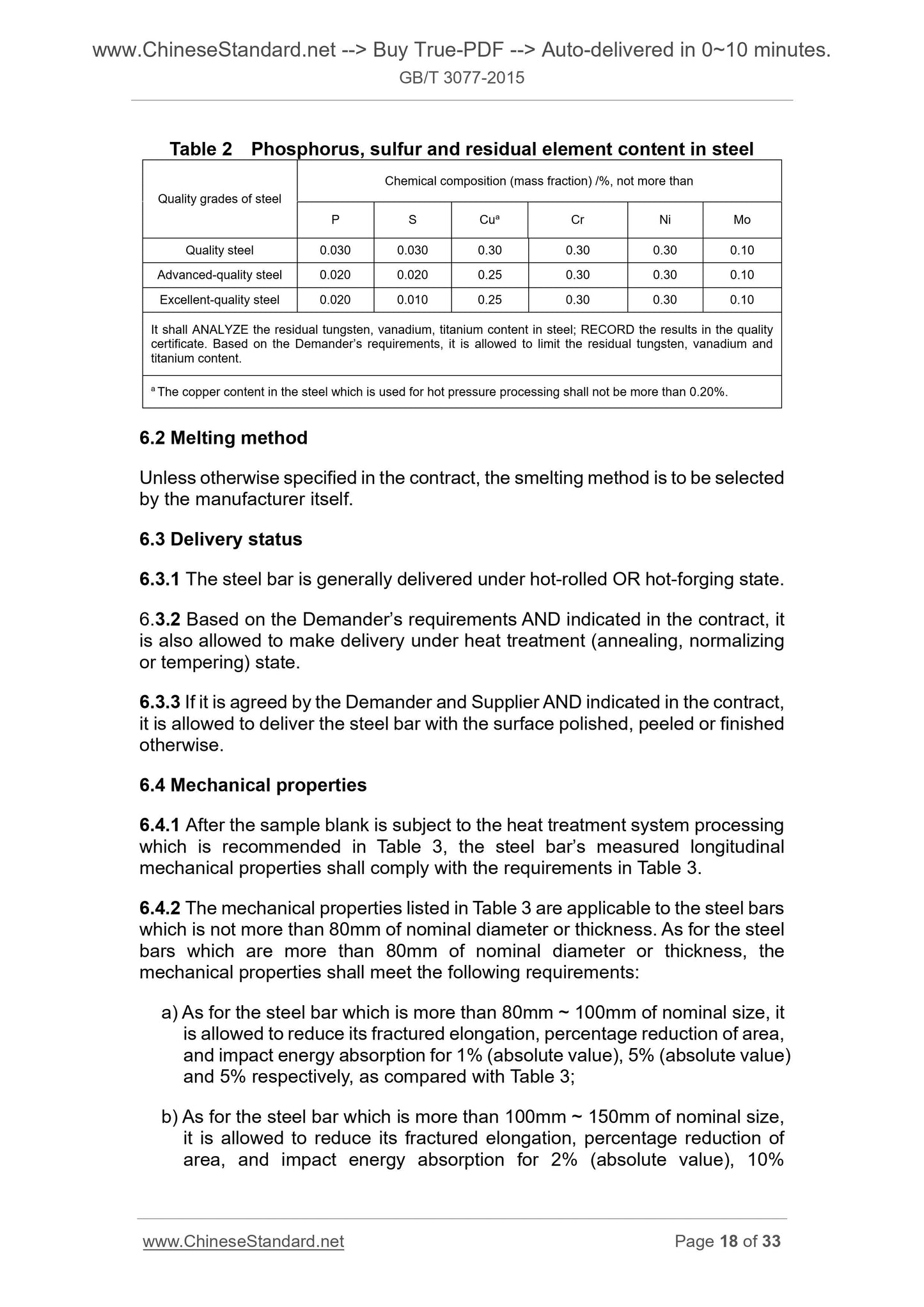
6.1.2 steel sulfur, and phosphorus content of residual elements shall be in accordance with Table 2.
6.1.3 Bars (or blank) finished chemical composition tolerances shall comply with the provisions of GB/T 222's.
Table 2 steel phosphorus, sulfur content and the content of residual elements
Quality grades of steel
Chemical composition (mass fraction) /%, not more than
PS Cua Cr Ni Mo
Stainless steel 0.030 0.030 0.30 0.30 0.30 0.10
High quality steel 0.020 0.020 0.25 0.30 0.30 0.10
Premium quality steel 0.020 0.010 0.25 0.30 0.30 0.10
Residual steel tungsten, vanadium, titanium content should be analyzed, the results recorded in the quality certificate. According to the requirements, it may be limited residual tungsten, vanadium and titanium content.
The copper content of a hot pressure processing of steel is not more than 0.20%.
6.2 Melting Method
Unless there are provisions in the contract, smelting methods discretion of the manufacturer.
6.3 Delivery Status
6.3.1 hot-rolled steel bars or forging generally state delivery.
6.3.2 According to the requirements, and indicate in the contract, you can also heat treatment (annealing, normalizing or tempering) state delivery.
6.3.3 agreement by both sides, and noted in the contract, the bar surfaces may be polished, peeling or other finishing methods of delivery.
6.4 Mechanical Properties
6.4.1 Sample blank according to Table 3 Recommended heat treatment processing system, longitudinal steel bars measuring mechanical properties shall conform to Table 3.
6.4.2 The mechanical properties listed in Table 3 are available in nominal diameter or thickness of not more than 80mm steel rod. Nominal diameter or thickness greater than the mechanical properties of steel bar 80mm shall meet the following requirements.
a) nominal size greater than 80mm ~ 100mm steel rod, allowing it fractured elongation, and reduction of the impact energy absorption than the specified in Table 3 were reduced by 1% (absolute value), 5% (absolute value) and 5%;
b) The nominal size greater than 100mm ~ 150mm steel rod, allowing it fractured elongation, and reduction of the impact energy absorption compared with Table 3 were reduced by 2% (absolute value), 10% (absolute value) and 10%;
c) nominal size greater than 150mm ~ 250mm steel rod, allowing it fractured elongation, and reduction of the impact energy absorption compared with Table 3 were decreased by 3% (absolute value), 15% (absolute value) and 15%;
d) allowing the sample to change the cross-section with a blank forging (rolling) 70mm ~ 80mm after sampling, the test results should be shown in Table 3.
6.4.3 In annealing or tempering state delivery of steel bars, its Brinell hardness shall conform to Table 3.
6.5 hot forging
According to the requirements, and indicate in the contract, it should be made of steel hot forging hot forging test sample after the test is highly original sample height of 1/3, after upsetting the sample should be crack . Nominal size greater than 80mm of steel bars, the supplier can ensure that the test may not be qualified.
6.6 times lower
6.6.1 cross-section of the bar of acid leaching low magnification should not have visual evide...
Get Quotation: Click GB/T 3077-2015 (Self-service in 1-minute)
Historical versions (Master-website): GB/T 3077-2015
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll-down if blank)
GB/T 3077-2015: Alloy Structure Steels
GB/T 3077-2015
Alloy structure steels
ICS 77.140.60
H40
National Standards of People's Republic of China
Replacing GB/T 3077-1999
Alloy structural steel
Issued on. 2015-12-10
2016-11-01 implementation
Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of People's Republic of China
Standardization Administration of China released
Table of Contents
Introduction Ⅲ
1 Scope 1
2 Normative references 1
3 Classification Code 2
4 order contents 3
5 size, shape, weight and tolerances 3
6 3 Technical requirements
6.1 Designation and chemical composition 3
6.2 Smelting 11
6.3 Delivery Status 11
6.4 Mechanical properties 11
6.5 hot forging 18
6.6 Low 18 times
6.7 Non-metallic inclusions 18
6.8 grain size 18
6.9 decarburization 18
6.10 Surface quality 19
6.11 special requirements 19
7 Test Method 20
20 8 Inspection Rules
8.1 inspection and acceptance 20
8.2 Batch Rule 20
8.3 the number of samples and sampling position 21
8.4 reinspection and decision rules 21
9 packaging, marking and certification 21
Appendix A (informative) This standard grades and standards similar foreign brands control 22
Foreword
This standard was drafted in accordance with GB/T 1.1-2009 given rules.
This standard replaces GB/T 3077-1999 "alloy structural steel."
This standard compared with GB/T 3077-1999, the main technical content amended as follows.
--- Modify the metallurgical quality classification according to the requirements (see Table 2, Table 4,6.7 and 68, 1999 edition Table 2, Table 4);
B --- boron content of the steel is adjusted to 0.0005% from the lower limit of 0.0008% (see Table 1);
--- Delete all with a letter grade of "A", but the same grade chemical composition is adjusted to the chemical composition of the original with the letters A grades (see Table 1, Table 1, 1999);
--- Increased 25MnB, 35MnB, 25CrMo, 50CrMo, 34CrNi2,15CrNiMo, 30CrNiMo, 30Cr2Ni2Mo,
30Cr2Ni4Mo, 34Cr2Ni2Mo, 35Cr2Ni4Mo, 40CrNi2Mo in 12 grades and technical requirements (see Tables 1 and 3, 1999 edition of Tables 1 and 3);
--- Adjust the steel sulfur and phosphorus content (Table 2, Table 2, 1999);
--- The surface defects and imperfections subdivided into defect (see 610, 1999 Version 6.6.);
--- Modify the surface quality of description and included in GB/T 28300 standard (see 610, 1999 edition 6.6.);
--- Modify the "nonmetallic inclusions" requirement (see 67, 1999. Version 6.9.);
--- Increased "grain size" requirement (see 6.8);
--- Modify the "special requirements" (see 611, 1999 edition 6.10.);
--- Increasing the numerical rounding requirements (see 7.2);
--- The standard grades and increased foreign standards similar grades table (see Appendix A).
This standard was proposed by the National Iron and Steel Association.
This standard by the National Steel Standardization Technical Committee (SAC/TC183) centralized.
This standard was drafted. Daye Special Steel Co., Ltd., Metallurgical Industry Information Standards Institute, Baoshan Iron and Steel Co., Ltd., Shijiazhuang Iron and Steel Co., Ltd., Fujian Sanming Iron and Steel (Group) Co., Ltd., Suzhou Su letter Special Steel Co., Ltd. Hubei tricyclic forging Co.,
Beijing Jiaotong University.
The main drafters of this standard. Huang Chenggang, Libo Peng, Luan Yan, Qiang Dai, Zhang Shuping, Mengrui Ying, Liu Jianfeng, not Lee Fang Hui Weijun, Liu Ping, stone in mind Bin, Sun Zhicheng, co-generation flat, Ding Hui.
This standard replaces the standards previously issued as follows.
--- GB/T 3077-1982, GB/T 3077-1988, GB/T 3077-1999.
Alloy structural steel
1 Scope
This standard specifies the classification of alloy steel and code, ordering the content, size, shape, weight and tolerance, technical requirements, test methods, inspection rules, packaging, marking and quality certification.
This standard applies to the nominal diameter or thickness of not more than 250mm of hot-rolled and forged alloy steel bars. Negotiated by both sides,
Also can supply nominal diameter or thickness greater than 250mm hot-rolled and forged alloy steel bars (hereinafter referred to as the bar).
The standards required grade and chemical composition are also applicable to steel ingot, billet and their products.
2 Normative references
The following documents for the application of this document is essential. For cited documents with dates, only the dated edition applies to this document. For undated references, the latest edition (including any amendments) applies to this document.
GB/T 222 chemical composition of finished steel tolerance
GB/T 223.4 steel and alloy - Determination of manganese content or visual titration potentiometric titration
GB/T 223.5 steel measuring soluble silicon and total silicon content reduced silicon molybdate salt spectrophotometric method
GB/T 223.9 steel and aluminum alloys - Determination of chromium content Azure S Spectrophotometry
Determination of GB/T 223.11 steel and alloy chromium content of visual titration or potentiometric titration
GB/T 223.13 Methods for chemical analysis of iron, steel and alloy The ammonium ferrous sulfate titration method for the determination of vanadium content
Spectrophotometric determination of titanium content GB/T 223.16 Methods for chemical analysis of iron, steel and alloy The chromotropic acid
GB/T 223.18 Methods for chemical analysis of iron, steel and alloy The sodium thiosulfate separation - determination of copper content Iodometry
GB/T 223.23 steel and alloy - Determination of nickel content dimethylglyoxime spectrophotometry
GB/T 223.26 steel and alloy - Determination of molybdenum content - Thiocyanate spectrophotometric
GB/T 223.43 steel and alloy of tungsten content - Gravimetric method and spectrophotometry
GB/T 223.49 Methods for chemical analysis of iron, steel and alloy Extraction separation - chlorophosphonazo mA Spectrophotometric determination of total rare earths
GB/T 223.59 Steel and Alloy Determination of phosphorus content by bismuth phosphomolybdate blue spectrophotometric method and antimony phosphomolybdate blue spectrophotometry
GB/T 223.60 Methods for chemical analysis of iron, steel and alloy perchloric acid dehydration gravimetric method for the determination of silicon content
GB/T 223.67 steel and alloy sulfur content - Methylene blue spectrophotometric method
GB/T 223.69 after carbon and alloy steel - Determination of the pipe furnace combustion gas volumetric method
GB/T 223.75 Determination of methanol distillation steel and alloy of boron content - Curcumin spectrophotometric
Determination of depth of decarburization GB/T 224 steel
GB/T 225 steel end quench hardenability test methods (Jominy test)
GB/T 226 steel macrostructure and defect etching test method
RT Test Method. Test Part 1 GB/T 228.1 metallic materials tensile
GB/T 229 metal Charpy pendulum impact test method
GB/T 231.1 metallic materials Brinell hardness test - Part 1. Test methods
GB/T 702 hot-rolled steel bars - Dimensions, shape, weight and tolerance
GB/T 908 forged steel bars size, shape, weight and tolerance
GB/T 1979 structure steel macrostructure and defect rating FIG.
General provisions GB/T 2101 steel acceptance, packaging, marking and quality certificate
GB/T 2975 Steel and Steel Products mechanical testing location and sample preparation
GB/T 4162 wrought steel rod ultrasonic testing method
GB/T 4336 carbon steel and low alloy steel spark source atomic emission spectrometry method (conventional method)
GB/T 6394 Determination of average grain size of metal
GB/T 6402 Steel Forgings Ultrasonic Testing Method
Low magnification GB/T 7736 steel defects Ultrasonic Inspection Act
GB/T 8170-2008 revised value represents about rules and limit values and judgment
GB/T 10561 Steel - Determination of content of nonmetallic inclusions - Micrographic method standards diagrams
GB/T 11261 steel oxygen content measured pulse heating inert gas fusion - infrared absorption method
GB/T 13298 metal microstructure inspection method
Microstructure GB/T 13299 Evaluation Method of Steel
GB/T 15711 Bars tower hairline acid leaching test methods
GB/T 17505 Steel and steel products General technical delivery requirements
GB/T 20066 Steel and iron - Sampling and determination of the chemical composition of the sample with a sample preparation method
GB/T 20123 Steel - Determination of total carbon and sulfur content of the high-frequency induction furnace combustion infrared absorption method (conventional method)
GB/T 20124 Steel - Determination of nitrogen content of inert gas fusion thermal conductivity method (conventional method)
GB/T 21834 in low-alloy steel multi-element distribution measurement metal position statistic distribution analysis
GB/T 28300 hot-rolled bars and wire rod surface quality class technical delivery conditions
Determination of YB/T 4306 steel and alloy nitrogen content of the inert gas fusion thermal conductivity method
YB/T 5293 Test methods for metallic materials upsetting
3 Classification Code
3.1 Bars by metallurgical quality is divided into the following three categories.
a) high quality steel;
b) high quality steel (grades after adding "A");
c) high-grade steel post (Grade plus "E").
Bars processing method by the use of 3.2 points following two categories.
a) the UP pressure working steel;
1) hot pressure processing UHP;
2) upsetting steel UF;
3) cold drawn blank UCD;
b) cutting steel UC.
3.3 according to the type of surface the bar divided into the following five categories.
a) pressure processing surface SPP;
b) pickling SA;
c) blasting (sand) the SS;
d) stripping SF;
e) polishing SP.
4 ordering content
According to the standard order contract or order should include the following.
a) the standard number;
b) the product name;
c) grades or Unified numbering;
d) control of residual elements (if required, see Table 2);
e) Delivery of weight (or number);
f) the size, shape and tolerance;
g) using the processing method (not indicated, by cutting steel);
h) heat treatment delivery or special surface state of delivery (if required, see 6.3.2 and 6.3.3);
i) hot forging (if required, see 6.5);
j) decarburization (if required, see 6.9);
k) special requirements (if required, see 6.11).
5 size, shape, weight and tolerance
5.1 hot-rolled steel bar size, shape, weight and tolerances shall comply with the relevant provisions of GB/T 702, the specific requirements should be specified in the contract.
5.2 forging steel bar size, shape, weight and tolerances shall comply with the relevant provisions of GB/T 908, the specific requirements should be specified in the contract.
5.3 Other dimensions of the bar size, shape, weight and tolerances should conform to appropriate standards or negotiated by both sides, the specific requirements specified in the contract.
6 Technical Requirements
6.1 Designation and chemical composition
6.1.1 grade steel, unified digital code and chemical composition (melting analysis) shall comply with the requirements in Table 1.
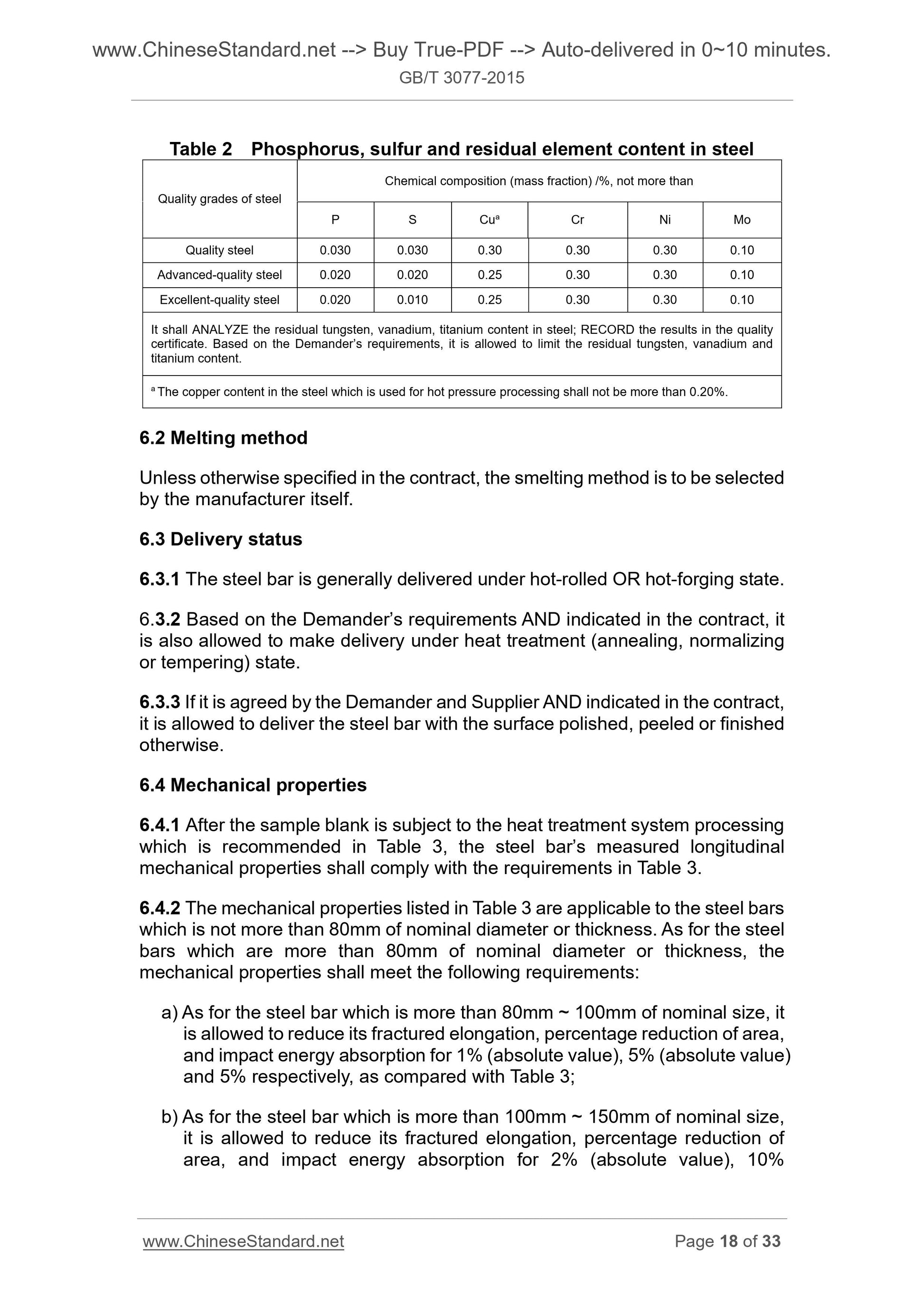
6.1.2 steel sulfur, and phosphorus content of residual elements shall be in accordance with Table 2.
6.1.3 Bars (or blank) finished chemical composition tolerances shall comply with the provisions of GB/T 222's.
Table 2 steel phosphorus, sulfur content and the content of residual elements
Quality grades of steel
Chemical composition (mass fraction) /%, not more than
PS Cua Cr Ni Mo
Stainless steel 0.030 0.030 0.30 0.30 0.30 0.10
High quality steel 0.020 0.020 0.25 0.30 0.30 0.10
Premium quality steel 0.020 0.010 0.25 0.30 0.30 0.10
Residual steel tungsten, vanadium, titanium content should be analyzed, the results recorded in the quality certificate. According to the requirements, it may be limited residual tungsten, vanadium and titanium content.
The copper content of a hot pressure processing of steel is not more than 0.20%.
6.2 Melting Method
Unless there are provisions in the contract, smelting methods discretion of the manufacturer.
6.3 Delivery Status
6.3.1 hot-rolled steel bars or forging generally state delivery.
6.3.2 According to the requirements, and indicate in the contract, you can also heat treatment (annealing, normalizing or tempering) state delivery.
6.3.3 agreement by both sides, and noted in the contract, the bar surfaces may be polished, peeling or other finishing methods of delivery.
6.4 Mechanical Properties
6.4.1 Sample blank according to Table 3 Recommended heat treatment processing system, longitudinal steel bars measuring mechanical properties shall conform to Table 3.
6.4.2 The mechanical properties listed in Table 3 are available in nominal diameter or thickness of not more than 80mm steel rod. Nominal diameter or thickness greater than the mechanical properties of steel bar 80mm shall meet the following requirements.
a) nominal size greater than 80mm ~ 100mm steel rod, allowing it fractured elongation, and reduction of the impact energy absorption than the specified in Table 3 were reduced by 1% (absolute value), 5% (absolute value) and 5%;
b) The nominal size greater than 100mm ~ 150mm steel rod, allowing it fractured elongation, and reduction of the impact energy absorption compared with Table 3 were reduced by 2% (absolute value), 10% (absolute value) and 10%;
c) nominal size greater than 150mm ~ 250mm steel rod, allowing it fractured elongation, and reduction of the impact energy absorption compared with Table 3 were decreased by 3% (absolute value), 15% (absolute value) and 15%;
d) allowing the sample to change the cross-section with a blank forging (rolling) 70mm ~ 80mm after sampling, the test results should be shown in Table 3.
6.4.3 In annealing or tempering state delivery of steel bars, its Brinell hardness shall conform to Table 3.
6.5 hot forging
According to the requirements, and indicate in the contract, it should be made of steel hot forging hot forging test sample after the test is highly original sample height of 1/3, after upsetting the sample should be crack . Nominal size greater than 80mm of steel bars, the supplier can ensure that the test may not be qualified.
6.6 times lower
6.6.1 cross-section of the bar of acid leaching low magnification should not have visual evide...
Share