1
/
of
9
PayPal, credit cards. Download editable-PDF and invoice in 1 second!
GB/T 29510-2013 English PDF (GBT29510-2013)
GB/T 29510-2013 English PDF (GBT29510-2013)
Regular price
$220.00 USD
Regular price
Sale price
$220.00 USD
Unit price
/
per
Shipping calculated at checkout.
Couldn't load pickup availability
Delivery: 3 seconds. Download true-PDF + Invoice.
Get QUOTATION in 1-minute: Click GB/T 29510-2013
Historical versions: GB/T 29510-2013
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll if blank)
GB/T 29510-2013: General requirements for the distribution of personal protection equipment
GB/T 29510-2013
NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE
PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 13.340.01
C 73
General requirements for the distribution of personal
protection equipment
ISSUED ON: MAY 09, 2013
IMPLEMENTED ON: FEBRUARY 01, 2014
Issued by: General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and
Quarantine;
Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of
China.
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
1 Scope ... 4
2 Normative references ... 4
3 Terms and definitions ... 5
4 Basic requirements ... 5
5 Principles and methods for identifying hazard and harmful factors ... 6
6 Distribution procedures ... 7
7 Classification, rating and scope of application ... 8
8 Distribution requirements ... 21
9 Management and training ... 22
Bibliography ... 24
General requirements for the distribution of personal
protection equipment
1 Scope
This Standard specifies basic requirements, identification principles and
methods of dangerous and harmful factors, equipment procedures,
classification, rating and scope of application, equipment requirements,
management and training for distribution of personal protection equipment.
This Standard is applicable to selection, distribution, use, maintenance and
scrap management for personal protection equipment of production and
business operation entity.
2 Normative references
The following referenced documents are indispensable for the application of
this document. For dated references, only the edition cited applies. For undated
references, the latest edition of the referenced document (including any
amendments) applies.
GB 2890-2009, Respiratory protection - Non-powered air-purifying
respirators
GB/T 6441, The classification for casualty accidents of enterprise staff and
workers
GB/T 11651-2009, Code of practice for selection of personal protective
equipment
GB/T 12903, Personal protective equipment terminology
GB/T 14366, Acoustics - Estimation of noise-induced hearing loss
GB/T 18664-2002, Selection, use and maintenance of respiratory protective
equipment
GB/T 23466-2009, Guideline for selection of hearing protectors
GB/T 23468-2009, Code of practice for safety use of fall protection
equipment
4.5 When multiple protection equipment is required at the same time, the use
compatibility and functional substitution shall be considered to avoid protection
failure.
5 Principles and methods for identifying hazard and
harmful factors
5.1 Identification principle
5.1.1 Identify hazard and harmful factors based on scientific, systematic and
comprehensive basic principles.
5.1.2 According to safety science theory, national laws, regulations, standards
and professional knowledge, according to the characteristics of different
workplaces, production processes and operating environments, identify
possible hazard and harmful factors.
5.1.3 Systematically analyze hazard and harmful factors in all links of
production and operation activities. Determine the location of the hazard and
harmful factors, the hazards, the ways and consequences of the accident.
5.1.4 Identify in terms of personnel, equipment and facilities, environmental
conditions, management systems. It shall not only analyze hazard and harmful
factors existing in normal production operations, but also possible hazard and
harmful factors in the case of changes in technology, materials, processes,
equipment damage or failure, and personnel operation errors.
5.2 Identification method
5.2.1 The production and business operation entity shall, according to the
accident categories specified in GB 6441, the hazard factors in the "Category
of Occupational Disease Hazard Factors" published by the Ministry of Health
and other occupational health regulations, identify hazard and harmful factors.
5.2.2 Professionals shall analyze the hazard and harmful factors in the working
environment by means of on-site investigation, measurement, inspection of
relevant records, safety checklists, inquiry and communication. Determine
hazard and harmful factors, types of injuries, likelihood, extent and
consequences of harm to humans.
5.2.3 When identifying hazard and harmful factors, it shall analyze mainly from
the following aspects:
- Normal working condition;
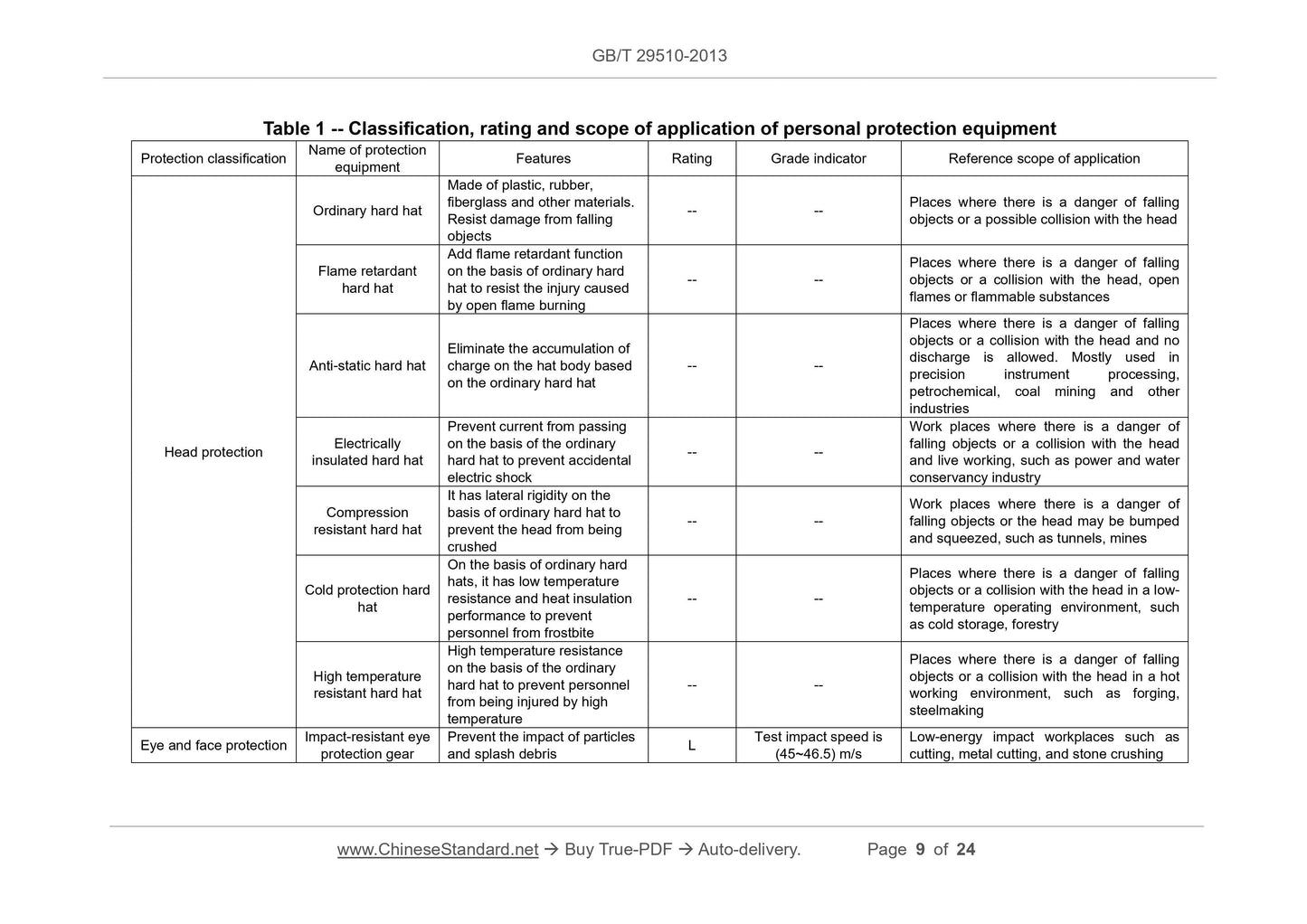
Table 1 -- Classification, rating and scope of application of personal protection equipment
Protection classification Name of protection equipment Features Rating Grade indicator Reference scope of application
Head protection
Ordinary hard hat
Made of plastic, rubber,
fiberglass and other materials.
Resist damage from falling
objects
-- -- Places where there is a danger of falling objects or a possible collision with the head
Flame retardant
hard hat
Add flame retardant function
on the basis of ordinary hard
hat to resist the injury caused
by open flame burning
-- --
Places where there is a danger of falling
objects or a collision with the head, open
flames or flammable substances
Anti-static hard hat
Eliminate the accumulation of
charge on the hat body based
on the ordinary hard hat
-- --
Places where there is a danger of falling
objects or a collision with the head and no
discharge is allowed. Mostly used in
precision instrument processing,
petrochemical, coal mining and other
industries
Electrically
insulated hard hat
Prevent current from passing
on the basis of the ordinary
hard hat to prevent accidental
electric shock
-- --
Work places where there is a danger of
falling objects or a collision with the head
and live working, such as power and water
conservancy industry
Compression
resistant hard hat
It has lateral rigidity on the
basis of ordinary hard hat to
prevent the head from being
crushed
-- --
Work places where there is a danger of
falling objects or the head may be bumped
and squeezed, such as tunnels, mines
Cold protection hard
hat
On the basis of ordinary hard
hats, it has low temperature
resistance and heat insulation
performance to prevent
personnel from frostbite
-- --
Places where there is a danger of falling
objects or a collision with the head in a low-
temperature operating environment, such
as cold storage, forestry
High temperature
resistant hard hat
High temperature resistance
on the basis of the ordinary
hard hat to prevent personnel
from being injured by high
temperature
-- --
Places where there is a danger of falling
objects or a collision with the head in a hot
working environment, such as forging,
steelmaking
Eye and face protection Impact-resistant eye protection gear
Prevent the impact of particles
and splash debris L
Test impact speed is
(45~46.5) m/s
Low-energy impact workplaces such as
cutting, metal cutting, and stone crushing
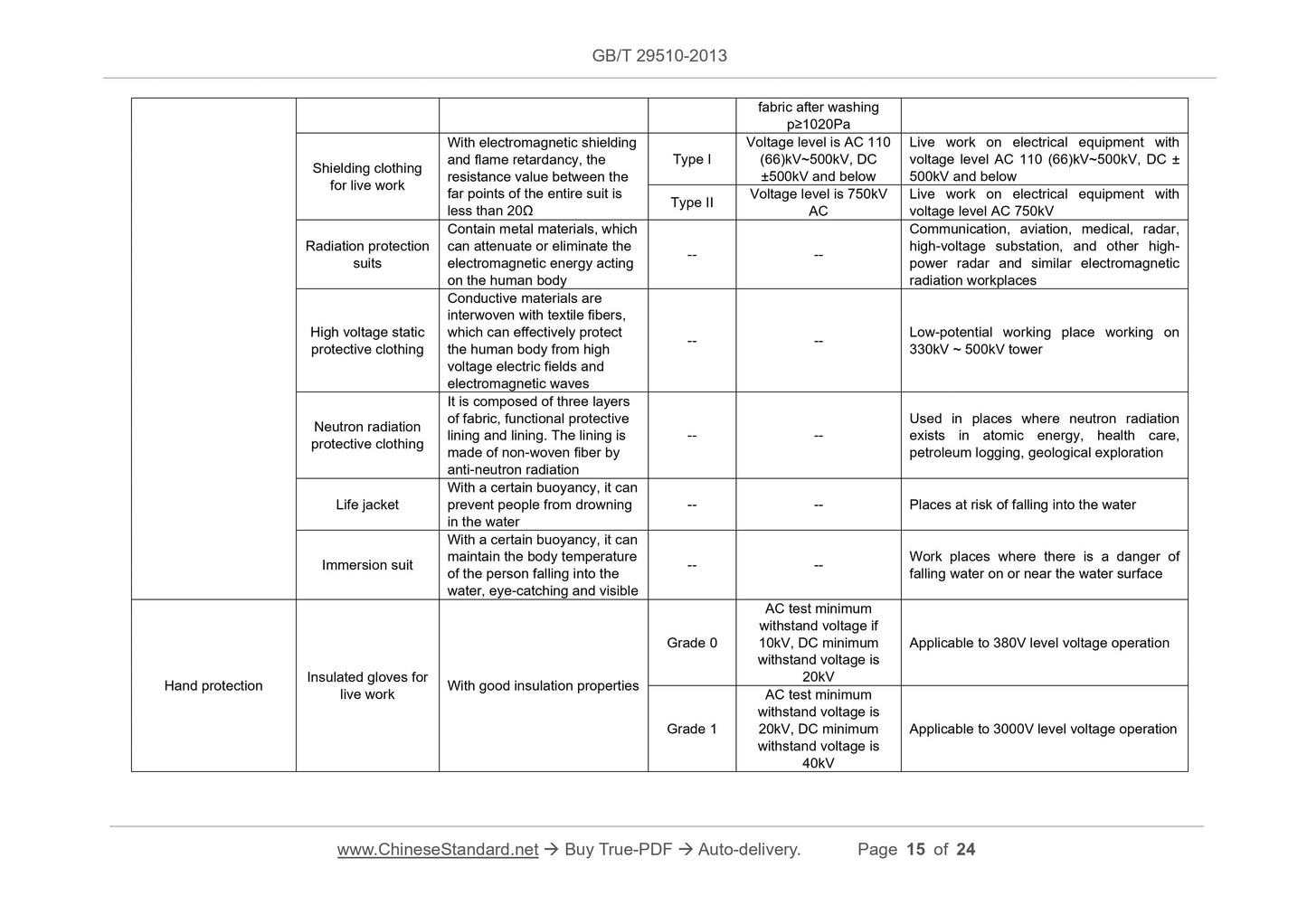
fabric after washing
p≥1020Pa
Shielding clothing
for live work
With electromagnetic shielding
and flame retardancy, the
resistance value between the
far points of the entire suit is
less than 20Ω
Type I
Voltage level is AC 110
(66)kV~500kV, DC
±500kV and below
Live work on electrical equipment with
voltage level AC 110 (66)kV~500kV, DC ±
500kV and below
Type II Voltage level is 750kV AC
Live work on electrical equipment with
voltage level AC 750kV
Radiation prote...
Get QUOTATION in 1-minute: Click GB/T 29510-2013
Historical versions: GB/T 29510-2013
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll if blank)
GB/T 29510-2013: General requirements for the distribution of personal protection equipment
GB/T 29510-2013
NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE
PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 13.340.01
C 73
General requirements for the distribution of personal
protection equipment
ISSUED ON: MAY 09, 2013
IMPLEMENTED ON: FEBRUARY 01, 2014
Issued by: General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and
Quarantine;
Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of
China.
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
1 Scope ... 4
2 Normative references ... 4
3 Terms and definitions ... 5
4 Basic requirements ... 5
5 Principles and methods for identifying hazard and harmful factors ... 6
6 Distribution procedures ... 7
7 Classification, rating and scope of application ... 8
8 Distribution requirements ... 21
9 Management and training ... 22
Bibliography ... 24
General requirements for the distribution of personal
protection equipment
1 Scope
This Standard specifies basic requirements, identification principles and
methods of dangerous and harmful factors, equipment procedures,
classification, rating and scope of application, equipment requirements,
management and training for distribution of personal protection equipment.
This Standard is applicable to selection, distribution, use, maintenance and
scrap management for personal protection equipment of production and
business operation entity.
2 Normative references
The following referenced documents are indispensable for the application of
this document. For dated references, only the edition cited applies. For undated
references, the latest edition of the referenced document (including any
amendments) applies.
GB 2890-2009, Respiratory protection - Non-powered air-purifying
respirators
GB/T 6441, The classification for casualty accidents of enterprise staff and
workers
GB/T 11651-2009, Code of practice for selection of personal protective
equipment
GB/T 12903, Personal protective equipment terminology
GB/T 14366, Acoustics - Estimation of noise-induced hearing loss
GB/T 18664-2002, Selection, use and maintenance of respiratory protective
equipment
GB/T 23466-2009, Guideline for selection of hearing protectors
GB/T 23468-2009, Code of practice for safety use of fall protection
equipment
4.5 When multiple protection equipment is required at the same time, the use
compatibility and functional substitution shall be considered to avoid protection
failure.
5 Principles and methods for identifying hazard and
harmful factors
5.1 Identification principle
5.1.1 Identify hazard and harmful factors based on scientific, systematic and
comprehensive basic principles.
5.1.2 According to safety science theory, national laws, regulations, standards
and professional knowledge, according to the characteristics of different
workplaces, production processes and operating environments, identify
possible hazard and harmful factors.
5.1.3 Systematically analyze hazard and harmful factors in all links of
production and operation activities. Determine the location of the hazard and
harmful factors, the hazards, the ways and consequences of the accident.
5.1.4 Identify in terms of personnel, equipment and facilities, environmental
conditions, management systems. It shall not only analyze hazard and harmful
factors existing in normal production operations, but also possible hazard and
harmful factors in the case of changes in technology, materials, processes,
equipment damage or failure, and personnel operation errors.
5.2 Identification method
5.2.1 The production and business operation entity shall, according to the
accident categories specified in GB 6441, the hazard factors in the "Category
of Occupational Disease Hazard Factors" published by the Ministry of Health
and other occupational health regulations, identify hazard and harmful factors.
5.2.2 Professionals shall analyze the hazard and harmful factors in the working
environment by means of on-site investigation, measurement, inspection of
relevant records, safety checklists, inquiry and communication. Determine
hazard and harmful factors, types of injuries, likelihood, extent and
consequences of harm to humans.
5.2.3 When identifying hazard and harmful factors, it shall analyze mainly from
the following aspects:
- Normal working condition;
Table 1 -- Classification, rating and scope of application of personal protection equipment
Protection classification Name of protection equipment Features Rating Grade indicator Reference scope of application
Head protection
Ordinary hard hat
Made of plastic, rubber,
fiberglass and other materials.
Resist damage from falling
objects
-- -- Places where there is a danger of falling objects or a possible collision with the head
Flame retardant
hard hat
Add flame retardant function
on the basis of ordinary hard
hat to resist the injury caused
by open flame burning
-- --
Places where there is a danger of falling
objects or a collision with the head, open
flames or flammable substances
Anti-static hard hat
Eliminate the accumulation of
charge on the hat body based
on the ordinary hard hat
-- --
Places where there is a danger of falling
objects or a collision with the head and no
discharge is allowed. Mostly used in
precision instrument processing,
petrochemical, coal mining and other
industries
Electrically
insulated hard hat
Prevent current from passing
on the basis of the ordinary
hard hat to prevent accidental
electric shock
-- --
Work places where there is a danger of
falling objects or a collision with the head
and live working, such as power and water
conservancy industry
Compression
resistant hard hat
It has lateral rigidity on the
basis of ordinary hard hat to
prevent the head from being
crushed
-- --
Work places where there is a danger of
falling objects or the head may be bumped
and squeezed, such as tunnels, mines
Cold protection hard
hat
On the basis of ordinary hard
hats, it has low temperature
resistance and heat insulation
performance to prevent
personnel from frostbite
-- --
Places where there is a danger of falling
objects or a collision with the head in a low-
temperature operating environment, such
as cold storage, forestry
High temperature
resistant hard hat
High temperature resistance
on the basis of the ordinary
hard hat to prevent personnel
from being injured by high
temperature
-- --
Places where there is a danger of falling
objects or a collision with the head in a hot
working environment, such as forging,
steelmaking
Eye and face protection Impact-resistant eye protection gear
Prevent the impact of particles
and splash debris L
Test impact speed is
(45~46.5) m/s
Low-energy impact workplaces such as
cutting, metal cutting, and stone crushing
fabric after washing
p≥1020Pa
Shielding clothing
for live work
With electromagnetic shielding
and flame retardancy, the
resistance value between the
far points of the entire suit is
less than 20Ω
Type I
Voltage level is AC 110
(66)kV~500kV, DC
±500kV and below
Live work on electrical equipment with
voltage level AC 110 (66)kV~500kV, DC ±
500kV and below
Type II Voltage level is 750kV AC
Live work on electrical equipment with
voltage level AC 750kV
Radiation prote...
Share