1
/
of
8
PayPal, credit cards. Download editable-PDF and invoice in 1 second!
GB/T 7184-2008 English PDF (GB/T7184-2008)
GB/T 7184-2008 English PDF (GB/T7184-2008)
Regular price
$145.00
Regular price
Sale price
$145.00
Unit price
/
per
Shipping calculated at checkout.
Couldn't load pickup availability
GB/T 7184-2008: Small and medium power diesel engines -- Measurement and evaluation of vibration
Delivery: 9 seconds. Download (and Email) true-PDF + Invoice.
Newer version: (Replacing this standard) GB/T 7184-2023
Get Quotation: Click GB/T 7184-2008 (Self-service in 1-minute)
Historical versions (Master-website): GB/T 7184-2023
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll-down if blank)
GB/T 7184-2008
GB
NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE
PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 27.020
J 90
Replacing GB/T 7184-1987, GB/T 10397-2003
Small and medium power diesel engines -
Measurement and evaluation of vibration
ISSUED ON. AUGUST 11, 2008
IMPLEMENTED ON. FEBRUARY 01, 2009
Issued by. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and
Quarantine;
Standardization Administration of PRC.
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
Introduction ... 4
1 Scope ... 6
2 Normative references ... 6
3 Terms and definitions ... 7
4 Method for vibration measurement ... 7
5 Rating criteria for vibration ... 11
Appendix A (Normative) Rating of machine’s vibration ... 13
Appendix B (Informative) Record for measurement of vibration of reciprocating
diesel engine ... 15
Appendix C (Informative) Nomogram of grade of vibration severity ... 17
Appendix D (Informative) Classification of machine’s vibration ... 19
References ... 21
Foreword
This standard is a revision of GB/T 7184-1987 “Small and medium power diesel
engines - Measurement and evaluation of vibration” and GB/T 10397-2003
“Small and medium power engines - Evaluation of vibration”.
The main differences between this standard and the revised standard are as
follows.
- EXTEND the scope of application;
- IMPROVE the vibration measurement and rating scales;
- MODIFY the conditions of measurement;
- ADD Appendix D, to provide a reference table for the classification of
vibration of reciprocating diesel engine.
Appendix A of this standard is normative. Appendix B, Appendix C and
Appendix D are informative.
This standard, from the date of implementation, replaces GB/T 7184-1987 and
GB/T 10397-2003.
This standard was proposed by the China Machinery Industry Federation.
This standard shall be under the jurisdiction of the National Internal Combustion
Engine Standardization Technical Committee (SAC/TC 177).
Drafting organizations of this standard. Shanghai Internal Combustion Engine
Research Institute, Mianyang Xinchen Power Machinery Co., Ltd., Guangxi
Yuchai Machinery Group Co., Ltd., Shanghai Automotive Group Co., Ltd.
Technology Center.
The main drafters of this standard. Yuan Weiping, Ye Huaihan, Cai Xiangru,
Wang Liqiang, Wang Jianzhong, Wang Hongjian, Luo Zhijian, Chen Weifang.
This standard replaces the standard previously issued as follows.
- GB/T 7184-1987;
- GB 10397-1989, GB/T 10397-2003.
Small and medium power diesel engines -
Measurement and evaluation of vibration
1 Scope
This standard specifies the measurement methods and rating criteria for the
vibration of the non-rotating and non-reciprocating parts of reciprocating diesel
engines. Shaft vibrations (including torsional vibrations) are outside the scope
of this standard.
This standard is applicable to the reciprocating-piston diesel engines with rigid
or flexible support. The typical applications are diesel engines for low-speed
trucks, three-wheeled vehicles, tractors, irrigation pumps, marine main engines,
marine auxiliary engines, generator sets, etc.
This standard also applies to matched machines that are driven by
reciprocating machines or that drive reciprocating machines. For the purposes
of this, it shall follow the relevant criteria and rating for assessment.
This standard does not apply to reciprocating diesel engines which have a
power greater than 100 kW and is installed on road vehicles (such as industrial
trucks).
The rating criteria as provided by this standard apply to operational monitoring
and acceptance tests, to assess the adverse effects of mechanical vibration of
diesel engines on equipment which is directly installed on diesel engines.
The rating criteria as provided in this standard do not apply to the assessment
of internal parts of diesel engines. For example, problems related to valves,
pistons, piston rings, etc. may not be reflected in the measurement, the
identification of these problems requires the use of research techniques. The
same noise is also not within the scope of this standard.
2 Normative references
The provisions in following documents become the provisions of this standard
through reference in this standard. For the dated references, the subsequent
amendments (excluding corrections) or revisions do not apply to this standard;
however, parties who reach an agreement based on this standard are
encouraged to study if the latest versions of these documents are applicable.
For undated references, the latest edition of the referenced document applies.
accuracy as required by the measuring system. For the reciprocating diesel
engine which has a power of 100 kW or less, it only requires measure the root
mean square of the velocity, which can also be obtained indirect measurement
through signal processing.
Both the frequency response and the measured vibration amplitude are related
to the method of fixing the sensor. It is especially important to maintain a reliable
fixation between the sensor and the diesel engine at high vibration values. For
example, the GB/T 14412 has a guide on the installation of accelerometer.
4.2 Position of measuring point and direction of measurement
In order to ensure that the rating of vibration measurement is as uniform as
possible, thus carrying out accurate comparison of different diesel engines, the
recommended positions of measurement are as shown in Figures 1 ~ 4. Usually
it must carry out measurement at these positions of measuring points along the
three primary directions as related to the diesel engine.
The diesel engine as shown in Figures 1 ~ 4 is only an example. For different
types of diesel engines (such as star-shaped engines), it may use the similar
measuring points.
If, based on the experience of similar diesel engines, it can predict the position
of the maximum vibration severity, it is not necessary to consider all the
measuring points as specified in the Figure. However, it shall include the
positions of the bearing that is easily accessible to the load. For the acceptance
test, if the number of measuring points used is small, it shall be agreed
otherwise between the manufacturer and the customer.
If it wants to study it more carefully or compare it, it shall give priority to using
the measuring points in Figures 1 ~ 4.
When selecting the appropriate measuring points, it shall consider the structural
arrangement and installation restrictions of the specific diesel engine under
testing. All the selected measuring points shall be able to properly fix the
vibration sensor on the main structure of the diesel engine.
Measuring the vibration of parts as installed in a diesel engine can provide
useful information about the failure, but the guidelines as listed in this standard
apply only to the position of the measuring points as given in Figures 1 ~ 4 on
the main structure of the diesel engine.
Example
It is marked at the right edge of the rack, at the diesel engine’s coupling end, along the Y
(horizontal) direction as follows.
the maximum vibration which occurs within the range of rated power and speed
under normal operation.
4.4 Recording of measurement results
The records of measurement results shall include the basic data of the diesel
engine and the use of the measurement system, which shall be included in
Table B.1 and Table B.2 in of Appendix B which are used as the measurement
record.
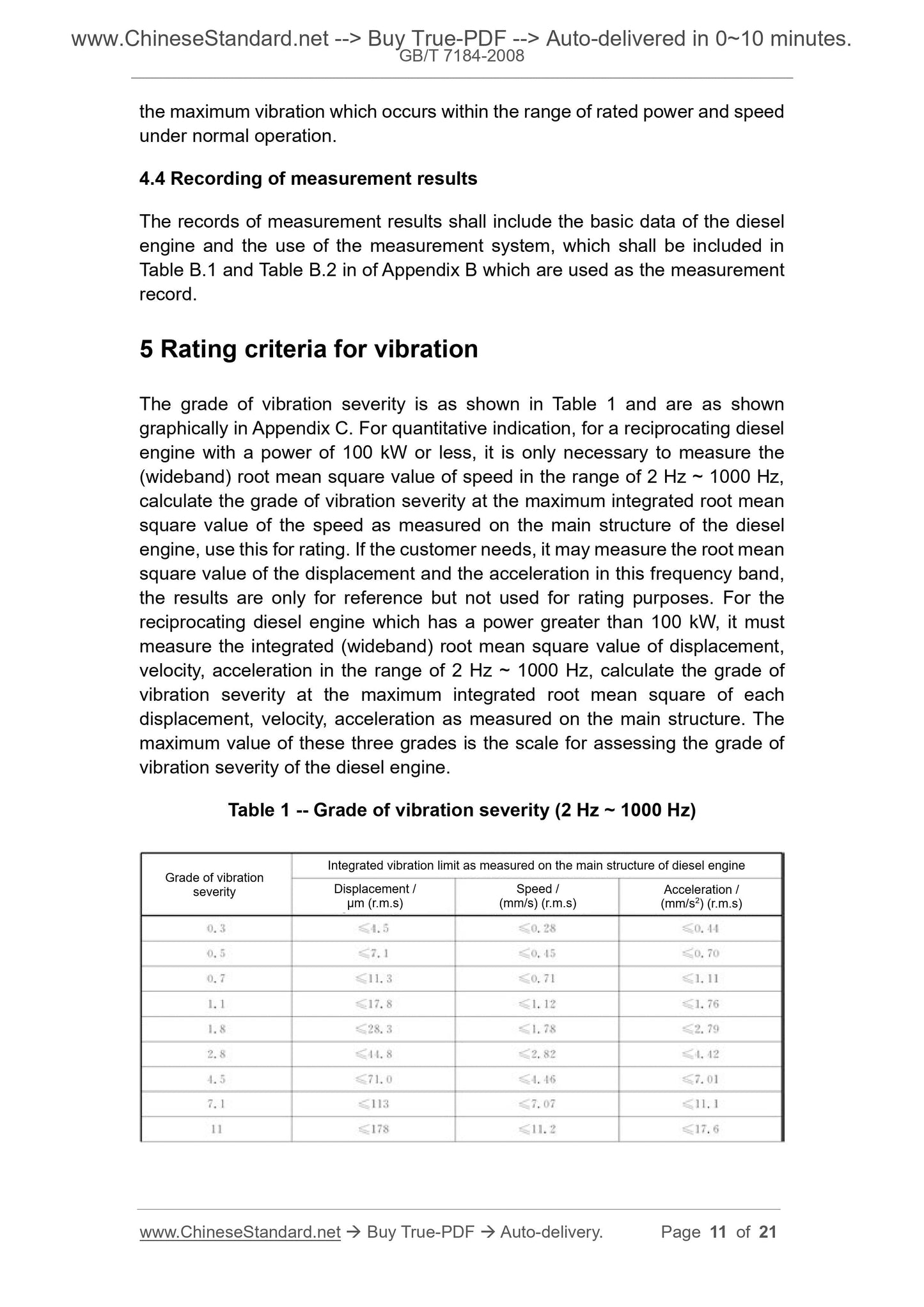
5 Rating criteria for vibration
The grade of vibration severity is as shown in Table 1 and are as shown
graphically in Appendix C. For quantitative indication, for a reciprocating diesel
engine with a power of 100 kW or less, it is only necessary to measure the
(wideband) root mean square value of speed in the range of 2 Hz ~ 1000 Hz,
calculate the grade of vibration severity at the maximum integrated root mean
square value of the speed as measured on the main structure of the diesel
engine, use this for rating. If the customer needs, it may measure the root mean
square value of the displacement and the acceleration in this frequency band,
the results are only for reference but not used for rating purposes. For the
reciprocating diesel engine which has a power greater than 100 kW, it must
measure the integrated (wideband) root mean square value of displacement,
velocity, acceleration in the range of 2 Hz ~ 1000 Hz, calculate the grade of
vibration severity at the maximum integrated root mean square of each
displacement, velocity, acceleration as measured on the main structure. The
maximum value of these three grades is the scale for assessing the grade of
vibration severity of the diesel engine.
Table 1 -- Grade of vibration severity (2 Hz ~ 1000 Hz)
Grade of vibration
severity
Integrated vibration limit as measured on the main structure of diesel engine
Displacement /
μm (r.m.s)
Speed /
(mm/s) (r.m.s)
Acceleration /
(mm/s2) (r.m.s)
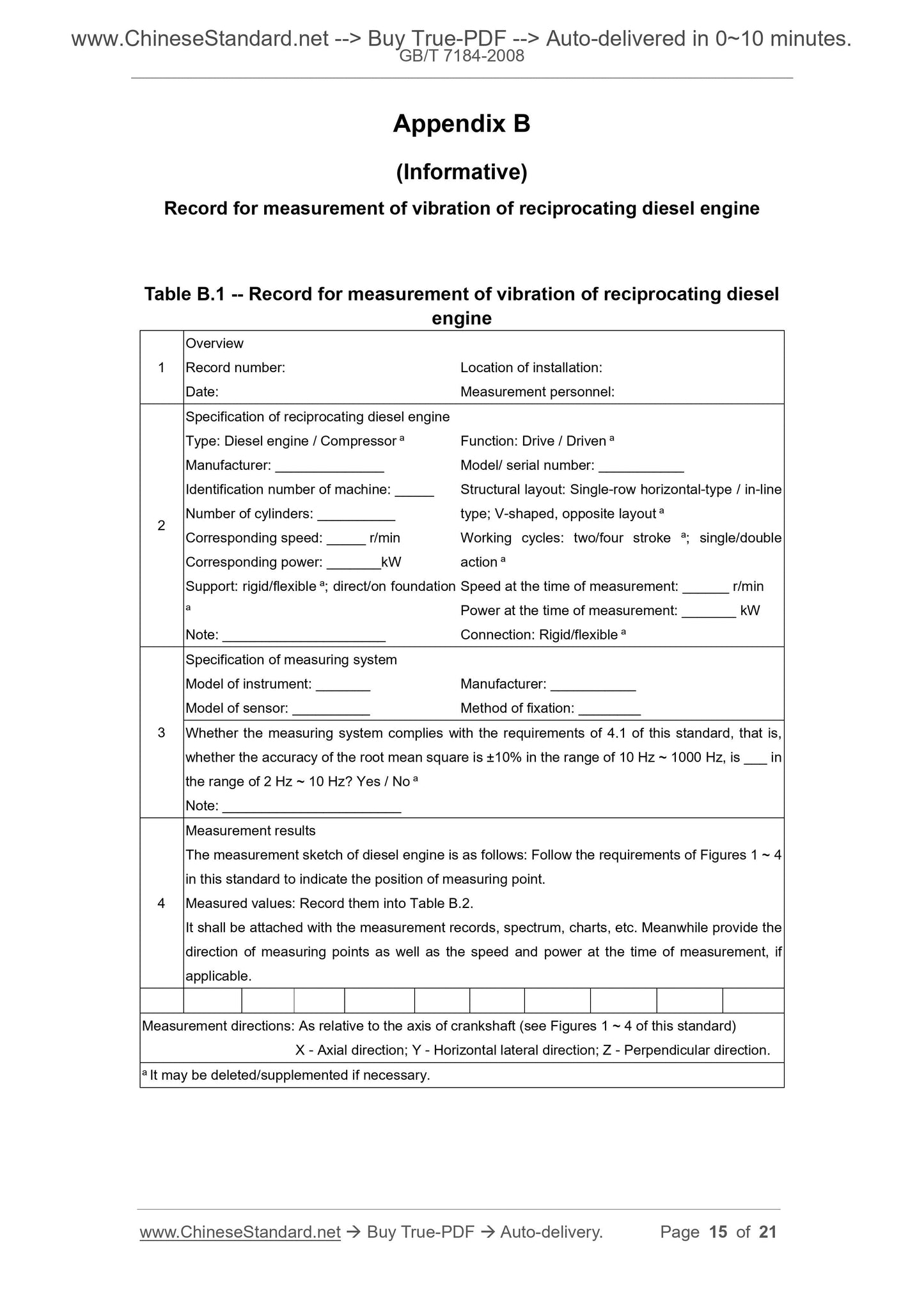
Appendix B
(Informative)
Record for measurement of vibration of reciprocating diesel engine
Table B.1 -- Record for measurement of vibration of reciprocating diesel
engine
Overview
Record number.
Date.
Location of installation.
Measurement personnel.
Specification of reciprocating diesel engine
Type. Diesel engine / Compressor a
Identification number of machine. _____
Corresponding speed. _____ r/min
Support. rigid/flexible a; direct/on foundation
Function. Drive / Driven a
Structural layout. Single-row horizontal-type / in-line
type; V-shaped, opposite layout a
Working cycles. two/four stroke a; single/double
action a
Connection. Rigid/flexible a
Specification of measuring system
Whether the measuring system complies with the requirements of 4.1 of this standard, that is,
whether the accuracy of the root mean square is ±10% in the range of 10 Hz ~ 1000 Hz, is ___ in
the range of 2 Hz ~ 10 Hz? Yes / No a
Measurement results
The measurement sketch of diesel engine is as follows. Follow the requirements of Figures 1 ~ 4
in this standard to indicate the position of measuring point.
Measured values. Record them into Table B.2.
It shall be attached with the measurement records, spectrum, charts, etc. Meanwhile provide the
direction of measuring points as well as the speed and power at the time of measurement, if
applicable.
Measurement directions. As relative to the axis of crankshaft (see Figures 1 ~ 4 of this standard)
X - Axial direction; Y - Horizontal lateral direction; Z - Perpendicular direction.
a It may be deleted/supplemented if necessary.
GB/T 7184-2008
GB
NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE
PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 27.020
J 90
Replacing GB/T 7184-1987, GB/T 10397-2003
Small and medium power diesel engines -
Measurement and evaluation of vibration
ISSUED ON. AUGUST 11, 2008
IMPLEMENTED ON. FEBRUARY 01, 2009
Issued by. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and
Quarantine;
Standardization Administration of PRC.
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
Introduction ... 4
1 Scope ... 6
2 Normative references ... 6
3 Terms and definitions ... 7
4 Method for vibration measurement ... 7
5 Rating criteria for vibration ... 11
Appendix A (Normative) Rating of machine’s vibration ... 13
Appendix B (Informative) Record for measurement of vibration of reciprocating
diesel engine ... 15
Appendix C (Informative) Nomogram of grade of vibration severity ... 17
Appendix D (Informative) Classification of machine’s vibration ... 19
References ... 21
Foreword
This standard is a revision of GB/T 7184-1987 “Small and medium power diesel
engines - Measurement and evaluation of vibration” and GB/T 10397-2003
“Small and medium power engines - Evaluation of vibration”.
The main differences between this standard and the revised standard are as
follows.
- EXTEND the scope of application;
- IMPROVE the vibration measurement and rating scales;
- MODIFY the conditions of measurement;
- ADD Appendix D, to provide a reference table for the classification of
vibration of reciprocating diesel engine.
Appendix A of this standard is normative. Appendix B, Appendix C and
Appendix D are informative.
This standard, from the date of implementation, replaces GB/T 7184-1987 and
GB/T 10397-2003.
This standard was proposed by the China Machinery Industry Federation.
This standard shall be under the jurisdiction of the National Internal Combustion
Engine Standardization Technical Committee (SAC/TC 177).
Drafting organizations of this standard. Shanghai Internal Combustion Engine
Research Institute, Mianyang Xinchen Power Machinery Co., Ltd., Guangxi
Yuchai Machinery Group Co., Ltd., Shanghai Automotive Group Co., Ltd.
Technology Center.
The main drafters of this standard. Yuan Weiping, Ye Huaihan, Cai Xiangru,
Wang Liqiang, Wang Jianzhong, Wang Hongjian, Luo Zhijian, Chen Weifang.
This standard replaces the standard previously issued as follows.
- GB/T 7184-1987;
- GB 10397-1989, GB/T 10397-2003.
Small and medium power diesel engines -
Measurement and evaluation of vibration
1 Scope
This standard specifies the measurement methods and rating criteria for the
vibration of the non-rotating and non-reciprocating parts of reciprocating diesel
engines. Shaft vibrations (including torsional vibrations) are outside the scope
of this standard.
This standard is applicable to the reciprocating-piston diesel engines with rigid
or flexible support. The typical applications are diesel engines for low-speed
trucks, three-wheeled vehicles, tractors, irrigation pumps, marine main engines,
marine auxiliary engines, generator sets, etc.
This standard also applies to matched machines that are driven by
reciprocating machines or that drive reciprocating machines. For the purposes
of this, it shall follow the relevant criteria and rating for assessment.
This standard does not apply to reciprocating diesel engines which have a
power greater than 100 kW and is installed on r...
Delivery: 9 seconds. Download (and Email) true-PDF + Invoice.
Newer version: (Replacing this standard) GB/T 7184-2023
Get Quotation: Click GB/T 7184-2008 (Self-service in 1-minute)
Historical versions (Master-website): GB/T 7184-2023
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll-down if blank)
GB/T 7184-2008
GB
NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE
PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 27.020
J 90
Replacing GB/T 7184-1987, GB/T 10397-2003
Small and medium power diesel engines -
Measurement and evaluation of vibration
ISSUED ON. AUGUST 11, 2008
IMPLEMENTED ON. FEBRUARY 01, 2009
Issued by. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and
Quarantine;
Standardization Administration of PRC.
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
Introduction ... 4
1 Scope ... 6
2 Normative references ... 6
3 Terms and definitions ... 7
4 Method for vibration measurement ... 7
5 Rating criteria for vibration ... 11
Appendix A (Normative) Rating of machine’s vibration ... 13
Appendix B (Informative) Record for measurement of vibration of reciprocating
diesel engine ... 15
Appendix C (Informative) Nomogram of grade of vibration severity ... 17
Appendix D (Informative) Classification of machine’s vibration ... 19
References ... 21
Foreword
This standard is a revision of GB/T 7184-1987 “Small and medium power diesel
engines - Measurement and evaluation of vibration” and GB/T 10397-2003
“Small and medium power engines - Evaluation of vibration”.
The main differences between this standard and the revised standard are as
follows.
- EXTEND the scope of application;
- IMPROVE the vibration measurement and rating scales;
- MODIFY the conditions of measurement;
- ADD Appendix D, to provide a reference table for the classification of
vibration of reciprocating diesel engine.
Appendix A of this standard is normative. Appendix B, Appendix C and
Appendix D are informative.
This standard, from the date of implementation, replaces GB/T 7184-1987 and
GB/T 10397-2003.
This standard was proposed by the China Machinery Industry Federation.
This standard shall be under the jurisdiction of the National Internal Combustion
Engine Standardization Technical Committee (SAC/TC 177).
Drafting organizations of this standard. Shanghai Internal Combustion Engine
Research Institute, Mianyang Xinchen Power Machinery Co., Ltd., Guangxi
Yuchai Machinery Group Co., Ltd., Shanghai Automotive Group Co., Ltd.
Technology Center.
The main drafters of this standard. Yuan Weiping, Ye Huaihan, Cai Xiangru,
Wang Liqiang, Wang Jianzhong, Wang Hongjian, Luo Zhijian, Chen Weifang.
This standard replaces the standard previously issued as follows.
- GB/T 7184-1987;
- GB 10397-1989, GB/T 10397-2003.
Small and medium power diesel engines -
Measurement and evaluation of vibration
1 Scope
This standard specifies the measurement methods and rating criteria for the
vibration of the non-rotating and non-reciprocating parts of reciprocating diesel
engines. Shaft vibrations (including torsional vibrations) are outside the scope
of this standard.
This standard is applicable to the reciprocating-piston diesel engines with rigid
or flexible support. The typical applications are diesel engines for low-speed
trucks, three-wheeled vehicles, tractors, irrigation pumps, marine main engines,
marine auxiliary engines, generator sets, etc.
This standard also applies to matched machines that are driven by
reciprocating machines or that drive reciprocating machines. For the purposes
of this, it shall follow the relevant criteria and rating for assessment.
This standard does not apply to reciprocating diesel engines which have a
power greater than 100 kW and is installed on road vehicles (such as industrial
trucks).
The rating criteria as provided by this standard apply to operational monitoring
and acceptance tests, to assess the adverse effects of mechanical vibration of
diesel engines on equipment which is directly installed on diesel engines.
The rating criteria as provided in this standard do not apply to the assessment
of internal parts of diesel engines. For example, problems related to valves,
pistons, piston rings, etc. may not be reflected in the measurement, the
identification of these problems requires the use of research techniques. The
same noise is also not within the scope of this standard.
2 Normative references
The provisions in following documents become the provisions of this standard
through reference in this standard. For the dated references, the subsequent
amendments (excluding corrections) or revisions do not apply to this standard;
however, parties who reach an agreement based on this standard are
encouraged to study if the latest versions of these documents are applicable.
For undated references, the latest edition of the referenced document applies.
accuracy as required by the measuring system. For the reciprocating diesel
engine which has a power of 100 kW or less, it only requires measure the root
mean square of the velocity, which can also be obtained indirect measurement
through signal processing.
Both the frequency response and the measured vibration amplitude are related
to the method of fixing the sensor. It is especially important to maintain a reliable
fixation between the sensor and the diesel engine at high vibration values. For
example, the GB/T 14412 has a guide on the installation of accelerometer.
4.2 Position of measuring point and direction of measurement
In order to ensure that the rating of vibration measurement is as uniform as
possible, thus carrying out accurate comparison of different diesel engines, the
recommended positions of measurement are as shown in Figures 1 ~ 4. Usually
it must carry out measurement at these positions of measuring points along the
three primary directions as related to the diesel engine.
The diesel engine as shown in Figures 1 ~ 4 is only an example. For different
types of diesel engines (such as star-shaped engines), it may use the similar
measuring points.
If, based on the experience of similar diesel engines, it can predict the position
of the maximum vibration severity, it is not necessary to consider all the
measuring points as specified in the Figure. However, it shall include the
positions of the bearing that is easily accessible to the load. For the acceptance
test, if the number of measuring points used is small, it shall be agreed
otherwise between the manufacturer and the customer.
If it wants to study it more carefully or compare it, it shall give priority to using
the measuring points in Figures 1 ~ 4.
When selecting the appropriate measuring points, it shall consider the structural
arrangement and installation restrictions of the specific diesel engine under
testing. All the selected measuring points shall be able to properly fix the
vibration sensor on the main structure of the diesel engine.
Measuring the vibration of parts as installed in a diesel engine can provide
useful information about the failure, but the guidelines as listed in this standard
apply only to the position of the measuring points as given in Figures 1 ~ 4 on
the main structure of the diesel engine.
Example
It is marked at the right edge of the rack, at the diesel engine’s coupling end, along the Y
(horizontal) direction as follows.
the maximum vibration which occurs within the range of rated power and speed
under normal operation.
4.4 Recording of measurement results
The records of measurement results shall include the basic data of the diesel
engine and the use of the measurement system, which shall be included in
Table B.1 and Table B.2 in of Appendix B which are used as the measurement
record.
5 Rating criteria for vibration
The grade of vibration severity is as shown in Table 1 and are as shown
graphically in Appendix C. For quantitative indication, for a reciprocating diesel
engine with a power of 100 kW or less, it is only necessary to measure the
(wideband) root mean square value of speed in the range of 2 Hz ~ 1000 Hz,
calculate the grade of vibration severity at the maximum integrated root mean
square value of the speed as measured on the main structure of the diesel
engine, use this for rating. If the customer needs, it may measure the root mean
square value of the displacement and the acceleration in this frequency band,
the results are only for reference but not used for rating purposes. For the
reciprocating diesel engine which has a power greater than 100 kW, it must
measure the integrated (wideband) root mean square value of displacement,
velocity, acceleration in the range of 2 Hz ~ 1000 Hz, calculate the grade of
vibration severity at the maximum integrated root mean square of each
displacement, velocity, acceleration as measured on the main structure. The
maximum value of these three grades is the scale for assessing the grade of
vibration severity of the diesel engine.
Table 1 -- Grade of vibration severity (2 Hz ~ 1000 Hz)
Grade of vibration
severity
Integrated vibration limit as measured on the main structure of diesel engine
Displacement /
μm (r.m.s)
Speed /
(mm/s) (r.m.s)
Acceleration /
(mm/s2) (r.m.s)
Appendix B
(Informative)
Record for measurement of vibration of reciprocating diesel engine
Table B.1 -- Record for measurement of vibration of reciprocating diesel
engine
Overview
Record number.
Date.
Location of installation.
Measurement personnel.
Specification of reciprocating diesel engine
Type. Diesel engine / Compressor a
Identification number of machine. _____
Corresponding speed. _____ r/min
Support. rigid/flexible a; direct/on foundation
Function. Drive / Driven a
Structural layout. Single-row horizontal-type / in-line
type; V-shaped, opposite layout a
Working cycles. two/four stroke a; single/double
action a
Connection. Rigid/flexible a
Specification of measuring system
Whether the measuring system complies with the requirements of 4.1 of this standard, that is,
whether the accuracy of the root mean square is ±10% in the range of 10 Hz ~ 1000 Hz, is ___ in
the range of 2 Hz ~ 10 Hz? Yes / No a
Measurement results
The measurement sketch of diesel engine is as follows. Follow the requirements of Figures 1 ~ 4
in this standard to indicate the position of measuring point.
Measured values. Record them into Table B.2.
It shall be attached with the measurement records, spectrum, charts, etc. Meanwhile provide the
direction of measuring points as well as the speed and power at the time of measurement, if
applicable.
Measurement directions. As relative to the axis of crankshaft (see Figures 1 ~ 4 of this standard)
X - Axial direction; Y - Horizontal lateral direction; Z - Perpendicular direction.
a It may be deleted/supplemented if necessary.
GB/T 7184-2008
GB
NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE
PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 27.020
J 90
Replacing GB/T 7184-1987, GB/T 10397-2003
Small and medium power diesel engines -
Measurement and evaluation of vibration
ISSUED ON. AUGUST 11, 2008
IMPLEMENTED ON. FEBRUARY 01, 2009
Issued by. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and
Quarantine;
Standardization Administration of PRC.
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
Introduction ... 4
1 Scope ... 6
2 Normative references ... 6
3 Terms and definitions ... 7
4 Method for vibration measurement ... 7
5 Rating criteria for vibration ... 11
Appendix A (Normative) Rating of machine’s vibration ... 13
Appendix B (Informative) Record for measurement of vibration of reciprocating
diesel engine ... 15
Appendix C (Informative) Nomogram of grade of vibration severity ... 17
Appendix D (Informative) Classification of machine’s vibration ... 19
References ... 21
Foreword
This standard is a revision of GB/T 7184-1987 “Small and medium power diesel
engines - Measurement and evaluation of vibration” and GB/T 10397-2003
“Small and medium power engines - Evaluation of vibration”.
The main differences between this standard and the revised standard are as
follows.
- EXTEND the scope of application;
- IMPROVE the vibration measurement and rating scales;
- MODIFY the conditions of measurement;
- ADD Appendix D, to provide a reference table for the classification of
vibration of reciprocating diesel engine.
Appendix A of this standard is normative. Appendix B, Appendix C and
Appendix D are informative.
This standard, from the date of implementation, replaces GB/T 7184-1987 and
GB/T 10397-2003.
This standard was proposed by the China Machinery Industry Federation.
This standard shall be under the jurisdiction of the National Internal Combustion
Engine Standardization Technical Committee (SAC/TC 177).
Drafting organizations of this standard. Shanghai Internal Combustion Engine
Research Institute, Mianyang Xinchen Power Machinery Co., Ltd., Guangxi
Yuchai Machinery Group Co., Ltd., Shanghai Automotive Group Co., Ltd.
Technology Center.
The main drafters of this standard. Yuan Weiping, Ye Huaihan, Cai Xiangru,
Wang Liqiang, Wang Jianzhong, Wang Hongjian, Luo Zhijian, Chen Weifang.
This standard replaces the standard previously issued as follows.
- GB/T 7184-1987;
- GB 10397-1989, GB/T 10397-2003.
Small and medium power diesel engines -
Measurement and evaluation of vibration
1 Scope
This standard specifies the measurement methods and rating criteria for the
vibration of the non-rotating and non-reciprocating parts of reciprocating diesel
engines. Shaft vibrations (including torsional vibrations) are outside the scope
of this standard.
This standard is applicable to the reciprocating-piston diesel engines with rigid
or flexible support. The typical applications are diesel engines for low-speed
trucks, three-wheeled vehicles, tractors, irrigation pumps, marine main engines,
marine auxiliary engines, generator sets, etc.
This standard also applies to matched machines that are driven by
reciprocating machines or that drive reciprocating machines. For the purposes
of this, it shall follow the relevant criteria and rating for assessment.
This standard does not apply to reciprocating diesel engines which have a
power greater than 100 kW and is installed on r...
Share