1
/
of
12
PayPal, credit cards. Download editable-PDF and invoice in 1 second!
GB/T 3094-2012 English PDF (GB/T3094-2012)
GB/T 3094-2012 English PDF (GB/T3094-2012)
Regular price
$85.00 USD
Regular price
Sale price
$85.00 USD
Unit price
/
per
Shipping calculated at checkout.
Couldn't load pickup availability
Delivery: 3 seconds. Download true-PDF + Invoice.
Get Quotation: Click GB/T 3094-2012 (Self-service in 1-minute)
Historical versions (Master-website): GB/T 3094-2012
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll-down if blank)
GB/T 3094-2012: Cold drawn shaped steel tubes
GB/T 3094-2012
GB
NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE
PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 77.140.75
H48
Replacing GB/T 3094-2000
Cold Drawn Shaped Steel Tubes
ISSUED ON. MAY 11, 2012
IMPLEMENTED ON. FEBRUARY 1, 2013
Issued by. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and
Quarantine (AQSIQ);
Standardization Administration (SAC) of the People's
Republic of China.
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
1 Scope ... 4
2 Normative References ... 4
3 Classification and Designation ... 6
4 Ordering Information ... 6
5 Shape, Dimension and Weight ... 7
6 Technical Requirements ... 9
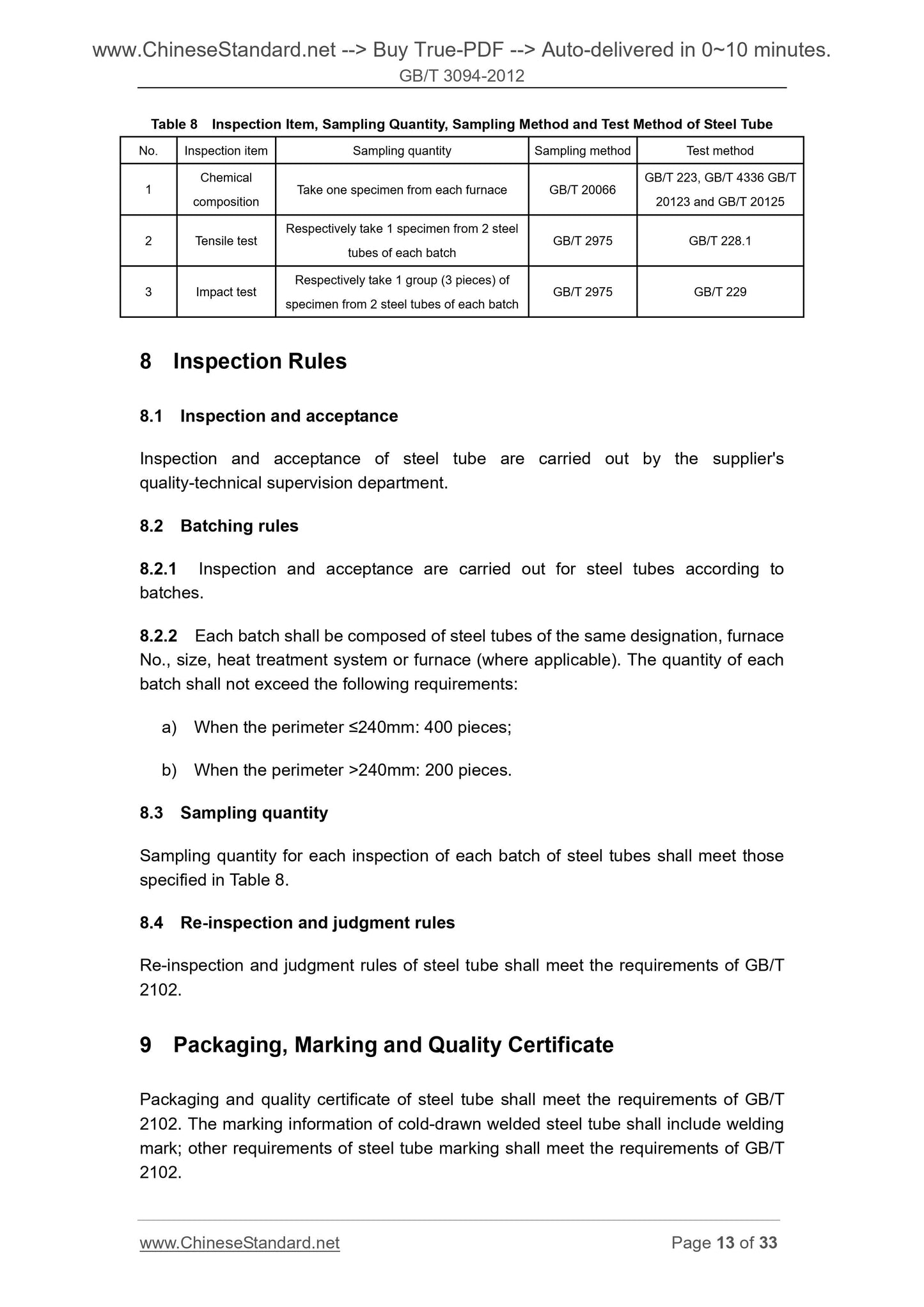
7 Test Methods ... 12
8 Inspection Rules ... 13
9 Packaging, Marking and Quality Certificate ... 13
Appendix A (Normative) Shape and Dimension of Steel Tube ... 14
Appendix B (Normative) Determination Method for Twist Value of Shaped Steel
Tube ... 32
Foreword
This Standard is drafted according to the rules given in GB/T 1.1-2009.
This Standard is revised by reference to ASTM A 500-07 "Standard Specification for
Cold-formed Welded and Seamless Carbon Steel Structural Tubing in Rounds and
Shapes".
This Standard replace GB/T 3094-2000 "Cold Drawn Shaped Steel Tubes" (GB/T
3094-2000). Compared with GB/T 3094-2000, the main changes of this Standard are
as follows.
- Quality grades of steel designations Q215, Q235, Q345 and Q390 are added;
Q295 is deleted;
- Ordering information is added;
- Curvature and twist value requirements are modified;
- Marking example is deleted;
- General length is modified;
- Mechanical performance of steel tube is modified;
- Requirements for impact test of steel tube are added;
- Size and dimension of steel tube in Appendix A are modified.
This Standard was proposed by China Iron and Steel Association.
This Standard shall be under the jurisdiction of the National Technical Committee on
Iron and Steel of Standardization Administration of China (SAC/TC 183).
Drafting organizations of this Standard. Shanghai Shaped Steel Tube Co., Ltd. AND
Jiangsu Jieda Specific New Material Co., Ltd.
Chief drafting staffs of this Standard. Gao Zhijian, Chen Hongqi, Zhu Sujian, Xue
Jianliang, Wang Wei, Hu Hongwei, Yang Wenyi and Lei Liangliang.
The previous editions replaced by this Standard are as follows.
- GB 3094-1982;
- GB/T 3094-2000.
Cold Drawn Shaped Steel Tubes
1 Scope
This Standard specifies the classification, designation, ordering information, shape,
dimension, technical requirements, test method, inspection rule, packaging, marking
and quality certificate of cold drawn shaped steel tubes.
This Standard is applicable to cold-drawn simple-section shaped tube (hereinafter
referred to as steel tube).
2 Normative References
The following referenced documents are indispensable for the application of this
document. For dated references, only the edition cited applies. For undated
references, the latest edition of the normative document (including any amendments)
applies.
GB/T 222 Permissible Tolerances for Chemical Composition of Steel Products
GB/T 223.5 Steel and Iron - Determination of Acid-soluble Silicon and Total
Silicon Content - Reduced Molybdosilicate Spectrophotometric Method
GB/T 223.9 Iron, Steel and Alloy - Determination of Aluminum Content - Chrom
Azurol S Photometric Method
GB/T 223.12 GB/T 223.62 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Iron, Steel and Alloy
- The Sodium Carbonate Separation - Diphenyl Carbazide Photometric Method for
the Determination of Chromium Content
GB/T 223.14 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Iron, Steel and Alloy - The
N-benzoy-N-phenylhydroxylamine Extraction Photometric Method for the
Determination of Vanadium Content
GB/T 223.17 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Iron, Steel and Alloy - The
Diantipyrylmethane Photometric Method for the Determination of Titanium Content
GB/T 223.19 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Iron, Steel and Alloy - The
Neocuproine - Chloroform Extraction Photometric Method for the Determination of
Copper Content
GB/T 223.23 Iron Steel and Alloy - Determination of Nickel Content - The
Dimethylglyoxime Spectrophotometric Method
GB/T 223.40 Iron Steel and Alloy - Determination of Niobium Content by the
Sulphochlorophenol S Spectrophotometric Method
GB/T 223.59 Iron Steel and Alloy - Determination of Phosphorus Content -
Bismuth Phosphomolybdate Blue Spectrophotometric Method and Antimony
Phosphomolybdate Blue Spectrophotometric Method
GB/T 223.60 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Iron, Steel and Alloy - The
Perchloric Acid Dehydration Gravimetric Method for the Determination of Silicon
Content
GB/T 223.62 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Iron, Steel and Alloy - The Butyl
Acetate Extraction Photometric Method for the Determination of Phosphorus
Content
GB/T 223.63 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Iron, Steel and Alloy - The
Sodium (Potassium) Periodate Photometric Method for the Determination of
Manganese Content
GB/T 223.64 Iron Steel and Alloy - Determination of Manganese Content - Flame
Atomic Absorption Spectrometric Method
GB/T 223.68 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Iron, Steel and Alloy - The
Potassium Iodate Titration Method after Combustion in the Pipe Furnace for the
Determination of Sulfur Content
GB/T 223.69 Iron Steel and Alloy - Determination of Carbon Contents -
Gas-volumetric Method after Combustion in the Pipe Furnace
GB/T 223.71 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Iron, Steel and Alloy - The
Gravimetric Method after Combustion in the Pipe Furnace for the Determination of
Carbon Content
GB/T 223.72 Iron Steel and Alloy - Determination of Sulfur Content - Gravimetric
Method
GB/T 228.1 Metallic Materials - Tensile Testing - Part 1. Method of Test at Room
Temperature
GB/T 229 Metallic Materials - Charpy Pendulum Impact Test Method
GB/T 699 Quality Carbon Structural Steels
GB/T 700 Carbon Structural Steels
GB/T 1591 High Strength Low Alloy Structural Steels
GB/T 2102 Acceptance, Packing, Marking and Certification of Pipe
GB/T 2975 Steel and Steel Products - Location and Preparation of Test Pieces for
Mechanical Testing
GB/T 3077 Alloy Structure Steels
GB/T 4336 Standard Test Method for Spark Discharge Atomic Emission
Spectrometric Analysis of Carbon and Low-alloy Steel (Routine Method)
GB/T 20066 Steel and Iron - Sampling and Preparation of Samples for the
Determination of Chemical Composition
GB/T 20123 Steel and Iron - Determination of Total Carbon and Sulfur Content
Infrared Absorption Method after Combustion in an Induction Furnace (Routine
Method)
GB/T 20125 Low-alloy Steel - Determination of Multi-element Contents -
Inductively Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission Spectrometric Method
3 Classification and Designation
Classification and designation of steel tubes according to section shape are as
follows.
a) Square steel tube D-1;
b) Rectangle steel tube D-2;
c) Elliptical steel tube D-3;
d) Flat oval steel tube D-4;
e) Inside and outside hexagonal steel tube D-5;
f) Rectangular trapezoid steel tube D-6.
4 Ordering Information
The contract or order for ordering steel tubes according to this Standard shall include
but not limited to the following contents.
a) Standard No.;
b) Product name;
c) Designation and quality grade of steel (if applicable);
d) Size and dimension;
e) Ordering quantity (total weight or total length);
f) Delivery state;
g) Special requirements.
5 Shape, Dimension and Weight
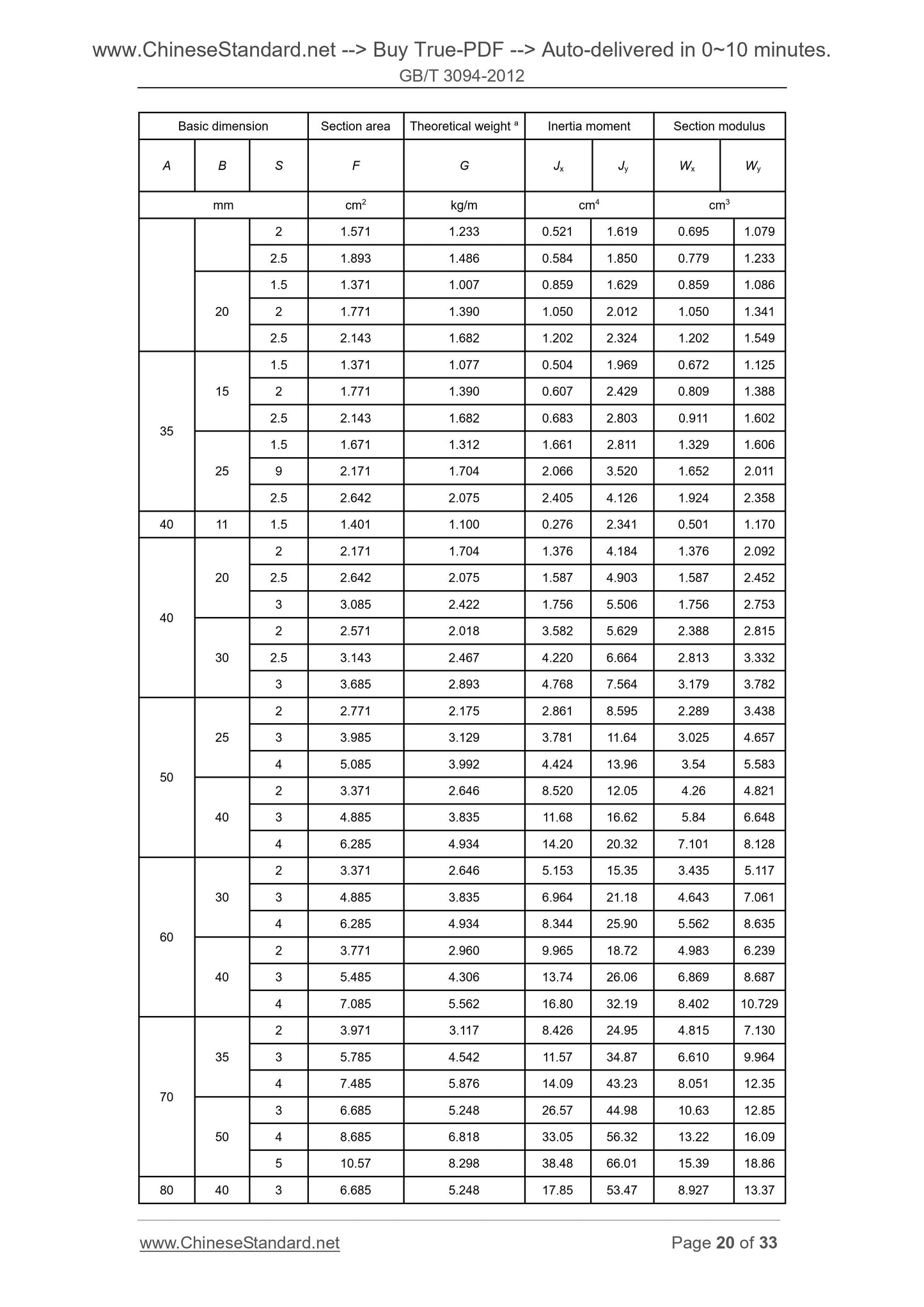
5.1 Shape and dimension
The shape and dimension of steel tube shall respectively meet the requirements of
Figures A.1~A.6 and Tables A.1~A.6 in Appendix A. As negotiated by the supplier and
the purchaser, steel tube with shape and/or size beyond those specified in Figures
A.1~A.6 and Tables A.1~A.6 in Appendix A may be supplied.
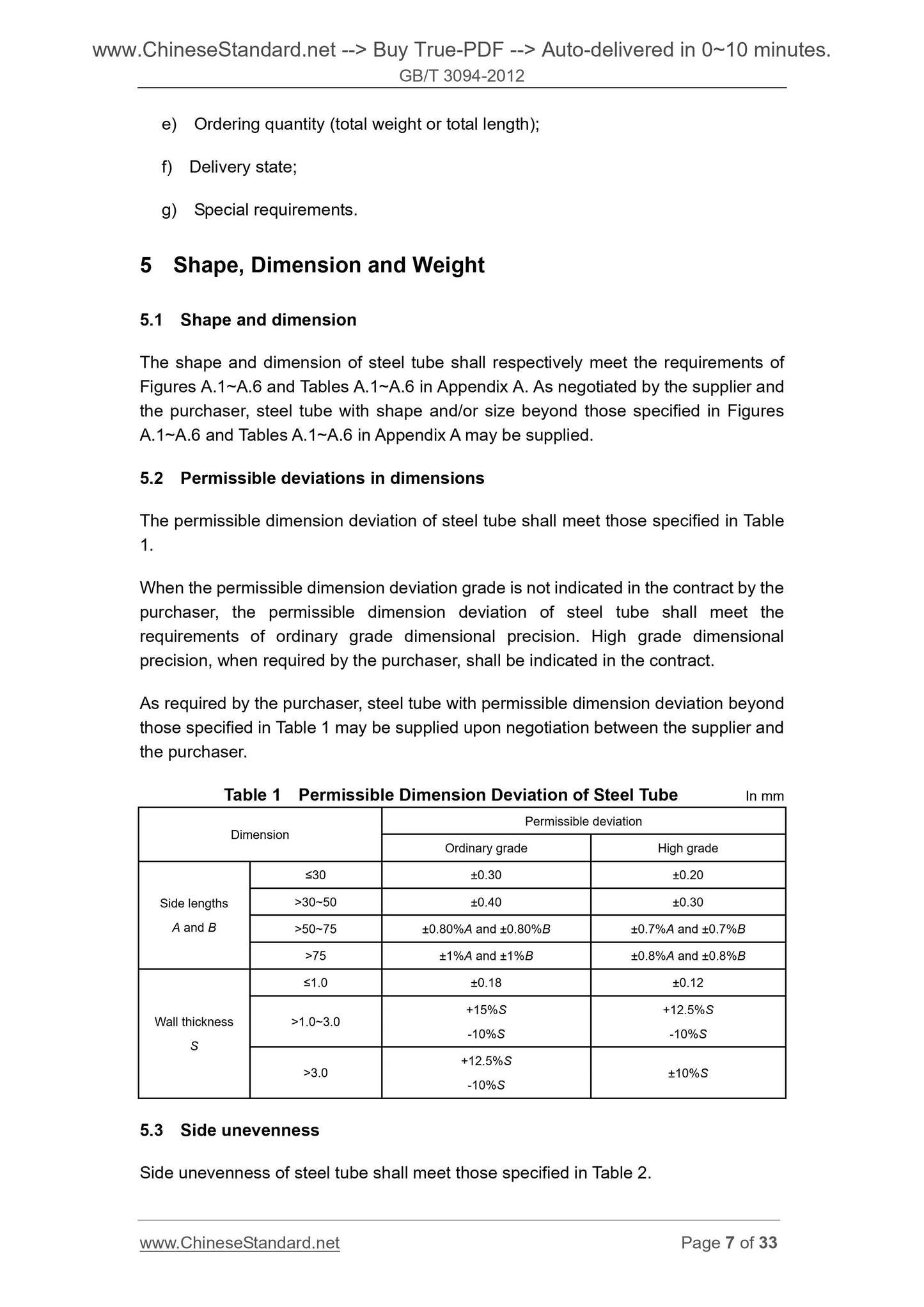
5.2 Permissible deviations in dimensions
The permissible dimension deviation of steel tube shall meet those specified in Table
1.
When the permissible dimension deviation grade is not indicated in the contract by the
purchaser, the permissible dimension deviation of steel tube shall meet the
requirements of ordinary grade dimensional precision. High grade dimensional
precision, when required by the purchaser, shall be indicated in the contract.
As required by the purchaser, steel tube with permissible dimension deviation beyond
those specified in Table 1 may be supplied upon negotiation between the supplier and
the purchaser.
Table 1 Permissible Dimension Deviation of Steel Tube In mm
Dimension
Permissible deviation
Ordinary grade High grade
Side lengths
A and B
≤30 ±0.30 ±0.20
>30~50 ±0.40 ±0.30
>50~75 ±0.80%A and ±0.80%B ±0.7%A and ±0.7%B
>75 ±1%A and ±1%B ±0.8%A and ±0.8%B
Wall thickness
≤1.0 ±0.18 ±0.12
>1.0~3.0 +15%S -10%S
+12.5%S
-10%S
>3.0 +12.5%S -10%S ±10%S
5.3 Side unevenness
Side unevenness of steel tube shall meet those specified in Table 2.
Table 5 Twist Value of Steel Tube
Side length of steel tube/mm Permissible twist value/(mm/m)
≤30 ≤1.5
>30~75 ≤2.0
>75 ≤2.5
5.7 Length
5.7.1 General length
The general length of steel tube is 2000~9000mm.
As required by the purchaser, steel tube with length beyond those specified may be
supplied upon negotiation between the supplier and the purchaser and when
indicated in the contract.
5.7.2 Specified length and multiple length
5.7.2.1 As required by the purchaser, steel tube may be delivered with specified
length or multiple length upon negotiation between the supplier and the purchaser and
when indicated in the contract
5.7.2.2 The specified length and multiple length shall be within the range of general
length. The permissible deviation of the specified length is 15
mm; while that of the
total multiple length is 10
mm; each multiple length shall be remained with a notch
allowance of 5~10mm.
5.8 End shape
End faces on both ends of steel tube shall be vertical to the axis of steel tube, and the
burr on notch shall be removed.
5.9 Weight
The steel tube is delivered according to actual weight. When indicated in the contract,
it may also be delivered according to the theoretical weight. See Appendix A for the
calculation formula of theoretical weight (with steel density of 7.85 kg/dm3).
6 Technical Requirements
6.1 Designation and chemical composition of steel
6.1.1 For quality carbon structural steels with designations of 10, 20, 35 and 45, the
chemical composition (heat analysis) shall meet the requirements of GB/T 699.
For carbon structural steels with designations of Q195, Q215 and Q235, the chemical
composition (heat analysis) shall meet the requirements of GB/T 700.
For high strength low alloy structural steels with designations of Q345 and Q390, the
chemical composition (heat analysis) shall meet the requirements of GB/T 1591.
As required by the purchaser, structural alloy steel tube may be supplied upon
negotiation between the supplier and the purchaser, and its designation and chemical
composition (heat analysis) shall meet the requirements of GB/T 3077.
6.1.2 Chemical analysis for finished product, when required by the purchaser, shall
be indicated in the contract. The permissible deviation for chemical composition of
finished steel tube shall meet the requirements of GB/T 222.
6.1.3 As required by the purchaser, steel tube of other designation may be supplied
upon negotiation between the supplier and the purchaser.
6.2 Manufacturing method
6.2.1 Steel tube shall be manufactured of seamless steel tube through cold-drawn
forming.
6.2.2 As required by the purchaser, steel tube may be manufactured of welded steel
tube through cold-drawn forming upon negotiation between the supplier and the
purchaser and when indicated in the contract. The weld of cold-drawn welded steel
tube shall be kept away from round corner.
6.3 Delivery state
The steel tube shall be delivered in cold-drawn state. As required by the purchaser,
the steel tube may be delivered in heat treatment state upon negotiation between the
supplier and the purchaser and when indicated in the contract.
6.4 Mechanical performance
6.4.1 Steel tube delivered in cold-drawn state is not subject to mechanical
performance test. When the steel tube is delivered in heat treatment state, the
longitudinal mechanical performance of steel tube shall meet those specified in Table
6 while that of the structural alloy steel tube shall meet those specified in GB/T 3077.
6.4.2 For Q195, Q215, Q235, Q345 and Q390 steel tubes delivered in heat
treatment state, when the perimeter is not less than 240mm and the wall thickness is
not less than 10mm, impact test shall be carried out; thereof the impact absorbed
energy (KV2) of Charpy V-notch shall meet those specified in Table 6. The width of
impact specimen shall be 10mm, 7.5mm or 5mm (the largest dimension is taken if
possible); when it fails to cut 5mm-wide specimen, impact test may not be carried out.
The impact absorbed energy in Table 6 is the required value of Charpy V-notch of
Table 7 Decline Factor for Impact Absorbed Energy of Small-dimension Specimen
Size of specimen Dimension of specimen (high × width)/(mm×mm) Decline factor
Standard specimen 10×10 1
Small specimen 10×7.5 0.75
Small specimen 10×5 0.50
6.5 Surface quality
6.5.1 The internal and external surfaces of steel tube shall be free from crack, fold,
scab, creasing and delamination. These defects shall be completely removed with
removed depth not exceed the negative deviation of nominal wall thickness. The
actual wall thickness of the removal point shall not be less than the permissible
minimum deviation of the wall thickness.
6.5.2 Other local defects not exceed the negative deviation of wall thickness are
permissible.
6.5.3 For internal and external surfaces of steel tube delivered in cold treatment
state, the phosphate and lubricant layers are permissible during manufacturing
process. As required by the purchaser, the supplier may rem...
Get Quotation: Click GB/T 3094-2012 (Self-service in 1-minute)
Historical versions (Master-website): GB/T 3094-2012
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll-down if blank)
GB/T 3094-2012: Cold drawn shaped steel tubes
GB/T 3094-2012
GB
NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE
PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 77.140.75
H48
Replacing GB/T 3094-2000
Cold Drawn Shaped Steel Tubes
ISSUED ON. MAY 11, 2012
IMPLEMENTED ON. FEBRUARY 1, 2013
Issued by. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and
Quarantine (AQSIQ);
Standardization Administration (SAC) of the People's
Republic of China.
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
1 Scope ... 4
2 Normative References ... 4
3 Classification and Designation ... 6
4 Ordering Information ... 6
5 Shape, Dimension and Weight ... 7
6 Technical Requirements ... 9
7 Test Methods ... 12
8 Inspection Rules ... 13
9 Packaging, Marking and Quality Certificate ... 13
Appendix A (Normative) Shape and Dimension of Steel Tube ... 14
Appendix B (Normative) Determination Method for Twist Value of Shaped Steel
Tube ... 32
Foreword
This Standard is drafted according to the rules given in GB/T 1.1-2009.
This Standard is revised by reference to ASTM A 500-07 "Standard Specification for
Cold-formed Welded and Seamless Carbon Steel Structural Tubing in Rounds and
Shapes".
This Standard replace GB/T 3094-2000 "Cold Drawn Shaped Steel Tubes" (GB/T
3094-2000). Compared with GB/T 3094-2000, the main changes of this Standard are
as follows.
- Quality grades of steel designations Q215, Q235, Q345 and Q390 are added;
Q295 is deleted;
- Ordering information is added;
- Curvature and twist value requirements are modified;
- Marking example is deleted;
- General length is modified;
- Mechanical performance of steel tube is modified;
- Requirements for impact test of steel tube are added;
- Size and dimension of steel tube in Appendix A are modified.
This Standard was proposed by China Iron and Steel Association.
This Standard shall be under the jurisdiction of the National Technical Committee on
Iron and Steel of Standardization Administration of China (SAC/TC 183).
Drafting organizations of this Standard. Shanghai Shaped Steel Tube Co., Ltd. AND
Jiangsu Jieda Specific New Material Co., Ltd.
Chief drafting staffs of this Standard. Gao Zhijian, Chen Hongqi, Zhu Sujian, Xue
Jianliang, Wang Wei, Hu Hongwei, Yang Wenyi and Lei Liangliang.
The previous editions replaced by this Standard are as follows.
- GB 3094-1982;
- GB/T 3094-2000.
Cold Drawn Shaped Steel Tubes
1 Scope
This Standard specifies the classification, designation, ordering information, shape,
dimension, technical requirements, test method, inspection rule, packaging, marking
and quality certificate of cold drawn shaped steel tubes.
This Standard is applicable to cold-drawn simple-section shaped tube (hereinafter
referred to as steel tube).
2 Normative References
The following referenced documents are indispensable for the application of this
document. For dated references, only the edition cited applies. For undated
references, the latest edition of the normative document (including any amendments)
applies.
GB/T 222 Permissible Tolerances for Chemical Composition of Steel Products
GB/T 223.5 Steel and Iron - Determination of Acid-soluble Silicon and Total
Silicon Content - Reduced Molybdosilicate Spectrophotometric Method
GB/T 223.9 Iron, Steel and Alloy - Determination of Aluminum Content - Chrom
Azurol S Photometric Method
GB/T 223.12 GB/T 223.62 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Iron, Steel and Alloy
- The Sodium Carbonate Separation - Diphenyl Carbazide Photometric Method for
the Determination of Chromium Content
GB/T 223.14 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Iron, Steel and Alloy - The
N-benzoy-N-phenylhydroxylamine Extraction Photometric Method for the
Determination of Vanadium Content
GB/T 223.17 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Iron, Steel and Alloy - The
Diantipyrylmethane Photometric Method for the Determination of Titanium Content
GB/T 223.19 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Iron, Steel and Alloy - The
Neocuproine - Chloroform Extraction Photometric Method for the Determination of
Copper Content
GB/T 223.23 Iron Steel and Alloy - Determination of Nickel Content - The
Dimethylglyoxime Spectrophotometric Method
GB/T 223.40 Iron Steel and Alloy - Determination of Niobium Content by the
Sulphochlorophenol S Spectrophotometric Method
GB/T 223.59 Iron Steel and Alloy - Determination of Phosphorus Content -
Bismuth Phosphomolybdate Blue Spectrophotometric Method and Antimony
Phosphomolybdate Blue Spectrophotometric Method
GB/T 223.60 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Iron, Steel and Alloy - The
Perchloric Acid Dehydration Gravimetric Method for the Determination of Silicon
Content
GB/T 223.62 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Iron, Steel and Alloy - The Butyl
Acetate Extraction Photometric Method for the Determination of Phosphorus
Content
GB/T 223.63 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Iron, Steel and Alloy - The
Sodium (Potassium) Periodate Photometric Method for the Determination of
Manganese Content
GB/T 223.64 Iron Steel and Alloy - Determination of Manganese Content - Flame
Atomic Absorption Spectrometric Method
GB/T 223.68 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Iron, Steel and Alloy - The
Potassium Iodate Titration Method after Combustion in the Pipe Furnace for the
Determination of Sulfur Content
GB/T 223.69 Iron Steel and Alloy - Determination of Carbon Contents -
Gas-volumetric Method after Combustion in the Pipe Furnace
GB/T 223.71 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Iron, Steel and Alloy - The
Gravimetric Method after Combustion in the Pipe Furnace for the Determination of
Carbon Content
GB/T 223.72 Iron Steel and Alloy - Determination of Sulfur Content - Gravimetric
Method
GB/T 228.1 Metallic Materials - Tensile Testing - Part 1. Method of Test at Room
Temperature
GB/T 229 Metallic Materials - Charpy Pendulum Impact Test Method
GB/T 699 Quality Carbon Structural Steels
GB/T 700 Carbon Structural Steels
GB/T 1591 High Strength Low Alloy Structural Steels
GB/T 2102 Acceptance, Packing, Marking and Certification of Pipe
GB/T 2975 Steel and Steel Products - Location and Preparation of Test Pieces for
Mechanical Testing
GB/T 3077 Alloy Structure Steels
GB/T 4336 Standard Test Method for Spark Discharge Atomic Emission
Spectrometric Analysis of Carbon and Low-alloy Steel (Routine Method)
GB/T 20066 Steel and Iron - Sampling and Preparation of Samples for the
Determination of Chemical Composition
GB/T 20123 Steel and Iron - Determination of Total Carbon and Sulfur Content
Infrared Absorption Method after Combustion in an Induction Furnace (Routine
Method)
GB/T 20125 Low-alloy Steel - Determination of Multi-element Contents -
Inductively Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission Spectrometric Method
3 Classification and Designation
Classification and designation of steel tubes according to section shape are as
follows.
a) Square steel tube D-1;
b) Rectangle steel tube D-2;
c) Elliptical steel tube D-3;
d) Flat oval steel tube D-4;
e) Inside and outside hexagonal steel tube D-5;
f) Rectangular trapezoid steel tube D-6.
4 Ordering Information
The contract or order for ordering steel tubes according to this Standard shall include
but not limited to the following contents.
a) Standard No.;
b) Product name;
c) Designation and quality grade of steel (if applicable);
d) Size and dimension;
e) Ordering quantity (total weight or total length);
f) Delivery state;
g) Special requirements.
5 Shape, Dimension and Weight
5.1 Shape and dimension
The shape and dimension of steel tube shall respectively meet the requirements of
Figures A.1~A.6 and Tables A.1~A.6 in Appendix A. As negotiated by the supplier and
the purchaser, steel tube with shape and/or size beyond those specified in Figures
A.1~A.6 and Tables A.1~A.6 in Appendix A may be supplied.
5.2 Permissible deviations in dimensions
The permissible dimension deviation of steel tube shall meet those specified in Table
1.
When the permissible dimension deviation grade is not indicated in the contract by the
purchaser, the permissible dimension deviation of steel tube shall meet the
requirements of ordinary grade dimensional precision. High grade dimensional
precision, when required by the purchaser, shall be indicated in the contract.
As required by the purchaser, steel tube with permissible dimension deviation beyond
those specified in Table 1 may be supplied upon negotiation between the supplier and
the purchaser.
Table 1 Permissible Dimension Deviation of Steel Tube In mm
Dimension
Permissible deviation
Ordinary grade High grade
Side lengths
A and B
≤30 ±0.30 ±0.20
>30~50 ±0.40 ±0.30
>50~75 ±0.80%A and ±0.80%B ±0.7%A and ±0.7%B
>75 ±1%A and ±1%B ±0.8%A and ±0.8%B
Wall thickness
≤1.0 ±0.18 ±0.12
>1.0~3.0 +15%S -10%S
+12.5%S
-10%S
>3.0 +12.5%S -10%S ±10%S
5.3 Side unevenness
Side unevenness of steel tube shall meet those specified in Table 2.
Table 5 Twist Value of Steel Tube
Side length of steel tube/mm Permissible twist value/(mm/m)
≤30 ≤1.5
>30~75 ≤2.0
>75 ≤2.5
5.7 Length
5.7.1 General length
The general length of steel tube is 2000~9000mm.
As required by the purchaser, steel tube with length beyond those specified may be
supplied upon negotiation between the supplier and the purchaser and when
indicated in the contract.
5.7.2 Specified length and multiple length
5.7.2.1 As required by the purchaser, steel tube may be delivered with specified
length or multiple length upon negotiation between the supplier and the purchaser and
when indicated in the contract
5.7.2.2 The specified length and multiple length shall be within the range of general
length. The permissible deviation of the specified length is 15
mm; while that of the
total multiple length is 10
mm; each multiple length shall be remained with a notch
allowance of 5~10mm.
5.8 End shape
End faces on both ends of steel tube shall be vertical to the axis of steel tube, and the
burr on notch shall be removed.
5.9 Weight
The steel tube is delivered according to actual weight. When indicated in the contract,
it may also be delivered according to the theoretical weight. See Appendix A for the
calculation formula of theoretical weight (with steel density of 7.85 kg/dm3).
6 Technical Requirements
6.1 Designation and chemical composition of steel
6.1.1 For quality carbon structural steels with designations of 10, 20, 35 and 45, the
chemical composition (heat analysis) shall meet the requirements of GB/T 699.
For carbon structural steels with designations of Q195, Q215 and Q235, the chemical
composition (heat analysis) shall meet the requirements of GB/T 700.
For high strength low alloy structural steels with designations of Q345 and Q390, the
chemical composition (heat analysis) shall meet the requirements of GB/T 1591.
As required by the purchaser, structural alloy steel tube may be supplied upon
negotiation between the supplier and the purchaser, and its designation and chemical
composition (heat analysis) shall meet the requirements of GB/T 3077.
6.1.2 Chemical analysis for finished product, when required by the purchaser, shall
be indicated in the contract. The permissible deviation for chemical composition of
finished steel tube shall meet the requirements of GB/T 222.
6.1.3 As required by the purchaser, steel tube of other designation may be supplied
upon negotiation between the supplier and the purchaser.
6.2 Manufacturing method
6.2.1 Steel tube shall be manufactured of seamless steel tube through cold-drawn
forming.
6.2.2 As required by the purchaser, steel tube may be manufactured of welded steel
tube through cold-drawn forming upon negotiation between the supplier and the
purchaser and when indicated in the contract. The weld of cold-drawn welded steel
tube shall be kept away from round corner.
6.3 Delivery state
The steel tube shall be delivered in cold-drawn state. As required by the purchaser,
the steel tube may be delivered in heat treatment state upon negotiation between the
supplier and the purchaser and when indicated in the contract.
6.4 Mechanical performance
6.4.1 Steel tube delivered in cold-drawn state is not subject to mechanical
performance test. When the steel tube is delivered in heat treatment state, the
longitudinal mechanical performance of steel tube shall meet those specified in Table
6 while that of the structural alloy steel tube shall meet those specified in GB/T 3077.
6.4.2 For Q195, Q215, Q235, Q345 and Q390 steel tubes delivered in heat
treatment state, when the perimeter is not less than 240mm and the wall thickness is
not less than 10mm, impact test shall be carried out; thereof the impact absorbed
energy (KV2) of Charpy V-notch shall meet those specified in Table 6. The width of
impact specimen shall be 10mm, 7.5mm or 5mm (the largest dimension is taken if
possible); when it fails to cut 5mm-wide specimen, impact test may not be carried out.
The impact absorbed energy in Table 6 is the required value of Charpy V-notch of
Table 7 Decline Factor for Impact Absorbed Energy of Small-dimension Specimen
Size of specimen Dimension of specimen (high × width)/(mm×mm) Decline factor
Standard specimen 10×10 1
Small specimen 10×7.5 0.75
Small specimen 10×5 0.50
6.5 Surface quality
6.5.1 The internal and external surfaces of steel tube shall be free from crack, fold,
scab, creasing and delamination. These defects shall be completely removed with
removed depth not exceed the negative deviation of nominal wall thickness. The
actual wall thickness of the removal point shall not be less than the permissible
minimum deviation of the wall thickness.
6.5.2 Other local defects not exceed the negative deviation of wall thickness are
permissible.
6.5.3 For internal and external surfaces of steel tube delivered in cold treatment
state, the phosphate and lubricant layers are permissible during manufacturing
process. As required by the purchaser, the supplier may rem...
Share