1
/
von
11
PayPal, credit cards. Download editable-PDF & invoice in 1 second!
GB 1886.3-2021 English PDF (GB1886.3-2021)
GB 1886.3-2021 English PDF (GB1886.3-2021)
Normaler Preis
$125.00 USD
Normaler Preis
Verkaufspreis
$125.00 USD
Grundpreis
/
pro
Versand wird beim Checkout berechnet
Verfügbarkeit für Abholungen konnte nicht geladen werden
Delivery: 3 seconds. Download true-PDF + Invoice.
Get QUOTATION in 1-minute: Click GB 1886.3-2021
Historical versions: GB 1886.3-2021
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll if blank)
GB 1886.3-2021: National food safety standard - Food additives - Calcium hydrogen phosphate
GB 1886.3-2021
GB
NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE
PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
National food safety standard -
Food additives - Calcium hydrogen phosphate
食品添加剂 磷酸氢钙
ISSUED ON: FEBRUARY 22, 2021
IMPLEMENTED ON: AUGUST 22, 2021
Issued by: National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China;
State Administration for Market Regulation.
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
1 Scope ... 4
2 Molecular formula and relative molecular mass ... 4
3 Technical requirements ... 4
Annex A Inspection methods ... 6
National food safety standard -
Food additives - Calcium hydrogen phosphate
1 Scope
This Standard is applicable to the food additive calcium hydrogen phosphate
produced with calcium hydroxide (or calcium carbonate, calcium oxide) and
food additive phosphoric acid (including wet-process phosphoric acid) as raw
materials.
2 Molecular formula and relative molecular mass
2.1 Molecular formula
Calcium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate: CaHPO4·2H2O
Anhydrous calcium hydrogen phosphate: CaHPO4
2.2 Relative molecular mass
Calcium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate: 172.09 (according to 2018
international relative atomic mass)
Anhydrous calcium hydrogen phosphate: 136.06 (according to 2018
international relative atomic mass)
3 Technical requirements
3.1 Sensory requirements
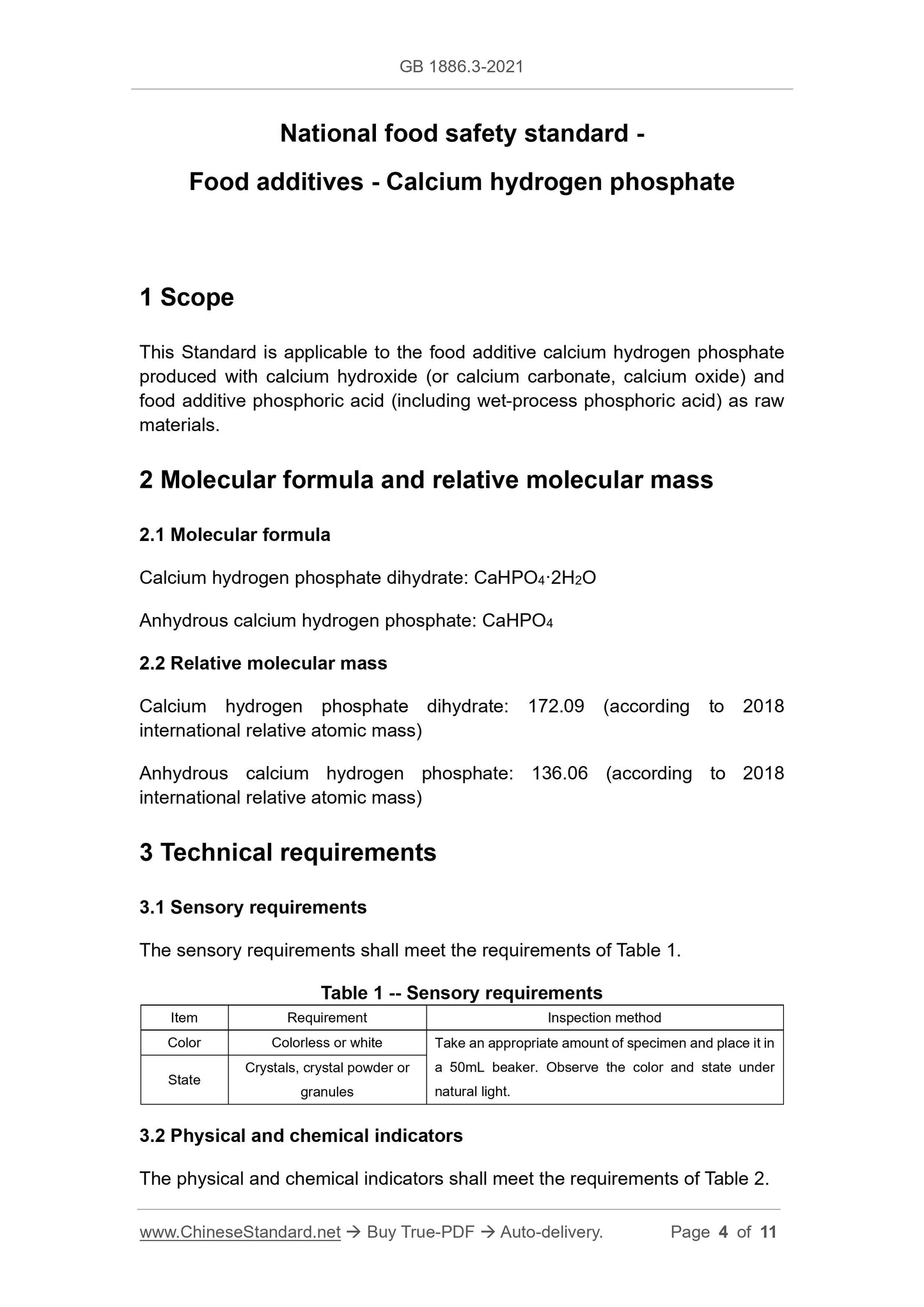
The sensory requirements shall meet the requirements of Table 1.
Table 1 -- Sensory requirements
3.2 Physical and chemical indicators
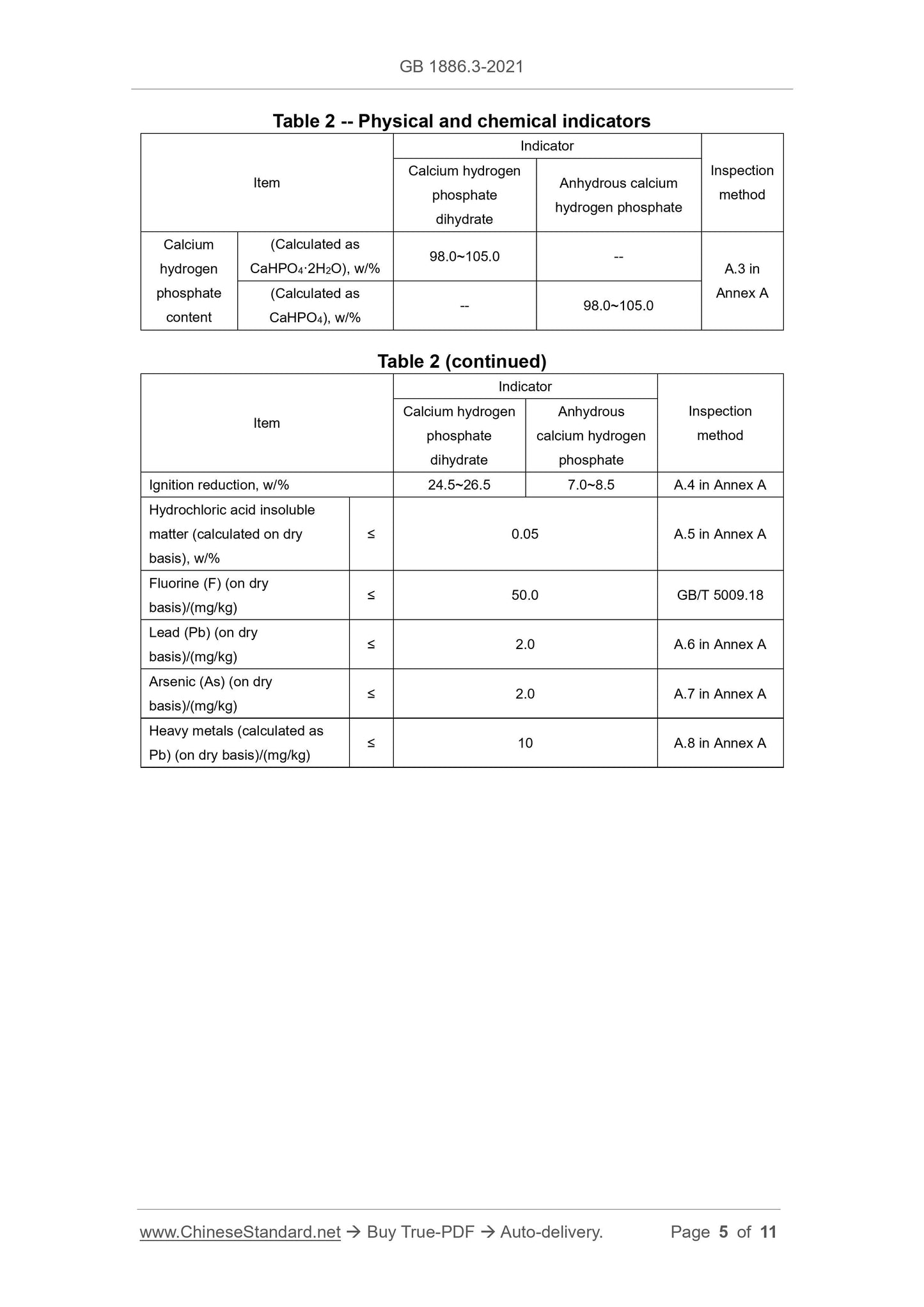
The physical and chemical indicators shall meet the requirements of Table 2.
Annex A
Inspection methods
WARNING: Some reagents used in this test method are toxic or corrosive.
Appropriate safety and protection measures shall be taken during
operation. When necessary, it shall be carried out in a fume hood. If it
splashes on the skin, it shall be rinsed with water immediately. The severe
cases shall be treated immediately.
A.1 General
The reagents and water used in this Standard refer to analytically-pure reagents
and grade three water specified in GB/T 6682 when other requirements are not
indicated. All standard solutions, preparations and products used in the test for
impurity determination shall be prepared in accordance with the provisions of
GB/T 601, GB/T 602, and GB/T 603 when other requirements are not specified.
The solution used refers to an aqueous solution when it is not specified which
solvent is used for preparation.
A.2 Identification test
A.2.1 Reagents and materials
A.2.1.1 Hydrochloric acid solution: 1+3.
A.2.1.2 Ammonia solution: 1+1.
A.2.1.3 Nitric acid solution: 1+1.
A.2.1.4 Ammonium oxalate solution: 35g/L. Weigh 3.5g of ammonium oxalate
[(NH4))2C2O4·H2O] and dissolve it in water. Dilute to 100mL.
A.2.1.5 Ammonium molybdate solution: 60g/L. Weigh 6g of ammonium
molybdate [(NH4)6Mo7O24·4H2O] and dissolve it in 50mL of water. While stirring,
slowly add the nitric acid solution to about 100mL. Store in a brown reagent
bottle.
A.2.2 Identification method
A.2.2.1 Identification of calcium ion
Weigh about 0.1g of specimen. Add 5mL of water, 5mL of hydrochloric acid
solution to make the specimen dissolved. Add 2.5mL of ammonia solution
dropwise while shaking. Then add 5mL of ammonium oxalate solution to
generate white precipitation.
A.2.2.2 Identification of phosphate ion
Weigh about 0.1g of specimen. Add nitric acid solution dropwise until the
specimen is dissolved and then exceed by 1mL. Heat to 40°C~50°C. Add 10mL
of ammonium molybdate solution to generate yellow precipitation.
A.3 Determination of calcium hydrogen phosphate content
A.3.1 Method summary
In the test solution, use triethanolamine as a masking agent. Under the acidic
conditions, add the standard titration solution of disodium
ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid dropwise to the end point. Use sodium
hydroxide solution to adjust the pH of the test solution within the pH range of
the hydroxynaphthol blue indicator color development. Continue to titrate the
remaining calcium.
A.3.2 Reagents and materials
A.3.2.1 Triethanolamine.
A.3.2.2 Hydrochloric acid solution: 1+1.
A.3.2.3 Sodium hydroxide solution: 450g/L.
A.3.2.4 Standard titration solution of disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid:
c(EDTA)=0.05mol/L.
A.3.2.5 Hydroxynaphthol blue indicator.
A.3.3 Instruments and equipment
Magnetic stirrer.
A.3.4 Analysis steps
A.3.4.1 Preparation of test solution
Weigh 2.5g of specimen, to the nearest of 0.0002g. Place in a 100mL beaker.
Add 20mL of hydrochloric acid solution to dissolve. Transfer completely into a
250mL volumetric flask. Add water to the scale mark. Shake well. This solution
shall be the test solution.
A.3.4.2 Determination
Accurately pipette 25mLof test solution in a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask. Add
100mL of water, 0.5mL of triethanolamine. Add 0.3g of hydroxynaphthol blue
A.4.1.1 High temperature furnace: The temperature control range is
800°C~825°C.
A.4.1.2 Porcelain crucible: 30mL.
A.4.2 Analysis steps
Weigh 3g of specimen, to the nearest of 0.0002g. Place in a porcelain crucible
that has been burnt at 800°C~825°C to a constant mass. Burn at 800°C~825°C
until the mass is constant.
A.4.3 Result calculation
The mass fraction w2 of ignition reduction is calculated according to formula
(A.2).
Where,
m2 - The mass of the crucible and the specimen before burning, in grams (g);
m3 - The mass of the crucible and the specimen after burning, in grams (g);
m4 - The specimen mass, in grams (g).
The test results are based on the arithmetic mean of the parallel determination
results. The absolute difference between two independent determination results
obtained under repeatability conditions is not more than 0.2%.
A.5 Determination of insoluble matter in hydrochloric acid
A.5.1 Reagents and materials
Hydrochloric acid solution: 1+1.
A.5.2 Instruments and equipment
A.5.2.1 Glass sand crucible: The aperture of the filter plate is 5μm~15μm.
A.5.2.2 Electric heating constant temperature drying oven: The temperature
control range is 105°C±2°C.
A.5.3 Analysis steps
Weigh 10g of specimen, to the nearest of 0.01g. Place in a 250mL beaker. Add
40mL of hydrochloric acid solution and 60mL of water. Heat to dissolve. Add
Get QUOTATION in 1-minute: Click GB 1886.3-2021
Historical versions: GB 1886.3-2021
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll if blank)
GB 1886.3-2021: National food safety standard - Food additives - Calcium hydrogen phosphate
GB 1886.3-2021
GB
NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE
PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
National food safety standard -
Food additives - Calcium hydrogen phosphate
食品添加剂 磷酸氢钙
ISSUED ON: FEBRUARY 22, 2021
IMPLEMENTED ON: AUGUST 22, 2021
Issued by: National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China;
State Administration for Market Regulation.
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
1 Scope ... 4
2 Molecular formula and relative molecular mass ... 4
3 Technical requirements ... 4
Annex A Inspection methods ... 6
National food safety standard -
Food additives - Calcium hydrogen phosphate
1 Scope
This Standard is applicable to the food additive calcium hydrogen phosphate
produced with calcium hydroxide (or calcium carbonate, calcium oxide) and
food additive phosphoric acid (including wet-process phosphoric acid) as raw
materials.
2 Molecular formula and relative molecular mass
2.1 Molecular formula
Calcium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate: CaHPO4·2H2O
Anhydrous calcium hydrogen phosphate: CaHPO4
2.2 Relative molecular mass
Calcium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate: 172.09 (according to 2018
international relative atomic mass)
Anhydrous calcium hydrogen phosphate: 136.06 (according to 2018
international relative atomic mass)
3 Technical requirements
3.1 Sensory requirements
The sensory requirements shall meet the requirements of Table 1.
Table 1 -- Sensory requirements
3.2 Physical and chemical indicators
The physical and chemical indicators shall meet the requirements of Table 2.
Annex A
Inspection methods
WARNING: Some reagents used in this test method are toxic or corrosive.
Appropriate safety and protection measures shall be taken during
operation. When necessary, it shall be carried out in a fume hood. If it
splashes on the skin, it shall be rinsed with water immediately. The severe
cases shall be treated immediately.
A.1 General
The reagents and water used in this Standard refer to analytically-pure reagents
and grade three water specified in GB/T 6682 when other requirements are not
indicated. All standard solutions, preparations and products used in the test for
impurity determination shall be prepared in accordance with the provisions of
GB/T 601, GB/T 602, and GB/T 603 when other requirements are not specified.
The solution used refers to an aqueous solution when it is not specified which
solvent is used for preparation.
A.2 Identification test
A.2.1 Reagents and materials
A.2.1.1 Hydrochloric acid solution: 1+3.
A.2.1.2 Ammonia solution: 1+1.
A.2.1.3 Nitric acid solution: 1+1.
A.2.1.4 Ammonium oxalate solution: 35g/L. Weigh 3.5g of ammonium oxalate
[(NH4))2C2O4·H2O] and dissolve it in water. Dilute to 100mL.
A.2.1.5 Ammonium molybdate solution: 60g/L. Weigh 6g of ammonium
molybdate [(NH4)6Mo7O24·4H2O] and dissolve it in 50mL of water. While stirring,
slowly add the nitric acid solution to about 100mL. Store in a brown reagent
bottle.
A.2.2 Identification method
A.2.2.1 Identification of calcium ion
Weigh about 0.1g of specimen. Add 5mL of water, 5mL of hydrochloric acid
solution to make the specimen dissolved. Add 2.5mL of ammonia solution
dropwise while shaking. Then add 5mL of ammonium oxalate solution to
generate white precipitation.
A.2.2.2 Identification of phosphate ion
Weigh about 0.1g of specimen. Add nitric acid solution dropwise until the
specimen is dissolved and then exceed by 1mL. Heat to 40°C~50°C. Add 10mL
of ammonium molybdate solution to generate yellow precipitation.
A.3 Determination of calcium hydrogen phosphate content
A.3.1 Method summary
In the test solution, use triethanolamine as a masking agent. Under the acidic
conditions, add the standard titration solution of disodium
ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid dropwise to the end point. Use sodium
hydroxide solution to adjust the pH of the test solution within the pH range of
the hydroxynaphthol blue indicator color development. Continue to titrate the
remaining calcium.
A.3.2 Reagents and materials
A.3.2.1 Triethanolamine.
A.3.2.2 Hydrochloric acid solution: 1+1.
A.3.2.3 Sodium hydroxide solution: 450g/L.
A.3.2.4 Standard titration solution of disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid:
c(EDTA)=0.05mol/L.
A.3.2.5 Hydroxynaphthol blue indicator.
A.3.3 Instruments and equipment
Magnetic stirrer.
A.3.4 Analysis steps
A.3.4.1 Preparation of test solution
Weigh 2.5g of specimen, to the nearest of 0.0002g. Place in a 100mL beaker.
Add 20mL of hydrochloric acid solution to dissolve. Transfer completely into a
250mL volumetric flask. Add water to the scale mark. Shake well. This solution
shall be the test solution.
A.3.4.2 Determination
Accurately pipette 25mLof test solution in a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask. Add
100mL of water, 0.5mL of triethanolamine. Add 0.3g of hydroxynaphthol blue
A.4.1.1 High temperature furnace: The temperature control range is
800°C~825°C.
A.4.1.2 Porcelain crucible: 30mL.
A.4.2 Analysis steps
Weigh 3g of specimen, to the nearest of 0.0002g. Place in a porcelain crucible
that has been burnt at 800°C~825°C to a constant mass. Burn at 800°C~825°C
until the mass is constant.
A.4.3 Result calculation
The mass fraction w2 of ignition reduction is calculated according to formula
(A.2).
Where,
m2 - The mass of the crucible and the specimen before burning, in grams (g);
m3 - The mass of the crucible and the specimen after burning, in grams (g);
m4 - The specimen mass, in grams (g).
The test results are based on the arithmetic mean of the parallel determination
results. The absolute difference between two independent determination results
obtained under repeatability conditions is not more than 0.2%.
A.5 Determination of insoluble matter in hydrochloric acid
A.5.1 Reagents and materials
Hydrochloric acid solution: 1+1.
A.5.2 Instruments and equipment
A.5.2.1 Glass sand crucible: The aperture of the filter plate is 5μm~15μm.
A.5.2.2 Electric heating constant temperature drying oven: The temperature
control range is 105°C±2°C.
A.5.3 Analysis steps
Weigh 10g of specimen, to the nearest of 0.01g. Place in a 250mL beaker. Add
40mL of hydrochloric acid solution and 60mL of water. Heat to dissolve. Add
Share