1
/
of
7
www.ChineseStandard.us -- Field Test Asia Pte. Ltd.
GB/T 34560.6-2017 English PDF (GB/T34560.6-2017)
GB/T 34560.6-2017 English PDF (GB/T34560.6-2017)
Regular price
$150.00
Regular price
Sale price
$150.00
Unit price
/
per
Shipping calculated at checkout.
Couldn't load pickup availability
GB/T 34560.6-2017: Structural steels -- Part 6: Technical delivery conditions for seismic-improved structural steels for building
Delivery: 9 seconds. Download (& Email) true-PDF + Invoice.
Get Quotation: Click GB/T 34560.6-2017 (Self-service in 1-minute)
Historical versions (Master-website): GB/T 34560.6-2017
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll-down if blank)
GB/T 34560.6-2017
NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE
PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 77.140.01
H 40
Structural steels - Part 6: Technical delivery conditions
for seismic-improved structural steels for building
(ISO 630-6:2014, MOD)
ISSUED ON: OCTOBER 14, 2017
IMPLEMENTED ON: JULY 01, 2018
Issued by: General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and
Quarantine of the PRC;
Standardization Administration of the PRC.
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
1 Scope ... 5
2 Normative references ... 5
3 Terms and definitions ... 7
4 Classification and designation representation ... 8
5 Order content ... 8
6 Dimension, shape, weight and tolerance ... 9
7 Technical requirements ... 9
8 Test methods ... 13
9 Inspection rules ... 14
10 Package, mark, and certification ... 15
Annex A (Informative) Structural changes in this Part compared to ISO 630-
6:2014 ... 16
Annex B (Informative) Technical differences between this Part and ISO 630-
6:2014 and their causes ... 17
Annex C (Normative) Chemical composition, mechanical and processing
properties of Q390, Q420, and Q460 steels ... 19
Annex D (Normative) Carbon equivalent formulas and requirements ... 22
Structural steels - Part 6: Technical delivery conditions
for seismic-improved structural steels for building
1 Scope
This Part of GB/T 34560 specifies the terms and definitions, classification and
designation representation, order content, dimension, shape, weight and
tolerance, technical requirements, test methods, inspection rules, package,
mark, and certification of seismic-improved structural steels for building.
This Part applies to steel plates with a thickness of 6 mm~150 mm, wide flat
steels, and hot-rolled section steels with flange thickness not more than 140
mm (hereinafter referred to as “steels”).
2 Normative references
The following documents are indispensable for the application of this document.
For the dated references, only the editions with the dates indicated are
applicable to this document. For the undated references, the latest edition
(including all the amendments) are applicable to this document.
GB/T 222 Permissible Tolerances for Chemical Composition of Steel
Products
GB/T 223.3 Methods for chemical analysis of iron, steel and alloy - The
diantipyrylmethane phosphomolybdate gravimetric method for the
determination of phosphorus content
GB/T 223.10 Methods for chemical analysis of iron, steel and alloy - The
cupferron separation-chrome azurol S photometric method for the
determination of aluminium content
GB/T 223.11 Iron, steel and alloy - Determination of chromium content -
Visual titration or potentiometric titration method
GB/T 223.14 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Iron, Steel and Alloy - The N-
Benzoy-N-Phenylhydroxylamine Extraction Photometric Method for the
Determination of Vanadium Content
GB/T 223.17 Methods for chemical analysis of iron, steel and alloy - The
diantipyrylmethane photometric method for the determination of titanium
content
GB/T 223.18 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Iron, Steel and Alloy - The
Sodium Thiosulfate Separation Iodimetric Method for the Determination of
Copper Content
GB/T 223.23 Iron, Steel and Alloy - Determination of Nickel Content - The
Dimethylglyoxime Spectrophotometric Method
GB/T 223.26 Iron, steel and alloy - Determination of molybdenum content -
The thiocyanate spectrophotometric method
GB/T 223.27 Methods for chemical analysis of iron, steel and alloy - The
thiocyanate-butyl acetate extraction spectrophotometric method for the
determination of molybdenum content
GB/T 223.40 Iron, Steel and Alloy - Determination of Niobium Content by the
Sulphochlorophenol S Spectrophotometric Method
GB/T 223.60 Methods for chemical analysis of iron, steel and alloy - The
perchloric acid dehydration gravimetric method for the determination of
silicon content
GB/T 223.63 Methods for chemical analysis of iron, steel and alloy - The
sodium (potassium) periodate photometric method for the determination of
manganese content
GB/T 223.68 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Iron, Steel and Alloy - The
Potassium Iodate Titration Method after Combustion in the Pipe Furnace for
the Determination of Sulfur Content
GB/T 223.69 Iron, steel and alloy - Determination of carbon contents - Gas-
volumetric method after combustion in the pipe furnace
GB/T 223.75 Iron steel and alloy - Determination of boron content - Methanol
distillation-curcumin photometric method
GB/T 223.76 Methods for chemical analysis of iron, steel and alloy - The
flame atomic absorption spectrometric method for the determination of
vanadium content
GB/T 228.1 Metallic materials - Tensile testing - Part 1: Method of test at
room temperature (GB/T 228.1-2010, ISO 6892-1:2009 MOD)
GB/T 229 Metallic materials - Charpy pendulum impact test method (GB/T
229-2007, ISO 148-1:2006, MOD)
4 Classification and designation representation
4.1 According to GB/T 13304.1, the steel of this Part is classified into unalloyed
steel and low-alloy steel.
4.2 The steel designation consists of four parts: the first letter Q of Chinese
phonetic alphabet representing “Qu” of yield strength, specified minimum upper
yield strength value, the initials “KZ” of Chinese phonetic alphabet for “seismic-
improved”, quality grade symbol (C, D, E, F).
Example: Q3450KZE
Where:
Q - The first letter of Chinese phonetic alphabet of “Qu” for yield strength of steel;
345 - The specified minimum upper yield strength value, in megapascals (MPa);
KZ - Represent “seismic-improved”;
E - The quality grade is Grade E.
4.3 When the purchaser requires the steel plate to have the through-thickness
(Z-direction) characteristics, after the above specified designation, ADD the
through-thickness characteristics level of the steel plate, such as Q345KZEZ25.
5 Order content
5.1 Contracts or orders for ordering according to this Part shall include the
following:
a) Standard number;
b) Product type;
c) Steel grade + delivery condition + quality grade;
d) Dimension, shape, and tolerance;
e) Selected content of all requirements;
f) Type of inspection document.
5.2 Through negotiation between the supplier and the purchaser, and indicated
in the contract, the following content may be selected as the order content of
this Part. If the purchaser does not specify when providing the inquiry and order,
7.1.8 Through negotiation between the supplier and the purchaser, the
chemical composition inspection of steel products may be carried out.
Permissible tolerances for chemical composition of products shall meet the
requirements of GB/T 222.
7.2 Smelting method
The steel shall be smelted by an oxygen converter or an electric furnace. Unless
otherwise specified, the smelting method shall be selected by the supplier.
7.3 Delivery condition
The steels are generally delivered in the hot-rolled condition. Unless otherwise
agreed, the hot-rolled condition, normalized rolled, normalized or quenched and
tempered condition are allowed at the manufacturer’s discretion. The thermo-
mechanical rolling is not allowed at the manufacturer’s discretion. Through
negotiation between the supplier and the purchaser, thermo-mechanical rolling
may be applied to any steel grade. The delivery condition shall be stated in the
contract.
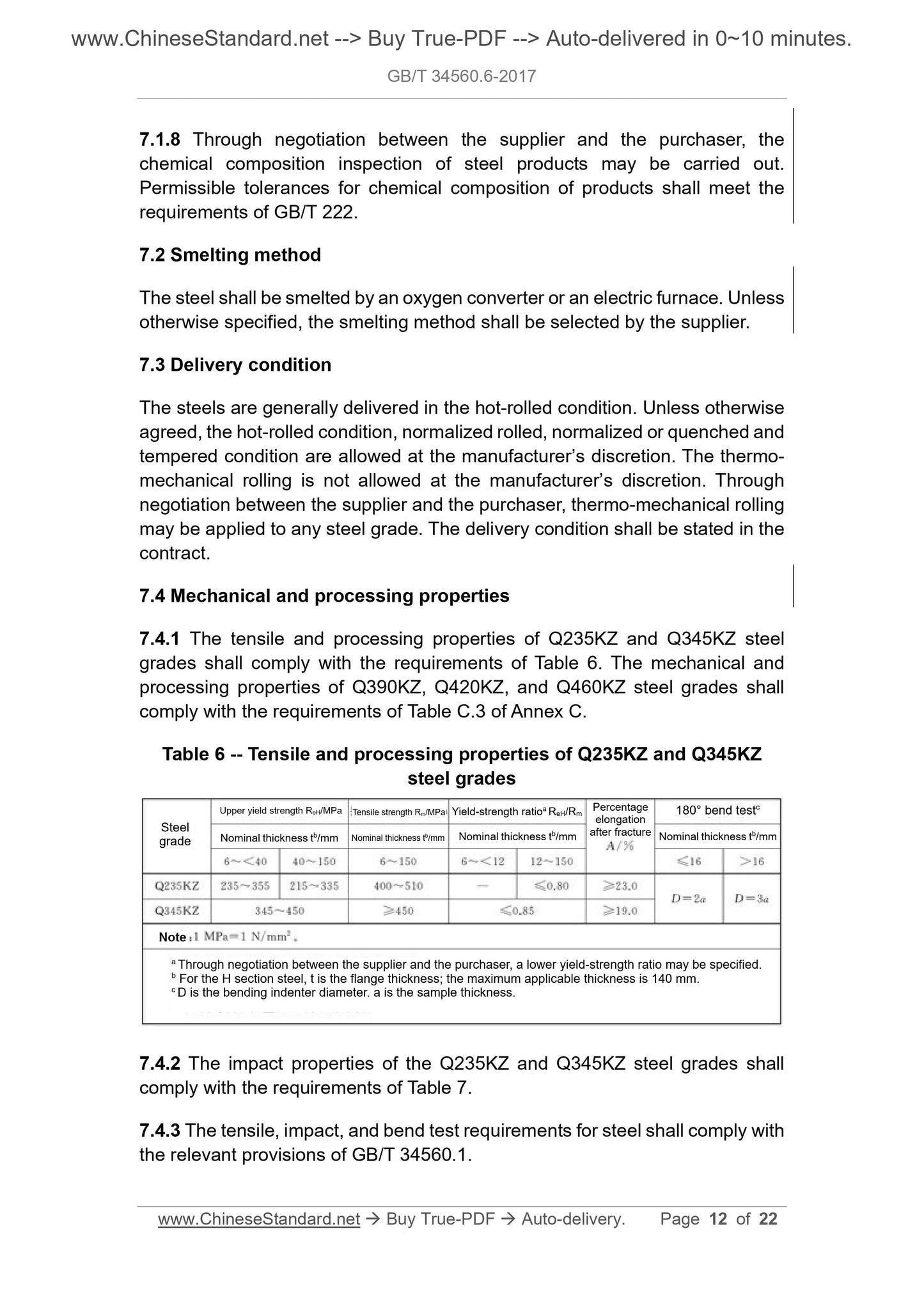
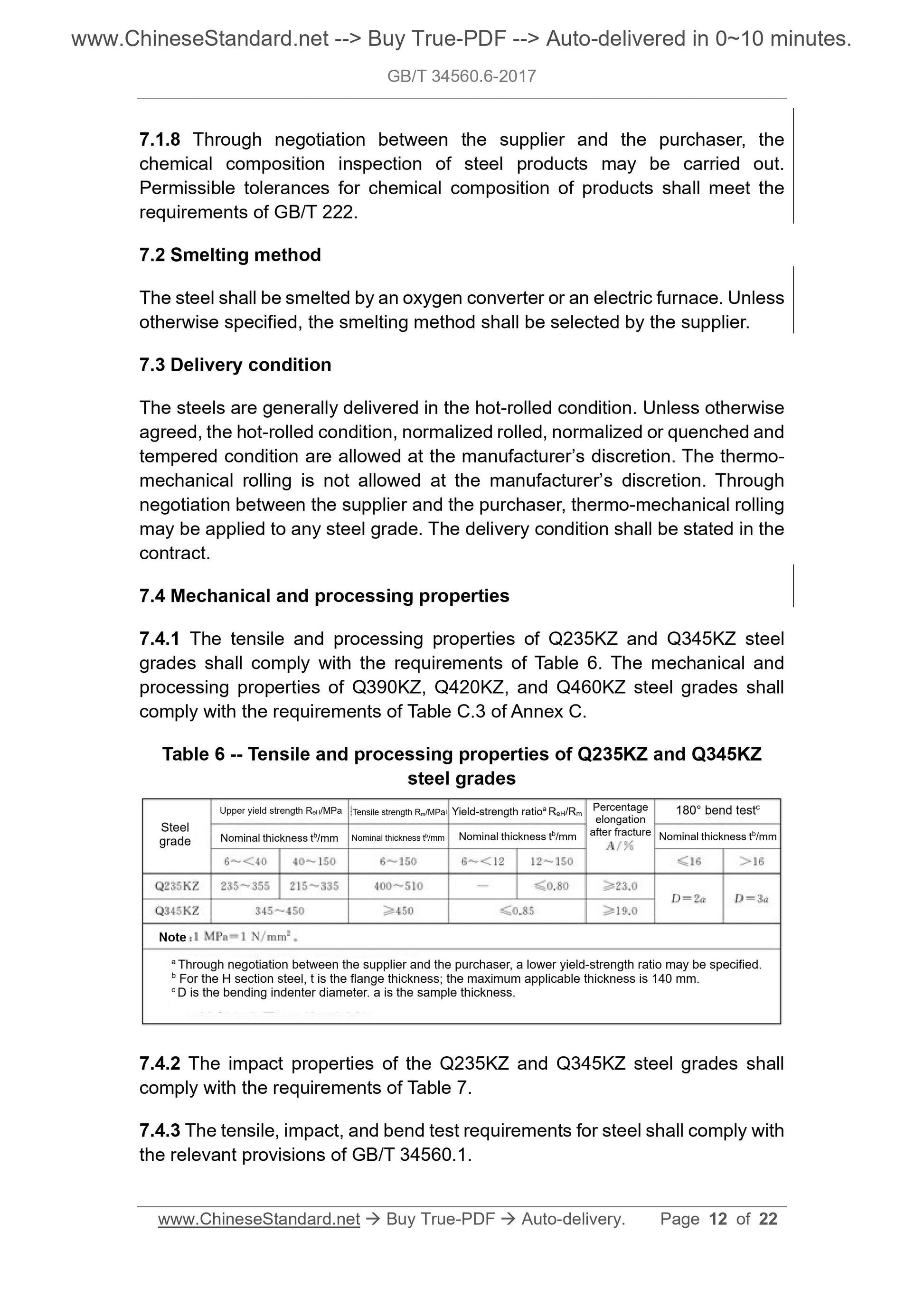
7.4 Mechanical and processing properties
7.4.1 The tensile and processing properties of Q235KZ and Q345KZ steel
grades shall comply with the requirements of Table 6. The mechanical and
processing properties of Q390KZ, Q420KZ, and Q460KZ steel grades shall
comply with the requirements of Table C.3 of Annex C.
Table 6 -- Tensile and processing properties of Q235KZ and Q345KZ
steel grades
7.4.2 The impact properties of the Q235KZ and Q345KZ steel grades shall
comply with the requirements of Table 7.
7.4.3 The tensile, impact, and bend test requirements for steel shall comply with
the relevant provisions of GB/T 34560.1.
Steel
grade
Upper yield strength ReH/MPa
Nominal thickness tb/mm Nominal thickness tb/mm Nominal thickness tb/mm Nominal thickness tb/mm
Tensile strength Rm/MPa Yield-strength ratioa ReH/Rm 180° bend testc Percentage elongation
after fracture
Note
a Through negotiation between the supplier and the purchaser, a lower yield-strength ratio may be specified.
b For the H section steel, t is the flange thickness; the maximum applicable thickness is 140 mm.
c D is the bending indenter diameter. a is the sample thickness.
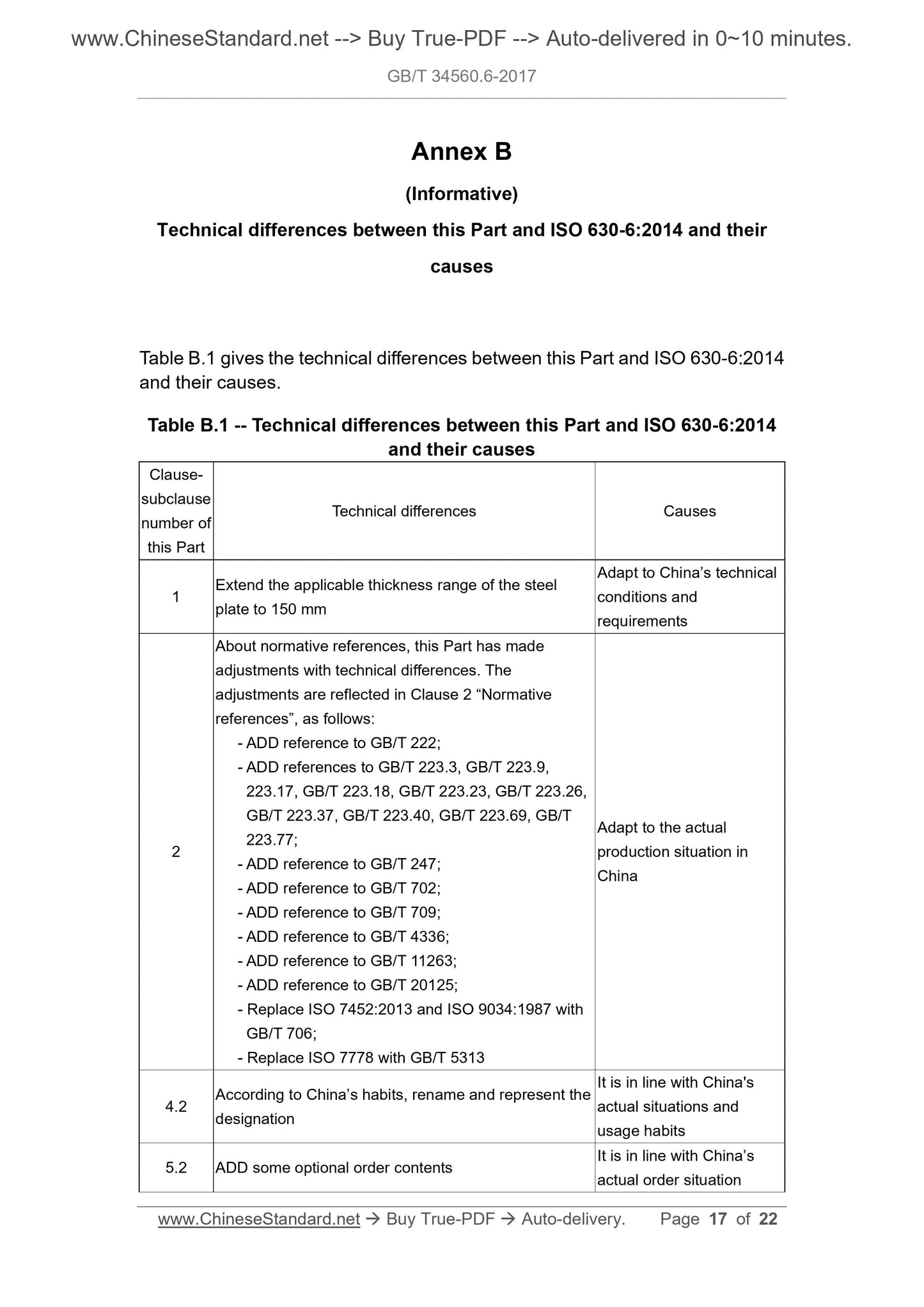
Annex B
(Informative)
Technical differences between this Part and ISO 630-6:2014 and their
causes
Table B.1 gives the technical differences between this Part and ISO 630-6:2014
and their causes.
Table B.1 -- Technical differences between this Part and ISO 630-6:2014
and their causes
Clause-
subclause
number of
this Part
Technical differences Causes
1 Extend the applicable thickness range of the steel plate to 150 mm
Adapt to China’s technical
conditions and
requirements
About normative references, this Part has made
adjustments with technical differences. The
adjustments are reflected in Clause 2 “Normative
references”, as follows:
- ADD reference to GB/T 222;
- ADD references to GB/T 223.3, GB/T 223.9,
223.17, GB/T 223.18, GB/T 223.23, GB/T 223.26,
GB/T 223.37, GB/T 223.40, GB/T 223.69, GB/T
223.77;
- ADD reference to GB/T 247;
- ADD reference to GB/T 702;
- ADD reference to GB/T 709;
- ADD reference to GB/T 4336;
- ADD reference to GB/T 11263;
- ADD reference to GB/T 20125;
- Replace ISO 7452:2013 and ISO 9034:1987 with
GB/T 706;
- Replace ISO 7778 with GB/T 5313
Adapt to the actual
production situation in
China
4.2 According to China’s habits, rename and represent the designation
It is in line with China's
actual situations and
usage habits
5.2 ADD some optional order contents It is in line with China’s actual order situation
GB/T 34560.6-2017
NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE
PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 77.140.01
H 40
Structural steels - Part 6: Technical delivery conditions
for seismic-improved structural steels for building
(ISO 630-6:2014, MOD)
ISSUED ON: OCTOBER 14, 2017
IMPLEMENTED ON: JULY 01, 2018
Issued by: General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and
Quarantine of the PRC;
Standardization Administration of the PRC.
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
1 Scope ... 5
2 Normative references ... 5
3 Terms and definitions ... 7
4 Classification and designation representation ... 8
5 Order content ... 8
6 Dimension, shape, weight and tolerance ... 9
7 Technical requirements ... 9
8 Test methods ... 13
9 Inspection rules ... 14
10 Package, mark, and certification ... 15
Annex A (Informative) Structural changes in this Part compared to ISO 630-
6:2014 ... 16
Annex B (Informative) Technical differences between this Part and ISO 630-
6:2014 and their causes ... 17
Annex C (Normative) Chemical composition, mechanical and processing
properties of Q390, Q420, and Q460 steels ... 19
Annex D (Normative) Carbon equivalent formulas and requirements ... 22
Structural steels - Part 6: Technical delivery conditions
for seismic-improved structural steels for building
1 Scope
This Part of GB/T 34560 specifies the terms and definitions, classification and
designation representation, order content, dimension, shape, weight and
tolerance, technical requirements, test methods, inspection rules, package,
mark, and certification of seismic-improved structural steels for building.
This Part applies to steel plates with a thickness of 6 mm~150 mm, wide flat
steels, and hot-rolled section steels with flange thickness not more than 140
mm (hereinafter referred to as “steels”).
2 Normative references
The following documents are indispensable for the application of this document.
For the dated references, only the editions with the dates indicated are
applicable to this document. For the undated references, the latest edition
(including all the amendments) are applicable to this document.
GB/T 222 Permissible Tolerances for Chemical Composition of Steel
Products
GB/T 223.3 Methods for chemical analysis of iron, steel and alloy - The
diantipyrylmethane phosphomolybdate gravimetric method for the
determination of phosphorus content
GB/T 223.10 Methods for chemical analysis of iron, steel and alloy - The
cupferron separation-chrome azurol S photometric method for the
determination of aluminium content
GB/T 223.11 Iron, steel and alloy - Determination of chromium content -
Visual titration or potentiometric titration method
GB/T 223.14 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Iron, Steel and Alloy - The N-
Benzoy-N-Phenylhydroxylamine Extraction Photometric Method for the
Determination of Vanadium Content
GB/T 223.17 Methods for chemical analysis of iron, steel and alloy - The
diantipyrylmethane photometric method for the determination of titanium
content
GB/T 223.18 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Iron, Steel and Alloy - The
Sodium Thiosulfate Separation Iodimetric Method for the Determination of
Copper Content
GB/T 223.23 Iron, Steel and Alloy - Determination of Nickel Content - The
Dimethylglyoxime Spectrophotometric Method
GB/T 223.26 Iron, steel and alloy - Determination of molybdenum content -
The thiocyanate spectrophotometric method
GB/T 223.27 Methods for chemical analysis of iron, steel and alloy - The
thiocyanate-butyl acetate extraction spectrophotometric method for the
determination of molybdenum content
GB/T 223.40 Iron, Steel and Alloy - Determination of Niobium Content by the
Sulphochlorophenol S Spectrophotometric Method
GB/T 223.60 Methods for chemical analysis of iron, steel and alloy - The
perchloric acid dehydration gravimetric method for the determination of
silicon content
GB/T 223.63 Methods for chemical analysi...
Delivery: 9 seconds. Download (& Email) true-PDF + Invoice.
Get Quotation: Click GB/T 34560.6-2017 (Self-service in 1-minute)
Historical versions (Master-website): GB/T 34560.6-2017
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll-down if blank)
GB/T 34560.6-2017
NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE
PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 77.140.01
H 40
Structural steels - Part 6: Technical delivery conditions
for seismic-improved structural steels for building
(ISO 630-6:2014, MOD)
ISSUED ON: OCTOBER 14, 2017
IMPLEMENTED ON: JULY 01, 2018
Issued by: General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and
Quarantine of the PRC;
Standardization Administration of the PRC.
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
1 Scope ... 5
2 Normative references ... 5
3 Terms and definitions ... 7
4 Classification and designation representation ... 8
5 Order content ... 8
6 Dimension, shape, weight and tolerance ... 9
7 Technical requirements ... 9
8 Test methods ... 13
9 Inspection rules ... 14
10 Package, mark, and certification ... 15
Annex A (Informative) Structural changes in this Part compared to ISO 630-
6:2014 ... 16
Annex B (Informative) Technical differences between this Part and ISO 630-
6:2014 and their causes ... 17
Annex C (Normative) Chemical composition, mechanical and processing
properties of Q390, Q420, and Q460 steels ... 19
Annex D (Normative) Carbon equivalent formulas and requirements ... 22
Structural steels - Part 6: Technical delivery conditions
for seismic-improved structural steels for building
1 Scope
This Part of GB/T 34560 specifies the terms and definitions, classification and
designation representation, order content, dimension, shape, weight and
tolerance, technical requirements, test methods, inspection rules, package,
mark, and certification of seismic-improved structural steels for building.
This Part applies to steel plates with a thickness of 6 mm~150 mm, wide flat
steels, and hot-rolled section steels with flange thickness not more than 140
mm (hereinafter referred to as “steels”).
2 Normative references
The following documents are indispensable for the application of this document.
For the dated references, only the editions with the dates indicated are
applicable to this document. For the undated references, the latest edition
(including all the amendments) are applicable to this document.
GB/T 222 Permissible Tolerances for Chemical Composition of Steel
Products
GB/T 223.3 Methods for chemical analysis of iron, steel and alloy - The
diantipyrylmethane phosphomolybdate gravimetric method for the
determination of phosphorus content
GB/T 223.10 Methods for chemical analysis of iron, steel and alloy - The
cupferron separation-chrome azurol S photometric method for the
determination of aluminium content
GB/T 223.11 Iron, steel and alloy - Determination of chromium content -
Visual titration or potentiometric titration method
GB/T 223.14 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Iron, Steel and Alloy - The N-
Benzoy-N-Phenylhydroxylamine Extraction Photometric Method for the
Determination of Vanadium Content
GB/T 223.17 Methods for chemical analysis of iron, steel and alloy - The
diantipyrylmethane photometric method for the determination of titanium
content
GB/T 223.18 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Iron, Steel and Alloy - The
Sodium Thiosulfate Separation Iodimetric Method for the Determination of
Copper Content
GB/T 223.23 Iron, Steel and Alloy - Determination of Nickel Content - The
Dimethylglyoxime Spectrophotometric Method
GB/T 223.26 Iron, steel and alloy - Determination of molybdenum content -
The thiocyanate spectrophotometric method
GB/T 223.27 Methods for chemical analysis of iron, steel and alloy - The
thiocyanate-butyl acetate extraction spectrophotometric method for the
determination of molybdenum content
GB/T 223.40 Iron, Steel and Alloy - Determination of Niobium Content by the
Sulphochlorophenol S Spectrophotometric Method
GB/T 223.60 Methods for chemical analysis of iron, steel and alloy - The
perchloric acid dehydration gravimetric method for the determination of
silicon content
GB/T 223.63 Methods for chemical analysis of iron, steel and alloy - The
sodium (potassium) periodate photometric method for the determination of
manganese content
GB/T 223.68 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Iron, Steel and Alloy - The
Potassium Iodate Titration Method after Combustion in the Pipe Furnace for
the Determination of Sulfur Content
GB/T 223.69 Iron, steel and alloy - Determination of carbon contents - Gas-
volumetric method after combustion in the pipe furnace
GB/T 223.75 Iron steel and alloy - Determination of boron content - Methanol
distillation-curcumin photometric method
GB/T 223.76 Methods for chemical analysis of iron, steel and alloy - The
flame atomic absorption spectrometric method for the determination of
vanadium content
GB/T 228.1 Metallic materials - Tensile testing - Part 1: Method of test at
room temperature (GB/T 228.1-2010, ISO 6892-1:2009 MOD)
GB/T 229 Metallic materials - Charpy pendulum impact test method (GB/T
229-2007, ISO 148-1:2006, MOD)
4 Classification and designation representation
4.1 According to GB/T 13304.1, the steel of this Part is classified into unalloyed
steel and low-alloy steel.
4.2 The steel designation consists of four parts: the first letter Q of Chinese
phonetic alphabet representing “Qu” of yield strength, specified minimum upper
yield strength value, the initials “KZ” of Chinese phonetic alphabet for “seismic-
improved”, quality grade symbol (C, D, E, F).
Example: Q3450KZE
Where:
Q - The first letter of Chinese phonetic alphabet of “Qu” for yield strength of steel;
345 - The specified minimum upper yield strength value, in megapascals (MPa);
KZ - Represent “seismic-improved”;
E - The quality grade is Grade E.
4.3 When the purchaser requires the steel plate to have the through-thickness
(Z-direction) characteristics, after the above specified designation, ADD the
through-thickness characteristics level of the steel plate, such as Q345KZEZ25.
5 Order content
5.1 Contracts or orders for ordering according to this Part shall include the
following:
a) Standard number;
b) Product type;
c) Steel grade + delivery condition + quality grade;
d) Dimension, shape, and tolerance;
e) Selected content of all requirements;
f) Type of inspection document.
5.2 Through negotiation between the supplier and the purchaser, and indicated
in the contract, the following content may be selected as the order content of
this Part. If the purchaser does not specify when providing the inquiry and order,
7.1.8 Through negotiation between the supplier and the purchaser, the
chemical composition inspection of steel products may be carried out.
Permissible tolerances for chemical composition of products shall meet the
requirements of GB/T 222.
7.2 Smelting method
The steel shall be smelted by an oxygen converter or an electric furnace. Unless
otherwise specified, the smelting method shall be selected by the supplier.
7.3 Delivery condition
The steels are generally delivered in the hot-rolled condition. Unless otherwise
agreed, the hot-rolled condition, normalized rolled, normalized or quenched and
tempered condition are allowed at the manufacturer’s discretion. The thermo-
mechanical rolling is not allowed at the manufacturer’s discretion. Through
negotiation between the supplier and the purchaser, thermo-mechanical rolling
may be applied to any steel grade. The delivery condition shall be stated in the
contract.
7.4 Mechanical and processing properties
7.4.1 The tensile and processing properties of Q235KZ and Q345KZ steel
grades shall comply with the requirements of Table 6. The mechanical and
processing properties of Q390KZ, Q420KZ, and Q460KZ steel grades shall
comply with the requirements of Table C.3 of Annex C.
Table 6 -- Tensile and processing properties of Q235KZ and Q345KZ
steel grades
7.4.2 The impact properties of the Q235KZ and Q345KZ steel grades shall
comply with the requirements of Table 7.
7.4.3 The tensile, impact, and bend test requirements for steel shall comply with
the relevant provisions of GB/T 34560.1.
Steel
grade
Upper yield strength ReH/MPa
Nominal thickness tb/mm Nominal thickness tb/mm Nominal thickness tb/mm Nominal thickness tb/mm
Tensile strength Rm/MPa Yield-strength ratioa ReH/Rm 180° bend testc Percentage elongation
after fracture
Note
a Through negotiation between the supplier and the purchaser, a lower yield-strength ratio may be specified.
b For the H section steel, t is the flange thickness; the maximum applicable thickness is 140 mm.
c D is the bending indenter diameter. a is the sample thickness.
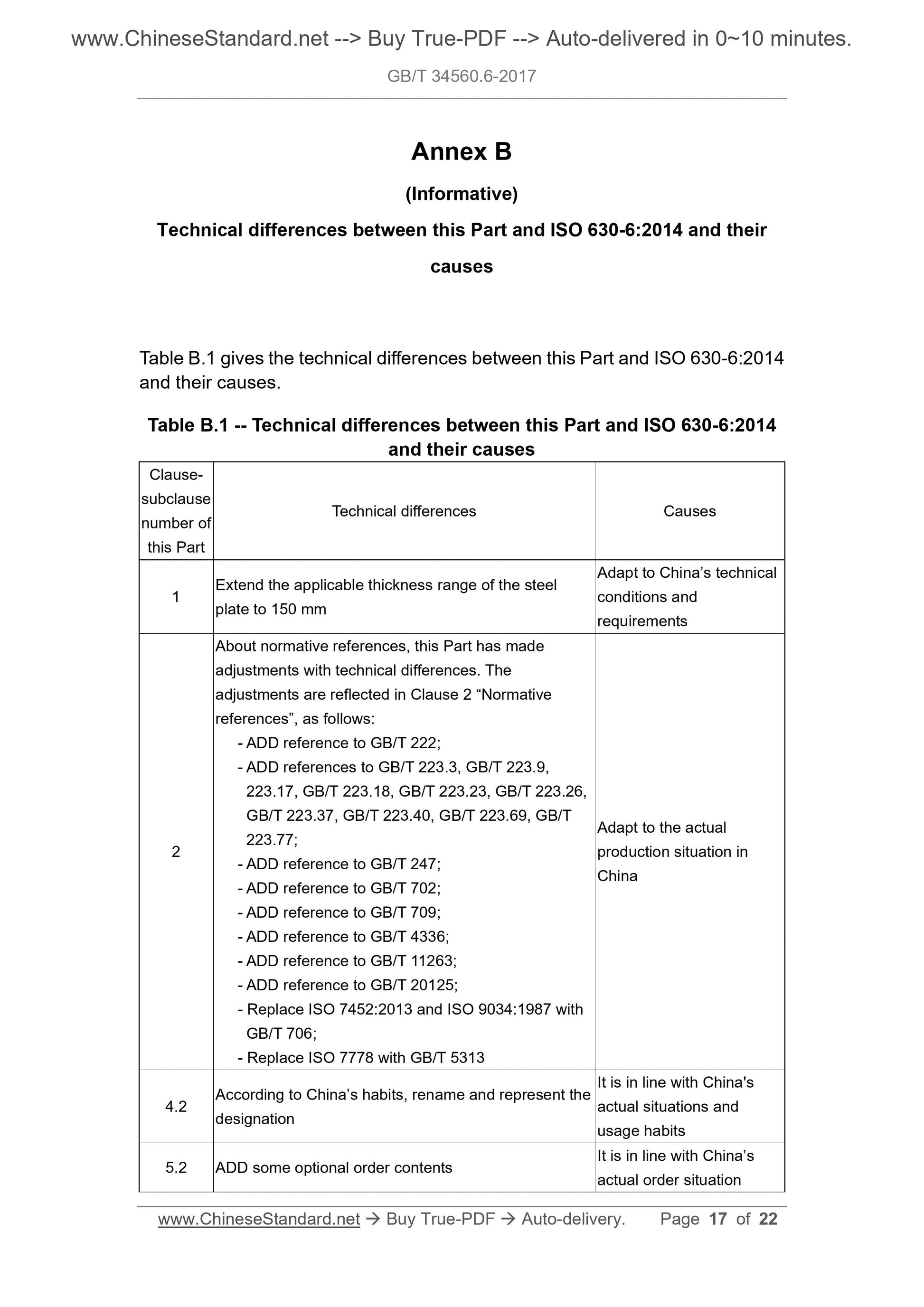
Annex B
(Informative)
Technical differences between this Part and ISO 630-6:2014 and their
causes
Table B.1 gives the technical differences between this Part and ISO 630-6:2014
and their causes.
Table B.1 -- Technical differences between this Part and ISO 630-6:2014
and their causes
Clause-
subclause
number of
this Part
Technical differences Causes
1 Extend the applicable thickness range of the steel plate to 150 mm
Adapt to China’s technical
conditions and
requirements
About normative references, this Part has made
adjustments with technical differences. The
adjustments are reflected in Clause 2 “Normative
references”, as follows:
- ADD reference to GB/T 222;
- ADD references to GB/T 223.3, GB/T 223.9,
223.17, GB/T 223.18, GB/T 223.23, GB/T 223.26,
GB/T 223.37, GB/T 223.40, GB/T 223.69, GB/T
223.77;
- ADD reference to GB/T 247;
- ADD reference to GB/T 702;
- ADD reference to GB/T 709;
- ADD reference to GB/T 4336;
- ADD reference to GB/T 11263;
- ADD reference to GB/T 20125;
- Replace ISO 7452:2013 and ISO 9034:1987 with
GB/T 706;
- Replace ISO 7778 with GB/T 5313
Adapt to the actual
production situation in
China
4.2 According to China’s habits, rename and represent the designation
It is in line with China's
actual situations and
usage habits
5.2 ADD some optional order contents It is in line with China’s actual order situation
GB/T 34560.6-2017
NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE
PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 77.140.01
H 40
Structural steels - Part 6: Technical delivery conditions
for seismic-improved structural steels for building
(ISO 630-6:2014, MOD)
ISSUED ON: OCTOBER 14, 2017
IMPLEMENTED ON: JULY 01, 2018
Issued by: General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and
Quarantine of the PRC;
Standardization Administration of the PRC.
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
1 Scope ... 5
2 Normative references ... 5
3 Terms and definitions ... 7
4 Classification and designation representation ... 8
5 Order content ... 8
6 Dimension, shape, weight and tolerance ... 9
7 Technical requirements ... 9
8 Test methods ... 13
9 Inspection rules ... 14
10 Package, mark, and certification ... 15
Annex A (Informative) Structural changes in this Part compared to ISO 630-
6:2014 ... 16
Annex B (Informative) Technical differences between this Part and ISO 630-
6:2014 and their causes ... 17
Annex C (Normative) Chemical composition, mechanical and processing
properties of Q390, Q420, and Q460 steels ... 19
Annex D (Normative) Carbon equivalent formulas and requirements ... 22
Structural steels - Part 6: Technical delivery conditions
for seismic-improved structural steels for building
1 Scope
This Part of GB/T 34560 specifies the terms and definitions, classification and
designation representation, order content, dimension, shape, weight and
tolerance, technical requirements, test methods, inspection rules, package,
mark, and certification of seismic-improved structural steels for building.
This Part applies to steel plates with a thickness of 6 mm~150 mm, wide flat
steels, and hot-rolled section steels with flange thickness not more than 140
mm (hereinafter referred to as “steels”).
2 Normative references
The following documents are indispensable for the application of this document.
For the dated references, only the editions with the dates indicated are
applicable to this document. For the undated references, the latest edition
(including all the amendments) are applicable to this document.
GB/T 222 Permissible Tolerances for Chemical Composition of Steel
Products
GB/T 223.3 Methods for chemical analysis of iron, steel and alloy - The
diantipyrylmethane phosphomolybdate gravimetric method for the
determination of phosphorus content
GB/T 223.10 Methods for chemical analysis of iron, steel and alloy - The
cupferron separation-chrome azurol S photometric method for the
determination of aluminium content
GB/T 223.11 Iron, steel and alloy - Determination of chromium content -
Visual titration or potentiometric titration method
GB/T 223.14 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Iron, Steel and Alloy - The N-
Benzoy-N-Phenylhydroxylamine Extraction Photometric Method for the
Determination of Vanadium Content
GB/T 223.17 Methods for chemical analysis of iron, steel and alloy - The
diantipyrylmethane photometric method for the determination of titanium
content
GB/T 223.18 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Iron, Steel and Alloy - The
Sodium Thiosulfate Separation Iodimetric Method for the Determination of
Copper Content
GB/T 223.23 Iron, Steel and Alloy - Determination of Nickel Content - The
Dimethylglyoxime Spectrophotometric Method
GB/T 223.26 Iron, steel and alloy - Determination of molybdenum content -
The thiocyanate spectrophotometric method
GB/T 223.27 Methods for chemical analysis of iron, steel and alloy - The
thiocyanate-butyl acetate extraction spectrophotometric method for the
determination of molybdenum content
GB/T 223.40 Iron, Steel and Alloy - Determination of Niobium Content by the
Sulphochlorophenol S Spectrophotometric Method
GB/T 223.60 Methods for chemical analysis of iron, steel and alloy - The
perchloric acid dehydration gravimetric method for the determination of
silicon content
GB/T 223.63 Methods for chemical analysi...
Share