1
/
su
12
PayPal, credit cards. Download editable-PDF & invoice in 1 second!
YY/T 0987.2-2016 English PDF (YYT0987.2-2016)
YY/T 0987.2-2016 English PDF (YYT0987.2-2016)
Prezzo di listino
$140.00 USD
Prezzo di listino
Prezzo scontato
$140.00 USD
Prezzo unitario
/
per
Spese di spedizione calcolate al check-out.
Impossibile caricare la disponibilità di ritiro
Delivery: 3 seconds. Download true-PDF + Invoice.
Get QUOTATION in 1-minute: Click YY/T 0987.2-2016
Historical versions: YY/T 0987.2-2016
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll if blank)
YY/T 0987.2-2016: Implants for surgery--Magnetic resonance compatibility--Part 2: Magnetically induced displacement force test method
YY/T 0987.2-2016
YY
PHARMACEUTICAL INDUSTRY STANDARD
OF THE PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 11.040.40
C 35
Implants for Surgery - Magnetic Resonance
Compatibility - Part 2. Magnetically Induced
Displacement Force Test Method
外科植入物 磁共振兼容性
ISSUED ON. MARCH 23, 2016
IMPLEMENTED ON. JANUARY 1, 2017
Issued by. China Food and Drug Administration
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
1 Scope ... 5
2 Normative References ... 5
3 Terms and Definitions ... 6
4 Overview of Test Method ... 8
5 Significance and Application ... 8
6 Instruments and Equipment ... 9
7 Test Sample ... 9
8 Procedures ... 9
9 Data Processing ... 11
10 Report ... 11
Appendix A (Informative) Fundamental Principle ... 13
Bibliography ... 16
Implants for Surgery - Magnetic Resonance
Compatibility - Part 2. Magnetically Induced
Displacement Force Test Method
1 Scope
This Part of YY/T 0987 includes test method for magnetically induced displacement
force generated by medical devices as a result of static gradient magnetic field; a
comparison of magnetically induced displacement force and the weight of medical
devices.
This Part does not involve other possible safety questions. These safety questions
include, but are not limited to, magnetically induced torque, radio frequency heating
and radio frequency induced heating, noise, interaction among medical devices,
functions of medical devices and magnetic resonance system.
This Part is applicable to devices that can be hanged through wires. This Part is not
applicable to devices that cannot be hanged through wires. During the test, the weight
of wires used to hang devices shall be less than 1% of the weight of devices being
tested.
The test in this Part shall be conducted in a system, in which, the direction of
magnetically induced displacement force is horizontal.
This Part adopts numerical value under international system of units as the standard;
numerical value in the brackets shall merely be considered as reference.
This Part does not attempt to elaborate all the involved safety questions, even though
those safety questions are related with the usage. Determining appropriate safety and
health specifications and clarifying the applicability of management limit before
application is the responsibility on the users of this Standard.
2 Normative References
The following documents are indispensable to the application of this Standard. In terms
of references with a specified date, only versions with a specified date are applicable
to this Standard. The latest version (including all the modifications) of references
without a specified date is also applicable to this Standard.
YY/T 0987.1 Implants for Surgery - Magnetic Resonance Compatibility - Part 1.
Safety Marking
Magnetic resonance environment refers to the space within 0.5 mT (5G) line in MR
system, including the whole three-dimensional space around MR scanner. When 0.5
mT line is included in Faraday cage, the whole space shall be deemed as magnetic
resonance (MR) environment.
3.7 Magnetic Resonance Equipment
MR Equipment
Magnetic resonance equipment refers to medical electrical equipment that is expected
to be applied to in vivo magnetic resonance examination. Magnetic resonance
equipment includes all hardware and software parts from main power to display
monitor. Magnetic resonance equipment is programmable electrical medical system
(PEMS).
3.8 Magnetic Resonance System
MR System
Magnetic resonance system refers to the combination of magnetic resonance
equipment, accessories (including display, control and energy supply devices) and
controlled entry zone (if provided).
3.9 Magnetic Resonance Examination
MR Examination
Magnetic resonance examination refers to the process of gathering patients’ data
through magnetic resonance.
3.10 Magnetic Resonance; MR
Magnetic resonance refers to atomic particle swarm’s resonance absorption of
electromagnetic field energy in the magnetic field.
3.11 Medical Device
Manufacturer’s expected purposes for medical devices used on human beings, either
independent application or combined application, are as follows (any instruments,
equipment, appliances, materials or other items, including software if necessary).
---Diagnosis, prevention, monitoring, treatment or remission of diseases;
---Diagnosis, monitoring, treatment, remission or compensation of disabilities;
---Study, replacement or adjustment of anatomical or physiological process.
The primary expected effect on body surface and in vivo is not obtained through the
means of pharmacology, immunology or metabolism. However, these means might be
larger static magnetic field gradient is also less than 45°.
This test is insufficient to prove medical devices’ safety in magnetic resonance
environment.
6 Instruments and Equipment
Test device includes a solid non-magnetic bracket, which can hang medical devices to
be tested and do not generate displacement; a protractor (division value. 1°), which is
firmly installed on the bracket. The protractor’s 0° calibration tail is in the vertical
direction; medical device to be tested is hanged on a wire that is connected with the
protractor’s 0° calibration tail. In order to make the weight of the wire neglectable in
comparison with the medical device to be tested, the weight of the wire shall not
exceed 1% of the weight of the medical device. The wire shall be sufficiently long, so
that the medical device can be hanged onto the test device and naturally droop. The
movement of the wire shall not be restricted by the bracket or the protractor; the
hanged wire can be connected to any appropriate location of the medical device.
7 Test Sample
Medical devices which are evaluated in accordance with the test method in this Part
shall be representative finished products that have received final treatment (for
example, sterilization).
Before the test, medical devices to be tested shall not have any form of change.
8 Procedures
Any magnetic items that can generate large gradient horizontal magnetic field are
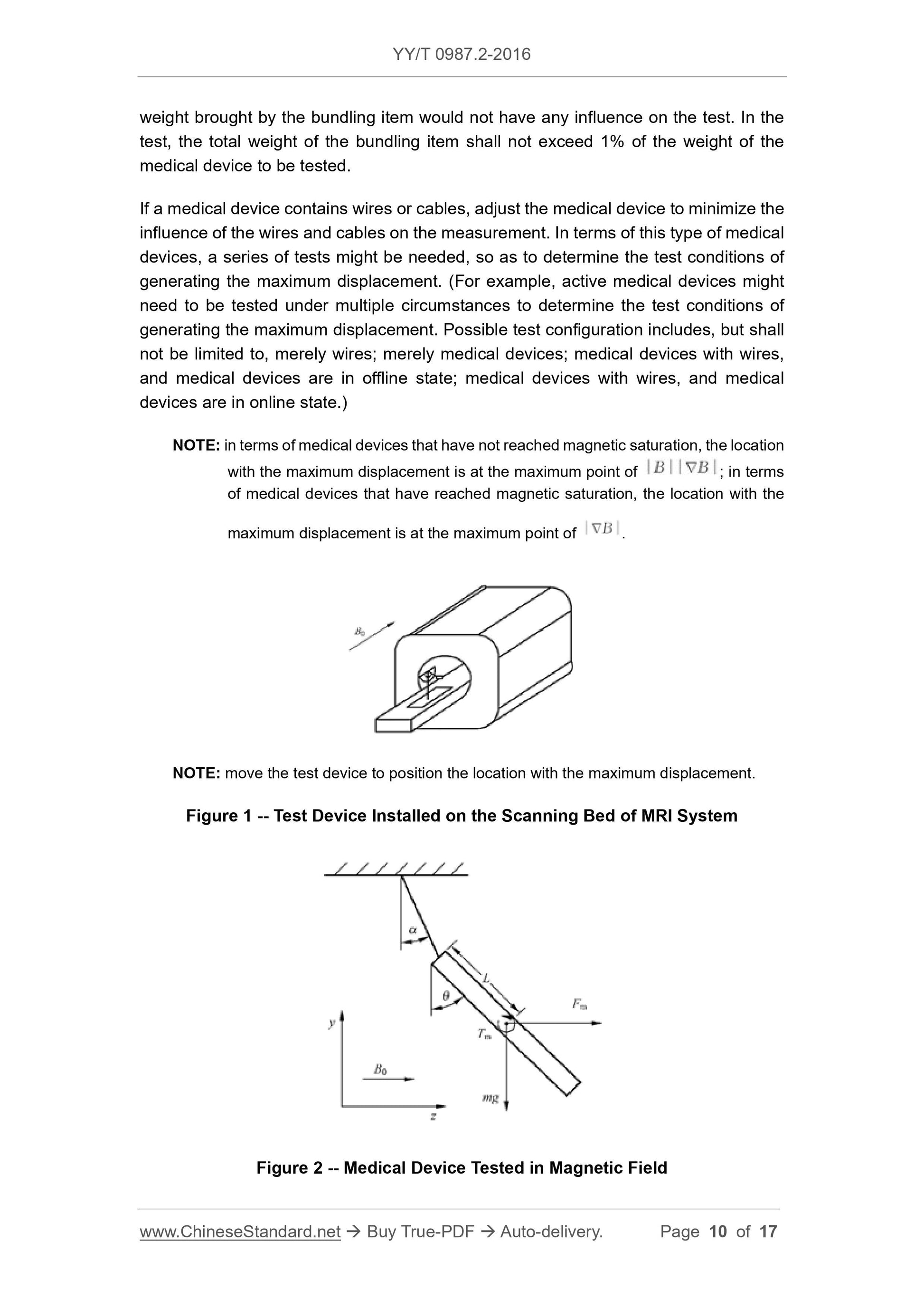
applicable to this test. Figure 1 illustrates the test device installed on the scanning bed
of MRI system. The medical device to be tested shall be hanged through a wire; the
hanged wire shall coincide with the protractor’s 0° calibration tail. Adjust the location of
the test device, so that the centroid of the medical device is at the point with the
maximum displacement (refer to NOTE). Mark the location with the maximum
displacement. All tests shall be repeatedly conducted in the same location. Grasp the
medical device; maintain the hanged wire in the vertical direction; then, release the
medical device. Record the medical device’s displacement angle from the vertical
location to the nearest 1° location (refer to Figure 2).
Repeat the above procedures. Test each sample for at least 3 times.
In order to place a medical device mostly at the point with the maximum displacement
angle, the medical device shall be bundled. If there is a medical device that uses
bundling item (for example, adhesive tape) in a test, it shall be proved that the extra
9 Data Processing
Use the absolute value of displacement angle measured in Chapter 8 to calculate
the average displacement angle. (The medical device being tested might not be
attracted by magnetic item but be repelled. Hence, in the calculation of the average
displacement angle, the absolute value of...
Get QUOTATION in 1-minute: Click YY/T 0987.2-2016
Historical versions: YY/T 0987.2-2016
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll if blank)
YY/T 0987.2-2016: Implants for surgery--Magnetic resonance compatibility--Part 2: Magnetically induced displacement force test method
YY/T 0987.2-2016
YY
PHARMACEUTICAL INDUSTRY STANDARD
OF THE PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 11.040.40
C 35
Implants for Surgery - Magnetic Resonance
Compatibility - Part 2. Magnetically Induced
Displacement Force Test Method
外科植入物 磁共振兼容性
ISSUED ON. MARCH 23, 2016
IMPLEMENTED ON. JANUARY 1, 2017
Issued by. China Food and Drug Administration
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
1 Scope ... 5
2 Normative References ... 5
3 Terms and Definitions ... 6
4 Overview of Test Method ... 8
5 Significance and Application ... 8
6 Instruments and Equipment ... 9
7 Test Sample ... 9
8 Procedures ... 9
9 Data Processing ... 11
10 Report ... 11
Appendix A (Informative) Fundamental Principle ... 13
Bibliography ... 16
Implants for Surgery - Magnetic Resonance
Compatibility - Part 2. Magnetically Induced
Displacement Force Test Method
1 Scope
This Part of YY/T 0987 includes test method for magnetically induced displacement
force generated by medical devices as a result of static gradient magnetic field; a
comparison of magnetically induced displacement force and the weight of medical
devices.
This Part does not involve other possible safety questions. These safety questions
include, but are not limited to, magnetically induced torque, radio frequency heating
and radio frequency induced heating, noise, interaction among medical devices,
functions of medical devices and magnetic resonance system.
This Part is applicable to devices that can be hanged through wires. This Part is not
applicable to devices that cannot be hanged through wires. During the test, the weight
of wires used to hang devices shall be less than 1% of the weight of devices being
tested.
The test in this Part shall be conducted in a system, in which, the direction of
magnetically induced displacement force is horizontal.
This Part adopts numerical value under international system of units as the standard;
numerical value in the brackets shall merely be considered as reference.
This Part does not attempt to elaborate all the involved safety questions, even though
those safety questions are related with the usage. Determining appropriate safety and
health specifications and clarifying the applicability of management limit before
application is the responsibility on the users of this Standard.
2 Normative References
The following documents are indispensable to the application of this Standard. In terms
of references with a specified date, only versions with a specified date are applicable
to this Standard. The latest version (including all the modifications) of references
without a specified date is also applicable to this Standard.
YY/T 0987.1 Implants for Surgery - Magnetic Resonance Compatibility - Part 1.
Safety Marking
Magnetic resonance environment refers to the space within 0.5 mT (5G) line in MR
system, including the whole three-dimensional space around MR scanner. When 0.5
mT line is included in Faraday cage, the whole space shall be deemed as magnetic
resonance (MR) environment.
3.7 Magnetic Resonance Equipment
MR Equipment
Magnetic resonance equipment refers to medical electrical equipment that is expected
to be applied to in vivo magnetic resonance examination. Magnetic resonance
equipment includes all hardware and software parts from main power to display
monitor. Magnetic resonance equipment is programmable electrical medical system
(PEMS).
3.8 Magnetic Resonance System
MR System
Magnetic resonance system refers to the combination of magnetic resonance
equipment, accessories (including display, control and energy supply devices) and
controlled entry zone (if provided).
3.9 Magnetic Resonance Examination
MR Examination
Magnetic resonance examination refers to the process of gathering patients’ data
through magnetic resonance.
3.10 Magnetic Resonance; MR
Magnetic resonance refers to atomic particle swarm’s resonance absorption of
electromagnetic field energy in the magnetic field.
3.11 Medical Device
Manufacturer’s expected purposes for medical devices used on human beings, either
independent application or combined application, are as follows (any instruments,
equipment, appliances, materials or other items, including software if necessary).
---Diagnosis, prevention, monitoring, treatment or remission of diseases;
---Diagnosis, monitoring, treatment, remission or compensation of disabilities;
---Study, replacement or adjustment of anatomical or physiological process.
The primary expected effect on body surface and in vivo is not obtained through the
means of pharmacology, immunology or metabolism. However, these means might be
larger static magnetic field gradient is also less than 45°.
This test is insufficient to prove medical devices’ safety in magnetic resonance
environment.
6 Instruments and Equipment
Test device includes a solid non-magnetic bracket, which can hang medical devices to
be tested and do not generate displacement; a protractor (division value. 1°), which is
firmly installed on the bracket. The protractor’s 0° calibration tail is in the vertical
direction; medical device to be tested is hanged on a wire that is connected with the
protractor’s 0° calibration tail. In order to make the weight of the wire neglectable in
comparison with the medical device to be tested, the weight of the wire shall not
exceed 1% of the weight of the medical device. The wire shall be sufficiently long, so
that the medical device can be hanged onto the test device and naturally droop. The
movement of the wire shall not be restricted by the bracket or the protractor; the
hanged wire can be connected to any appropriate location of the medical device.
7 Test Sample
Medical devices which are evaluated in accordance with the test method in this Part
shall be representative finished products that have received final treatment (for
example, sterilization).
Before the test, medical devices to be tested shall not have any form of change.
8 Procedures
Any magnetic items that can generate large gradient horizontal magnetic field are
applicable to this test. Figure 1 illustrates the test device installed on the scanning bed
of MRI system. The medical device to be tested shall be hanged through a wire; the
hanged wire shall coincide with the protractor’s 0° calibration tail. Adjust the location of
the test device, so that the centroid of the medical device is at the point with the
maximum displacement (refer to NOTE). Mark the location with the maximum
displacement. All tests shall be repeatedly conducted in the same location. Grasp the
medical device; maintain the hanged wire in the vertical direction; then, release the
medical device. Record the medical device’s displacement angle from the vertical
location to the nearest 1° location (refer to Figure 2).
Repeat the above procedures. Test each sample for at least 3 times.
In order to place a medical device mostly at the point with the maximum displacement
angle, the medical device shall be bundled. If there is a medical device that uses
bundling item (for example, adhesive tape) in a test, it shall be proved that the extra
9 Data Processing
Use the absolute value of displacement angle measured in Chapter 8 to calculate
the average displacement angle. (The medical device being tested might not be
attracted by magnetic item but be repelled. Hence, in the calculation of the average
displacement angle, the absolute value of...
Share