1
/
su
10
PayPal, credit cards. Download editable-PDF & invoice in 1 second!
GB 1886.250-2016 English PDF (GB1886.250-2016)
GB 1886.250-2016 English PDF (GB1886.250-2016)
Prezzo di listino
$120.00 USD
Prezzo di listino
Prezzo scontato
$120.00 USD
Prezzo unitario
/
per
Spese di spedizione calcolate al check-out.
Impossibile caricare la disponibilità di ritiro
Delivery: 3 seconds. Download true-PDF + Invoice.
Get QUOTATION in 1-minute: Click GB 1886.250-2016
Historical versions: GB 1886.250-2016
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll if blank)
GB 1886.250-2016: National Food Safety Standard -- Food Additives -- Sodium Phytate
GB 1886.250-2016
GB
NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE
PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
National Food Safety Standard - Food Additives -
Sodium Phytate
ISSUED ON: AUGUST 31, 2016
IMPLEMENTED ON: JANUARY 1, 2017
Issued by: National Health and Family Planning Commission of the
People’s Republic of China
Table of Contents
1 Scope ... 3
2 Molecular Formula, Structural Formula and Relative Molecular Mass ... 3
3 Technical Requirements ... 3
Appendix A Inspection Method ... 5
National Food Safety Standard - Food Additives -
Sodium Phytate
1 Scope
This Standard is applicable to food additive sodium phytate, which is made from rise
bran and corn germ as the raw materials, and through extraction, purification,
crystallization separation and drying.
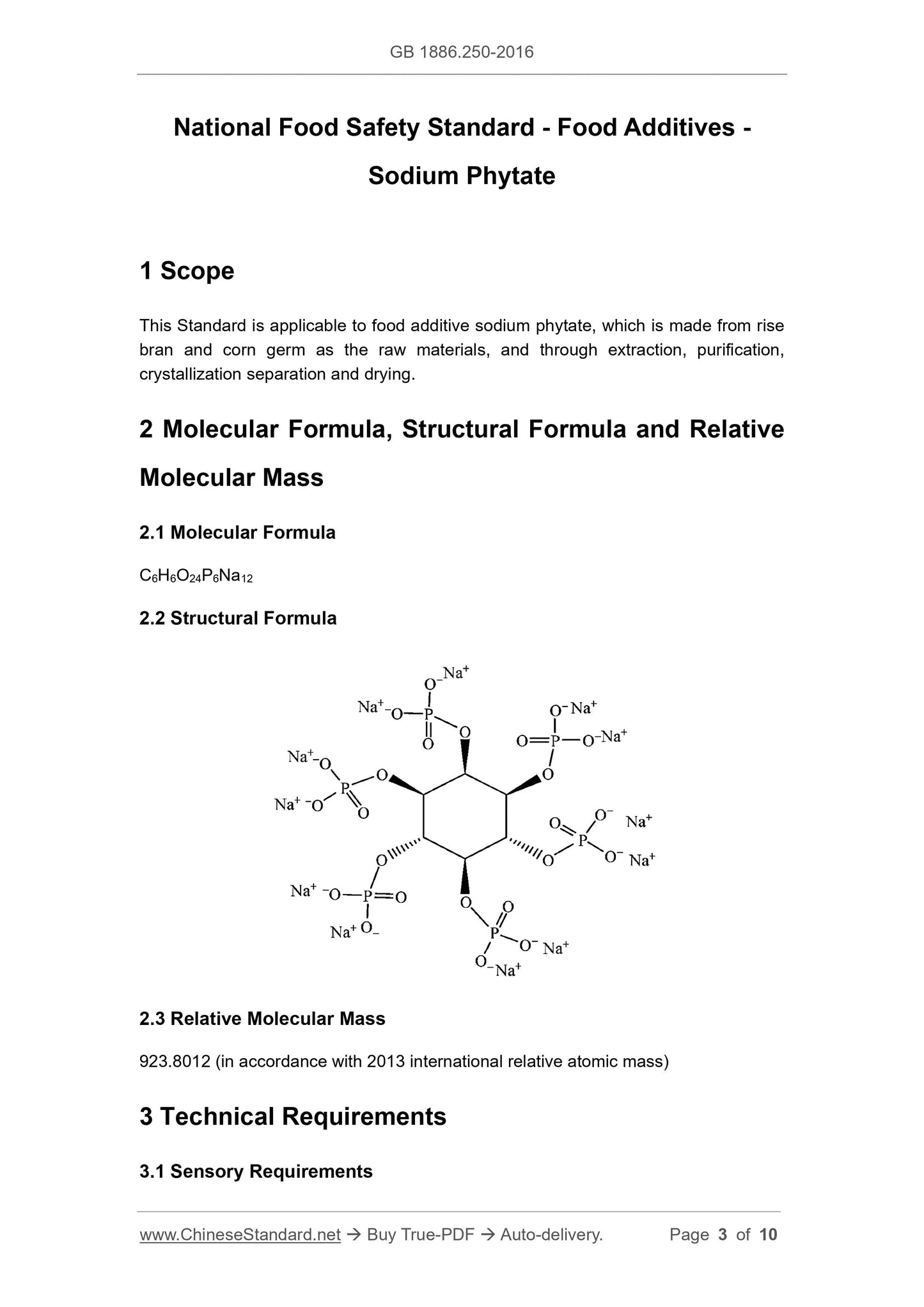
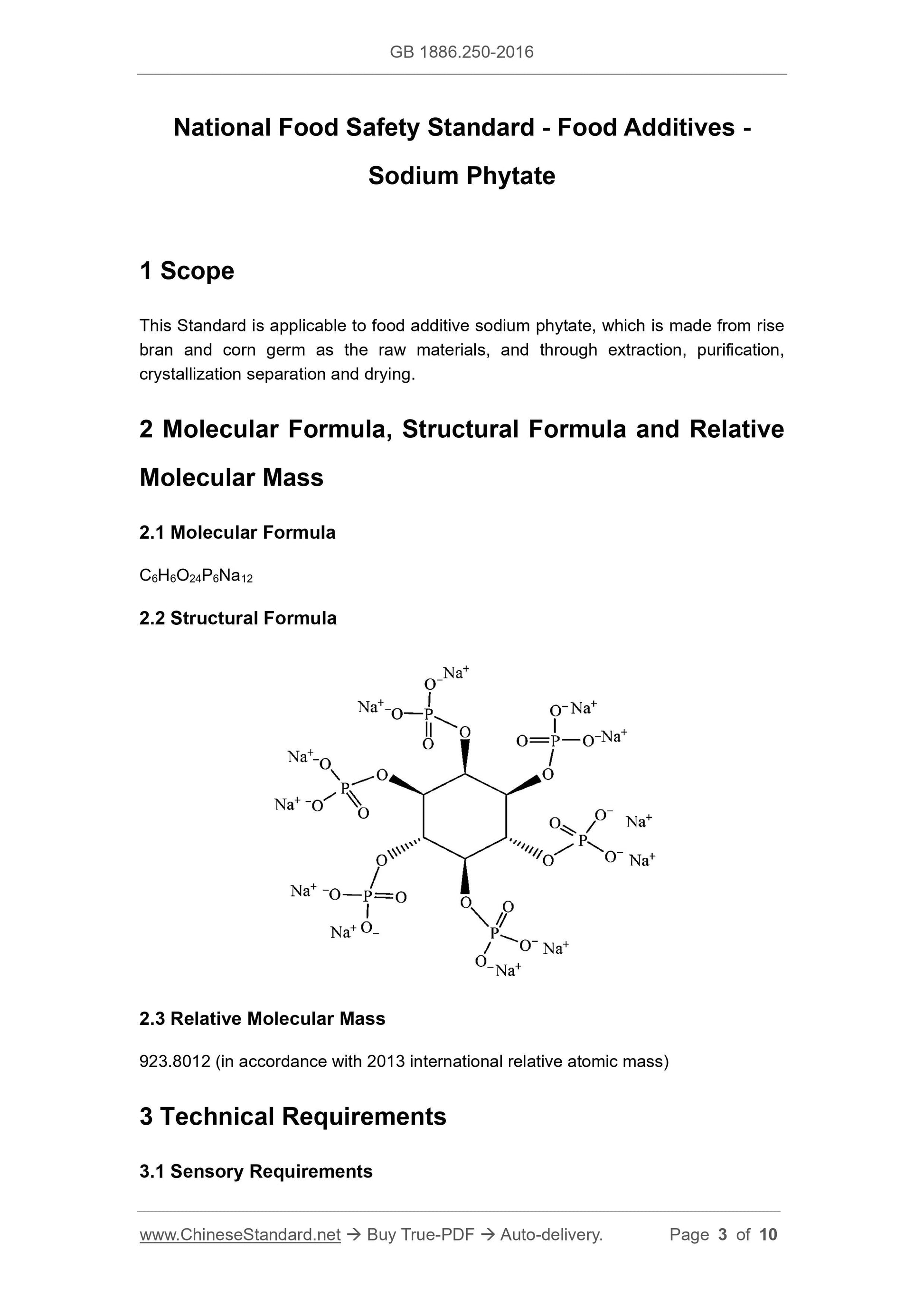
2 Molecular Formula, Structural Formula and Relative
Molecular Mass
2.1 Molecular Formula
C6H6O24P6Na12
2.2 Structural Formula
2.3 Relative Molecular Mass
923.8012 (in accordance with 2013 international relative atomic mass)
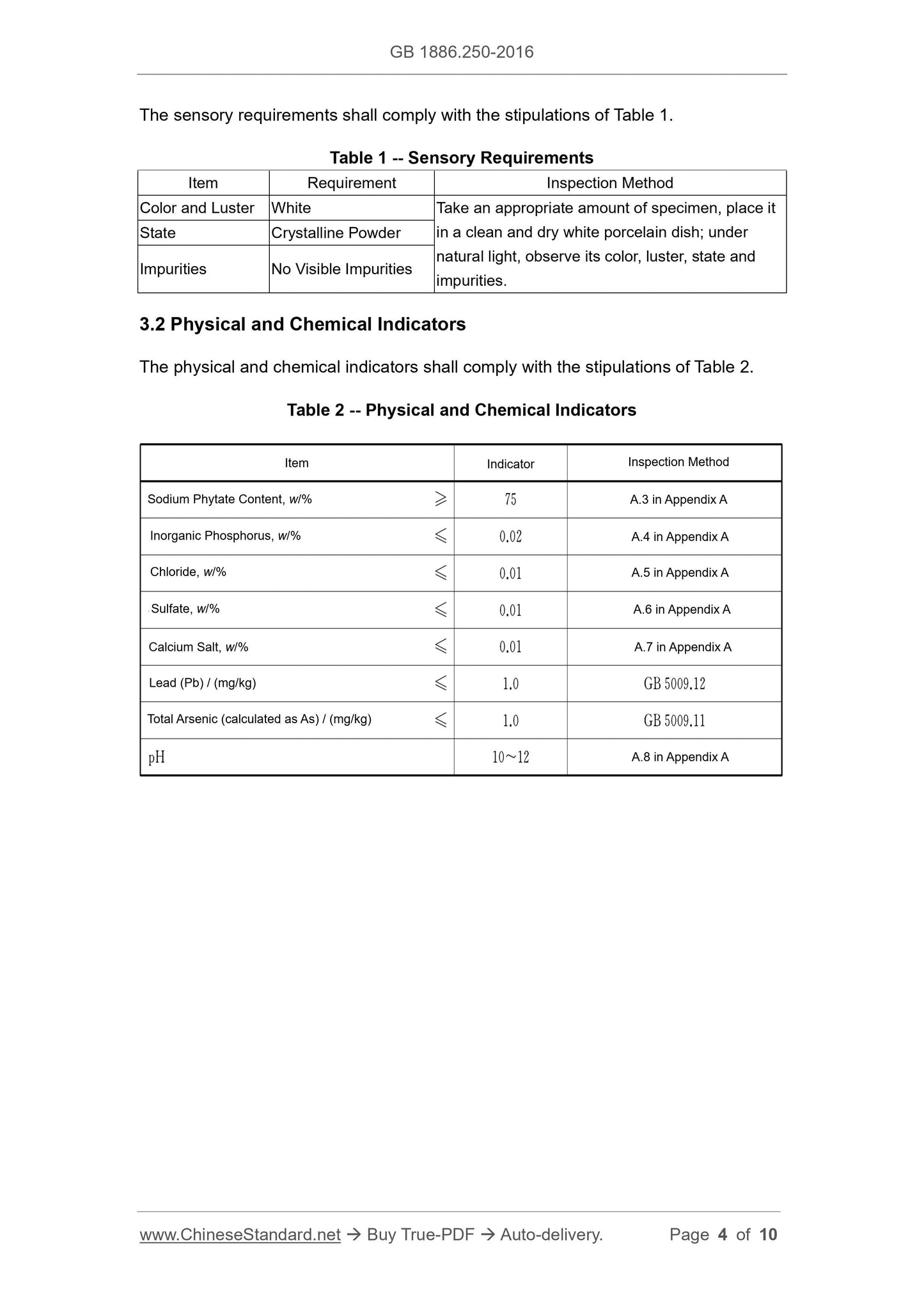
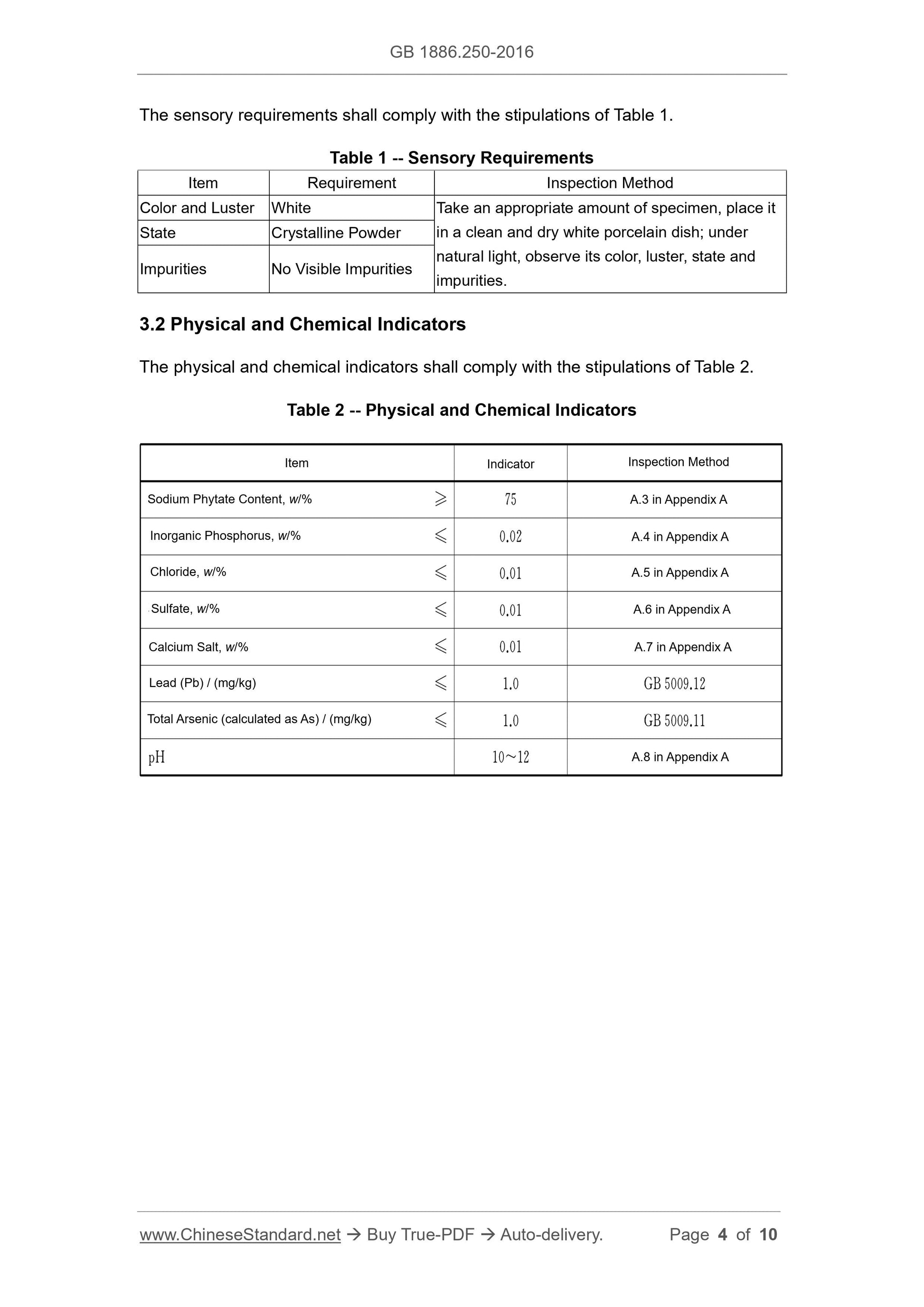
3 Technical Requirements
3.1 Sensory Requirements
Appendix A
Inspection Method
A.1 General Rules
When other requirements are not indicated, the reagents and water used in this
Standard refer to analytically pure reagents and Grade-3 water specified in GB/T 6682.
When other requirements are not indicated, the standard solutions, preparations and
products used for impurity determination shall be prepared in accordance with the
stipulations of GB/T 602 and GB/T 603. When it is not specified which solvent is used
for the preparation, the solutions used in the test refer to aqueous solutions.
A.2 Identification Test
A.2.1 Reagents and materials
A.2.1.1 Total arsenic and nitric acid solution: 1 + 3.
A.2.1.2 Sulfuric acid.
A.2.1.3 Hydrogen peroxide.
A.2.1.4 Calcium chloride solution: 75 g/L. Prepare it right before use.
A.2.1.5 Ammonium molybdate solution: 25 g/L.
A.2.2 Identification method
Take a small amount of 1% specimen solution; use nitric acid solution to neutralize it;
add a few drops of calcium chloride solution to generate white precipitate.
Take a small amount of 1% specimen solution; add 1 mL of sulfuric acid; heat it up to
reach complete carbonization. Then, dropwise add hydrogen peroxide, until it turns
light yellow and translucent; add ammonium molybdate solution to develop yellow.
A.3 Determination of Sodium Phytate Content
A.3.1 Method summary
Sodium phytate is digested by perchloric acid and nitric acid to generate sodium
phosphate. In nitric acid medium, phosphoric acid reacts with quin molybdenum ketone
reagent to generate yellow precipitate of quinoline phosphomolybdate, which is filtered,
washed, dried and weighed. Thus, the sodium phytate content in the sample can be
calculated.
m1---the mass of the precipitate, expressed in (g);
M1---the molar mass of phosphorus, expressed in (g/mol) [M (P) = 30.974];
M2---the molar mass of quinoline phosphomolybdate, expressed in (g/mol) {M [(C9H7N)
H3PO4 12MoO3] = 2212.74};
M3---the molar mass of sodium phytate, expressed in (g/mol) [M (C6H6O24P6Na12) =
923.8012];
6---the number of phosphorus in sodium phytate;
m2---the mass of the specimen, expressed in (g);
20---the volume of the specimen solution being tested, expressed in (mL);
100---the total volume of the specimen solution, expressed in (mL).
The arithmetic mean value of the parallel determination results shall prevail in the test
result. The absolute difference between two independent determination results
obtained under repeatability conditions is not greater than 0.2%.
A.4 Determination of Inorganic Phosphorus
A.4.1 Method summary
Under acidic conditions, add orthophosphate in the sodium phytate solution of ferric
chloride solution to generate yellow phosphorus vanadium molybdate complex with
vanadium molybdate. Use a spectrophotometer to measure its absorbance value at
420 nm. In accordance with the standard curve, calculate the inorganic phosphorus
content in the sample.
A.4.2 Reagents and materials
A.4.2.1 Ammonium vanadium molybdate solution: weigh-take 40 g of ammonium
molybdate [(NH4)6Mo7O24 4H2O], dissolve it in 400 mL of water to obtain solution A.
Weigh-take 1.0 g of ammonium metavanadate (NH4VO3), dissolve it in a mixed solvent
of 300 mL of water and 80 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid to obtain solution B. Add
solution A to solution B; use reagent water to dilute it to 1 L.
A.4.2.2 Ferric chloride solution: 10 g/L.
A.4.2.3 Phosphate standard stock solution: weigh-take 4.3865 g of potassium
dihydrogen phosphate, which is dried at 105 °C for 1 h; dissolve it in 100 mL of water;
transfer it into a 1 L volumetric flask. Use reagent water to dilute it to the scale, then,
shake it well. The concentration of this solution is 1.0 mg/mL.
A.4.2.4 Phosphate standard working solution: accurately draw 10.0 mL of the standard
Under acidic conditions, the chloride ions in the sodium phytate solution and the silver
nitrate solution generate white silver nitrate precipitate. Use the visual inspection
method to compare the turbidity with the standard solution.
A.5.2 Reagents and materials
A.5.2.1 Nitric acid solution: 1 + 4.
A.5.2.2 Silver nitrate solution: 0.1 mol/L.
A.5.2.3 Chloride standard solution: 0.1 mg/mL.
A.5.3 Analytical procedures
Weigh-take 1.0 g of the specimen, accurate to 0.01 g. Place it in a 25 mL colorimetric
tube; add 15 mL of water, then, use nitric acid solution to neutralize it to pH = 7. Add 1
mL of nitric acid solution to acidify the solution, then, add 1 mL of 0.1 mol/L silver nitrate
solution, reach a constant volume of 25 mL; shake it well and place it in the dark for 10
min. Take 1.0 mL of the chloride standard solution to a 25 mL colorimetric tube; add 15
mL of water; the rest of the steps are the same as the treatment of the specimen
solution. Observe the turbidity of the sample, which shall not be deeper than the
standard solution.
A.6 Determination of Sulfate
A.6.1 Method summary
Under acidic conditions, the sulfate ions in the sodium phytate solution and the barium
chloride solution generate barium sulfate precipitate. Use the visual inspection method
to compare the turbidity with the standard solution.
A.6.2 Reagents and materials
A.6.2.1 Nitric acid solution: 1 + 3.
A.6.2.2 Sulfate standard solution: 0.1 mg/mL.
A.6.3 Analytical procedures
Weigh-take 1.0 g of the specimen (accurate to 0.01 g); place it in a 25 mL colorimetric
tube. Add 20 mL of water, then, use nitric acid solution to neutralize it to pH = 7; the
remaining shall be carried out in accordance with the stipulations of GB/T 9728. Take
1.0 mL of sulfate standard solution to a 25 mL colorimetric tube; add 20 mL of water;
the rest of the steps are the same as the treatment of the specimen solution. Observe
the turbidity of the sample, which shall not be deeper than the standard solution.
A.7 Determination of Calcium Salt
Get QUOTATION in 1-minute: Click GB 1886.250-2016
Historical versions: GB 1886.250-2016
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll if blank)
GB 1886.250-2016: National Food Safety Standard -- Food Additives -- Sodium Phytate
GB 1886.250-2016
GB
NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE
PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
National Food Safety Standard - Food Additives -
Sodium Phytate
ISSUED ON: AUGUST 31, 2016
IMPLEMENTED ON: JANUARY 1, 2017
Issued by: National Health and Family Planning Commission of the
People’s Republic of China
Table of Contents
1 Scope ... 3
2 Molecular Formula, Structural Formula and Relative Molecular Mass ... 3
3 Technical Requirements ... 3
Appendix A Inspection Method ... 5
National Food Safety Standard - Food Additives -
Sodium Phytate
1 Scope
This Standard is applicable to food additive sodium phytate, which is made from rise
bran and corn germ as the raw materials, and through extraction, purification,
crystallization separation and drying.
2 Molecular Formula, Structural Formula and Relative
Molecular Mass
2.1 Molecular Formula
C6H6O24P6Na12
2.2 Structural Formula
2.3 Relative Molecular Mass
923.8012 (in accordance with 2013 international relative atomic mass)
3 Technical Requirements
3.1 Sensory Requirements
Appendix A
Inspection Method
A.1 General Rules
When other requirements are not indicated, the reagents and water used in this
Standard refer to analytically pure reagents and Grade-3 water specified in GB/T 6682.
When other requirements are not indicated, the standard solutions, preparations and
products used for impurity determination shall be prepared in accordance with the
stipulations of GB/T 602 and GB/T 603. When it is not specified which solvent is used
for the preparation, the solutions used in the test refer to aqueous solutions.
A.2 Identification Test
A.2.1 Reagents and materials
A.2.1.1 Total arsenic and nitric acid solution: 1 + 3.
A.2.1.2 Sulfuric acid.
A.2.1.3 Hydrogen peroxide.
A.2.1.4 Calcium chloride solution: 75 g/L. Prepare it right before use.
A.2.1.5 Ammonium molybdate solution: 25 g/L.
A.2.2 Identification method
Take a small amount of 1% specimen solution; use nitric acid solution to neutralize it;
add a few drops of calcium chloride solution to generate white precipitate.
Take a small amount of 1% specimen solution; add 1 mL of sulfuric acid; heat it up to
reach complete carbonization. Then, dropwise add hydrogen peroxide, until it turns
light yellow and translucent; add ammonium molybdate solution to develop yellow.
A.3 Determination of Sodium Phytate Content
A.3.1 Method summary
Sodium phytate is digested by perchloric acid and nitric acid to generate sodium
phosphate. In nitric acid medium, phosphoric acid reacts with quin molybdenum ketone
reagent to generate yellow precipitate of quinoline phosphomolybdate, which is filtered,
washed, dried and weighed. Thus, the sodium phytate content in the sample can be
calculated.
m1---the mass of the precipitate, expressed in (g);
M1---the molar mass of phosphorus, expressed in (g/mol) [M (P) = 30.974];
M2---the molar mass of quinoline phosphomolybdate, expressed in (g/mol) {M [(C9H7N)
H3PO4 12MoO3] = 2212.74};
M3---the molar mass of sodium phytate, expressed in (g/mol) [M (C6H6O24P6Na12) =
923.8012];
6---the number of phosphorus in sodium phytate;
m2---the mass of the specimen, expressed in (g);
20---the volume of the specimen solution being tested, expressed in (mL);
100---the total volume of the specimen solution, expressed in (mL).
The arithmetic mean value of the parallel determination results shall prevail in the test
result. The absolute difference between two independent determination results
obtained under repeatability conditions is not greater than 0.2%.
A.4 Determination of Inorganic Phosphorus
A.4.1 Method summary
Under acidic conditions, add orthophosphate in the sodium phytate solution of ferric
chloride solution to generate yellow phosphorus vanadium molybdate complex with
vanadium molybdate. Use a spectrophotometer to measure its absorbance value at
420 nm. In accordance with the standard curve, calculate the inorganic phosphorus
content in the sample.
A.4.2 Reagents and materials
A.4.2.1 Ammonium vanadium molybdate solution: weigh-take 40 g of ammonium
molybdate [(NH4)6Mo7O24 4H2O], dissolve it in 400 mL of water to obtain solution A.
Weigh-take 1.0 g of ammonium metavanadate (NH4VO3), dissolve it in a mixed solvent
of 300 mL of water and 80 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid to obtain solution B. Add
solution A to solution B; use reagent water to dilute it to 1 L.
A.4.2.2 Ferric chloride solution: 10 g/L.
A.4.2.3 Phosphate standard stock solution: weigh-take 4.3865 g of potassium
dihydrogen phosphate, which is dried at 105 °C for 1 h; dissolve it in 100 mL of water;
transfer it into a 1 L volumetric flask. Use reagent water to dilute it to the scale, then,
shake it well. The concentration of this solution is 1.0 mg/mL.
A.4.2.4 Phosphate standard working solution: accurately draw 10.0 mL of the standard
Under acidic conditions, the chloride ions in the sodium phytate solution and the silver
nitrate solution generate white silver nitrate precipitate. Use the visual inspection
method to compare the turbidity with the standard solution.
A.5.2 Reagents and materials
A.5.2.1 Nitric acid solution: 1 + 4.
A.5.2.2 Silver nitrate solution: 0.1 mol/L.
A.5.2.3 Chloride standard solution: 0.1 mg/mL.
A.5.3 Analytical procedures
Weigh-take 1.0 g of the specimen, accurate to 0.01 g. Place it in a 25 mL colorimetric
tube; add 15 mL of water, then, use nitric acid solution to neutralize it to pH = 7. Add 1
mL of nitric acid solution to acidify the solution, then, add 1 mL of 0.1 mol/L silver nitrate
solution, reach a constant volume of 25 mL; shake it well and place it in the dark for 10
min. Take 1.0 mL of the chloride standard solution to a 25 mL colorimetric tube; add 15
mL of water; the rest of the steps are the same as the treatment of the specimen
solution. Observe the turbidity of the sample, which shall not be deeper than the
standard solution.
A.6 Determination of Sulfate
A.6.1 Method summary
Under acidic conditions, the sulfate ions in the sodium phytate solution and the barium
chloride solution generate barium sulfate precipitate. Use the visual inspection method
to compare the turbidity with the standard solution.
A.6.2 Reagents and materials
A.6.2.1 Nitric acid solution: 1 + 3.
A.6.2.2 Sulfate standard solution: 0.1 mg/mL.
A.6.3 Analytical procedures
Weigh-take 1.0 g of the specimen (accurate to 0.01 g); place it in a 25 mL colorimetric
tube. Add 20 mL of water, then, use nitric acid solution to neutralize it to pH = 7; the
remaining shall be carried out in accordance with the stipulations of GB/T 9728. Take
1.0 mL of sulfate standard solution to a 25 mL colorimetric tube; add 20 mL of water;
the rest of the steps are the same as the treatment of the specimen solution. Observe
the turbidity of the sample, which shall not be deeper than the standard solution.
A.7 Determination of Calcium Salt
Share