1
/
of
9
www.ChineseStandard.us -- Field Test Asia Pte. Ltd.
JC/T 977-2005 English PDF (JC/T977-2005)
JC/T 977-2005 English PDF (JC/T977-2005)
Regular price
$160.00
Regular price
Sale price
$160.00
Unit price
/
per
Shipping calculated at checkout.
Couldn't load pickup availability
JC/T 977-2005: Chemically strengthened glass
Delivery: 9 seconds. Download (& Email) true-PDF + Invoice.
Get Quotation: Click JC/T 977-2005 (Self-service in 1-minute)
Historical versions (Master-website): JC/T 977-2005
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll-down if blank)
JC/T 977-2005
JC
BUILDING MATERIALS INDUSTRY STANDARD
OF THE PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 81.040.20
Q 33
Record No.. 15249-2005
Chemically strengthened glass
ISSUED ON. FEBRUARY 14, 2005
IMPLEMENTED ON. JULY 1, 2005
Issued by. National Development and Reform Commission
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
1 Scope ... 4
2 Normative references ... 4
3 Terms and definitions ... 4
4 Classification and marks... 5
5 Technical requirements ... 5
6 Test methods ... 11
7 Inspection rules ... 15
8 Package, marks, transport and storage ... 17
Appendix A ... 18
Appendix B ... 21
Foreword
This Standard was modified on the basis of European standard EN 12337-
1.2000 Glass in Building - Chemically Strengthened Soda Lime Silicate Glass
- Part 1. Definition and Description.
Compared with EN 12337-1.2000, the main technical differences are as follows.
- Deleted measurement method for squareness of planar rectangular
products; added requirements for diagonal difference;
- Added requirements and measurement methods for surface stress and
compressive stress layer depth by referring to ASTM C1422-99 Standard
Specification for Chemically Strengthened Flat Glass.
Appendix A of this Standard is normative. Appendix B is informative.
This Standard was proposed by China Building Materials Industry Association.
This Standard shall be under the jurisdiction of National Technical Committee
on Building Glass of Standardization Administration of China.
Main drafting organization of this Standard. Glass Science Institute of China
Building Materials Academy.
Drafting organizations of this Standard. China Southern Glass Technology
Holdings (Group) Co., Ltd., Beijing Gelin Jingfeng Fireproof Glass Co., Ltd..
Main drafters of this Standard. Yang Jianjun, Wang Rui, Gong Shuyi, Zhang
Baojun, Xiong Wei, Song Li, Shi Xinyong, Mo Jiao, Wu Huiting, Hu Yue.
This Standard was issued for the first time.
Chemically strengthened glass
1 Scope
This Standard specifies the term and definition, classification and marks,
technical requirements, test methods, inspection rules, package, marks,
transport and storage of chemically strengthened glass.
This Standard is applicable to flat chemically strengthened glass.
2 Normative references
The following standards contain the provisions which, through reference in this
Standard, constitute the provisions of this Standard. For dated references,
subsequent amendments (excluding corrections) or revisions do not apply to
this Standard. However, the parties who enter into agreement based on this
Standard are encouraged to investigate whether the latest versions of these
documents are applicable. For undated reference documents, the latest
versions apply to this Standard.
GB/T 1216 Micrometers
GB/T 5137.1-2002 Test Methods of Safety Glazing Materials Used on Road
Vehicle
GB 11614-1999 Float glass
GB/T 18144 Test method for measurement of stress in glass
JB/T 8788 Feeler gauges
3 Terms and definitions
The following terms and definitions apply to this document.
Chemically strengthened glass
Glass of which alkali metal ions of glass surface are replaced by other alkali
metal ions in molten salt, so as to improve mechanical strength.
Stain trace,
smog
There shall be no obvious stain trace, smog on the surface of chemically
tempered glass.
5.6 Edge and hole machining quality
5.6.1 Edge machining quality of chemically tempered glass
The edge of chemically tempered glass used in construction shall be chamfered
and fine grinded. The edge quality of chemically tempered glass used for non-
construction shall be determined by the seller and the buyer.
5.6.2 Hole edge machining quality
Hole edge machining quality shall be determined by the seller and the buyer.
5.6.2.1 The tolerance of hole aperture of chemically tempered glass products
used for construction shall comply with provisions of Table 6. This provision only
applies to the glass of which nominal thickness is not less than 4 mm. The
tolerance of hole aperture of chemically tempered glass used for non-
construction shall be determined by the seller and the buyer.
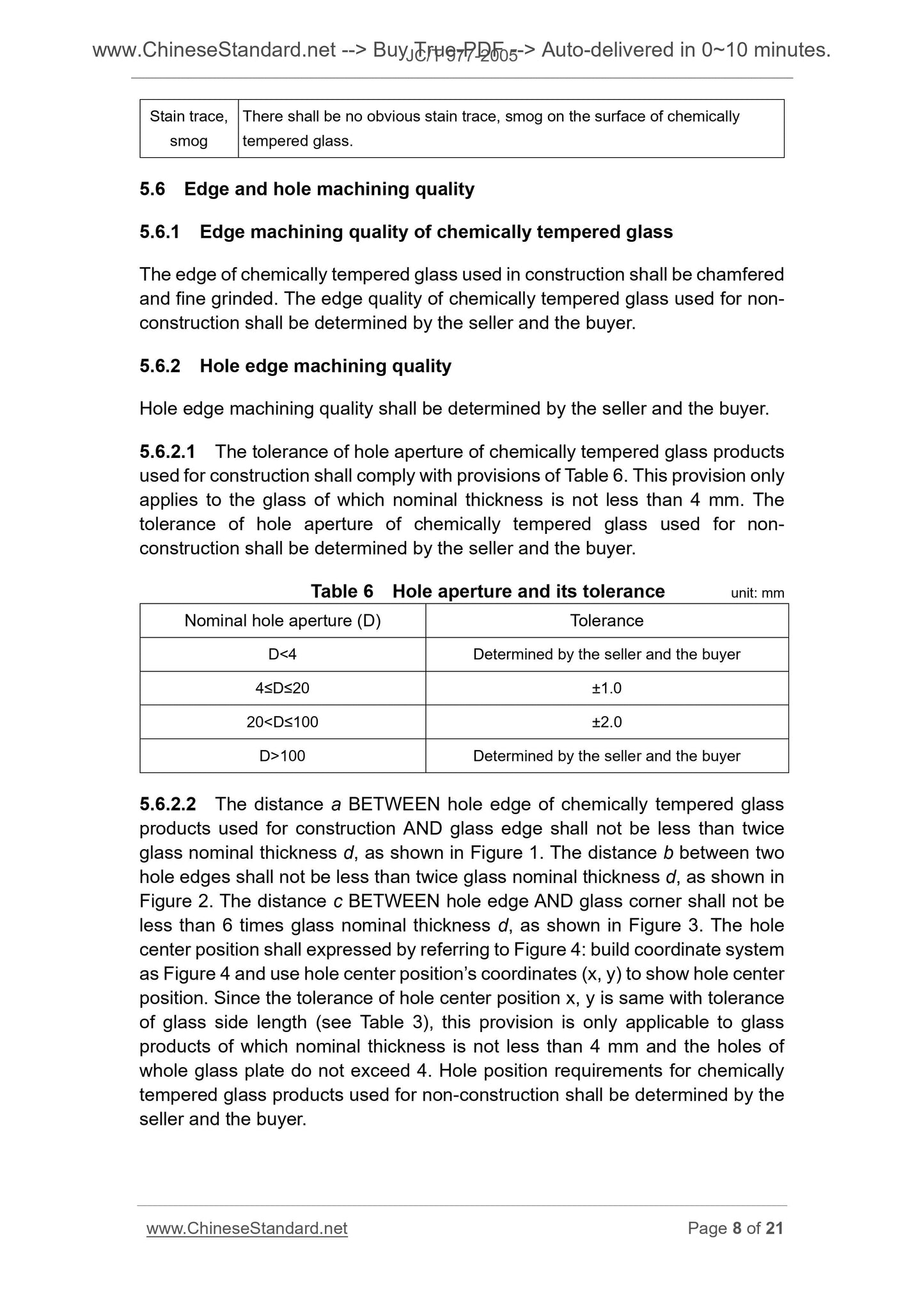
Table 6 Hole aperture and its tolerance unit. mm
Nominal hole aperture (D) Tolerance
D< 4 Determined by the seller and the buyer
4≤D≤20 ±1.0
20< D≤100 ±2.0
D>100 Determined by the seller and the buyer
5.6.2.2 The distance a BETWEEN hole edge of chemically tempered glass
products used for construction AND glass edge shall not be less than twice
glass nominal thickness d, as shown in Figure 1. The distance b between two
hole edges shall not be less than twice glass nominal thickness d, as shown in
Figure 2. The distance c BETWEEN hole edge AND glass corner shall not be
less than 6 times glass nominal thickness d, as shown in Figure 3. The hole
center position shall expressed by referring to Figure 4. build coordinate system
as Figure 4 and use hole center position’s coordinates (x, y) to show hole center
position. Since the tolerance of hole center position x, y is same with tolerance
of glass side length (see Table 3), this provision is only applicable to glass
products of which nominal thickness is not less than 4 mm and the holes of
whole glass plate do not exceed 4. Hole position requirements for chemically
tempered glass products used for non-construction shall be determined by the
seller and the buyer.
Category B 25< d≤50
Category C d>50
5.12 Impact resistance
Impact resistance of chemically tempered glass shall comply with provisions of
Table 10.
Table 10 Impact resistance of chemically tempered glass
Glass thickness d
mm
Impact height
m State after impact
d< 2 1.0 The specimen must not be
destroyed. d≥2 2.0
6 Test methods
6.1 Thickness determination
Use micrometer that complies with provisions of GB/T 1216, of which the
accuracy is 0.01 mm, or instrument of same accuracy to measure at
quadrilateral midpoint within 15 mm from glass plate edge. The arithmetic mean
of measurement results shall be its thickness value. Round it to one decimal
place.
6.2 Size determination
Use steel tape of which the minimum graduation is 1 mm to measure.
6.3 Diagonal difference
Use steel tape of which the minimum graduation is 1 mm to measure.
6.4 Appearance quality
Inspect in accordance with requirements of 5.3 in GB 11614-1999.
6.5 Edge and hole machining quality
Use caliper of which the minimum graduation is 0.1 mm to measure.
6.6 Curvature determination
Place the specimen at room temperature for more than 4h. When measuring,
make the specimen perpendicular and pad with two pads at 1/4 place under its
long side. Use a ruler or wire level closely against two sides of specimen or
stress.
7.1.2 Type inspection
Inspection items are all technical requirements stipulated by this Standard. In
case one of the following situation, type inspection shall be conducted.
a) trial type identification of new product or old product transferring
production;
b) after trial production, when there are major changes in structure, material,
process etc. which may affect product performance;
c) when normal production reaches one year;
d) when production resumes after the production is shutdown for more than
six months;
e) when there is significant difference between factory inspection results
and previous type inspection;
f) when type inspection requirements are requested by quality supervision
department.
7.2 Batching and sampling
7.2.1 Batching
Chemically tempered glasses, produced by same type of raw material under
same process conditions, shall be grouped as a batch.
7.2.2 Sampling
7.2.2.1 Thickness, size, appearance quality, curvature, surface stress shall be
randomly sampled according to Table 11.
7.2.2.2 For product’s technical requirements, if it uses product to inspect,
random sampling shall be conducted from this batch of products according to
the quantity required by inspection items. If it uses specimen to inspect, it shall
use the specimen of same-material, same-thickness and prepared under same-
process conditions as the products.
7.3 Determination rules
If the number of rejects of any one of thickness, size, appearance quality,
curvature and surface stress is greater than or equals to the number of rejects
in Table 11, then this inspection item of this product shall be deemed as
unqualified.
Appendix A
(Normative)
Bending strength test method
A.1 Test conditions
Ambient temperature. 23°C±5°C. Ambient humidity. 40%~70%. To avoid
thermal stress, during the whole process of test, the fluctuation of ambient
temperature shall not be greater than 1°C.
A.2 Specimen
Take 12 pieces of specimens to conduct the test. The length of each specimen
is 1100 mm ± 5 mm; the width is 360 mm ± 5 mm. When preparing specimen,
cutting edges shall be on the same surface of the specimen.
Within...
JC/T 977-2005
JC
BUILDING MATERIALS INDUSTRY STANDARD
OF THE PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 81.040.20
Q 33
Record No.. 15249-2005
Chemically strengthened glass
ISSUED ON. FEBRUARY 14, 2005
IMPLEMENTED ON. JULY 1, 2005
Issued by. National Development and Reform Commission
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
1 Scope ... 4
2 Normative references ... 4
3 Terms and definitions ... 4
4 Classification and marks... 5
5 Technical requirements ... 5
6 Test methods ... 11
7 Inspection rules ... 15
8 Package, marks, transport and storage ... 17
Appendix A ... 18
Appendix B ... 21
Foreword
This Standard was modified on the basis of European standard EN 12337-
1.2000 Glass in Building - Chemically Strengthened Soda Lime Silicate Glass
- Part 1. Definition and Description.
Compared with EN 12337-1.2000, the main technical differences are as follows.
- Deleted measurement method for squareness of planar rectangular
products; added requirements for diagonal difference;
- Added requirements and measurement methods for surface stress and
compressive stress layer depth by referring to ASTM C1422-99 Standard
Specification for Chemically Strengthened Flat Glass.
Appendix A of this Standard is normative. Appendix B is informative.
This Standard was proposed by China Building Materials Industry Association.
This Standard shall be under the jurisdiction of National Technical Committee
on Building Glass of Standardization Administration of China.
Main drafting organization of this Standard. Glass Science Institute of China
Building Materials Academy.
Drafting organizations of this Standard. China Southern Glass Technology
Holdings (Group) Co., Ltd., Beijing Gelin Jingfeng Fireproof Glass Co., Ltd..
Main drafters of this Standard. Yang Jianjun, Wang Rui, Gong Shuyi, Zhang
Baojun, Xiong Wei, Song Li, Shi Xinyong, Mo Jiao, Wu Huiting, Hu Yue.
This Standard was issued for the first time.
Chemically strengthened glass
1 Scope
This Standard specifies the term and definition, classification and marks,
technical requirements, test methods, inspection rules, package, marks,
transport and storage of chemically strengthened glass.
This Standard is applicable to flat chemically strengthened glass.
2 Normative references
The following standards contain the provisions which, through reference in this
Standard, constitute the provisions of this Standard. For dated references,
subsequent amendments (excluding corrections) or revisions do not apply to
this Standard. However, the parties who enter into agreement based on this
Standard are encouraged to investigate whether the latest versions of these
documents are applicable. For undated reference documents, the latest
versions apply to this Standard.
GB/T 1216 Micrometers
GB/T 5137.1-2002 Test Methods of Safety Glazing Materials Used on Road
Vehicle
GB 11614-1999 Float glass
GB/T 18144 Test method for measurement of stress in glass
JB/T 8788 Feeler gauges
3 Terms and definitions
The following terms and definitions apply to this document.
Chemically strengthened glass
Glass of which alkali metal ions of glass surface are replaced by other alkali
metal ions in molten salt, so as to improve mechanical strength.
Stain trace,
smog
There shall be no obvious stain trace, smog on the surface of chemically
tempered glass.
5.6 Edge and hole machining quality
5.6.1 Edge machining quality of chemically tempered glass
The edge of chemically tempered glass used in construction shall be chamfered
and fine grinded. The edge quality of chemically tempered glass used for non-
construction shall be determined by the seller and the buyer.
5.6.2 Hole edge machining quality
Hole edge machining quality shall be determined by the seller and the buyer.
5.6.2.1 The tolerance of hole aperture of chemically tempered glass products
used for construction shall comply with provisions of Table 6. This provision only
applies to the glass of which nominal thickness is not less than 4 mm. The
tolerance of hole aperture of chemically tempered glass used for non-
construction shall be determined by the seller and the buyer.
Table 6 Hole aperture and its tolerance unit. mm
Nominal hole aperture (D) Tolerance
D< 4 Determined by the seller and the buyer
4≤D≤20 ±1.0
20< D≤100 ±2.0
D>100 Determined by the seller and the buyer
5.6.2.2 The distance a BETWEEN hole edge of chemically tempered glass
products used for construction AND glass edge shall not be less than twice
glass nominal thickness d, as shown in Figure 1. The distance b between two
hole edges shall not be less than twice glass nominal thickness d, as shown in
Figure 2. The distance c BETWEEN hole edge AND glass corner shall not be
less than 6 times glass nominal thickness d, as shown in Figure 3. The hole
center position shall expressed by referring to Figure 4. build coordinate system
as Figure 4 and use hole center position’s coordinates (x, y) to show hole center ...
Delivery: 9 seconds. Download (& Email) true-PDF + Invoice.
Get Quotation: Click JC/T 977-2005 (Self-service in 1-minute)
Historical versions (Master-website): JC/T 977-2005
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll-down if blank)
JC/T 977-2005
JC
BUILDING MATERIALS INDUSTRY STANDARD
OF THE PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 81.040.20
Q 33
Record No.. 15249-2005
Chemically strengthened glass
ISSUED ON. FEBRUARY 14, 2005
IMPLEMENTED ON. JULY 1, 2005
Issued by. National Development and Reform Commission
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
1 Scope ... 4
2 Normative references ... 4
3 Terms and definitions ... 4
4 Classification and marks... 5
5 Technical requirements ... 5
6 Test methods ... 11
7 Inspection rules ... 15
8 Package, marks, transport and storage ... 17
Appendix A ... 18
Appendix B ... 21
Foreword
This Standard was modified on the basis of European standard EN 12337-
1.2000 Glass in Building - Chemically Strengthened Soda Lime Silicate Glass
- Part 1. Definition and Description.
Compared with EN 12337-1.2000, the main technical differences are as follows.
- Deleted measurement method for squareness of planar rectangular
products; added requirements for diagonal difference;
- Added requirements and measurement methods for surface stress and
compressive stress layer depth by referring to ASTM C1422-99 Standard
Specification for Chemically Strengthened Flat Glass.
Appendix A of this Standard is normative. Appendix B is informative.
This Standard was proposed by China Building Materials Industry Association.
This Standard shall be under the jurisdiction of National Technical Committee
on Building Glass of Standardization Administration of China.
Main drafting organization of this Standard. Glass Science Institute of China
Building Materials Academy.
Drafting organizations of this Standard. China Southern Glass Technology
Holdings (Group) Co., Ltd., Beijing Gelin Jingfeng Fireproof Glass Co., Ltd..
Main drafters of this Standard. Yang Jianjun, Wang Rui, Gong Shuyi, Zhang
Baojun, Xiong Wei, Song Li, Shi Xinyong, Mo Jiao, Wu Huiting, Hu Yue.
This Standard was issued for the first time.
Chemically strengthened glass
1 Scope
This Standard specifies the term and definition, classification and marks,
technical requirements, test methods, inspection rules, package, marks,
transport and storage of chemically strengthened glass.
This Standard is applicable to flat chemically strengthened glass.
2 Normative references
The following standards contain the provisions which, through reference in this
Standard, constitute the provisions of this Standard. For dated references,
subsequent amendments (excluding corrections) or revisions do not apply to
this Standard. However, the parties who enter into agreement based on this
Standard are encouraged to investigate whether the latest versions of these
documents are applicable. For undated reference documents, the latest
versions apply to this Standard.
GB/T 1216 Micrometers
GB/T 5137.1-2002 Test Methods of Safety Glazing Materials Used on Road
Vehicle
GB 11614-1999 Float glass
GB/T 18144 Test method for measurement of stress in glass
JB/T 8788 Feeler gauges
3 Terms and definitions
The following terms and definitions apply to this document.
Chemically strengthened glass
Glass of which alkali metal ions of glass surface are replaced by other alkali
metal ions in molten salt, so as to improve mechanical strength.
Stain trace,
smog
There shall be no obvious stain trace, smog on the surface of chemically
tempered glass.
5.6 Edge and hole machining quality
5.6.1 Edge machining quality of chemically tempered glass
The edge of chemically tempered glass used in construction shall be chamfered
and fine grinded. The edge quality of chemically tempered glass used for non-
construction shall be determined by the seller and the buyer.
5.6.2 Hole edge machining quality
Hole edge machining quality shall be determined by the seller and the buyer.
5.6.2.1 The tolerance of hole aperture of chemically tempered glass products
used for construction shall comply with provisions of Table 6. This provision only
applies to the glass of which nominal thickness is not less than 4 mm. The
tolerance of hole aperture of chemically tempered glass used for non-
construction shall be determined by the seller and the buyer.
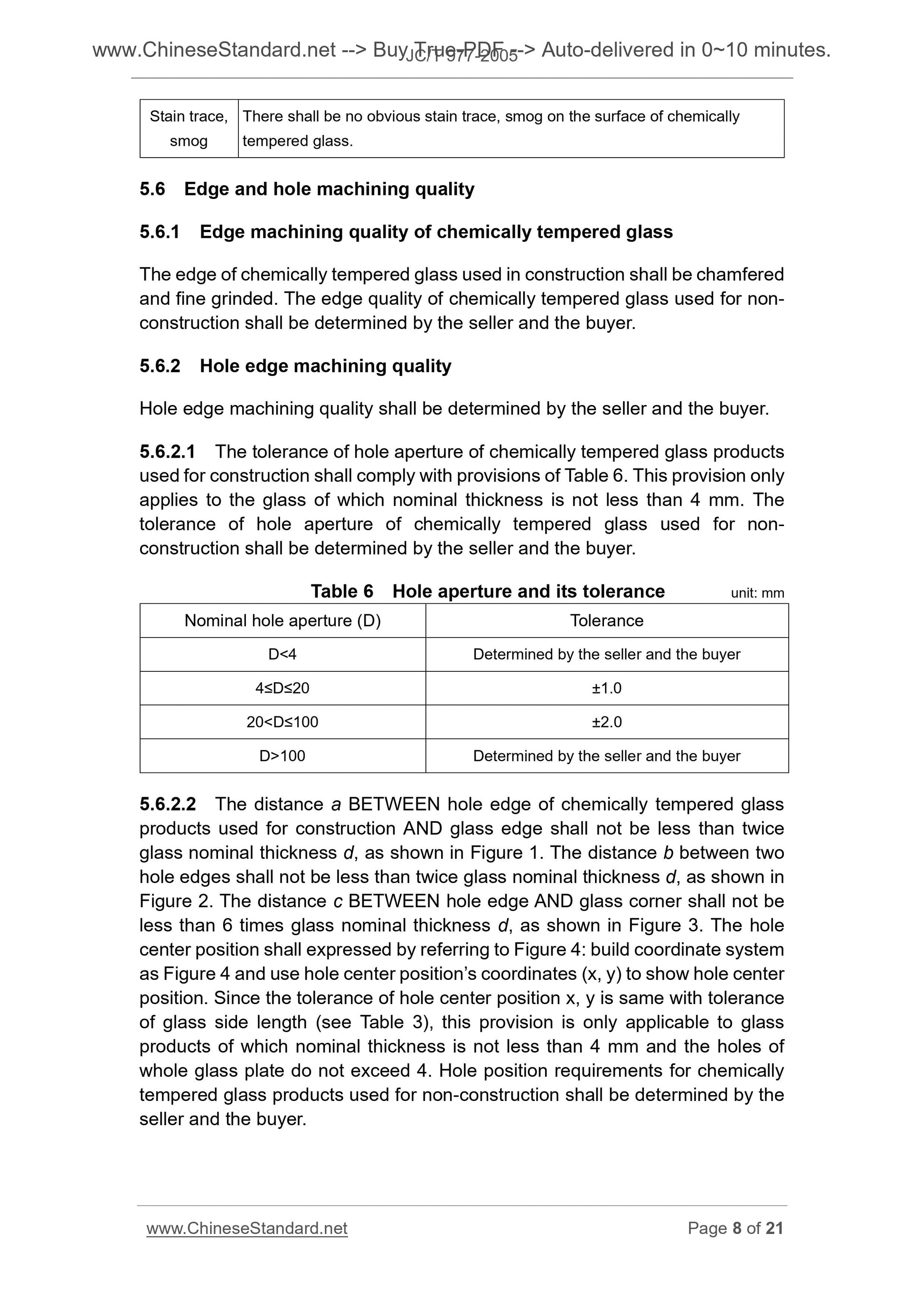
Table 6 Hole aperture and its tolerance unit. mm
Nominal hole aperture (D) Tolerance
D< 4 Determined by the seller and the buyer
4≤D≤20 ±1.0
20< D≤100 ±2.0
D>100 Determined by the seller and the buyer
5.6.2.2 The distance a BETWEEN hole edge of chemically tempered glass
products used for construction AND glass edge shall not be less than twice
glass nominal thickness d, as shown in Figure 1. The distance b between two
hole edges shall not be less than twice glass nominal thickness d, as shown in
Figure 2. The distance c BETWEEN hole edge AND glass corner shall not be
less than 6 times glass nominal thickness d, as shown in Figure 3. The hole
center position shall expressed by referring to Figure 4. build coordinate system
as Figure 4 and use hole center position’s coordinates (x, y) to show hole center
position. Since the tolerance of hole center position x, y is same with tolerance
of glass side length (see Table 3), this provision is only applicable to glass
products of which nominal thickness is not less than 4 mm and the holes of
whole glass plate do not exceed 4. Hole position requirements for chemically
tempered glass products used for non-construction shall be determined by the
seller and the buyer.
Category B 25< d≤50
Category C d>50
5.12 Impact resistance
Impact resistance of chemically tempered glass shall comply with provisions of
Table 10.
Table 10 Impact resistance of chemically tempered glass
Glass thickness d
mm
Impact height
m State after impact
d< 2 1.0 The specimen must not be
destroyed. d≥2 2.0
6 Test methods
6.1 Thickness determination
Use micrometer that complies with provisions of GB/T 1216, of which the
accuracy is 0.01 mm, or instrument of same accuracy to measure at
quadrilateral midpoint within 15 mm from glass plate edge. The arithmetic mean
of measurement results shall be its thickness value. Round it to one decimal
place.
6.2 Size determination
Use steel tape of which the minimum graduation is 1 mm to measure.
6.3 Diagonal difference
Use steel tape of which the minimum graduation is 1 mm to measure.
6.4 Appearance quality
Inspect in accordance with requirements of 5.3 in GB 11614-1999.
6.5 Edge and hole machining quality
Use caliper of which the minimum graduation is 0.1 mm to measure.
6.6 Curvature determination
Place the specimen at room temperature for more than 4h. When measuring,
make the specimen perpendicular and pad with two pads at 1/4 place under its
long side. Use a ruler or wire level closely against two sides of specimen or
stress.
7.1.2 Type inspection
Inspection items are all technical requirements stipulated by this Standard. In
case one of the following situation, type inspection shall be conducted.
a) trial type identification of new product or old product transferring
production;
b) after trial production, when there are major changes in structure, material,
process etc. which may affect product performance;
c) when normal production reaches one year;
d) when production resumes after the production is shutdown for more than
six months;
e) when there is significant difference between factory inspection results
and previous type inspection;
f) when type inspection requirements are requested by quality supervision
department.
7.2 Batching and sampling
7.2.1 Batching
Chemically tempered glasses, produced by same type of raw material under
same process conditions, shall be grouped as a batch.
7.2.2 Sampling
7.2.2.1 Thickness, size, appearance quality, curvature, surface stress shall be
randomly sampled according to Table 11.
7.2.2.2 For product’s technical requirements, if it uses product to inspect,
random sampling shall be conducted from this batch of products according to
the quantity required by inspection items. If it uses specimen to inspect, it shall
use the specimen of same-material, same-thickness and prepared under same-
process conditions as the products.
7.3 Determination rules
If the number of rejects of any one of thickness, size, appearance quality,
curvature and surface stress is greater than or equals to the number of rejects
in Table 11, then this inspection item of this product shall be deemed as
unqualified.
Appendix A
(Normative)
Bending strength test method
A.1 Test conditions
Ambient temperature. 23°C±5°C. Ambient humidity. 40%~70%. To avoid
thermal stress, during the whole process of test, the fluctuation of ambient
temperature shall not be greater than 1°C.
A.2 Specimen
Take 12 pieces of specimens to conduct the test. The length of each specimen
is 1100 mm ± 5 mm; the width is 360 mm ± 5 mm. When preparing specimen,
cutting edges shall be on the same surface of the specimen.
Within...
JC/T 977-2005
JC
BUILDING MATERIALS INDUSTRY STANDARD
OF THE PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 81.040.20
Q 33
Record No.. 15249-2005
Chemically strengthened glass
ISSUED ON. FEBRUARY 14, 2005
IMPLEMENTED ON. JULY 1, 2005
Issued by. National Development and Reform Commission
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
1 Scope ... 4
2 Normative references ... 4
3 Terms and definitions ... 4
4 Classification and marks... 5
5 Technical requirements ... 5
6 Test methods ... 11
7 Inspection rules ... 15
8 Package, marks, transport and storage ... 17
Appendix A ... 18
Appendix B ... 21
Foreword
This Standard was modified on the basis of European standard EN 12337-
1.2000 Glass in Building - Chemically Strengthened Soda Lime Silicate Glass
- Part 1. Definition and Description.
Compared with EN 12337-1.2000, the main technical differences are as follows.
- Deleted measurement method for squareness of planar rectangular
products; added requirements for diagonal difference;
- Added requirements and measurement methods for surface stress and
compressive stress layer depth by referring to ASTM C1422-99 Standard
Specification for Chemically Strengthened Flat Glass.
Appendix A of this Standard is normative. Appendix B is informative.
This Standard was proposed by China Building Materials Industry Association.
This Standard shall be under the jurisdiction of National Technical Committee
on Building Glass of Standardization Administration of China.
Main drafting organization of this Standard. Glass Science Institute of China
Building Materials Academy.
Drafting organizations of this Standard. China Southern Glass Technology
Holdings (Group) Co., Ltd., Beijing Gelin Jingfeng Fireproof Glass Co., Ltd..
Main drafters of this Standard. Yang Jianjun, Wang Rui, Gong Shuyi, Zhang
Baojun, Xiong Wei, Song Li, Shi Xinyong, Mo Jiao, Wu Huiting, Hu Yue.
This Standard was issued for the first time.
Chemically strengthened glass
1 Scope
This Standard specifies the term and definition, classification and marks,
technical requirements, test methods, inspection rules, package, marks,
transport and storage of chemically strengthened glass.
This Standard is applicable to flat chemically strengthened glass.
2 Normative references
The following standards contain the provisions which, through reference in this
Standard, constitute the provisions of this Standard. For dated references,
subsequent amendments (excluding corrections) or revisions do not apply to
this Standard. However, the parties who enter into agreement based on this
Standard are encouraged to investigate whether the latest versions of these
documents are applicable. For undated reference documents, the latest
versions apply to this Standard.
GB/T 1216 Micrometers
GB/T 5137.1-2002 Test Methods of Safety Glazing Materials Used on Road
Vehicle
GB 11614-1999 Float glass
GB/T 18144 Test method for measurement of stress in glass
JB/T 8788 Feeler gauges
3 Terms and definitions
The following terms and definitions apply to this document.
Chemically strengthened glass
Glass of which alkali metal ions of glass surface are replaced by other alkali
metal ions in molten salt, so as to improve mechanical strength.
Stain trace,
smog
There shall be no obvious stain trace, smog on the surface of chemically
tempered glass.
5.6 Edge and hole machining quality
5.6.1 Edge machining quality of chemically tempered glass
The edge of chemically tempered glass used in construction shall be chamfered
and fine grinded. The edge quality of chemically tempered glass used for non-
construction shall be determined by the seller and the buyer.
5.6.2 Hole edge machining quality
Hole edge machining quality shall be determined by the seller and the buyer.
5.6.2.1 The tolerance of hole aperture of chemically tempered glass products
used for construction shall comply with provisions of Table 6. This provision only
applies to the glass of which nominal thickness is not less than 4 mm. The
tolerance of hole aperture of chemically tempered glass used for non-
construction shall be determined by the seller and the buyer.
Table 6 Hole aperture and its tolerance unit. mm
Nominal hole aperture (D) Tolerance
D< 4 Determined by the seller and the buyer
4≤D≤20 ±1.0
20< D≤100 ±2.0
D>100 Determined by the seller and the buyer
5.6.2.2 The distance a BETWEEN hole edge of chemically tempered glass
products used for construction AND glass edge shall not be less than twice
glass nominal thickness d, as shown in Figure 1. The distance b between two
hole edges shall not be less than twice glass nominal thickness d, as shown in
Figure 2. The distance c BETWEEN hole edge AND glass corner shall not be
less than 6 times glass nominal thickness d, as shown in Figure 3. The hole
center position shall expressed by referring to Figure 4. build coordinate system
as Figure 4 and use hole center position’s coordinates (x, y) to show hole center ...
Share