1
/
su
12
PayPal, credit cards. Download editable-PDF & invoice in 1 second!
YY/T 0681.12-2022 English PDF (YYT0681.12-2022)
YY/T 0681.12-2022 English PDF (YYT0681.12-2022)
Prezzo di listino
$230.00 USD
Prezzo di listino
Prezzo scontato
$230.00 USD
Prezzo unitario
/
per
Spese di spedizione calcolate al check-out.
Impossibile caricare la disponibilità di ritiro
Delivery: 3 seconds. Download true-PDF + Invoice.
Get QUOTATION in 1-minute: Click YY/T 0681.12-2022
Historical versions: YY/T 0681.12-2022
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll if blank)
YY/T 0681.12-2022: Test methods for sterile medical device package - Part 12: Flex durability of flexible barrier materials
YY/T 0681.12-2022
YY
PHARMACEUTICAL INDUSTRY STANDARD
OF THE PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 11.080.20
CCS C 31
Replacing YY/T 0681.12-2014
Test methods for sterile medical device package - Part 12:
Flex durability of flexible barrier materials
ISSUED ON: MAY 18, 2022
IMPLEMENTED ON: JUNE 01, 2023
Issued by: National Medical Products Administration
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
Introduction ... 6
1 Scope ... 8
2 Normative references ... 8
3 Terms and definitions ... 8
4 Overview of test methods ... 8
5 Application ... 9
6 Test instruments ... 9
7 Specimen preparation ... 11
8 Conditioning ... 11
9 Procedures ... 11
10 Report ... 12
Annex A (informative) Pinhole counting test ... 14
Annex B (informative) Gas and/or water vapor transmission rate test ... 16
Bibliography ... 17
Test methods for sterile medical device package - Part 12:
Flex durability of flexible barrier materials
1 Scope
This document describes test methods for the flex durability of flexible barrier materials.
This document applies to the testing of the flex durability of flexible barrier materials.
2 Normative references
The following referenced documents are indispensable for the application of this
document. For dated references, only the edition cited applies. For undated references,
the latest edition of the referenced document (including any amendments) applies.
GB/T 2918, Plastics - Standard atmospheres for conditioning and testing
3 Terms and definitions
For the purposes of this document, the following terms and definitions apply.
3.1 pinhole
A small opening of no particular shape or size that passes completely through all layers
of a flexible barrier material.
3.2 flexible
Easy to fold, bend, twist by hand.
4 Overview of test methods
4.1 Unless otherwise specified, the flexing test is performed on specimens of flexible
barrier materials under standard atmospheric conditions. The flexing conditions, times
and flexing degree vary with the structure type of the specimen. The flexing action
consists of a twisting movement followed by a horizontal movement (in most cases).
Repeatedly twist and compress the specimen in this way. The frequency is 45 times/min.
4.2 The degree of damage to the structural and/or mechanical properties of the material
is judged by the flexing test. The properties to be evaluated in the flexing test determine
the appropriate level of test conditions. For flexible barrier film materials, the pinhole
counting test and gas and/or water vapor transmission rate test methods can be used,
see Annex A and Annex B. For the evaluation methods of breathable materials such as
paper and polyolefin nonwovens, please refer to standards such as GB/T 19633.1 or
YY/T 06981).
4.3 The various test conditions are summarized as follows:
a) Condition A: full flexing for 1h (that is, 2700 cycles);
b) Condition B: full flexing for 20mins (that is, 900 cycles);
c) Condition C: full flexing for 6mins (that is, 270 cycles);
d) Condition D: 20 cycles of full flexing;
e) Condition E: 20 cycles of partial flexing.
5 Application
5.1 The various conditions described in this test are to prevent the occurrence of too
many pinholes that are inconvenient to count and meaningless when testing a specimen
structure, and the occurrence of too few pinholes is also meaningless. Generally, the
number of pinholes on each sample shall be between 5~50. Material construction,
purpose of the test, and agreement between interested parties are important factors to
consider when selecting the level of test conditions.
5.2 This test method does not measure any part of wear associated with flux-to-break.
5.3 Failure of the integrity of one or more layers in a composite layer structure requires
a different test than the need to check for pinholes that penetrate completely through
the structure. Gas and/or water vapor transmission tests can be combined with the
flexing test to measure loss of layer integrity. However, any penetration test requiring a
differential pressure cannot measure the penetration coefficient in the presence of a
pinhole.
6 Test instruments
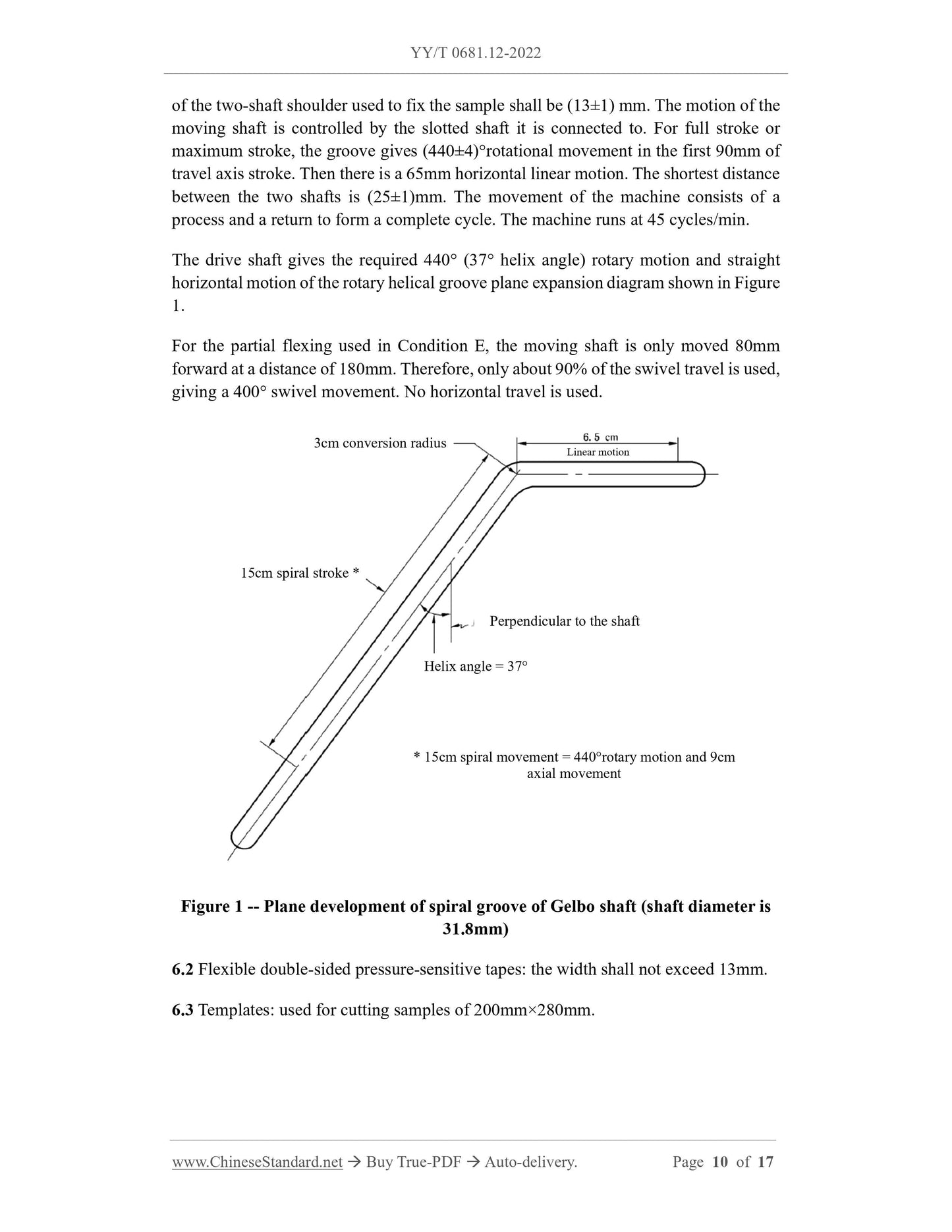
6.1 Flexing tester: is designed to be set up according to the specifications listed in
Chapter 9. The instrument shall mainly consist of a (90±1)mm diameter fixed shaft and
a (90±1)mm diameter moving shaft. When the moving shaft is at the initial position of
the stroke (that is, the maximum distance), the two shafts face to face are separated by
(180±2)mm. Both shafts shall have vents to protect the sample from pressure. The width
1) Test methods such as tensile strength and/or air permeability.
7 Specimen preparation
7.1 The samples are cut into sheets of 200mm × 280mm. The 200mm dimension is the
test direction. This is also the direction of the flexing tester shaft.
7.2 Four samples are flexed in each of their machine direction and cross direction. In
addition, four flexed samples are taken from positions adjacent to the samples in two
directions as control samples.
7.3 Leave open on both sides of the sample without sealing or taping it. Use a double-
sided pressure-sensitive adhesive tape with a width not exceeding 13mm to bond the
unsealed specimen into a cylindrical shape suitable for the shaft of the testing machine.
8 Conditioning
According to the provisions of GB/T 2918, the sample shall be conditioned for at least
24h under the conditions that the relative humidity is (50±5)% and the temperature is
(23±2)°C (unless otherwise specified between the supplier and the purchaser).
9 Procedures
9.1 Test environment
Unless otherwise specified, the flexing test is carried out under the conditions described
in Chapter 8.
9.2 Flexing conditions
9.2.1 Condition A
9.2.1.1 Setting of flexing tester
Set the flexing tester to maximum stroke. This setting gives the first 90mm of travel a
440° rotational movement. Then it is a 65mm horizontal linear motion. The frequency
is 45 cycles/min. With this setting, when the moving shaft is at the initial position, the
distance between the moving shaft and the end face of the fixed shaft is 180mm. When
the moving shaft moves to the shortest distance, the end face is 25mm away from the
fixed shaft.
9.2.1.2 Flexing test
Attach the flexible barrier samples that have been taped with double-sided pressure
sensitive tape to the two shafts of the flexing tester. Or directly fix the sample on the
testing machine. Turn on the flexing tester. Flex the sample for 1h at 45 cycles/min (that
is, a total of 2700 cycles).
9.2.2 Condition B
The test conditions are the same as Condition A. The samples are flexed for 20min at
45 cycles/min. (that is, a total of 900 cycles under full flexing and swirling action).
9.2.3 Condition C
The test conditions are the same as Condition A. The samples are flexed for 6min at 45
cycles/min. (that is, a total of 270 cycles under full flexing and swirling action).
9.2.4 Condition D
The test conditions are the same as Condition A. The samples are flexed for 20 times at
45 cycles/min. (that is, a total of 20 cycles under full flexing and swirling action).
9.2.5 Condition E
Set the flexing tester to the partial flexing described in 6.1. At this time, set the moving
shaft so that the moving shaft only moves 80mm of the 180mm distance (the maximum
distance between the two shafts or the initial position). Therefore, only about 90% of
the swivel travel is used, giving a swiv...
Get QUOTATION in 1-minute: Click YY/T 0681.12-2022
Historical versions: YY/T 0681.12-2022
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll if blank)
YY/T 0681.12-2022: Test methods for sterile medical device package - Part 12: Flex durability of flexible barrier materials
YY/T 0681.12-2022
YY
PHARMACEUTICAL INDUSTRY STANDARD
OF THE PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 11.080.20
CCS C 31
Replacing YY/T 0681.12-2014
Test methods for sterile medical device package - Part 12:
Flex durability of flexible barrier materials
ISSUED ON: MAY 18, 2022
IMPLEMENTED ON: JUNE 01, 2023
Issued by: National Medical Products Administration
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
Introduction ... 6
1 Scope ... 8
2 Normative references ... 8
3 Terms and definitions ... 8
4 Overview of test methods ... 8
5 Application ... 9
6 Test instruments ... 9
7 Specimen preparation ... 11
8 Conditioning ... 11
9 Procedures ... 11
10 Report ... 12
Annex A (informative) Pinhole counting test ... 14
Annex B (informative) Gas and/or water vapor transmission rate test ... 16
Bibliography ... 17
Test methods for sterile medical device package - Part 12:
Flex durability of flexible barrier materials
1 Scope
This document describes test methods for the flex durability of flexible barrier materials.
This document applies to the testing of the flex durability of flexible barrier materials.
2 Normative references
The following referenced documents are indispensable for the application of this
document. For dated references, only the edition cited applies. For undated references,
the latest edition of the referenced document (including any amendments) applies.
GB/T 2918, Plastics - Standard atmospheres for conditioning and testing
3 Terms and definitions
For the purposes of this document, the following terms and definitions apply.
3.1 pinhole
A small opening of no particular shape or size that passes completely through all layers
of a flexible barrier material.
3.2 flexible
Easy to fold, bend, twist by hand.
4 Overview of test methods
4.1 Unless otherwise specified, the flexing test is performed on specimens of flexible
barrier materials under standard atmospheric conditions. The flexing conditions, times
and flexing degree vary with the structure type of the specimen. The flexing action
consists of a twisting movement followed by a horizontal movement (in most cases).
Repeatedly twist and compress the specimen in this way. The frequency is 45 times/min.
4.2 The degree of damage to the structural and/or mechanical properties of the material
is judged by the flexing test. The properties to be evaluated in the flexing test determine
the appropriate level of test conditions. For flexible barrier film materials, the pinhole
counting test and gas and/or water vapor transmission rate test methods can be used,
see Annex A and Annex B. For the evaluation methods of breathable materials such as
paper and polyolefin nonwovens, please refer to standards such as GB/T 19633.1 or
YY/T 06981).
4.3 The various test conditions are summarized as follows:
a) Condition A: full flexing for 1h (that is, 2700 cycles);
b) Condition B: full flexing for 20mins (that is, 900 cycles);
c) Condition C: full flexing for 6mins (that is, 270 cycles);
d) Condition D: 20 cycles of full flexing;
e) Condition E: 20 cycles of partial flexing.
5 Application
5.1 The various conditions described in this test are to prevent the occurrence of too
many pinholes that are inconvenient to count and meaningless when testing a specimen
structure, and the occurrence of too few pinholes is also meaningless. Generally, the
number of pinholes on each sample shall be between 5~50. Material construction,
purpose of the test, and agreement between interested parties are important factors to
consider when selecting the level of test conditions.
5.2 This test method does not measure any part of wear associated with flux-to-break.
5.3 Failure of the integrity of one or more layers in a composite layer structure requires
a different test than the need to check for pinholes that penetrate completely through
the structure. Gas and/or water vapor transmission tests can be combined with the
flexing test to measure loss of layer integrity. However, any penetration test requiring a
differential pressure cannot measure the penetration coefficient in the presence of a
pinhole.
6 Test instruments
6.1 Flexing tester: is designed to be set up according to the specifications listed in
Chapter 9. The instrument shall mainly consist of a (90±1)mm diameter fixed shaft and
a (90±1)mm diameter moving shaft. When the moving shaft is at the initial position of
the stroke (that is, the maximum distance), the two shafts face to face are separated by
(180±2)mm. Both shafts shall have vents to protect the sample from pressure. The width
1) Test methods such as tensile strength and/or air permeability.
7 Specimen preparation
7.1 The samples are cut into sheets of 200mm × 280mm. The 200mm dimension is the
test direction. This is also the direction of the flexing tester shaft.
7.2 Four samples are flexed in each of their machine direction and cross direction. In
addition, four flexed samples are taken from positions adjacent to the samples in two
directions as control samples.
7.3 Leave open on both sides of the sample without sealing or taping it. Use a double-
sided pressure-sensitive adhesive tape with a width not exceeding 13mm to bond the
unsealed specimen into a cylindrical shape suitable for the shaft of the testing machine.
8 Conditioning
According to the provisions of GB/T 2918, the sample shall be conditioned for at least
24h under the conditions that the relative humidity is (50±5)% and the temperature is
(23±2)°C (unless otherwise specified between the supplier and the purchaser).
9 Procedures
9.1 Test environment
Unless otherwise specified, the flexing test is carried out under the conditions described
in Chapter 8.
9.2 Flexing conditions
9.2.1 Condition A
9.2.1.1 Setting of flexing tester
Set the flexing tester to maximum stroke. This setting gives the first 90mm of travel a
440° rotational movement. Then it is a 65mm horizontal linear motion. The frequency
is 45 cycles/min. With this setting, when the moving shaft is at the initial position, the
distance between the moving shaft and the end face of the fixed shaft is 180mm. When
the moving shaft moves to the shortest distance, the end face is 25mm away from the
fixed shaft.
9.2.1.2 Flexing test
Attach the flexible barrier samples that have been taped with double-sided pressure
sensitive tape to the two shafts of the flexing tester. Or directly fix the sample on the
testing machine. Turn on the flexing tester. Flex the sample for 1h at 45 cycles/min (that
is, a total of 2700 cycles).
9.2.2 Condition B
The test conditions are the same as Condition A. The samples are flexed for 20min at
45 cycles/min. (that is, a total of 900 cycles under full flexing and swirling action).
9.2.3 Condition C
The test conditions are the same as Condition A. The samples are flexed for 6min at 45
cycles/min. (that is, a total of 270 cycles under full flexing and swirling action).
9.2.4 Condition D
The test conditions are the same as Condition A. The samples are flexed for 20 times at
45 cycles/min. (that is, a total of 20 cycles under full flexing and swirling action).
9.2.5 Condition E
Set the flexing tester to the partial flexing described in 6.1. At this time, set the moving
shaft so that the moving shaft only moves 80mm of the 180mm distance (the maximum
distance between the two shafts or the initial position). Therefore, only about 90% of
the swivel travel is used, giving a swiv...
Share