PayPal, credit cards. Download editable-PDF and invoice in 1 second!
YS/T 575.17-2007 English PDF (YST575.17-2007)
YS/T 575.17-2007 English PDF (YST575.17-2007)
Precio habitual
$90.00 USD
Precio habitual
Precio de oferta
$90.00 USD
Precio unitario
/
por
Los gastos de envío se calculan en la pantalla de pago.
No se pudo cargar la disponibilidad de retiro
Delivery: 3 seconds. Download true-PDF + Invoice.
Get QUOTATION in 1-minute: Click YS/T 575.17-2007
Historical versions: YS/T 575.17-2007
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll if blank)
YS/T 575.17-2007: Methods for chemical analysis of bauxite. Part 17: Determination of sulfur content. Direct combustion-iodometric method
YS/T 575.17-2007
GB
NONFERROUS METAL INDUSTRY STANDARD
OF THE PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 71.100.10
Q 52
Replacing YS/T 575.17-2006
Methods for chemical analysis of bauxite -
Part 17. Determination of sulfur content -
Direct combustion - iodometric method
ISSUED ON. NOVEMBER 14, 2007
IMPLEMENTED ON. MAY 01, 2008
Issued by. National Development and Reform Commission
Table of Contents
1 Scope ... 5
2 Method Summary... 5
3 Reagents ... 5
4 Instrumentation ... 6
5 Samples ... 8
6 Analysis Steps ... 8
7 Calculation of Analysis Results ... 9
8 Precision ... 9
9 Quality assurance and control ... 10
Foreword
YS/T 575-2007 "Methods for chemical analysis of bauxite", the revision to YS/T
575-2006 (formerly GB/T 3257-1999), is divided into 24 parts.
-- Part 1. Determination of aluminum oxide content - EDTA titration method
-- Part 2. Determination of silica dioxide content - Gravimetric-molybdenum blue
photometric method
-- Part 3. Determination of silica dioxide content - Molybdenum blue photometric
method
-- Part 4. Iron oxide content - Potassium dichromate titration method
-- Part 5. Determination of iron trioxide content - Orthopenanthroline photometric
method
-- Part 6. Determination of titanium dioxide content - Diantipyryl methane
photometric method
-- Part 7. Determination of calcium oxide content - Flame atomic absorption
spectrophotometric method
-- Part 8. Determination of magnesium oxide content - Flame atomic absorption
spectrophotometric method
-- Part 9. Determination of content of potassium oxide and sodium oxide - Flame
atomic absorption spectrophotometric method
-- Part 10. Determination of manganese oxide content - Flame atomic absorption
spectrophotometric method
-- Part 11. Determination of chromium oxide content - Flame atomic absorption
spectrophotometric method
-- Part 12. Determination of vanadium pentoxide content - benzoyl phenyl
hydroxylamine photometric method
-- Part 13. Determination of zinc content - Flame atomic absorption
spectrophotometric method
-- Part 14. Determination of total rare earth oxide content - Tribromoarsenazo
photometric method
-- Part 15. Determination of gallium oxide content - Rhodamine B-extraction
photometric method
Methods for chemical analysis of bauxite -
Part 17. Determination of sulfur content -
Direct combustion - iodometric method
1 Scope
This Part specifies the determination method of sulfur content in bauxite.
This Part applies to the determination of sulfur content in bauxite. The determination
range. ≤3.00%.
2 Method Summary
In the presence of a flux, the sample is heated for decomposition in an oxygen stream at
1300°C±20°C; the sulfur dioxide generated is absorbed by water to form sulfurous acid;
use starch as the indicator; use iodine standard titration solution for titration, so as to
determine the sulfur content; the combined water in the sample influences the precision;
use rining method to eliminate.
3 Reagents
3.1 Lead sulfate. reference reagent.
3.2 Tin sheet (99.9%).
3.3 Sulfuric acid (ρ 1.84 g/mL).
3.4 Mixed flux. mix vanadium pentoxide and boron oxide of equal-mas; grind it finely; then
dry it under 105°C~110°C before use.
3.5 Potassium hydroxide (400 g/L).
3.6 Solution of potassium permanganate (50 g/L). dissolve 10g of potassium
permanganate in 200 mL of potassium hydroxide (3.5).
3.7 Absorption solution. use a little water to mix 0.5g of soluble starch; stir it into a paste;
add 100 mL of boiling water; stir and heat it to dissolve until transparent; use water to
dilute to 1L; drop-add iodine standard titration solution (3.8) until sky blue; transfer it to a
volumetric flask or under jar (3 in Figure 1); use water to dilute to 1 L; shake up; store it in
an amber bottle; use it after storage overnight.
3.8 Titration solution
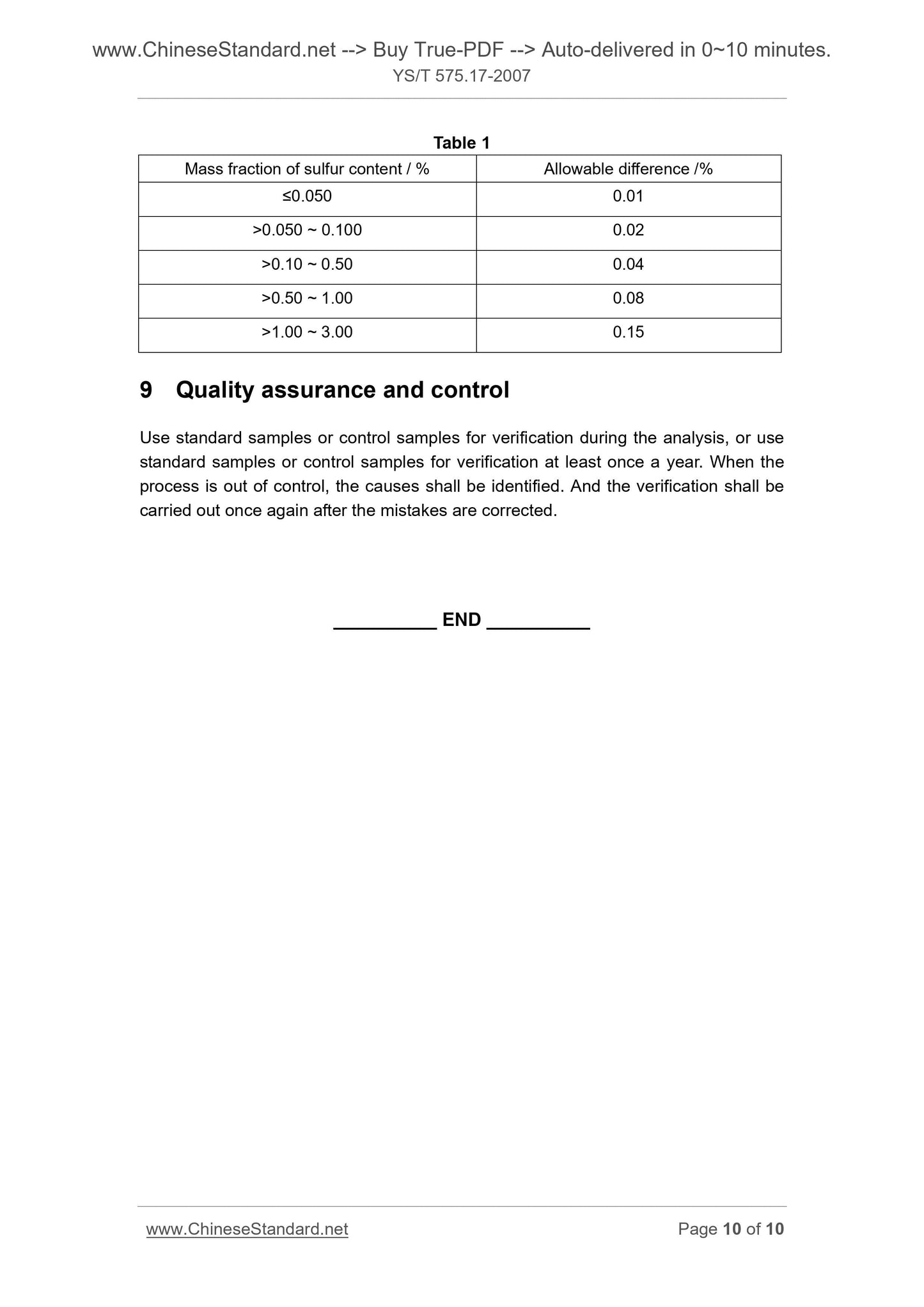
Table 1
Mass fraction of sulfur content / % Allowable difference /%
≤0.050 0.01
>0.050 ~ 0.100 0.02
>0.10 ~ 0.50 0.04
>0.50 ~ 1.00 0.08
>1.00 ~ 3.00 0.15
9 Quality assurance and control
Use standard samples or control samples for verification during the analysis, or use
standard samples or control samples for verification at least once a year. When the
process is out of control, the causes shall be identified. And the verification shall be
carried out once again after the mistakes are corrected.
Get QUOTATION in 1-minute: Click YS/T 575.17-2007
Historical versions: YS/T 575.17-2007
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll if blank)
YS/T 575.17-2007: Methods for chemical analysis of bauxite. Part 17: Determination of sulfur content. Direct combustion-iodometric method
YS/T 575.17-2007
GB
NONFERROUS METAL INDUSTRY STANDARD
OF THE PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 71.100.10
Q 52
Replacing YS/T 575.17-2006
Methods for chemical analysis of bauxite -
Part 17. Determination of sulfur content -
Direct combustion - iodometric method
ISSUED ON. NOVEMBER 14, 2007
IMPLEMENTED ON. MAY 01, 2008
Issued by. National Development and Reform Commission
Table of Contents
1 Scope ... 5
2 Method Summary... 5
3 Reagents ... 5
4 Instrumentation ... 6
5 Samples ... 8
6 Analysis Steps ... 8
7 Calculation of Analysis Results ... 9
8 Precision ... 9
9 Quality assurance and control ... 10
Foreword
YS/T 575-2007 "Methods for chemical analysis of bauxite", the revision to YS/T
575-2006 (formerly GB/T 3257-1999), is divided into 24 parts.
-- Part 1. Determination of aluminum oxide content - EDTA titration method
-- Part 2. Determination of silica dioxide content - Gravimetric-molybdenum blue
photometric method
-- Part 3. Determination of silica dioxide content - Molybdenum blue photometric
method
-- Part 4. Iron oxide content - Potassium dichromate titration method
-- Part 5. Determination of iron trioxide content - Orthopenanthroline photometric
method
-- Part 6. Determination of titanium dioxide content - Diantipyryl methane
photometric method
-- Part 7. Determination of calcium oxide content - Flame atomic absorption
spectrophotometric method
-- Part 8. Determination of magnesium oxide content - Flame atomic absorption
spectrophotometric method
-- Part 9. Determination of content of potassium oxide and sodium oxide - Flame
atomic absorption spectrophotometric method
-- Part 10. Determination of manganese oxide content - Flame atomic absorption
spectrophotometric method
-- Part 11. Determination of chromium oxide content - Flame atomic absorption
spectrophotometric method
-- Part 12. Determination of vanadium pentoxide content - benzoyl phenyl
hydroxylamine photometric method
-- Part 13. Determination of zinc content - Flame atomic absorption
spectrophotometric method
-- Part 14. Determination of total rare earth oxide content - Tribromoarsenazo
photometric method
-- Part 15. Determination of gallium oxide content - Rhodamine B-extraction
photometric method
Methods for chemical analysis of bauxite -
Part 17. Determination of sulfur content -
Direct combustion - iodometric method
1 Scope
This Part specifies the determination method of sulfur content in bauxite.
This Part applies to the determination of sulfur content in bauxite. The determination
range. ≤3.00%.
2 Method Summary
In the presence of a flux, the sample is heated for decomposition in an oxygen stream at
1300°C±20°C; the sulfur dioxide generated is absorbed by water to form sulfurous acid;
use starch as the indicator; use iodine standard titration solution for titration, so as to
determine the sulfur content; the combined water in the sample influences the precision;
use rining method to eliminate.
3 Reagents
3.1 Lead sulfate. reference reagent.
3.2 Tin sheet (99.9%).
3.3 Sulfuric acid (ρ 1.84 g/mL).
3.4 Mixed flux. mix vanadium pentoxide and boron oxide of equal-mas; grind it finely; then
dry it under 105°C~110°C before use.
3.5 Potassium hydroxide (400 g/L).
3.6 Solution of potassium permanganate (50 g/L). dissolve 10g of potassium
permanganate in 200 mL of potassium hydroxide (3.5).
3.7 Absorption solution. use a little water to mix 0.5g of soluble starch; stir it into a paste;
add 100 mL of boiling water; stir and heat it to dissolve until transparent; use water to
dilute to 1L; drop-add iodine standard titration solution (3.8) until sky blue; transfer it to a
volumetric flask or under jar (3 in Figure 1); use water to dilute to 1 L; shake up; store it in
an amber bottle; use it after storage overnight.
3.8 Titration solution
Table 1
Mass fraction of sulfur content / % Allowable difference /%
≤0.050 0.01
>0.050 ~ 0.100 0.02
>0.10 ~ 0.50 0.04
>0.50 ~ 1.00 0.08
>1.00 ~ 3.00 0.15
9 Quality assurance and control
Use standard samples or control samples for verification during the analysis, or use
standard samples or control samples for verification at least once a year. When the
process is out of control, the causes shall be identified. And the verification shall be
carried out once again after the mistakes are corrected.
Share