PayPal, credit cards. Download editable-PDF & invoice in 1 second!
QC/T 798-2008 English PDF (QCT798-2008)
QC/T 798-2008 English PDF (QCT798-2008)
Precio habitual
$150.00 USD
Precio habitual
Precio de oferta
$150.00 USD
Precio unitario
/
por
Los gastos de envío se calculan en la pantalla de pago.
No se pudo cargar la disponibilidad de retiro
Delivery: 3 seconds. Download true-PDF + Invoice.
Get QUOTATION in 1-minute: Click QC/T 798-2008
Historical versions: QC/T 798-2008
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll if blank)
QC/T 798-2008: Multi-layers plastic tubing for automotive fuel system
QC/T 798-2008
AUTOMOBILE INDUSTRY STANDARD
OF THE PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
Multilayers plastic tubing for automotive fuel system
ISSUED ON: FEBRUARY 01, 2008
IMPLEMENTED ON: JULY 01, 2008
Issued by: Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of PRC
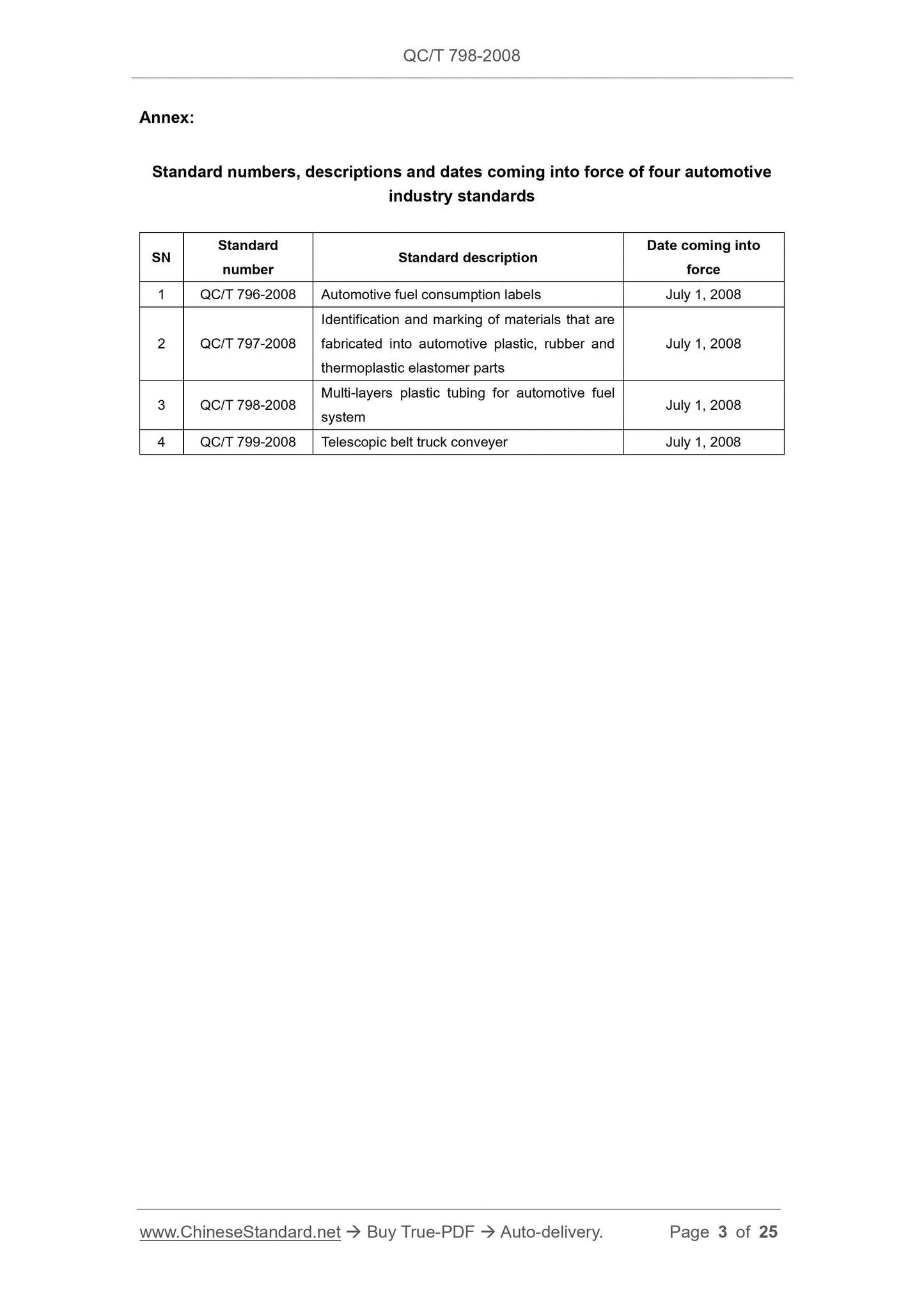
Annex:
Standard numbers, descriptions and dates coming into force of four automotive
industry standards
SN Standard number Standard description
Date coming into
force
1 QC/T 796-2008 Automotive fuel consumption labels July 1, 2008
2 QC/T 797-2008
Identification and marking of materials that are
fabricated into automotive plastic, rubber and
thermoplastic elastomer parts
July 1, 2008
3 QC/T 798-2008 Multi-layers plastic tubing for automotive fuel system July 1, 2008
4 QC/T 799-2008 Telescopic belt truck conveyer July 1, 2008
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 5
1 Scope ... 6
2 Normative references ... 6
3 Terms and definitions ... 6
4 Specification dimension ... 7
5 General requirements ... 8
6 Performance requirements ... 9
7 Test methods ... 10
8 Inspection rules ... 20
9 Markings and signs ... 21
10 Packaging, transportation, storage ... 22
Appendix A (Normative) Specifications for permeability resistance test ... 23
Multilayers plastic tubing for automotive fuel system
1 Scope
This standard specifies the dimensional specifications, appearance, technical
requirements, test methods, inspection rules, markings, packaging,
transportation, storage of multilayer plastic tubing for automotive fuel systems
(hereinafter referred to as multilayer tubing) and tube assemblies.
This standard is applicable to multilayer plastic fuel tubes which have a working
temperature between -40 °C and +115 °C (continuous use temperature shall
not exceed 90 °C) and maximum working pressure of not more than 0.7 MPa.
2 Normative references
The provisions in following documents become the provisions of this standard
through reference in this standard. For the dated references, the subsequent
amendments (excluding corrections) or revisions do not apply to this standard;
however, parties who reach an agreement based on this standard are
encouraged to study if the latest versions of these documents are applicable.
For undated references, the latest edition of the referenced document applies.
GB/T 528-1998 Determination of tensile stress-strain properties of
vulcanized rubber or thermoplastic rubber
GB/T 528-1998 Rubber, vulcanized or thermoplastic - Determination of
tensile stress-strain properties (ISO 527 -2: 1993 IDT)
GB/T 2828.1-2003 Sampling procedures for inspection by attributes - Part 1:
Sampling schemes indexed by acceptance quality limit (AQL) for lot-by-lot
inspection (ISO 2859-1:1999 IDT)
GB/T 2918-1998 Plastics - Standard atmospheres for conditioning and
testing (ISO 291:1997 IDT)
3 Terms and definitions
The following terms and definitions apply to this standard.
3.1
Multilayer plastic tubing
More than two layers of non-metallic plastic tubes which are made of
materials of different properties and different types, without connectors.
3.2
Tube assemblies
A combination of a multilayer tube and a tube joint which have a specified
length and shape.
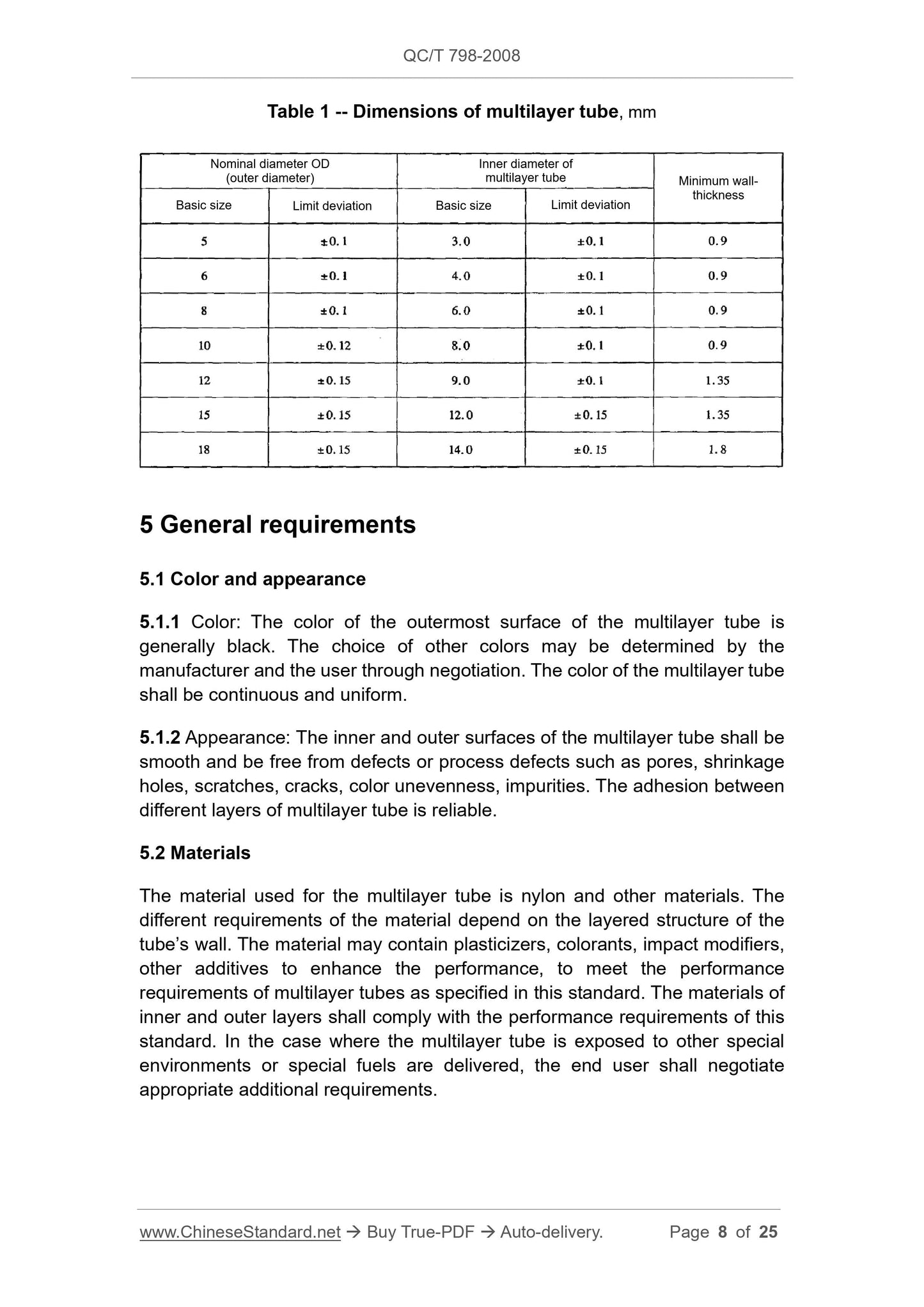
4 Specification dimension
4.1 Structure
The multilayer tube is a multilayer structure which contains the wall-thickness
of the main body. The name of material is generally indicated on the drawing. If
specified, it shall identify each layer of all tube layers.
4.2 Dimensions and tolerances
Table 1 provides the dimensions and wall-thickness of various types of
multilayer tubes of this standard. The thickness and tolerance for each layer
may be determined by the manufacturer and the user through negotiation. The
dimensions and tolerances of the multilayer tube are indicated by mm.
4.3 Wall-thickness
Multilayer tubes of different sizes which are made by materials of different
grades have different wall-thicknesses. The minimum wall-thickness of a
straight tube which has a nominal diameter equal to 10 mm is 0.9 mm. The
larger the nominal diameter, the larger the wall-thickness. The requirements for
wall-thickness are as detailed in Table 1.
Note: Some of the following factors influence the choice of wall-thickness:
a) High burst-pressure requirements mean higher wall-thickness
requirements;
b) The thicker the wall-thickness, the greater the minimum bending radius.
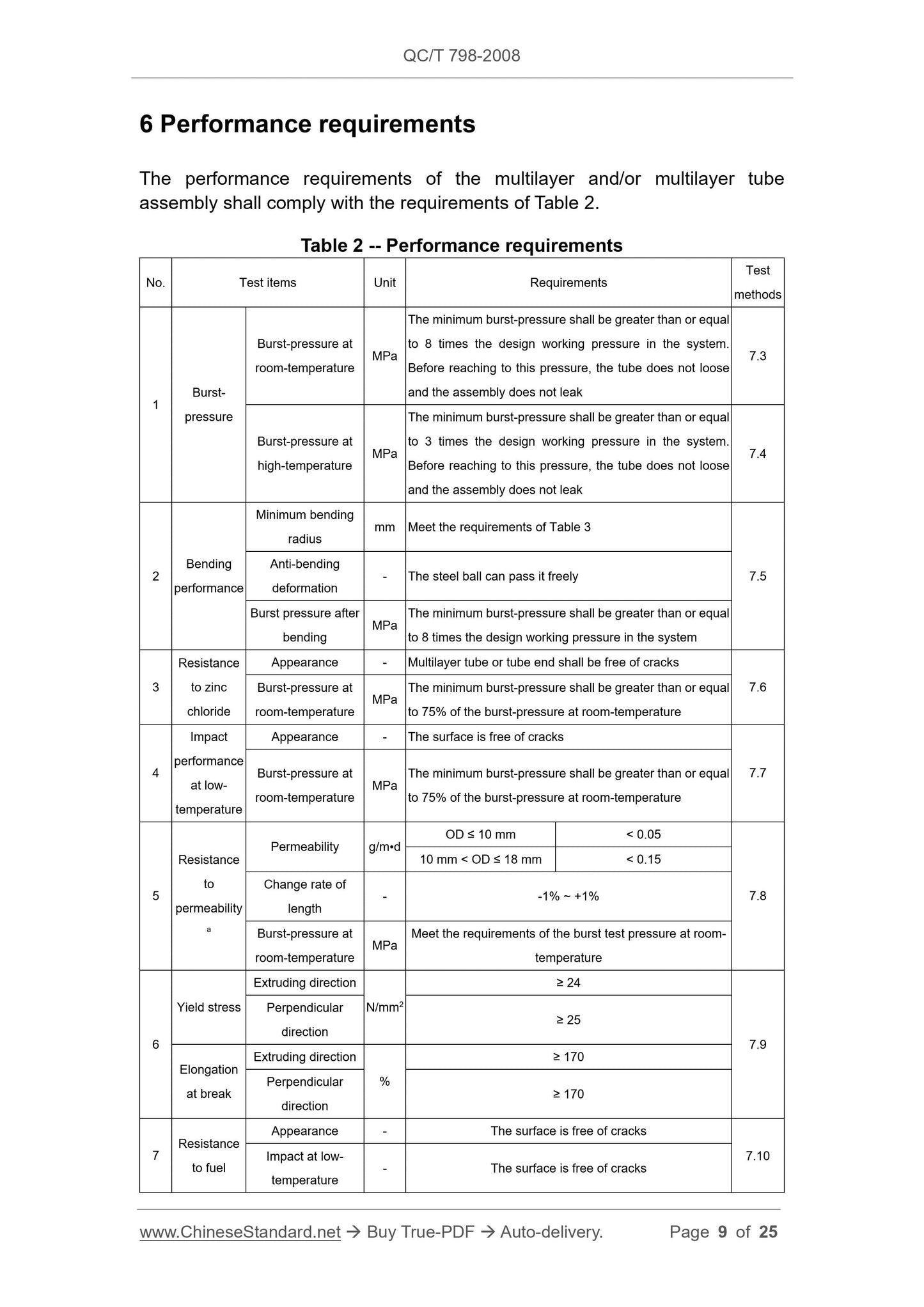
6 Performance requirements
The performance requirements of the multilayer and/or multilayer tube
assembly shall comply with the requirements of Table 2.
Table 2 -- Performance requirements
No. Test items Unit Requirements Test methods
1 Burst-pressure
Burst-pressure at
room-temperature MPa
The minimum burst-pressure shall be greater than or equal
to 8 times the design working pressure in the system.
Before reaching to this pressure, the tube does not loose
and the assembly does not leak
7.3
Burst-pressure at
high-temperature MPa
The minimum burst-pressure shall be greater than or equal
to 3 times the design working pressure in the system.
Before reaching to this pressure, the tube does not loose
and the assembly does not leak
7.4
2 Bending performance
Minimum bending
radius mm Meet the requirements of Table 3
7.5 Anti-bending deformation - The steel ball can pass it freely
Burst pressure after
bending MPa
The minimum burst-pressure shall be greater than or equal
to 8 times the design working pressure in the system
Resistance
to zinc
chloride
Appearance - Multilayer tube or tube end shall be free of cracks
7.6 Burst-pressure at
room-temperature MPa
The minimum burst-pressure shall be greater than or equal
to 75% of the burst-pressure at room-temperature
Impact
performance
at low-
temperature
Appearance - The surface is free of cracks
7.7 Burst-pressure at
room-temperature MPa
The minimum burst-pressure shall be greater than or equal
to 75% of the burst-pressure at room-temperature
Resistance
to
permeability
Permeability g/m•d
OD ≤ 10 mm < 0.05
7.8
10 mm < OD ≤ 18 mm < 0.15
Change rate of
length - -1% ~ +1%
Burst-pressure at
room-temperature MPa
Meet the requirements of the burst test pressure at room-
temperature
Yield stress
Extruding direction
N/mm2
≥ 24
7.9
Perpendicular
direction ≥ 25
Elongation
at break
Extruding direction
≥ 170
Perpendicular
direction ≥ 170
7 Resistance to fuel
Appearance - The surface is free of cracks
7.10 Impact at low-
temperature - The surface is free of cracks
7.3.3.1 At the ambient temperature of 23 °C ± 2 °C, carry out the test. The
internal test medium of the multilayer tube is liquid. Block one end of the
specimen. Connect the other end to the burst pressure testing machine. Then
at the rate of 7 MPa/min ± 1 MPa/min, increase pressure to the multilayer tube,
until it bursts. Record the maximum pressure during the test period. Use the
minimum value of the five specimens as the test result.
7.3.3.2 If the tubing/connection fails before reaching the burst-pressure, discard
the test data. If necessary, it may use the existing tubing connections plus the
auxiliary fixtures, to ensure that the test is carried out effectively.
7.3.3.3 The minimum burst-pressure of all specimens shall be greater than or
equal to 8 times the design wo...
Get QUOTATION in 1-minute: Click QC/T 798-2008
Historical versions: QC/T 798-2008
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll if blank)
QC/T 798-2008: Multi-layers plastic tubing for automotive fuel system
QC/T 798-2008
AUTOMOBILE INDUSTRY STANDARD
OF THE PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
Multilayers plastic tubing for automotive fuel system
ISSUED ON: FEBRUARY 01, 2008
IMPLEMENTED ON: JULY 01, 2008
Issued by: Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of PRC
Annex:
Standard numbers, descriptions and dates coming into force of four automotive
industry standards
SN Standard number Standard description
Date coming into
force
1 QC/T 796-2008 Automotive fuel consumption labels July 1, 2008
2 QC/T 797-2008
Identification and marking of materials that are
fabricated into automotive plastic, rubber and
thermoplastic elastomer parts
July 1, 2008
3 QC/T 798-2008 Multi-layers plastic tubing for automotive fuel system July 1, 2008
4 QC/T 799-2008 Telescopic belt truck conveyer July 1, 2008
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 5
1 Scope ... 6
2 Normative references ... 6
3 Terms and definitions ... 6
4 Specification dimension ... 7
5 General requirements ... 8
6 Performance requirements ... 9
7 Test methods ... 10
8 Inspection rules ... 20
9 Markings and signs ... 21
10 Packaging, transportation, storage ... 22
Appendix A (Normative) Specifications for permeability resistance test ... 23
Multilayers plastic tubing for automotive fuel system
1 Scope
This standard specifies the dimensional specifications, appearance, technical
requirements, test methods, inspection rules, markings, packaging,
transportation, storage of multilayer plastic tubing for automotive fuel systems
(hereinafter referred to as multilayer tubing) and tube assemblies.
This standard is applicable to multilayer plastic fuel tubes which have a working
temperature between -40 °C and +115 °C (continuous use temperature shall
not exceed 90 °C) and maximum working pressure of not more than 0.7 MPa.
2 Normative references
The provisions in following documents become the provisions of this standard
through reference in this standard. For the dated references, the subsequent
amendments (excluding corrections) or revisions do not apply to this standard;
however, parties who reach an agreement based on this standard are
encouraged to study if the latest versions of these documents are applicable.
For undated references, the latest edition of the referenced document applies.
GB/T 528-1998 Determination of tensile stress-strain properties of
vulcanized rubber or thermoplastic rubber
GB/T 528-1998 Rubber, vulcanized or thermoplastic - Determination of
tensile stress-strain properties (ISO 527 -2: 1993 IDT)
GB/T 2828.1-2003 Sampling procedures for inspection by attributes - Part 1:
Sampling schemes indexed by acceptance quality limit (AQL) for lot-by-lot
inspection (ISO 2859-1:1999 IDT)
GB/T 2918-1998 Plastics - Standard atmospheres for conditioning and
testing (ISO 291:1997 IDT)
3 Terms and definitions
The following terms and definitions apply to this standard.
3.1
Multilayer plastic tubing
More than two layers of non-metallic plastic tubes which are made of
materials of different properties and different types, without connectors.
3.2
Tube assemblies
A combination of a multilayer tube and a tube joint which have a specified
length and shape.
4 Specification dimension
4.1 Structure
The multilayer tube is a multilayer structure which contains the wall-thickness
of the main body. The name of material is generally indicated on the drawing. If
specified, it shall identify each layer of all tube layers.
4.2 Dimensions and tolerances
Table 1 provides the dimensions and wall-thickness of various types of
multilayer tubes of this standard. The thickness and tolerance for each layer
may be determined by the manufacturer and the user through negotiation. The
dimensions and tolerances of the multilayer tube are indicated by mm.
4.3 Wall-thickness
Multilayer tubes of different sizes which are made by materials of different
grades have different wall-thicknesses. The minimum wall-thickness of a
straight tube which has a nominal diameter equal to 10 mm is 0.9 mm. The
larger the nominal diameter, the larger the wall-thickness. The requirements for
wall-thickness are as detailed in Table 1.
Note: Some of the following factors influence the choice of wall-thickness:
a) High burst-pressure requirements mean higher wall-thickness
requirements;
b) The thicker the wall-thickness, the greater the minimum bending radius.
6 Performance requirements
The performance requirements of the multilayer and/or multilayer tube
assembly shall comply with the requirements of Table 2.
Table 2 -- Performance requirements
No. Test items Unit Requirements Test methods
1 Burst-pressure
Burst-pressure at
room-temperature MPa
The minimum burst-pressure shall be greater than or equal
to 8 times the design working pressure in the system.
Before reaching to this pressure, the tube does not loose
and the assembly does not leak
7.3
Burst-pressure at
high-temperature MPa
The minimum burst-pressure shall be greater than or equal
to 3 times the design working pressure in the system.
Before reaching to this pressure, the tube does not loose
and the assembly does not leak
7.4
2 Bending performance
Minimum bending
radius mm Meet the requirements of Table 3
7.5 Anti-bending deformation - The steel ball can pass it freely
Burst pressure after
bending MPa
The minimum burst-pressure shall be greater than or equal
to 8 times the design working pressure in the system
Resistance
to zinc
chloride
Appearance - Multilayer tube or tube end shall be free of cracks
7.6 Burst-pressure at
room-temperature MPa
The minimum burst-pressure shall be greater than or equal
to 75% of the burst-pressure at room-temperature
Impact
performance
at low-
temperature
Appearance - The surface is free of cracks
7.7 Burst-pressure at
room-temperature MPa
The minimum burst-pressure shall be greater than or equal
to 75% of the burst-pressure at room-temperature
Resistance
to
permeability
Permeability g/m•d
OD ≤ 10 mm < 0.05
7.8
10 mm < OD ≤ 18 mm < 0.15
Change rate of
length - -1% ~ +1%
Burst-pressure at
room-temperature MPa
Meet the requirements of the burst test pressure at room-
temperature
Yield stress
Extruding direction
N/mm2
≥ 24
7.9
Perpendicular
direction ≥ 25
Elongation
at break
Extruding direction
≥ 170
Perpendicular
direction ≥ 170
7 Resistance to fuel
Appearance - The surface is free of cracks
7.10 Impact at low-
temperature - The surface is free of cracks
7.3.3.1 At the ambient temperature of 23 °C ± 2 °C, carry out the test. The
internal test medium of the multilayer tube is liquid. Block one end of the
specimen. Connect the other end to the burst pressure testing machine. Then
at the rate of 7 MPa/min ± 1 MPa/min, increase pressure to the multilayer tube,
until it bursts. Record the maximum pressure during the test period. Use the
minimum value of the five specimens as the test result.
7.3.3.2 If the tubing/connection fails before reaching the burst-pressure, discard
the test data. If necessary, it may use the existing tubing connections plus the
auxiliary fixtures, to ensure that the test is carried out effectively.
7.3.3.3 The minimum burst-pressure of all specimens shall be greater than or
equal to 8 times the design wo...
Share