1
/
of
12
PayPal, credit cards. Download editable-PDF and invoice in 1 second!
JB/T 1255-2014 English PDF (JBT1255-2014)
JB/T 1255-2014 English PDF (JBT1255-2014)
Regular price
$85.00 USD
Regular price
Sale price
$85.00 USD
Unit price
/
per
Shipping calculated at checkout.
Couldn't load pickup availability
Delivery: 3 seconds. Download true-PDF + Invoice.
Get QUOTATION in 1-minute: Click JB/T 1255-2014
Historical versions: JB/T 1255-2014
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll if blank)
JB/T 1255-2014: Rolling bearings - Parts made from high-carbon chromium bearing steels - Specifications for heat treatment
JB/T 1255-2014
JB
INDUSTRY STANDARD OF THE
PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 21.100.20
J 11
Record Number.
Replacing JB/T 1255-2001
Rolling Bearings - Parts Made from High-carbon
Chromium Bearing Steels -
Specifications for Heat Treatment
ISSUED ON. MAY 6, 2014
IMPLEMENTED ON. OCTOBER 1, 2014
Issued by. Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of the
People’s Republic of China
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
1 Scope ... 5
2 Normative References ... 5
3 Technical Requirements ... 6
4 Test Method ... 9
Appendix A (Informative) Effective Wall Thickness of Ring and Effective
Diameter of Rollers ... 17
Appendix B (Normative) Test Specifications for Crushing Load of Steel
Ball and Crushing Load Values ... 19
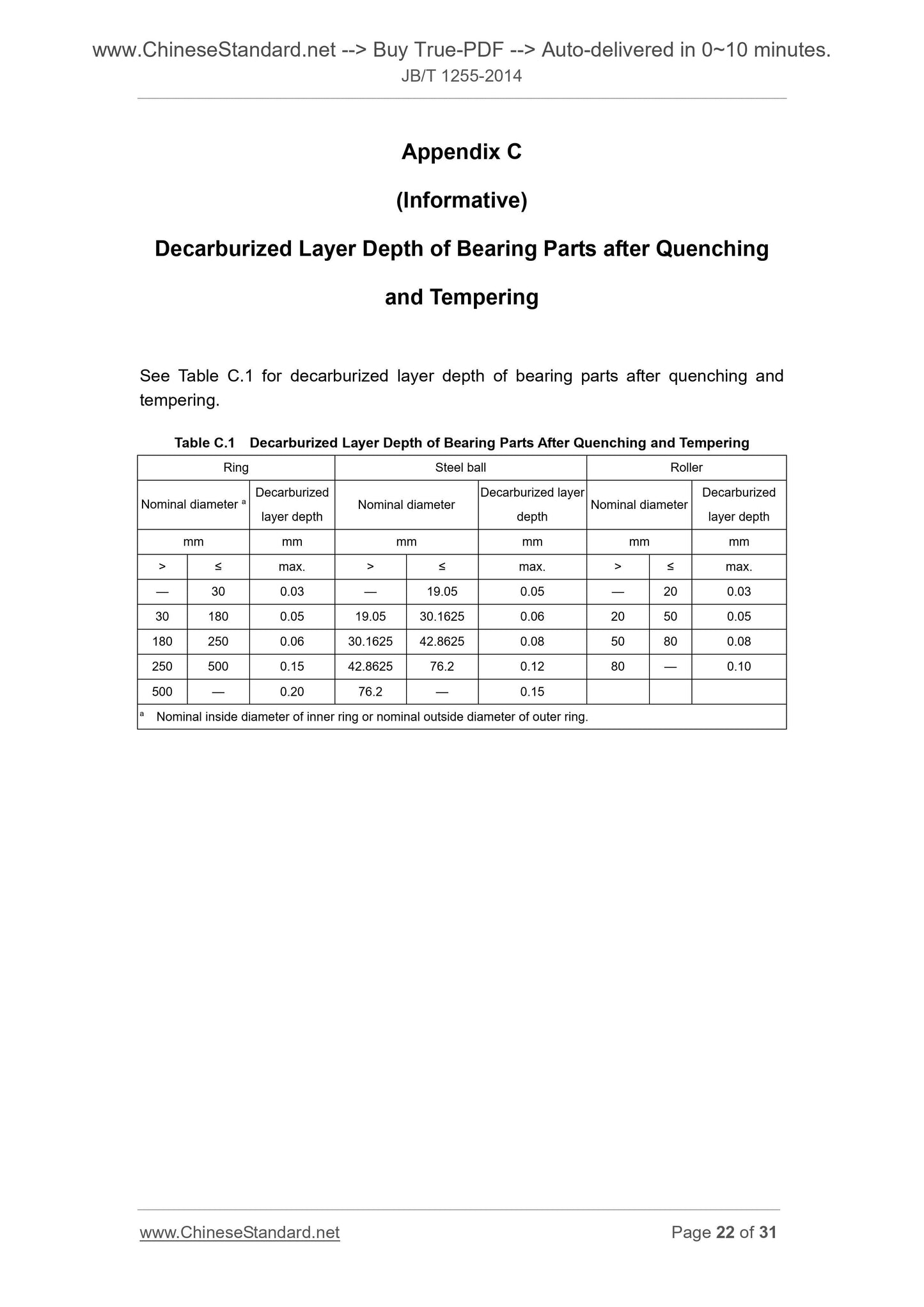
Appendix C (Informative) Decarburized Layer Depth of Bearing Parts
after Quenching and Tempering ... 22
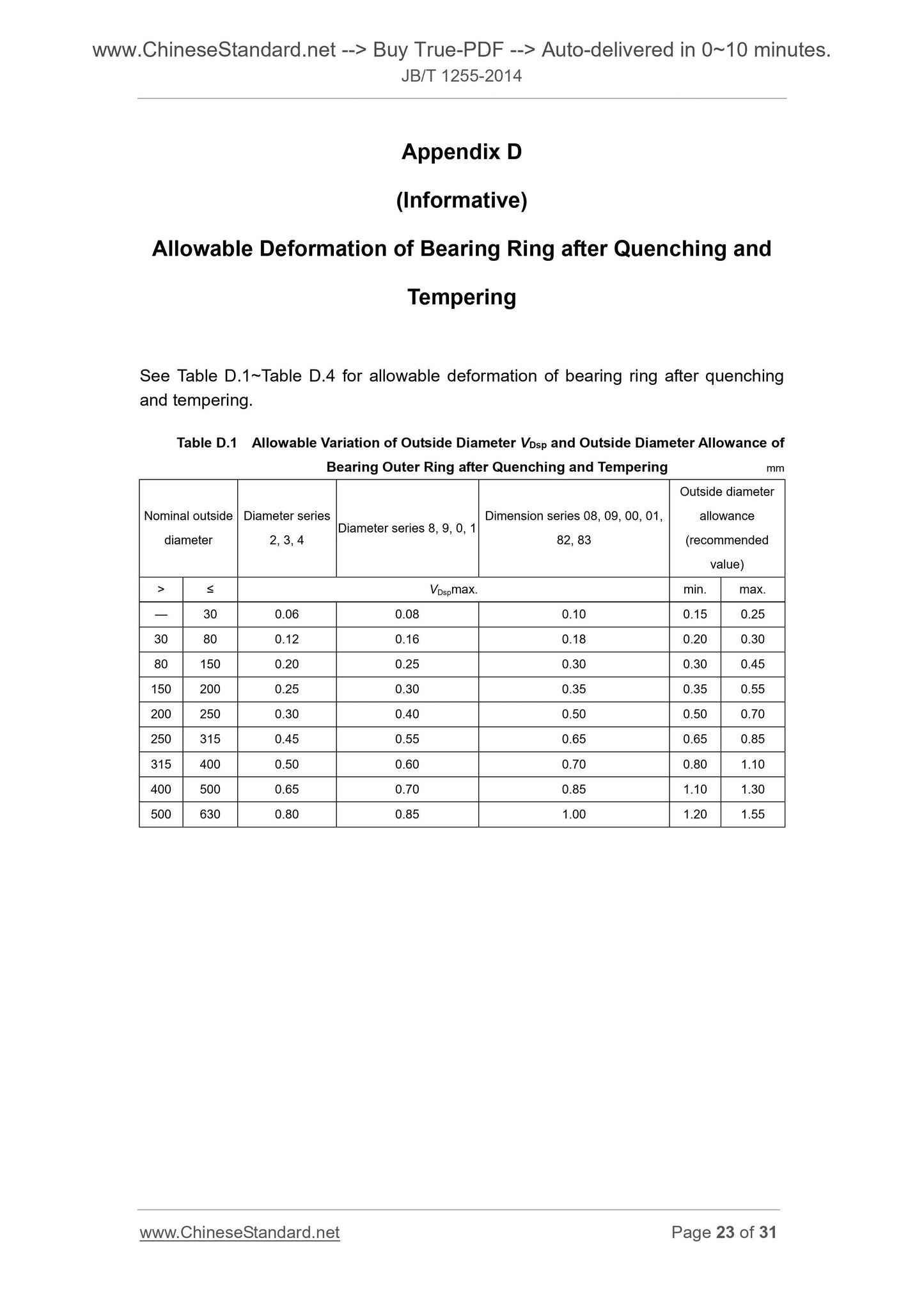
Appendix D (Informative) Allowable Deformation of Bearing Ring after
Quenching and Tempering ... 23
Appendix E (Informative) Residual Austenite Content of Bearing Parts
after Quenching and Tempering ... 26
Appendix F (Normative) Hardness Correction of Curved Surface ... 27
Appendix G (Normative) Acid Cleaning Inspection Specifications ... 29
Foreword
This standard is drafted according to the rules given in GB/T 1.1-2009.
This standard replaces JB/T 1255-2001 Specification for Heat-treatment of Rolling
Bearing Parts Made from High Carbon Chromium Steel.
Compared with JB/T 1255-2001, except editorial changes, this standard has the main
technical changes as follows.
— The standard name is modified (see cover and first page of this edition; cover
and first page of 2001 edition);
— Scope is partially modified (see Chapter 1 of this edition; Chapter 1 of 2001
edition);
— Technical requirements after spheroidizing annealing are modified (see Table 1
of this edition, Table 1 of 2001 edition);
— The hardness of partial bearing parts Martensite after quenching and tempering
is modified (see Table 2 of this edition; Table 2 of 2001 edition);
— The requirements for microscopic structure of partial bearing parts Martensite
after quenching and tempering are modified (see Table 4 of this edition; Table 4
of 2001 edition);
— The technical requirements of GCr15SiMo Bainite after isothermal quenching
are added (see Table 5 of this edition);
— The technical requirements of bearing parts Bainite after isothermal quenching
are modified (see Table 5 of this edition; Table 5 of 2001 edition);
— The technical requirements and test methods for residual austenite content and
appearance quality are added (see Table 6 and Table 7 of this edition);
— The technical requirements, test methods as well as grade figures for fractures
after quenching and tempering of bearing parts Martensite are deleted (see
Table 5, Table 7 and Fifth Grade Figure of 2001 edition);
— The test of microscopic structure after 1000× magnification is added (Table 7 of
2001 edition);
— The grade figures of annealed, quenched and tempered structure under 500
times of magnification are modified and the grade figures under 500×
magnification are added (see First and Second Grade Figures of this edition;
Rolling Bearings - Parts Made from High-carbon
Chromium Bearing Steels -
Specifications for Heat Treatment
1 Scope
This standard specifies the technical requirements and test methods of the annealed,
quenched and tempered rolling bearing ring and rolling element (hereinafter referred
to as "bearing parts") made from GCr15, GCr15SiMn, GCr15SiMo and GCr18Mo
steels which meet those specified in GB/T 18254-2002.
This standard is applicable to the heat treatment quality test of bearing parts during
process and finished parts made from above-mentioned steels and also applicable to
the heat treatment quality test of bearing parts made from other high-carbon
chromium steels. The bearing parts with special requirements shall be in accordance
with corresponding product drawings.
2 Normative References
The following referenced documents are indispensable for the application of this
document. For dated references, only the dated editions apply. For undated
references, the latest editions (including any amendments) apply.
GB/T 230.1 Metallic Materials - Rockwell Hardness Test - Part 1. Test method
(scales A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, K, N, T)
GB/T 231.1 Metallic Materials - Brinell Hardness Test - Part 1. Test Method
GB/T 1172 Conversion of Hardness and Strength for Ferrous Metal
GB/T 4340.1 Metallic Materials - Vickers Hardness - Part 1. Test Method
GB/T 6394 Metal - methods for Estimating the Average Grain Size
GB/T 17394 Metallic Materials - Leeb Hardness Test
GB/T 18254 High-carbon Chromium Bearing Steel
GB/T 24606 Rolling Bearings - Non-destructive Testing - Magnetic Particle
Testing
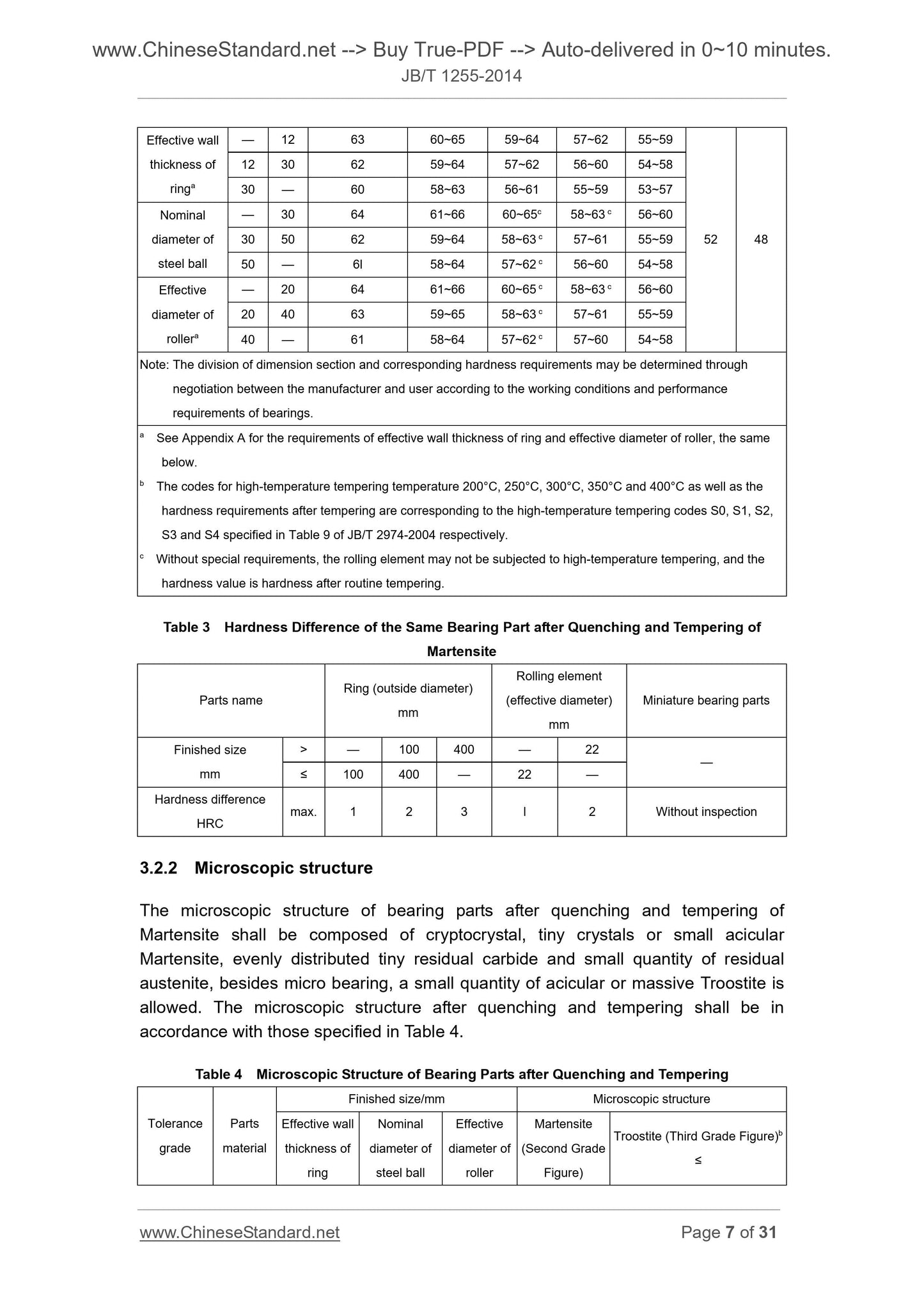
Effective wall
thickness of
ringa
— 12 63 60~65 59~64 57~62 55~59
12 30 62 59~64 57~62 56~60 54~58
30 — 60 58~63 56~61 55~59 53~57
Nominal
diameter of
steel ball
— 30 64 61~66 60~65c 58~63 c 56~60
30 50 62 59~64 58~63 c 57~61 55~59
50 — 6l 58~64 57~62 c 56~60 54~58
Effective
diameter of
rollera
— 20 64 61~66 60~65 c 58~63 c 56~60
20 40 63 59~65 58~63 c 57~61 55~59
40 — 61 58~64 57~62 c 57~60 54~58
Note. The division of dimension section and corresponding hardness requirements may be determined through
negotiation between the manufacturer and user according to the working conditions and performance
requirements of bearings.
a See Appendix A for the requirements of effective wall thickness of ring and effective diameter of roller, the same
below.
b The codes for high-temperature tempering temperature 200°C, 250°C, 300°C, 350°C and 400°C as well as the
hardness requirements after tempering are corresponding to the high-temperature tempering codes S0, S1, S2,
S3 and S4 specified in Table 9 of JB/T 2974-2004 respectively.
c Without special requirements, the rolling element may not be subjected to high-temperature tempering, and the
hardness value is hardness after routine tempering.
Table 3 Hardness Difference of the Same Bearing Part after Quenching and Tempering of
Martensite
Parts name Ring (outside diameter) mm
Rolling element
(effective diameter)
mm
Miniature bearing parts
Finished size
mm
> — 100 400 — 22
≤ 100 400 — 22 —
Hardness difference
HRC max. 1 2 3 l 2 Without inspection
3.2.2 Microscopic structure
The microscopic structure of bearing parts after quenching and tempering of
Martensite shall be composed of cryptocrystal, tiny crystals or small acicular
Martensite, evenly distributed tiny residual carbide and small quantity of residual
austenite, besides micro bearing, a small quantity of acicular or massive Troostite is
allowed. The microscopic structure after quenching and tempering shall be in
accordance with those specified in Table 4.
Table 4 Microscopic Structure of Bearing Parts after Quenching and Tempering
Tolerance
grade
Parts
material
Finished size/mm Microscopic structure
Effective wall
thickness of
ring
Nominal
diameter of
steel ball
Effective
diameter of
roller
Martensite
(Second Grade
Figure)
Troostite (Third Grade Figure)b
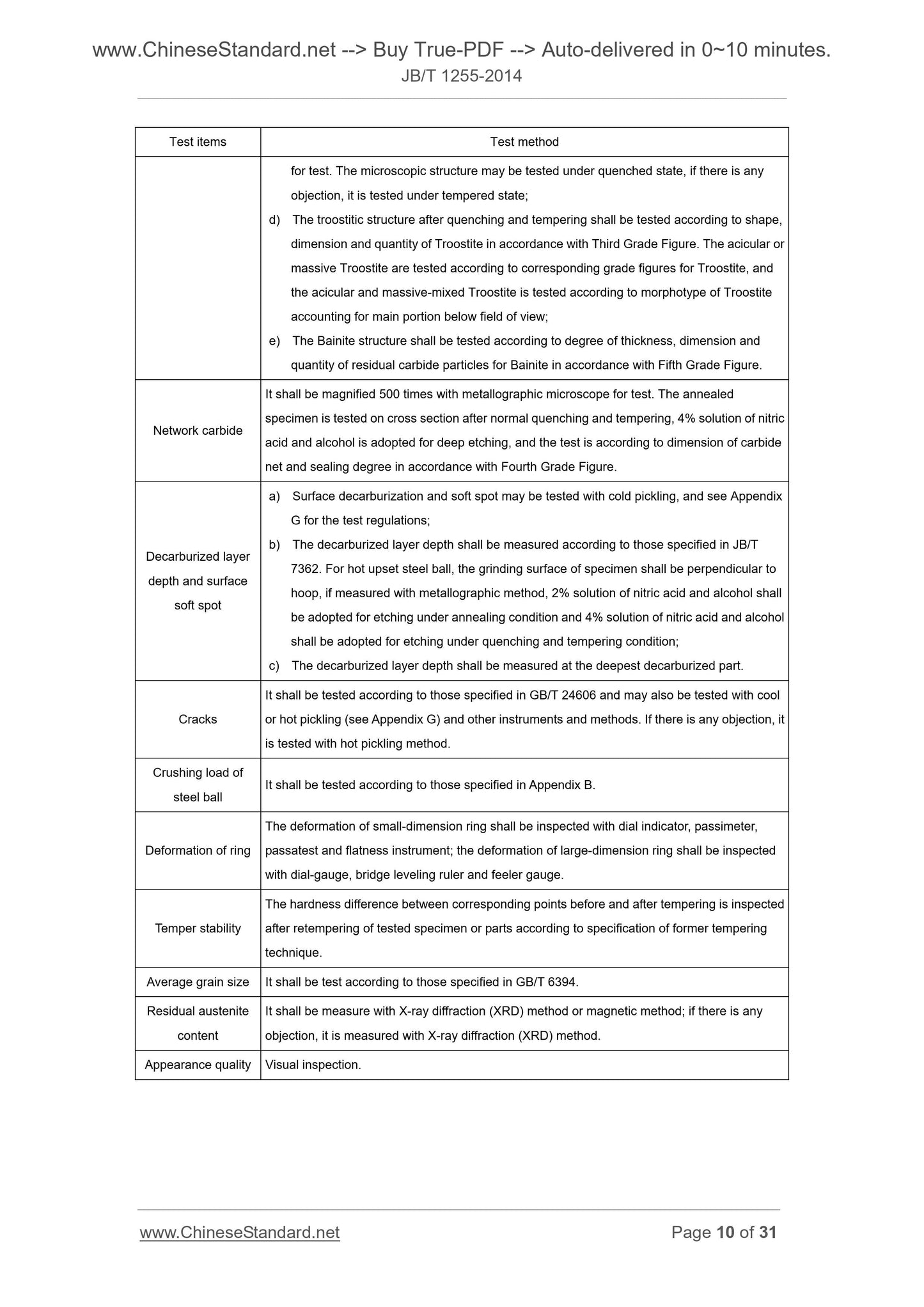
Test items Test method
for test. The microscopic structure may be tested under quenched state, if there is any
objection, it is tested under tempered state;
d) The troostitic structure after quen...
Get QUOTATION in 1-minute: Click JB/T 1255-2014
Historical versions: JB/T 1255-2014
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll if blank)
JB/T 1255-2014: Rolling bearings - Parts made from high-carbon chromium bearing steels - Specifications for heat treatment
JB/T 1255-2014
JB
INDUSTRY STANDARD OF THE
PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 21.100.20
J 11
Record Number.
Replacing JB/T 1255-2001
Rolling Bearings - Parts Made from High-carbon
Chromium Bearing Steels -
Specifications for Heat Treatment
ISSUED ON. MAY 6, 2014
IMPLEMENTED ON. OCTOBER 1, 2014
Issued by. Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of the
People’s Republic of China
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
1 Scope ... 5
2 Normative References ... 5
3 Technical Requirements ... 6
4 Test Method ... 9
Appendix A (Informative) Effective Wall Thickness of Ring and Effective
Diameter of Rollers ... 17
Appendix B (Normative) Test Specifications for Crushing Load of Steel
Ball and Crushing Load Values ... 19
Appendix C (Informative) Decarburized Layer Depth of Bearing Parts
after Quenching and Tempering ... 22
Appendix D (Informative) Allowable Deformation of Bearing Ring after
Quenching and Tempering ... 23
Appendix E (Informative) Residual Austenite Content of Bearing Parts
after Quenching and Tempering ... 26
Appendix F (Normative) Hardness Correction of Curved Surface ... 27
Appendix G (Normative) Acid Cleaning Inspection Specifications ... 29
Foreword
This standard is drafted according to the rules given in GB/T 1.1-2009.
This standard replaces JB/T 1255-2001 Specification for Heat-treatment of Rolling
Bearing Parts Made from High Carbon Chromium Steel.
Compared with JB/T 1255-2001, except editorial changes, this standard has the main
technical changes as follows.
— The standard name is modified (see cover and first page of this edition; cover
and first page of 2001 edition);
— Scope is partially modified (see Chapter 1 of this edition; Chapter 1 of 2001
edition);
— Technical requirements after spheroidizing annealing are modified (see Table 1
of this edition, Table 1 of 2001 edition);
— The hardness of partial bearing parts Martensite after quenching and tempering
is modified (see Table 2 of this edition; Table 2 of 2001 edition);
— The requirements for microscopic structure of partial bearing parts Martensite
after quenching and tempering are modified (see Table 4 of this edition; Table 4
of 2001 edition);
— The technical requirements of GCr15SiMo Bainite after isothermal quenching
are added (see Table 5 of this edition);
— The technical requirements of bearing parts Bainite after isothermal quenching
are modified (see Table 5 of this edition; Table 5 of 2001 edition);
— The technical requirements and test methods for residual austenite content and
appearance quality are added (see Table 6 and Table 7 of this edition);
— The technical requirements, test methods as well as grade figures for fractures
after quenching and tempering of bearing parts Martensite are deleted (see
Table 5, Table 7 and Fifth Grade Figure of 2001 edition);
— The test of microscopic structure after 1000× magnification is added (Table 7 of
2001 edition);
— The grade figures of annealed, quenched and tempered structure under 500
times of magnification are modified and the grade figures under 500×
magnification are added (see First and Second Grade Figures of this edition;
Rolling Bearings - Parts Made from High-carbon
Chromium Bearing Steels -
Specifications for Heat Treatment
1 Scope
This standard specifies the technical requirements and test methods of the annealed,
quenched and tempered rolling bearing ring and rolling element (hereinafter referred
to as "bearing parts") made from GCr15, GCr15SiMn, GCr15SiMo and GCr18Mo
steels which meet those specified in GB/T 18254-2002.
This standard is applicable to the heat treatment quality test of bearing parts during
process and finished parts made from above-mentioned steels and also applicable to
the heat treatment quality test of bearing parts made from other high-carbon
chromium steels. The bearing parts with special requirements shall be in accordance
with corresponding product drawings.
2 Normative References
The following referenced documents are indispensable for the application of this
document. For dated references, only the dated editions apply. For undated
references, the latest editions (including any amendments) apply.
GB/T 230.1 Metallic Materials - Rockwell Hardness Test - Part 1. Test method
(scales A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, K, N, T)
GB/T 231.1 Metallic Materials - Brinell Hardness Test - Part 1. Test Method
GB/T 1172 Conversion of Hardness and Strength for Ferrous Metal
GB/T 4340.1 Metallic Materials - Vickers Hardness - Part 1. Test Method
GB/T 6394 Metal - methods for Estimating the Average Grain Size
GB/T 17394 Metallic Materials - Leeb Hardness Test
GB/T 18254 High-carbon Chromium Bearing Steel
GB/T 24606 Rolling Bearings - Non-destructive Testing - Magnetic Particle
Testing
Effective wall
thickness of
ringa
— 12 63 60~65 59~64 57~62 55~59
12 30 62 59~64 57~62 56~60 54~58
30 — 60 58~63 56~61 55~59 53~57
Nominal
diameter of
steel ball
— 30 64 61~66 60~65c 58~63 c 56~60
30 50 62 59~64 58~63 c 57~61 55~59
50 — 6l 58~64 57~62 c 56~60 54~58
Effective
diameter of
rollera
— 20 64 61~66 60~65 c 58~63 c 56~60
20 40 63 59~65 58~63 c 57~61 55~59
40 — 61 58~64 57~62 c 57~60 54~58
Note. The division of dimension section and corresponding hardness requirements may be determined through
negotiation between the manufacturer and user according to the working conditions and performance
requirements of bearings.
a See Appendix A for the requirements of effective wall thickness of ring and effective diameter of roller, the same
below.
b The codes for high-temperature tempering temperature 200°C, 250°C, 300°C, 350°C and 400°C as well as the
hardness requirements after tempering are corresponding to the high-temperature tempering codes S0, S1, S2,
S3 and S4 specified in Table 9 of JB/T 2974-2004 respectively.
c Without special requirements, the rolling element may not be subjected to high-temperature tempering, and the
hardness value is hardness after routine tempering.
Table 3 Hardness Difference of the Same Bearing Part after Quenching and Tempering of
Martensite
Parts name Ring (outside diameter) mm
Rolling element
(effective diameter)
mm
Miniature bearing parts
Finished size
mm
> — 100 400 — 22
≤ 100 400 — 22 —
Hardness difference
HRC max. 1 2 3 l 2 Without inspection
3.2.2 Microscopic structure
The microscopic structure of bearing parts after quenching and tempering of
Martensite shall be composed of cryptocrystal, tiny crystals or small acicular
Martensite, evenly distributed tiny residual carbide and small quantity of residual
austenite, besides micro bearing, a small quantity of acicular or massive Troostite is
allowed. The microscopic structure after quenching and tempering shall be in
accordance with those specified in Table 4.
Table 4 Microscopic Structure of Bearing Parts after Quenching and Tempering
Tolerance
grade
Parts
material
Finished size/mm Microscopic structure
Effective wall
thickness of
ring
Nominal
diameter of
steel ball
Effective
diameter of
roller
Martensite
(Second Grade
Figure)
Troostite (Third Grade Figure)b
Test items Test method
for test. The microscopic structure may be tested under quenched state, if there is any
objection, it is tested under tempered state;
d) The troostitic structure after quen...
Share