1
/
of
7
PayPal, credit cards. Download editable-PDF & invoice In 1 second!
GB 1903.53-2021 English PDF (GB1903.53-2021)
GB 1903.53-2021 English PDF (GB1903.53-2021)
Regular price
$170.00 USD
Regular price
Sale price
$170.00 USD
Unit price
/
per
Shipping calculated at checkout.
Couldn't load pickup availability
Delivery: 3 seconds. Download true-PDF + Invoice.
Get QUOTATION in 1-minute: Click GB 1903.53-2021
Historical versions: GB 1903.53-2021
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll if blank)
GB 1903.53-2021: National Food Safety Standard - Food Nutrient Fortifier - D-calcium pantothenate
GB 1903.53-2021
GB
NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE
PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
National Food Safety Standard - Food Nutrient
Fortifier - D-calcium pantothenate
ISSUED ON: SEPTEMBER 07, 2021
IMPLEMENTED ON: MARCH 07, 2022
Issued by: National Health Commission of the People's Republic of
China;
State Administration for Market Regulation.
Table of Contents
1 Scope ... 3
2 Chemical name, molecular formula, structural formula and relative molecular
mass ... 3
3 Technical requirements ... 3
Appendix A Inspection methods ... 5
Appendix B Infrared spectrum of D-calcium pantothenate standard ... 13
Appendix C Chromatogram ... 14
National Food Safety Standard - Food Nutrient
Fortifier - D-calcium pantothenate
1 Scope
This Standard applies to the food nutrient fortifier D-calcium pantothenate,
which is obtained by acylation reaction of β-alanine calcium and D-pantoate
lactone.
2 Chemical name, molecular formula, structural
formula and relative molecular mass
2.1 Chemical name
D-(+)-N-(2,4-dihydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutyryl)-β-alanine calcium
2.2 Molecular formula
C18H32CaN2O10
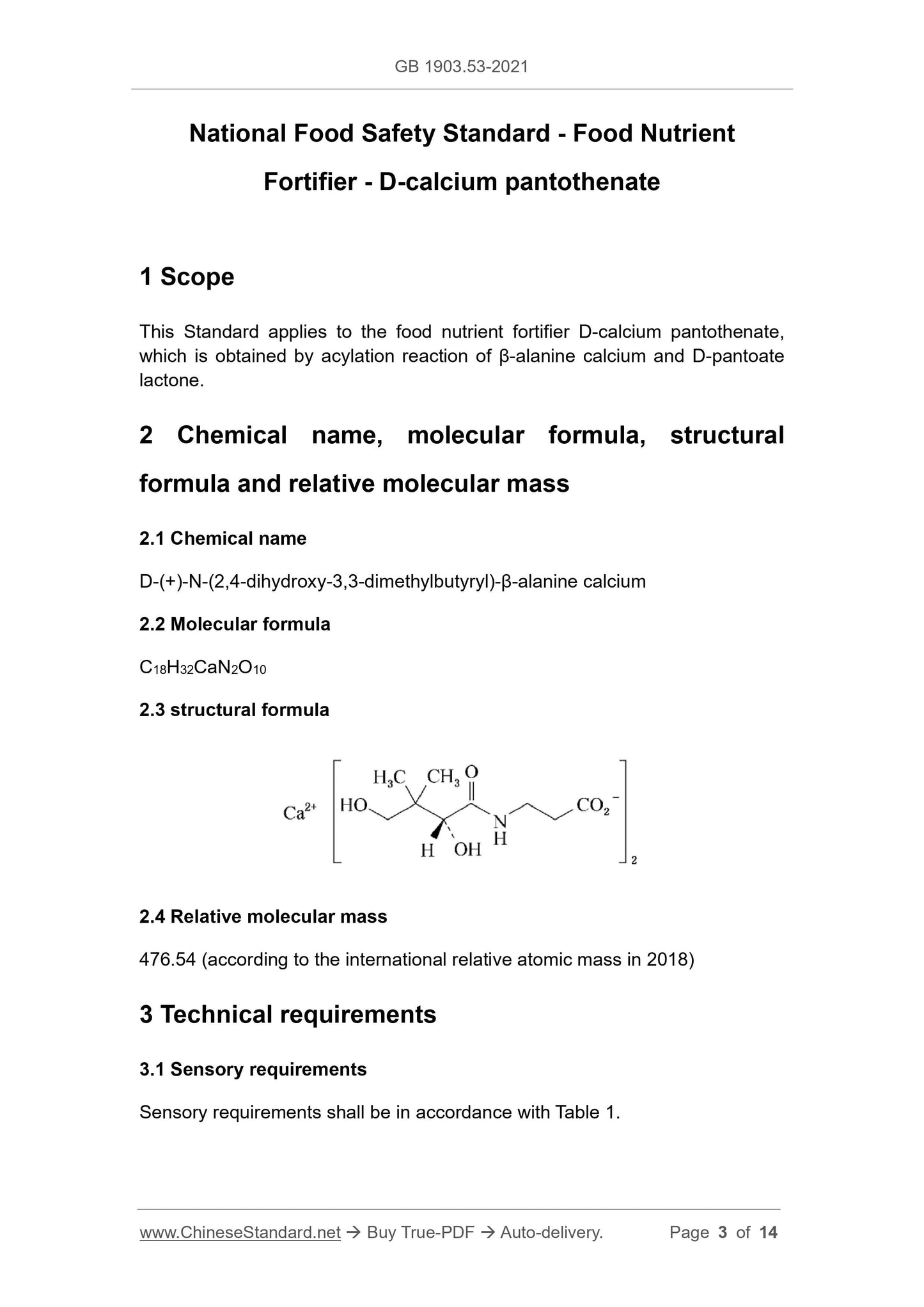
2.3 structural formula
2.4 Relative molecular mass
476.54 (according to the international relative atomic mass in 2018)
3 Technical requirements
3.1 Sensory requirements
Sensory requirements shall be in accordance with Table 1.
Appendix A
Inspection methods
A.1 General provisions
The reagents and water used in this Standard refer to analytical reagents and
grade-3 water that is specified in GB/T 6682, when other requirements are not
indicated. The standard solution, the standard solutions, preparations and
products for impurity determination, which are used in the test, are all prepared
in accordance with the provisions of GB/T 601, GB/T 602, and GB/T 603, when
no other requirements are specified. The solution used in the test, if not
indicated which solvent is used, refers to aqueous solution.
A.2 Identification test
A.2.1 Reagents and materials
A.2.1.1 Sodium hydroxide solution: 43 g/L.
A.2.1.2 Copper sulfate solution: 125 g/L.
A.2.1.3 Phenolphthalein indicator solution: 10 g/L.
A.2.1.4 Hydrochloric acid solution: c(HCl) = 1 mol/L.
A.2.1.5 Ferric trichloride solution: 90 g/L.
A.2.1.6 Ammonium oxalate solution: 35 g/L.
A.2.1.7 Glacial acetic acid.
A.2.1.8 Hydrochloric acid.
A.2.1.9 Potassium bromide: spectrally pure, dry product.
A.2.2 Identification method
A.2.2.1 Weigh about 50 mg of the sample; add 5 mL of sodium hydroxide
solution (A.2.1.1); shake; add 2 drops of copper sulfate solution (A.2.1.2), and
it appears blue-purple.
A.2.2.2 Weigh about 50 mg of the sample; add 5 mL of sodium hydroxide
solution (A.2.1.1); shake; boil for 1 min; let cool; add 1 drop of phenolphthalein
indicator solution (A.2.1.3); add hydrochloric acid solution (A.2.1.4) until the
solution fades; then, add another 0.5 mL of hydrochloric acid solution (A.2.1.4);
add 2 drops of ferric trichloride solution (A.2.1.5), and it appears bright yellow.
A.2.2.3 The identification reaction of the calcium salt in the aqueous solution of
this product: Weigh 0.5 g of the sample; add 5 mL of water to dissolve; add
ammonium oxalate solution (A.2.1.6), and a white precipitate appears; the
precipitate is insoluble in glacial acetic acid; but it is soluble in hydrochloric acid.
A.2.2.4 Infrared spectroscopy: use potassium bromide pellet technique, to test
according to GB/T 6040. The infrared spectrum of the sample shall be
consistent with the infrared spectrum of the D-calcium pantothenate standard.
Refer to Figure B.1 in Appendix B for the standard infrared spectrum of D-
calcium pantothenate.
A.2.2.5 Clarity: Weigh about 1.00 g of the sample; add 20 mL of water to
dissolve; the solution is clear and colorless.
A.2.2.6 Solubility: easily soluble in water and glycerin; slightly soluble in ethanol;
insoluble in trichloromethane or ether.
A.3 Determination of D-calcium pantothenate content (on a dry basis)
A.3.1 Method summary
Use high performance liquid chromatography for determination, C18
chromatographic column for separation, UV detector for detection, and the peak
area external standard method to quantitatively calculate the content of D-
calcium pantothenate in the sample.
A.3.2 Reagents and materials
A.3.2.1 Acetonitrile: chromatographically pure.
A.3.2.2 Disodium hydrogen phosphate.
A.3.2.3 Sodium hydroxide solution: 43 g/L.
A.3.2.4 Sodium dihydrogen phosphate solution: Weigh 3.2 g of sodium
dihydrogen phosphate (A.3.2.2) into a 1 L volumetric flask; use water to dilute
to the mark; mix well. Use sodium hydroxide solution (A.3.2.3) to adjust pH to
5.5.
A.3.2.5 D-sodium pantoate (CAS: 60979-68-2): content ≥97.0%.
A.3.2.6 D-calcium pantothenate standard (CAS:137-08-6): content ≥99.0%.
A.3.3 Instruments and apparatuses
A.4.2.2 Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid standard titration solution: c(EDTA)
= 0.05 mol/L.
A.4.2.3 Calcium purpurin indicator: Take 0.1 g of calcium purpurin; add 10 g of
anhydrous sodium sulfate; grind evenly, to get it.
A.4.3 Analysis steps
Weigh 0.5 g of the sample (accurate to 0.000 1 g); add 100 mL of water to
dissolve; add 15 mL of sodium hydroxide solution (A.4.2.1) and about 0.1 g of
calcium purpurin indicator (A.4.2.3); use Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid
standard titration solution (A.4.2.2) to titrate, until the solution turns from purple
to pure-blue.
A.4.4 Calculation results
The mass fraction w2 of calcium content (on a dry basis) is calculated according
to Formula (A.2).
Where:
V2 – the volume of the Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid standard titration
solution that is consumed by the sample solution, in milliliters (mL);
c3 – the concentration of the Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid standard
titration solution, in moles per liter (mol/L);
M – the molar mass of calcium, in grams per mole (g/mol), M(Ca) = 40.08;
m2 – mass of the sample, in grams (g);
X3 – loss on drying of the sample, mass fraction, %.
Express the calculation result to one decimal place. The absolute difference of
two independent test results under repeatability cannot exceed 0.6% of the
arithmetic mean value.
A.5 Determination of specific rotation
A.5.1 Instruments and apparatuses
A.5.1.1 Polarimeter.
A.5.1.2 Polarimetry tube.
A.5.2 Analysis steps
potassium mercuric iodide test solution (A.7.1.2); leave it for 1 min; if there is
no turbidity, it means that it passes the test.
A.8 Determination of alkalinity
A.8.1 Reagents and materials
A.8.1.1 Hydrochloric acid solution: 0.1 mol/L.
A.8.1.2 Phenolphthalein indicator solution: 10 g/L.
A.8.2 Analysis steps
Weigh about 1.0 g of the sample (accurate to 0.01 g); add 20 mL of carbon
dioxide-free water to dissolve; immediately add 1 mL of hydrochloric acid
solution (A.8.1.1) and 0.05 mL of phenolphthalein indicator solution (A.8.1.2); if
there is no pink color within 5 s, the test is passed.
A.9 Determination of loss on drying
Weigh 2.0 g ~ 5.0 g of the sample (accurate to 0.000 1 g); the following
operations are the same as the Method 1 of GB 5009.3-2016.
A.10 Determination of chloride
A.10.1 Reagents and materials
A.10.1.1 Nitric acid
A.10.1.2 Hydrochloric acid standard titration solution: 0.001 4 mol/L.
A.10.1.3 Nitric acid solution: Take 105 mL of nitric acid (A.10.1.1); add water to
dilute to 1 000 mL; shake well.
A.10.1.4 Silver nitrate solution: 0.1 mol/L.
A....
Get QUOTATION in 1-minute: Click GB 1903.53-2021
Historical versions: GB 1903.53-2021
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll if blank)
GB 1903.53-2021: National Food Safety Standard - Food Nutrient Fortifier - D-calcium pantothenate
GB 1903.53-2021
GB
NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE
PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
National Food Safety Standard - Food Nutrient
Fortifier - D-calcium pantothenate
ISSUED ON: SEPTEMBER 07, 2021
IMPLEMENTED ON: MARCH 07, 2022
Issued by: National Health Commission of the People's Republic of
China;
State Administration for Market Regulation.
Table of Contents
1 Scope ... 3
2 Chemical name, molecular formula, structural formula and relative molecular
mass ... 3
3 Technical requirements ... 3
Appendix A Inspection methods ... 5
Appendix B Infrared spectrum of D-calcium pantothenate standard ... 13
Appendix C Chromatogram ... 14
National Food Safety Standard - Food Nutrient
Fortifier - D-calcium pantothenate
1 Scope
This Standard applies to the food nutrient fortifier D-calcium pantothenate,
which is obtained by acylation reaction of β-alanine calcium and D-pantoate
lactone.
2 Chemical name, molecular formula, structural
formula and relative molecular mass
2.1 Chemical name
D-(+)-N-(2,4-dihydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutyryl)-β-alanine calcium
2.2 Molecular formula
C18H32CaN2O10
2.3 structural formula
2.4 Relative molecular mass
476.54 (according to the international relative atomic mass in 2018)
3 Technical requirements
3.1 Sensory requirements
Sensory requirements shall be in accordance with Table 1.
Appendix A
Inspection methods
A.1 General provisions
The reagents and water used in this Standard refer to analytical reagents and
grade-3 water that is specified in GB/T 6682, when other requirements are not
indicated. The standard solution, the standard solutions, preparations and
products for impurity determination, which are used in the test, are all prepared
in accordance with the provisions of GB/T 601, GB/T 602, and GB/T 603, when
no other requirements are specified. The solution used in the test, if not
indicated which solvent is used, refers to aqueous solution.
A.2 Identification test
A.2.1 Reagents and materials
A.2.1.1 Sodium hydroxide solution: 43 g/L.
A.2.1.2 Copper sulfate solution: 125 g/L.
A.2.1.3 Phenolphthalein indicator solution: 10 g/L.
A.2.1.4 Hydrochloric acid solution: c(HCl) = 1 mol/L.
A.2.1.5 Ferric trichloride solution: 90 g/L.
A.2.1.6 Ammonium oxalate solution: 35 g/L.
A.2.1.7 Glacial acetic acid.
A.2.1.8 Hydrochloric acid.
A.2.1.9 Potassium bromide: spectrally pure, dry product.
A.2.2 Identification method
A.2.2.1 Weigh about 50 mg of the sample; add 5 mL of sodium hydroxide
solution (A.2.1.1); shake; add 2 drops of copper sulfate solution (A.2.1.2), and
it appears blue-purple.
A.2.2.2 Weigh about 50 mg of the sample; add 5 mL of sodium hydroxide
solution (A.2.1.1); shake; boil for 1 min; let cool; add 1 drop of phenolphthalein
indicator solution (A.2.1.3); add hydrochloric acid solution (A.2.1.4) until the
solution fades; then, add another 0.5 mL of hydrochloric acid solution (A.2.1.4);
add 2 drops of ferric trichloride solution (A.2.1.5), and it appears bright yellow.
A.2.2.3 The identification reaction of the calcium salt in the aqueous solution of
this product: Weigh 0.5 g of the sample; add 5 mL of water to dissolve; add
ammonium oxalate solution (A.2.1.6), and a white precipitate appears; the
precipitate is insoluble in glacial acetic acid; but it is soluble in hydrochloric acid.
A.2.2.4 Infrared spectroscopy: use potassium bromide pellet technique, to test
according to GB/T 6040. The infrared spectrum of the sample shall be
consistent with the infrared spectrum of the D-calcium pantothenate standard.
Refer to Figure B.1 in Appendix B for the standard infrared spectrum of D-
calcium pantothenate.
A.2.2.5 Clarity: Weigh about 1.00 g of the sample; add 20 mL of water to
dissolve; the solution is clear and colorless.
A.2.2.6 Solubility: easily soluble in water and glycerin; slightly soluble in ethanol;
insoluble in trichloromethane or ether.
A.3 Determination of D-calcium pantothenate content (on a dry basis)
A.3.1 Method summary
Use high performance liquid chromatography for determination, C18
chromatographic column for separation, UV detector for detection, and the peak
area external standard method to quantitatively calculate the content of D-
calcium pantothenate in the sample.
A.3.2 Reagents and materials
A.3.2.1 Acetonitrile: chromatographically pure.
A.3.2.2 Disodium hydrogen phosphate.
A.3.2.3 Sodium hydroxide solution: 43 g/L.
A.3.2.4 Sodium dihydrogen phosphate solution: Weigh 3.2 g of sodium
dihydrogen phosphate (A.3.2.2) into a 1 L volumetric flask; use water to dilute
to the mark; mix well. Use sodium hydroxide solution (A.3.2.3) to adjust pH to
5.5.
A.3.2.5 D-sodium pantoate (CAS: 60979-68-2): content ≥97.0%.
A.3.2.6 D-calcium pantothenate standard (CAS:137-08-6): content ≥99.0%.
A.3.3 Instruments and apparatuses
A.4.2.2 Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid standard titration solution: c(EDTA)
= 0.05 mol/L.
A.4.2.3 Calcium purpurin indicator: Take 0.1 g of calcium purpurin; add 10 g of
anhydrous sodium sulfate; grind evenly, to get it.
A.4.3 Analysis steps
Weigh 0.5 g of the sample (accurate to 0.000 1 g); add 100 mL of water to
dissolve; add 15 mL of sodium hydroxide solution (A.4.2.1) and about 0.1 g of
calcium purpurin indicator (A.4.2.3); use Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid
standard titration solution (A.4.2.2) to titrate, until the solution turns from purple
to pure-blue.
A.4.4 Calculation results
The mass fraction w2 of calcium content (on a dry basis) is calculated according
to Formula (A.2).
Where:
V2 – the volume of the Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid standard titration
solution that is consumed by the sample solution, in milliliters (mL);
c3 – the concentration of the Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid standard
titration solution, in moles per liter (mol/L);
M – the molar mass of calcium, in grams per mole (g/mol), M(Ca) = 40.08;
m2 – mass of the sample, in grams (g);
X3 – loss on drying of the sample, mass fraction, %.
Express the calculation result to one decimal place. The absolute difference of
two independent test results under repeatability cannot exceed 0.6% of the
arithmetic mean value.
A.5 Determination of specific rotation
A.5.1 Instruments and apparatuses
A.5.1.1 Polarimeter.
A.5.1.2 Polarimetry tube.
A.5.2 Analysis steps
potassium mercuric iodide test solution (A.7.1.2); leave it for 1 min; if there is
no turbidity, it means that it passes the test.
A.8 Determination of alkalinity
A.8.1 Reagents and materials
A.8.1.1 Hydrochloric acid solution: 0.1 mol/L.
A.8.1.2 Phenolphthalein indicator solution: 10 g/L.
A.8.2 Analysis steps
Weigh about 1.0 g of the sample (accurate to 0.01 g); add 20 mL of carbon
dioxide-free water to dissolve; immediately add 1 mL of hydrochloric acid
solution (A.8.1.1) and 0.05 mL of phenolphthalein indicator solution (A.8.1.2); if
there is no pink color within 5 s, the test is passed.
A.9 Determination of loss on drying
Weigh 2.0 g ~ 5.0 g of the sample (accurate to 0.000 1 g); the following
operations are the same as the Method 1 of GB 5009.3-2016.
A.10 Determination of chloride
A.10.1 Reagents and materials
A.10.1.1 Nitric acid
A.10.1.2 Hydrochloric acid standard titration solution: 0.001 4 mol/L.
A.10.1.3 Nitric acid solution: Take 105 mL of nitric acid (A.10.1.1); add water to
dilute to 1 000 mL; shake well.
A.10.1.4 Silver nitrate solution: 0.1 mol/L.
A....
Share