1
/
of
7
PayPal, credit cards. Download editable-PDF & invoice in 1 second!
GB/T 12361-2016 English PDF (GB/T12361-2016)
GB/T 12361-2016 English PDF (GB/T12361-2016)
Regular price
$125.00 USD
Regular price
Sale price
$125.00 USD
Unit price
/
per
Shipping calculated at checkout.
Couldn't load pickup availability
Delivery: 3 seconds. Download true-PDF + Invoice.
Get QUOTATION in 1-minute: Click GB/T 12361-2016
Historical versions: GB/T 12361-2016
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll if blank)
GB/T 12361-2016: Steel die forgings -- General specification
GB/T 12361-2016
GB
NATIONAL STANDARD
OF THE PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 77.140.85
J 32
Replacing GB/T 12361-2003
Steel Die Forgings – General Specification
ISSUED ON. DECEMBER 13, 2016
IMPLEMENTED ON. JULY 1, 2017
Issued by. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and
Quarantine of the People's Republic of China;
Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of
China.
3. No action is required - Full-copy of this standard will be automatically and
immediately delivered to your EMAIL address in 0~60 minutes.
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
1 Application Scope ... 5
2 Normative References ... 5
3 Terms and Definitions ... 6
4 Classification of Forgings ... 6
5 Specifications ... 7
6 Test Methods ... 9
7 Inspection Rules ... 10
8 Marking, Quality Certification, Packaging and Transportation ... 12
Annex A (Normative) Draft Angles and Fillet Radii of Forgings ... 14
Foreword
This Standard was drafted in accordance with the rules given in GB/T 1.1-2009.
This Standard replaces GB/T 12361-2003, General Specification of Steel Die Forgings.
Compared with GB/T 12361-2003, the major changes in addition to editorial
modifications are as follows.
-- “furnace (tank) number” is changed into “furnace number” (see 3.1; 3.1 of edition
2003);
-- “for the same production card” is deleted (3.3 of edition 2003);
-- standard GB/T 5216 for the steels selected for forgings is added (see 5.2.1);
-- “The steels selected shall be used in production only after they are qualified by
reinspection. The reinspection items shall be determined as specified in steel
inspection standards.” is changed into “Steels shall be re-inspected in
accordance with the inspection items determined by the supplier and the
purchaser.” (see 5.2.3; 5.2.3 of edition 2003);
-- “isothermal annealing” is changed into “isothermal normalizing”, and “controlled-
temperature cooling” is changed into “controlled cooling” [see 5.3.5.1 d), e);
5.3.5.1 d), e) of edition 2003];
-- “and when it is unable to take samples from forgings” is deleted (5.3.7.3);
-- “and when the supplier is able to satisfy” is deleted (5.4.1 of edition 2003);
-- “If the heat treatment furnace number and manufacture batch under the same
furnace number are required, the addition of the provisions such as strengthened
shot blasting may possibly be added” (5.4.2 of edition 2003);
-- “white patches” is deleted (7.4.1 of edition 2003);
-- “for the convenience of die manufacture, standard cutting tools are used” is
deleted (A.1.3 of edition 2003);
-- “But it is preferably not less than 3°” is deleted (A.1.4.1 of edition 2003).
This Standard was proposed by and shall be under the jurisdiction of the National
Technical Committee 74 on Forging and Pressing of Standardization Administration of
China (SAC/TC 74).
The drafting organizations of this Standard. Dongfeng Forging Co., Ltd., Beijing
Research Institute of Mechanical and Electrical Technology.
The main drafters of this Standard. Wu Yujian, Wu Tingsong, Wei Wei, Zhou Lin, Zhao
Yeqin, Chen Wenjing, Cheng Chenwen.
Steel Die Forgings – General Specification
1 Application Scope
This Standard specifies the classification, specifications, test methods, inspection rules,
marking, quality certification, packaging and transportation of steel die forgings
(hereinafter referred to as “forgings”).
This Standard applies to structural steel die forgings which are produced with forging-
press equipment such as forging hammer, hot die forging press, screw press and
horizontal forging machine. This Standard may also work as the reference for the
forgings of other steel types.
This Standard is the basis for product designer to determine the specifications of
forgings and the supplier and purchaser to sign technical agreements, as well as the
basis for the acceptance of forgings.
2 Normative References
The following referenced documents are indispensable for the application of this
document. For dated references, only the edition dated applies to this document. For
undated references, the latest edition of the referenced documents (including all
amendments) applies to this Standard.
GB/T 224, Determination of Depth of Decarburization of Steels
GB/T 226, Test Method for Macrostructure and Defect of Steel by Etching
GB/T 228.1, Metallic Materials – Tensile Testing – Part 1. Method of Test at Room
Temperature
GB/T 229, Metallic Materials – Charpy Pendulum Impact Test Method
GB/T 230 (all parts), Metallic Materials – Rockwell Hardness Test
GB/T 231 (all parts), Metallic Materials – Brinell Hardness Test
GB/T 321, Preferred Numbers – Series of Preferred Numbers
GB/T 699, Quality Carbon Structural steels
GB/T 700, Carbon Structural Steels
GB/T 2828 (all parts), Sampling Procedures for Inspection by Attributes
GB/T 2829, Sampling Procedures and Tables for Periodic Inspection by Attributes
(Apply to Inspection of Process Stability)
GB/T 3077, Alloy Structural steels
GB/T 5216, Structural Steels with Specified Hardenability Bands
GB/T 6394, Metal – Methods for Estimating the Average Grain Size
GB/T 7232, Terminology of Metal Heat Treatment
GB/T 12362, Tolerances and machining - allowances of Steel Die Forgings
GB/T 12363, Classification of Forging Functions
3 Terms and Definitions
For the purposes of this document, the following terms and definitions apply.
3.1
steel-smelting furnace number
The furnace number marked on steel products of a steel mill.
3.2
heat treatment furnace number
The heat treatment furnace number consists of all of the same type of forgings which
are produced at one time or continuously in the same heat treatment furnace in
accordance with the same process specifications.
3.3
manufacture batch
A manufacture batch is all forgings which are produced continuously during the forging
process in accordance with the same process specifications.
4 Classification of Forgings
4.1 Forgings are classified in accordance with GB/T 12363.
4.2 The categories of forgings shall be indicated in the product drawings and forging
drawings. Those unindicated are of category IV.
4.3 Indication method.
Overburning of any category of forgings is not allowed. Overburned forgings shall be
scrapped.
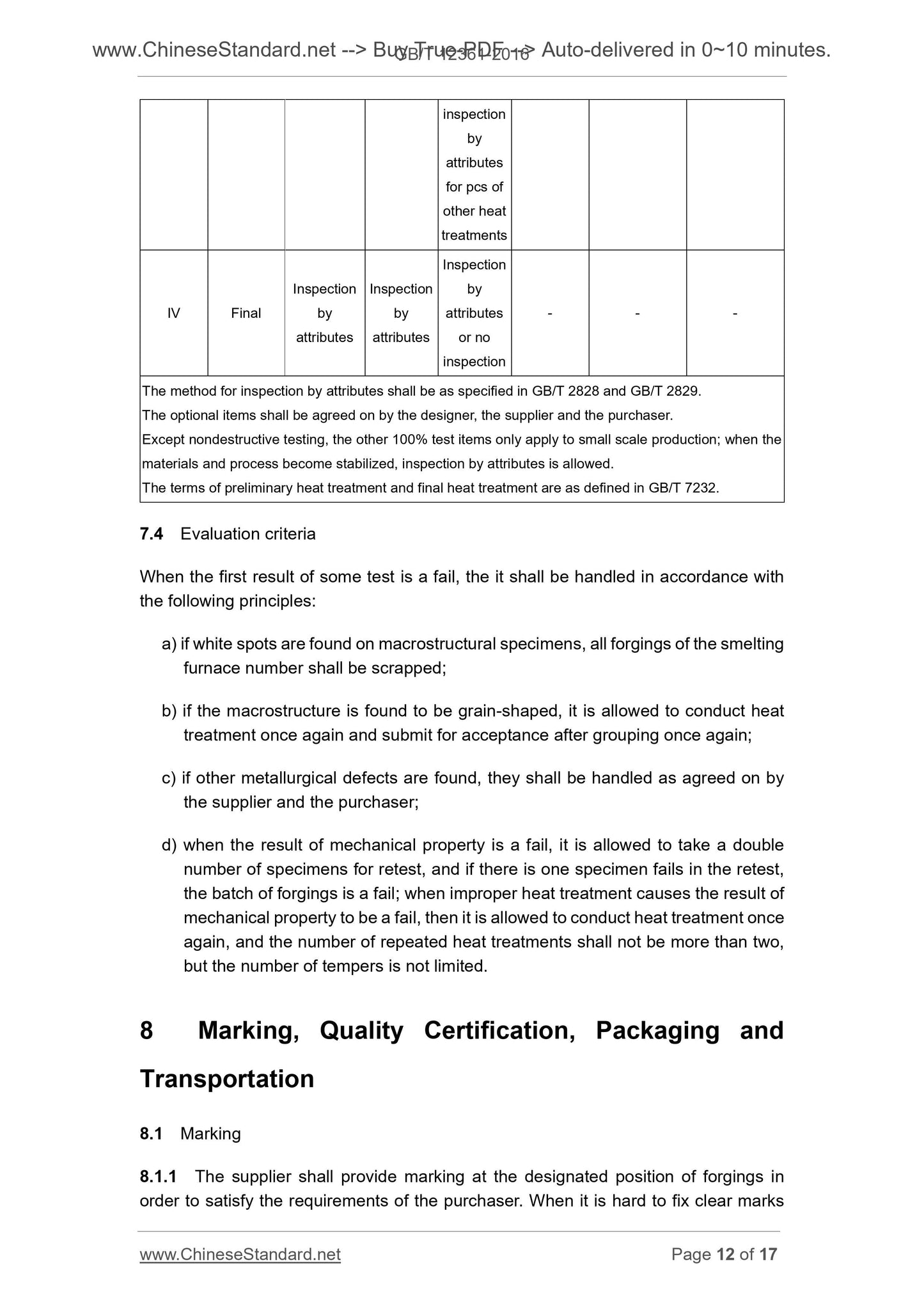
5.3.5 Heat treatment of forgings
5.3.5.1 The heat treatment deliver condition of forgings shall be indicated on forging
drawings, normally including.
a) quenching-tempering;
b) normalizing before tempering;
c) normalizing or annealing;
d) isothermal normalizing;
e) controlled cooling for non-quenched and tempered steel and others;
f) no heat treatment.
5.3.5.2 The fluctuation range of the hardness values of forgings after the heat
treatment is as specified in Table 1.
Table 1 -- Fluctuation Range of Brinell Hardness Values of Forgings
Unit. mm
EXAMPLE. The normalizing hardness of 20CrMnTi steel forgings is the Brinell
hardness indentation diameter dB = 4.2 mm ~ 4.8 mm.
5.3.5.3 The position of hardness testing of forgings shall be indicated on forging
drawings.
5.3.6 Surface cleaning of forgings
The surface oxide skin of forgings shall be removed. The surface cleaning methods
include shot blasting, sand blasting and tumbling.
5.3.7 Quality test of forgings
5.3.7.1 The content of quality test of forgings normally includes geometrical
dimensions, surface defects and hardness.
5.3.7.2 In accordance with the requi...
Get QUOTATION in 1-minute: Click GB/T 12361-2016
Historical versions: GB/T 12361-2016
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll if blank)
GB/T 12361-2016: Steel die forgings -- General specification
GB/T 12361-2016
GB
NATIONAL STANDARD
OF THE PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 77.140.85
J 32
Replacing GB/T 12361-2003
Steel Die Forgings – General Specification
ISSUED ON. DECEMBER 13, 2016
IMPLEMENTED ON. JULY 1, 2017
Issued by. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and
Quarantine of the People's Republic of China;
Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of
China.
3. No action is required - Full-copy of this standard will be automatically and
immediately delivered to your EMAIL address in 0~60 minutes.
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
1 Application Scope ... 5
2 Normative References ... 5
3 Terms and Definitions ... 6
4 Classification of Forgings ... 6
5 Specifications ... 7
6 Test Methods ... 9
7 Inspection Rules ... 10
8 Marking, Quality Certification, Packaging and Transportation ... 12
Annex A (Normative) Draft Angles and Fillet Radii of Forgings ... 14
Foreword
This Standard was drafted in accordance with the rules given in GB/T 1.1-2009.
This Standard replaces GB/T 12361-2003, General Specification of Steel Die Forgings.
Compared with GB/T 12361-2003, the major changes in addition to editorial
modifications are as follows.
-- “furnace (tank) number” is changed into “furnace number” (see 3.1; 3.1 of edition
2003);
-- “for the same production card” is deleted (3.3 of edition 2003);
-- standard GB/T 5216 for the steels selected for forgings is added (see 5.2.1);
-- “The steels selected shall be used in production only after they are qualified by
reinspection. The reinspection items shall be determined as specified in steel
inspection standards.” is changed into “Steels shall be re-inspected in
accordance with the inspection items determined by the supplier and the
purchaser.” (see 5.2.3; 5.2.3 of edition 2003);
-- “isothermal annealing” is changed into “isothermal normalizing”, and “controlled-
temperature cooling” is changed into “controlled cooling” [see 5.3.5.1 d), e);
5.3.5.1 d), e) of edition 2003];
-- “and when it is unable to take samples from forgings” is deleted (5.3.7.3);
-- “and when the supplier is able to satisfy” is deleted (5.4.1 of edition 2003);
-- “If the heat treatment furnace number and manufacture batch under the same
furnace number are required, the addition of the provisions such as strengthened
shot blasting may possibly be added” (5.4.2 of edition 2003);
-- “white patches” is deleted (7.4.1 of edition 2003);
-- “for the convenience of die manufacture, standard cutting tools are used” is
deleted (A.1.3 of edition 2003);
-- “But it is preferably not less than 3°” is deleted (A.1.4.1 of edition 2003).
This Standard was proposed by and shall be under the jurisdiction of the National
Technical Committee 74 on Forging and Pressing of Standardization Administration of
China (SAC/TC 74).
The drafting organizations of this Standard. Dongfeng Forging Co., Ltd., Beijing
Research Institute of Mechanical and Electrical Technology.
The main drafters of this Standard. Wu Yujian, Wu Tingsong, Wei Wei, Zhou Lin, Zhao
Yeqin, Chen Wenjing, Cheng Chenwen.
Steel Die Forgings – General Specification
1 Application Scope
This Standard specifies the classification, specifications, test methods, inspection rules,
marking, quality certification, packaging and transportation of steel die forgings
(hereinafter referred to as “forgings”).
This Standard applies to structural steel die forgings which are produced with forging-
press equipment such as forging hammer, hot die forging press, screw press and
horizontal forging machine. This Standard may also work as the reference for the
forgings of other steel types.
This Standard is the basis for product designer to determine the specifications of
forgings and the supplier and purchaser to sign technical agreements, as well as the
basis for the acceptance of forgings.
2 Normative References
The following referenced documents are indispensable for the application of this
document. For dated references, only the edition dated applies to this document. For
undated references, the latest edition of the referenced documents (including all
amendments) applies to this Standard.
GB/T 224, Determination of Depth of Decarburization of Steels
GB/T 226, Test Method for Macrostructure and Defect of Steel by Etching
GB/T 228.1, Metallic Materials – Tensile Testing – Part 1. Method of Test at Room
Temperature
GB/T 229, Metallic Materials – Charpy Pendulum Impact Test Method
GB/T 230 (all parts), Metallic Materials – Rockwell Hardness Test
GB/T 231 (all parts), Metallic Materials – Brinell Hardness Test
GB/T 321, Preferred Numbers – Series of Preferred Numbers
GB/T 699, Quality Carbon Structural steels
GB/T 700, Carbon Structural Steels
GB/T 2828 (all parts), Sampling Procedures for Inspection by Attributes
GB/T 2829, Sampling Procedures and Tables for Periodic Inspection by Attributes
(Apply to Inspection of Process Stability)
GB/T 3077, Alloy Structural steels
GB/T 5216, Structural Steels with Specified Hardenability Bands
GB/T 6394, Metal – Methods for Estimating the Average Grain Size
GB/T 7232, Terminology of Metal Heat Treatment
GB/T 12362, Tolerances and machining - allowances of Steel Die Forgings
GB/T 12363, Classification of Forging Functions
3 Terms and Definitions
For the purposes of this document, the following terms and definitions apply.
3.1
steel-smelting furnace number
The furnace number marked on steel products of a steel mill.
3.2
heat treatment furnace number
The heat treatment furnace number consists of all of the same type of forgings which
are produced at one time or continuously in the same heat treatment furnace in
accordance with the same process specifications.
3.3
manufacture batch
A manufacture batch is all forgings which are produced continuously during the forging
process in accordance with the same process specifications.
4 Classification of Forgings
4.1 Forgings are classified in accordance with GB/T 12363.
4.2 The categories of forgings shall be indicated in the product drawings and forging
drawings. Those unindicated are of category IV.
4.3 Indication method.
Overburning of any category of forgings is not allowed. Overburned forgings shall be
scrapped.
5.3.5 Heat treatment of forgings
5.3.5.1 The heat treatment deliver condition of forgings shall be indicated on forging
drawings, normally including.
a) quenching-tempering;
b) normalizing before tempering;
c) normalizing or annealing;
d) isothermal normalizing;
e) controlled cooling for non-quenched and tempered steel and others;
f) no heat treatment.
5.3.5.2 The fluctuation range of the hardness values of forgings after the heat
treatment is as specified in Table 1.
Table 1 -- Fluctuation Range of Brinell Hardness Values of Forgings
Unit. mm
EXAMPLE. The normalizing hardness of 20CrMnTi steel forgings is the Brinell
hardness indentation diameter dB = 4.2 mm ~ 4.8 mm.
5.3.5.3 The position of hardness testing of forgings shall be indicated on forging
drawings.
5.3.6 Surface cleaning of forgings
The surface oxide skin of forgings shall be removed. The surface cleaning methods
include shot blasting, sand blasting and tumbling.
5.3.7 Quality test of forgings
5.3.7.1 The content of quality test of forgings normally includes geometrical
dimensions, surface defects and hardness.
5.3.7.2 In accordance with the requi...
Share