1
/
of
11
PayPal, credit cards. Download editable-PDF & invoice in 1 second!
GB 16796-2009 English PDF (GB16796-2009)
GB 16796-2009 English PDF (GB16796-2009)
Regular price
$140.00 USD
Regular price
Sale price
$140.00 USD
Unit price
/
per
Shipping calculated at checkout.
Couldn't load pickup availability
Delivery: 3 seconds. Download true-PDF + Invoice.Newer version: (Replacing this standard) GB 16796-2022
Get QUOTATION in 1-minute: Click GB 16796-2009
Historical versions: GB 16796-2009
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll if blank)
GB 16796-2009: Safety requirements and test methods for security alarm equipment
GB 16796-2009
GB
NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE
PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 13.310
A 91
Replacing GB 16796-1997
Safety requirements and test methods for
security alarm equipment
ISSUED ON. SEPTEMBER 30, 2009
IMPLEMENTED ON. JUNE 1, 2010
Issued by. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and
Quarantine of the People's Republic of China;
Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of
China.
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
1 Scope ... 5
2 Normative references ... 5
3 Terms and definitions ... 6
4 Test conditions ... 8
5 Technical requirements and test methods ... 10
Annex A ... 22
Annex B ... 23
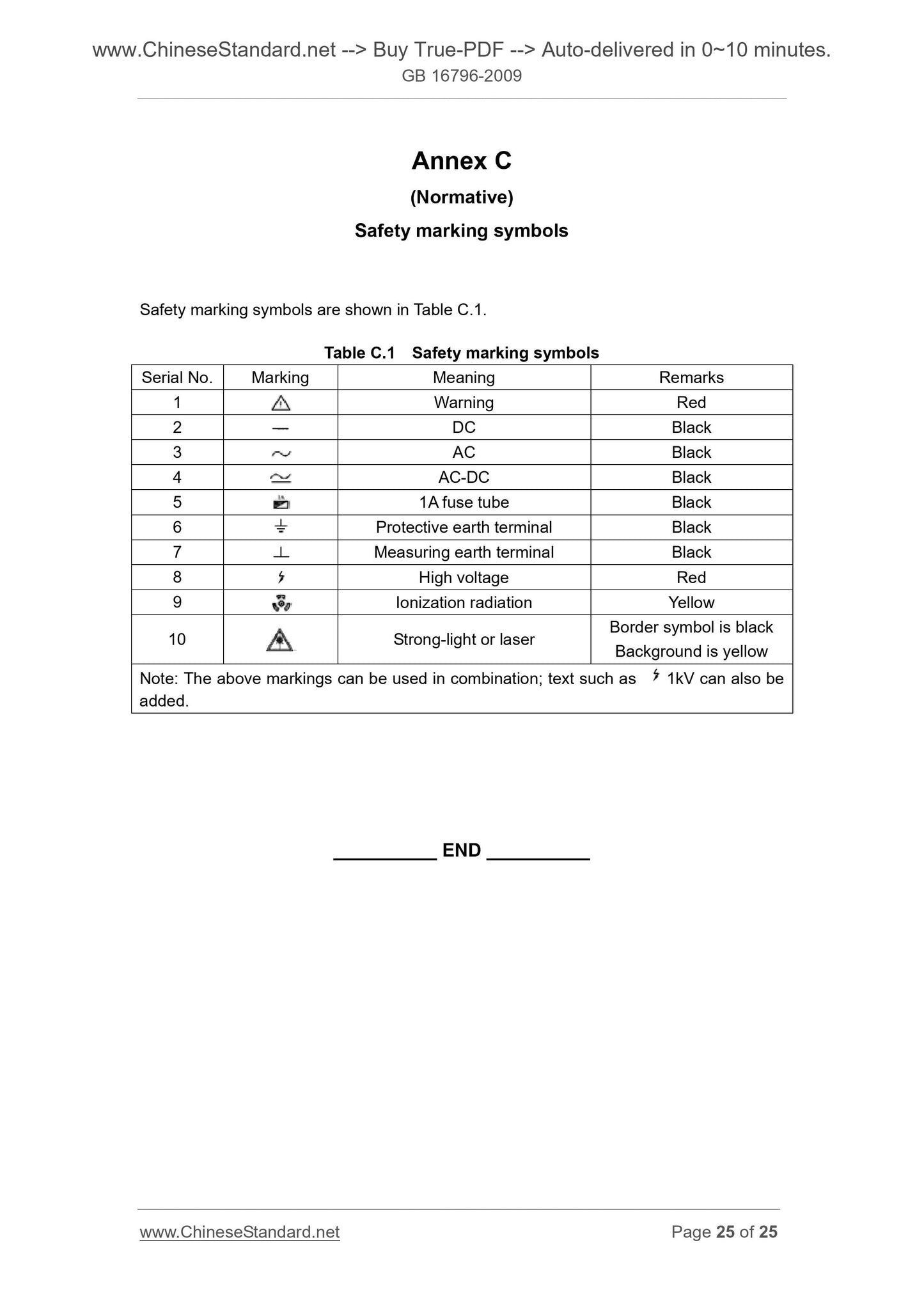
Annex C ... 25
Foreword
All the technical contents in this Standard are mandatory.
This Standard replaces GB 16796-1997 Safety Requirements and Test Methods for
Security Alarm Equipment.
Main differences between this Standard and GB 16796-1997 are as follows.
- Added the general test conditions;
- Added the temperature rise and ignition technical requirements for the device under
fault conditions;
- Added the technical requirements for the anti-acoustic pressure;
- Added the technical requirements for the components, batteries, monitors and
displays;
- Modified the description of the accessible part;
- Modified the technical requirements and measurement methods of the creepage
distance and the electric clearance;
- Modified the technical requirements and test methods of lightning protection;
- Modified the technical requirements of the power cord;
- Modified the technical requirements of the contact resistance;
- Modified the technical requirements of the anti-laser radiation;
- Modified the technical requirements of the anti-ionization radiation;
- Modified the technical requirements of the anti-microwave radiation;
- Modified the technical requirements of the anti-ultrasonic pressure.
Annex A, Annex B and Annex C of this Standard are normative.
This Standard was proposed by the Ministry of Public Security of the People’s Republic of
China.
This Standard shall be under the jurisdiction of Standardization Technical Committee for
Security and Protection Alarm Systems of China (SAC/TC 100).
Safety requirements and test methods for
security alarm equipment
1 Scope
This Standard specifies the basic safety technical requirements, test methods and
inspection rules which shall be followed by security alarm equipment in the areas such as
marking, anti-electric shock, anti-lightning, anti-overheating, anti-implosion and burst inside,
anti-laser radiation, anti-ionization radiation, anti-microwave radiation, anti-ultrasonic
pressure and mechanical safety. It is the fundamental basis of safety requirements for the
design, manufacture, installation, use, inspection, and formulating all kinds of security
alarm equipment.
This Standard applies to a various security alarm equipment.
2 Normative references
The articles contained in the following documents have become part of this Standard
when they are quoted herein. For the dated documents so quoted, all the modifications
(excluding corrections) or revisions made thereafter shall not be applicable to this
Standard. For the undated documents so quoted, the latest editions shall be applicable to
this Standard.
GB 4208-2008 Degrees of protection provided by enclosure (IP code) (IEC
60529.2001, IDT)
GB 4793.1-2007 Safety requirements for electrical equipment for measurement,
control, and laboratory use - Part 1. General requirements (IEC 61010-1.2001, IDT)
GB 4943-2001 Safety of information technology equipment (idt IEC 60950-1.1999)
GB 7247.1-2001 Safety of laser products - Part 1. Equipment classification,
requirements and users guide (idt IEC 60825-1.1993)
GB 8898-2001 Audio, video and similar electronic apparatus - Safety requirements
(eqv IEC 60065.1998)
GB/T 17626.5-2008 Electromagnetic compatibility - Testing and measurement
techniques - Surge immunity test (IEC 61000-4-5.2005, IDT)
3 Terms and definitions
For the purpose of this Standard, the following terms and definitions shall apply.
3.1
Accessible part
The places, after the product is installed properly, where are accessible by using
articulated test-finger (see Annex A).
3.2
Basic insulation
The insulation added by the dangerous charged components to provide basic protection
against electric shock.
[See 2.6.3 of GB 8898-2001]
3.3
Supplementary insulation
The independent insulation that is used except the basic insulation, so as to provide
protection against electric shock in the event of the failure of the basic insulation.
[See 2.6.5 of GB 8898-2001]
3.4
Reinforced insulation
The single insulation that is added for dangerous charged components; the anti-electric
shock grade is equivalent to double insulation.
[See 2.6.6 of GB 8898-2001]
3.5
Double insulation
Insulation that has simultaneously both the basic insulation and supplementary insulation.
[See 2.6.4 of GB 8898-2001]
3.6
[See 3.4.2 of GB 7247.1-2001]
3.13
Accessible emission limit
The allowable maximum emission limits within the specified category.
[See 3.16 of GB 7247.1-2001]
3.14
Irradiance
The quotient OF the radiation flux d reflected on the surface-element at a point of the
surface AND the area dA of that surface-element.
Symbols. E=d/dA Measurement unit. W/m2 (W∙m-2)
[See 3.35 of GB 7247.1-2001]
3.15
Ionization radiation
A kind of radiation that is generated by sufficient energy to make the electrons leave the
atom.
3.16
Microwave radiation
It generally refers to the radiation with the wavelength range of 1mm~30cm.
3.17
Exceed sound press
The sound intensity of which the frequency range is 20 kHz~100 kHz.
4 Test conditions
4.1 Test guidelines
4.1.1 If a test specified in this Standard may be destructive, then a model prototype
which can stand for the evaluated state is allowed to use.
4.3 Fault conditions
According to the structure and schematic diagram of the equipment, determine the fault
conditions that may easily cause damages. According to the most convenient principle,
when exerting the following fault conditions successively, it shall not damage the
equipment, cause fire or electric shock.
a) Reversed polarity of power supply;
b) Short circuit of output end;
c) Hand-touching input end;
d) The leads connected wrongly (except for the leads can not be connected wrongly
by structural constraints);
e) Stop the forced cooling of the fan;
f) Secondary winding transformer is short circuit; short circuit of primary winding and
secondary winding, short circuit of each winding with core and shield if there exists
any core and shield;
g) The two poles of the capacitor are shorted; if there is enclosure, each pole is
shorted to the metal enclosure;
h) In above test, if there is fault display, the test is 2min; if there is no fault display, the
test is 4h; during the test, it shall not damage the equipment or cause a fire or
electric shock.
Note. If fuse is disconnected or can not operate properly, then it is deemed as fault
display.
5 Technical requirements and test methods
5.1 Equipment safety classification
According to different anti-electric shock protective measures provided by the equipment,
the equipment can be divided into three classes.
Class I equipment. anti-electric shock does not only rely on ba...
Get QUOTATION in 1-minute: Click GB 16796-2009
Historical versions: GB 16796-2009
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll if blank)
GB 16796-2009: Safety requirements and test methods for security alarm equipment
GB 16796-2009
GB
NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE
PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 13.310
A 91
Replacing GB 16796-1997
Safety requirements and test methods for
security alarm equipment
ISSUED ON. SEPTEMBER 30, 2009
IMPLEMENTED ON. JUNE 1, 2010
Issued by. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and
Quarantine of the People's Republic of China;
Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of
China.
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
1 Scope ... 5
2 Normative references ... 5
3 Terms and definitions ... 6
4 Test conditions ... 8
5 Technical requirements and test methods ... 10
Annex A ... 22
Annex B ... 23
Annex C ... 25
Foreword
All the technical contents in this Standard are mandatory.
This Standard replaces GB 16796-1997 Safety Requirements and Test Methods for
Security Alarm Equipment.
Main differences between this Standard and GB 16796-1997 are as follows.
- Added the general test conditions;
- Added the temperature rise and ignition technical requirements for the device under
fault conditions;
- Added the technical requirements for the anti-acoustic pressure;
- Added the technical requirements for the components, batteries, monitors and
displays;
- Modified the description of the accessible part;
- Modified the technical requirements and measurement methods of the creepage
distance and the electric clearance;
- Modified the technical requirements and test methods of lightning protection;
- Modified the technical requirements of the power cord;
- Modified the technical requirements of the contact resistance;
- Modified the technical requirements of the anti-laser radiation;
- Modified the technical requirements of the anti-ionization radiation;
- Modified the technical requirements of the anti-microwave radiation;
- Modified the technical requirements of the anti-ultrasonic pressure.
Annex A, Annex B and Annex C of this Standard are normative.
This Standard was proposed by the Ministry of Public Security of the People’s Republic of
China.
This Standard shall be under the jurisdiction of Standardization Technical Committee for
Security and Protection Alarm Systems of China (SAC/TC 100).
Safety requirements and test methods for
security alarm equipment
1 Scope
This Standard specifies the basic safety technical requirements, test methods and
inspection rules which shall be followed by security alarm equipment in the areas such as
marking, anti-electric shock, anti-lightning, anti-overheating, anti-implosion and burst inside,
anti-laser radiation, anti-ionization radiation, anti-microwave radiation, anti-ultrasonic
pressure and mechanical safety. It is the fundamental basis of safety requirements for the
design, manufacture, installation, use, inspection, and formulating all kinds of security
alarm equipment.
This Standard applies to a various security alarm equipment.
2 Normative references
The articles contained in the following documents have become part of this Standard
when they are quoted herein. For the dated documents so quoted, all the modifications
(excluding corrections) or revisions made thereafter shall not be applicable to this
Standard. For the undated documents so quoted, the latest editions shall be applicable to
this Standard.
GB 4208-2008 Degrees of protection provided by enclosure (IP code) (IEC
60529.2001, IDT)
GB 4793.1-2007 Safety requirements for electrical equipment for measurement,
control, and laboratory use - Part 1. General requirements (IEC 61010-1.2001, IDT)
GB 4943-2001 Safety of information technology equipment (idt IEC 60950-1.1999)
GB 7247.1-2001 Safety of laser products - Part 1. Equipment classification,
requirements and users guide (idt IEC 60825-1.1993)
GB 8898-2001 Audio, video and similar electronic apparatus - Safety requirements
(eqv IEC 60065.1998)
GB/T 17626.5-2008 Electromagnetic compatibility - Testing and measurement
techniques - Surge immunity test (IEC 61000-4-5.2005, IDT)
3 Terms and definitions
For the purpose of this Standard, the following terms and definitions shall apply.
3.1
Accessible part
The places, after the product is installed properly, where are accessible by using
articulated test-finger (see Annex A).
3.2
Basic insulation
The insulation added by the dangerous charged components to provide basic protection
against electric shock.
[See 2.6.3 of GB 8898-2001]
3.3
Supplementary insulation
The independent insulation that is used except the basic insulation, so as to provide
protection against electric shock in the event of the failure of the basic insulation.
[See 2.6.5 of GB 8898-2001]
3.4
Reinforced insulation
The single insulation that is added for dangerous charged components; the anti-electric
shock grade is equivalent to double insulation.
[See 2.6.6 of GB 8898-2001]
3.5
Double insulation
Insulation that has simultaneously both the basic insulation and supplementary insulation.
[See 2.6.4 of GB 8898-2001]
3.6
[See 3.4.2 of GB 7247.1-2001]
3.13
Accessible emission limit
The allowable maximum emission limits within the specified category.
[See 3.16 of GB 7247.1-2001]
3.14
Irradiance
The quotient OF the radiation flux d reflected on the surface-element at a point of the
surface AND the area dA of that surface-element.
Symbols. E=d/dA Measurement unit. W/m2 (W∙m-2)
[See 3.35 of GB 7247.1-2001]
3.15
Ionization radiation
A kind of radiation that is generated by sufficient energy to make the electrons leave the
atom.
3.16
Microwave radiation
It generally refers to the radiation with the wavelength range of 1mm~30cm.
3.17
Exceed sound press
The sound intensity of which the frequency range is 20 kHz~100 kHz.
4 Test conditions
4.1 Test guidelines
4.1.1 If a test specified in this Standard may be destructive, then a model prototype
which can stand for the evaluated state is allowed to use.
4.3 Fault conditions
According to the structure and schematic diagram of the equipment, determine the fault
conditions that may easily cause damages. According to the most convenient principle,
when exerting the following fault conditions successively, it shall not damage the
equipment, cause fire or electric shock.
a) Reversed polarity of power supply;
b) Short circuit of output end;
c) Hand-touching input end;
d) The leads connected wrongly (except for the leads can not be connected wrongly
by structural constraints);
e) Stop the forced cooling of the fan;
f) Secondary winding transformer is short circuit; short circuit of primary winding and
secondary winding, short circuit of each winding with core and shield if there exists
any core and shield;
g) The two poles of the capacitor are shorted; if there is enclosure, each pole is
shorted to the metal enclosure;
h) In above test, if there is fault display, the test is 2min; if there is no fault display, the
test is 4h; during the test, it shall not damage the equipment or cause a fire or
electric shock.
Note. If fuse is disconnected or can not operate properly, then it is deemed as fault
display.
5 Technical requirements and test methods
5.1 Equipment safety classification
According to different anti-electric shock protective measures provided by the equipment,
the equipment can be divided into three classes.
Class I equipment. anti-electric shock does not only rely on ba...
Share