1
/
of
9
PayPal, credit cards. Download editable-PDF and invoice in 1 second!
JB/T 5000.3-2007 English PDF (JB/T5000.3-2007)
JB/T 5000.3-2007 English PDF (JB/T5000.3-2007)
Regular price
$85.00 USD
Regular price
Sale price
$85.00 USD
Unit price
/
per
Shipping calculated at checkout.
Couldn't load pickup availability
Delivery: 3 seconds. Download true-PDF + Invoice.
Get QUOTATION in 1-minute: Click JB/T 5000.3-2007
Historical versions: JB/T 5000.3-2007
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll if blank)
JB/T 5000.3-2007: Heavy mechanical general techniques - Part 3: And standards welding
JB/T 5000.3-2007
JB
NATIONAL MACHINERY INDUSTRY STANDARD
OF THE PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 25.160
J 33
Record number. 21697-2007
Replacing JB/T 5000.3-1998
Heavy mechanical general techniques
- Part 3. And standards welding
ISSUED ON. AUGUST 28, 2007
IMPLEMENTED ON. FEBRUARY 1, 2008
Issued by. National Development and Reform Commission, People’s
Republic of China
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
1 Scope ... 5
2 Normative references ... 5
3 General requirements ... 6
4 Preliminary straightening of steel ... 7
5 Forming bending of steel ... 8
6 Welding assembly ... 11
7 Welding ... 12
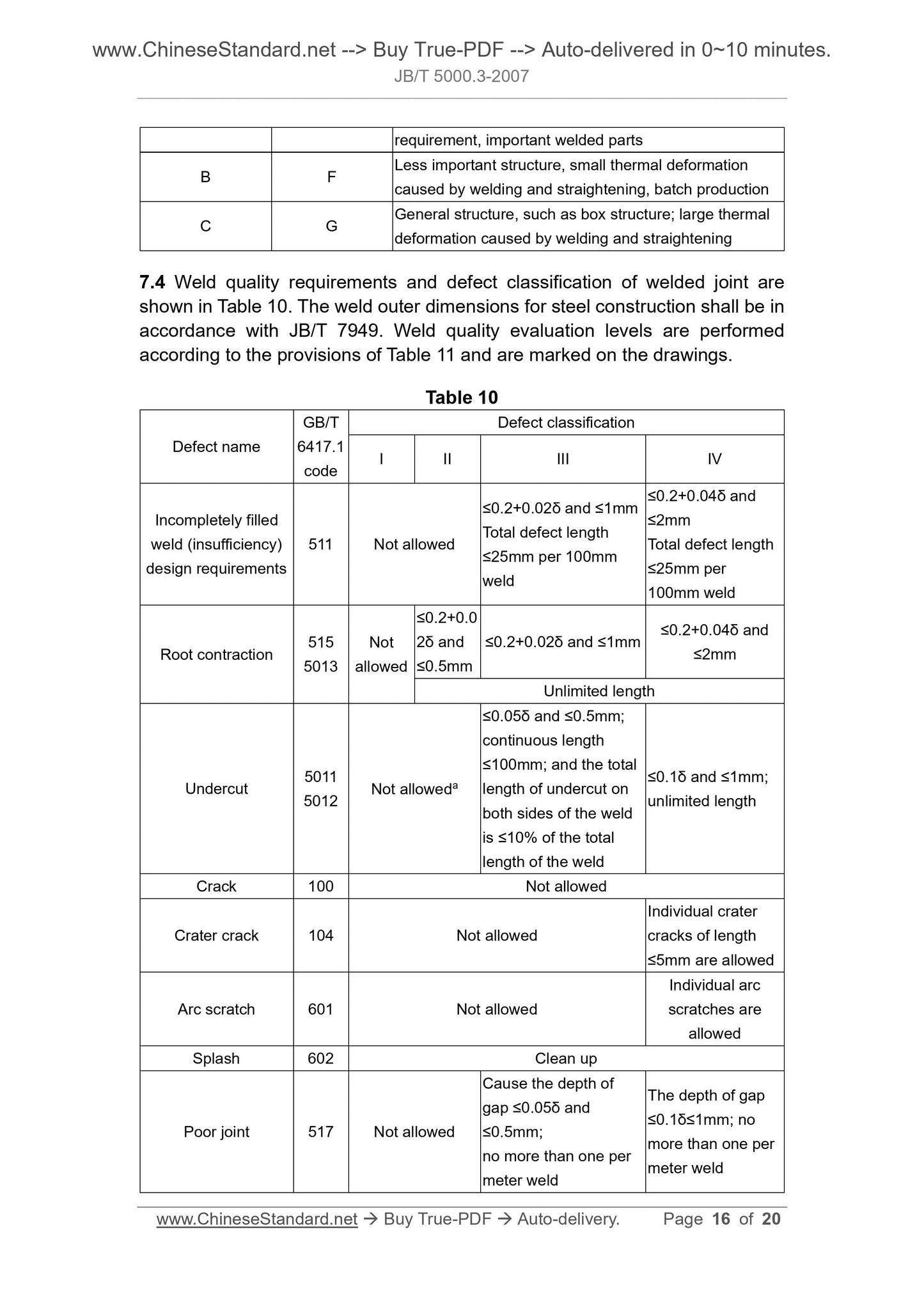
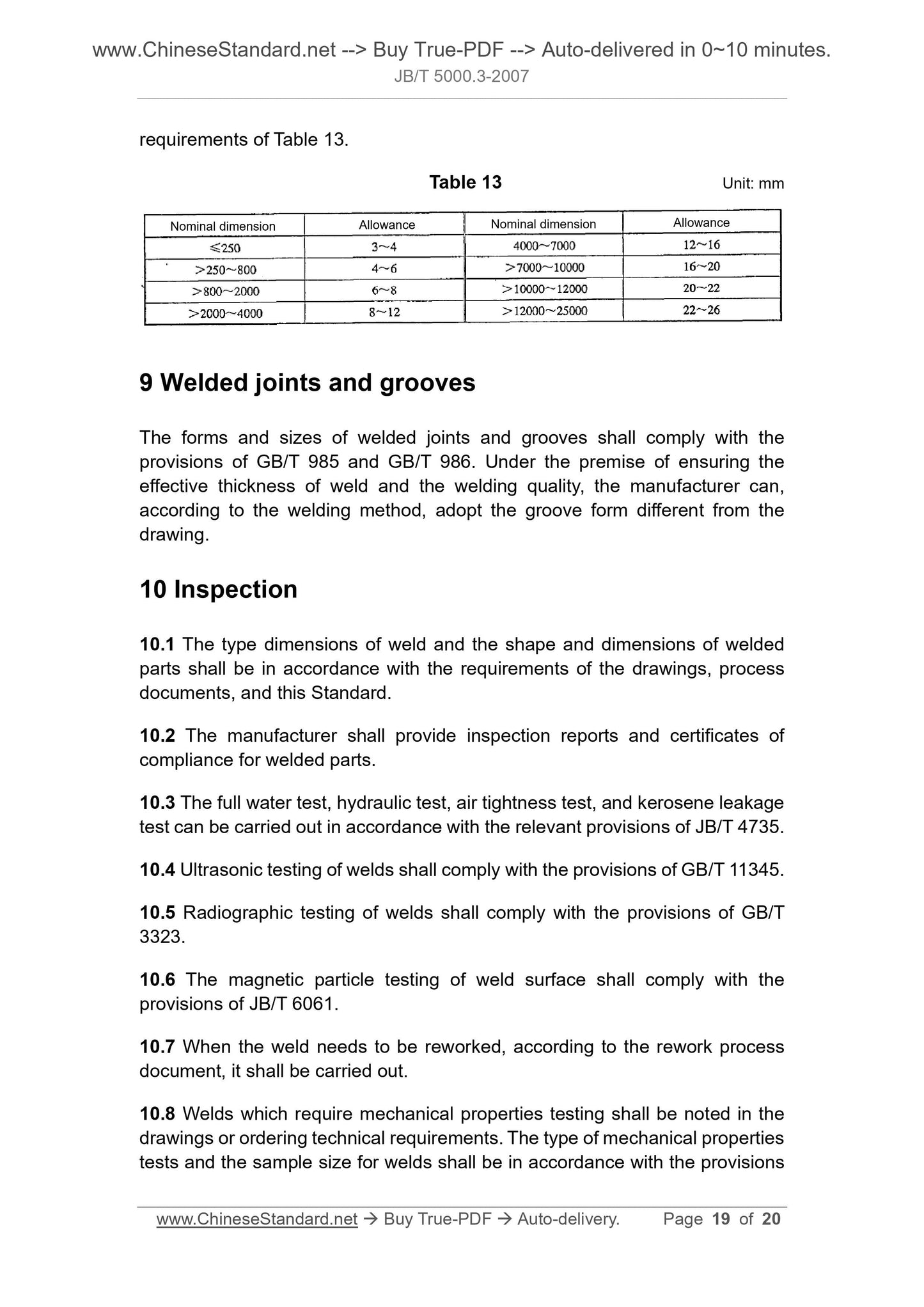
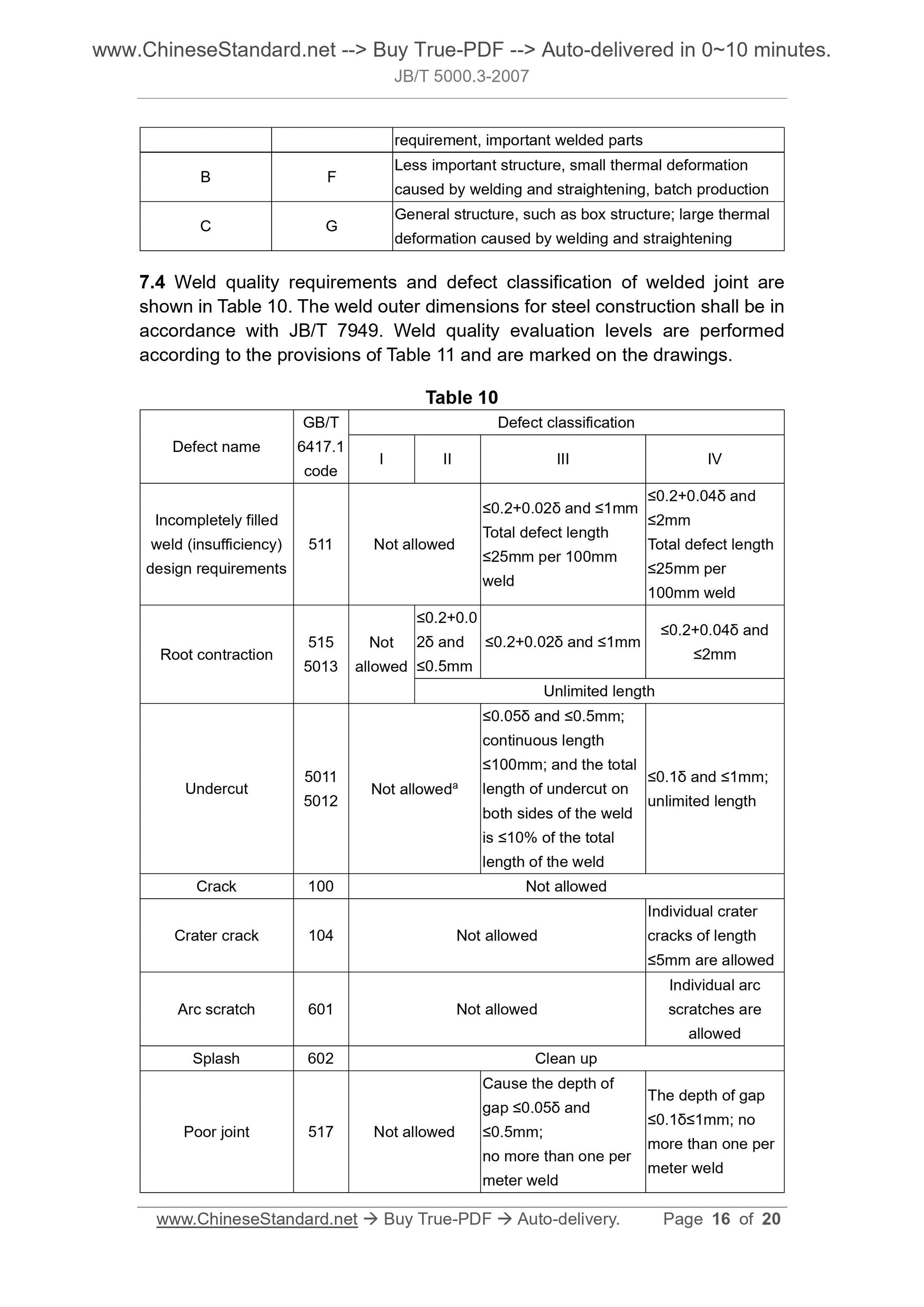
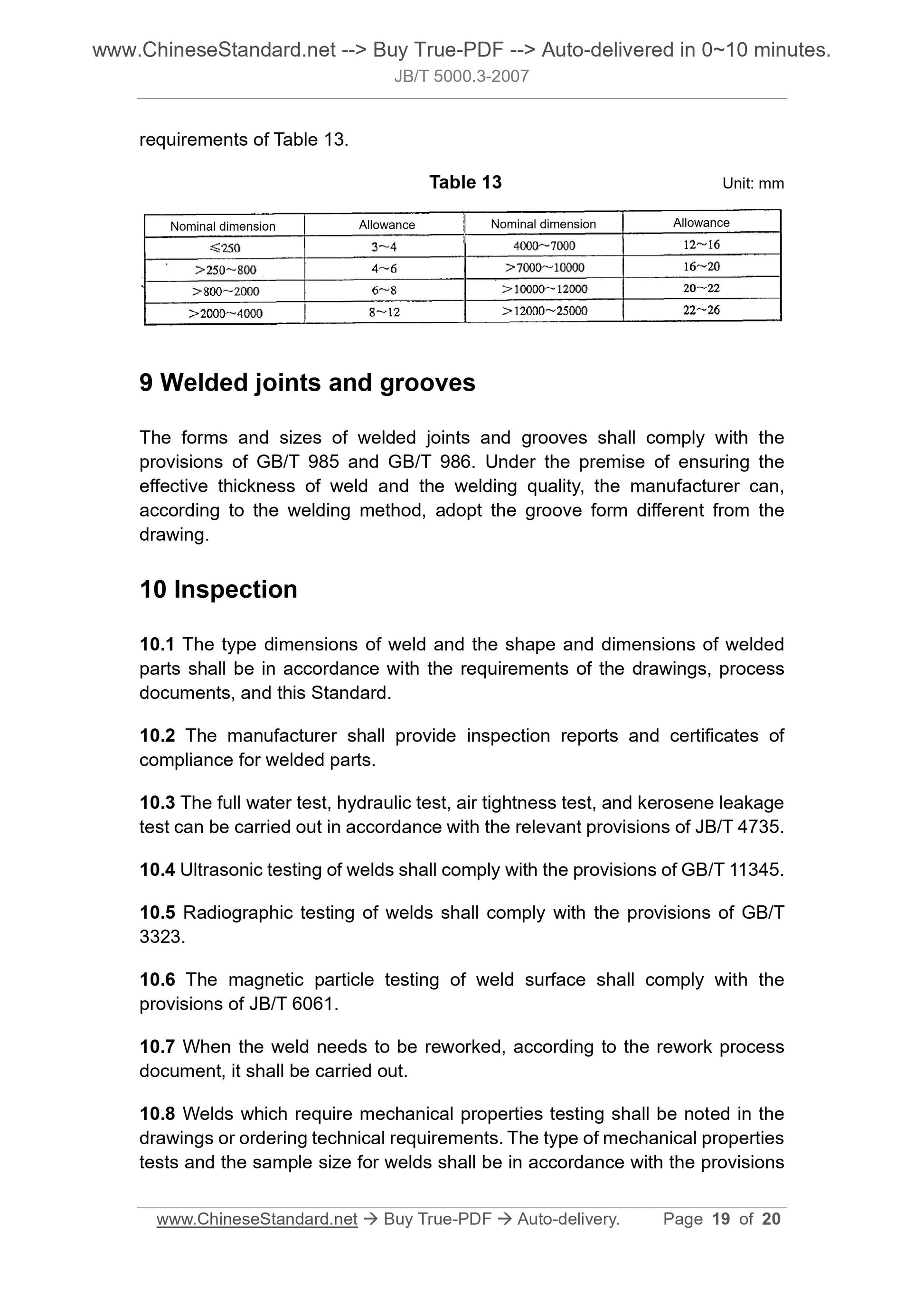
8 Machining allowance of welded structural parts ... 18
9 Welded joints and grooves ... 19
10 Inspection ... 19
11 Drawing indications ... 20
Foreword
JB/T 5000 “Heavy mechanical general techniques and standards” is divided
into 15 parts.
- Part 1. Check of product;
- Part 2. Oxygen cutting workpiece;
- Part 3. And standards welding [Translator note. should be “Welding”];
- Part 4. Iron Casting;
- Part 5. Non-ferrous casting;
- Part 6. Steel Castings;
- Part 7. Repair welding for steel castings;
- Part 8. Forging;
- Part 9. Cutting;
- Part 10. Assembly;
- Part 11. Attached piping;
- Part 12. Paint;
- Part 13. Packing;
- Part 14. Non-destructive inspection of cast steel;
- Part 15. Non-destructive inspection of forged steel.
This Part is Part 3 of JB/T 5000.
This Part replaces JB/T 5000.3-1998 “The heavy mechanical general
techniques and standards - Welding”.
As compared with JB/T 5000.3-1998, the main changes of this Part are as
follows.
- ADD the requirement for chamfering the edges and corners of the bent steel
part when the steel is rolled.
- ADD length, weld angle, and quality requirements for tack weld.
Heavy mechanical general techniques
- Part 3. And standards welding
1 Scope
This Part of JB/T 5000 specifies the technical requirements, inspection methods,
and drawing indications of steel welded parts.
This Part applies to steel welded parts by shielded metal arc welding, gas
shielded welding, and submerged arc welding in heavy machinery and
components.
Where there are no special requirements in product drawings, technical
documents, and ordering technical conditions, the provisions of this Part shall
be complied with.
2 Normative references
The clauses in the following documents, by reference in this Part of JB/T 5000,
constitute the clauses of this Part. For the dated references, the subsequent
amendments (not including errata content) or revisions do not apply to this Part.
However, parties which have reached an agreement according to this Part are
encouraged to study whether the latest edition of these documents can be used.
For the undated references, the latest edition is applicable to this Part.
GB/T 324 Welds - symbolic representation on drawings (GB/T 324-1988, eqv
ISO 2553.1989)
GB/T 985 Basic forms and sizes of weld grooves for gas welding, manual
arc welding and gas-shielded welding
GB/T 986 Basic forms and sizes of weld grooves for submerged arc welding
GB/T 2649 Methods of sampling for mechanical properties tests of welded
joint
GB/T 2650 Impact test methods on welded joints
GB/T 2651 Tensile test method on welded joints
GB/T 2652 Tensile test methods on weld and deposited metal
GB/T 2653 Methods of bend and compression tests for welded joint
GB/T 2654 Methods of hardness tests for welded joint and surfacing metal
GB/T 3323 Radiographic examination of fusion welded joints in metallic
materials (GB/T 3323-2005, EN 135.1997, MOD)
GB/T 11345 Non-destructive testing of welds - Ultrasonic testing -
Techniques, testing levels, and assessment
JB/T 3223 Welding material quality management procedures
JB/T 4735 Steel welded atmospheric pressure vessels
JB/T 5000.2 Heavy mechanical general techniques and standards - Part 2.
Oxygen cutting workpiece
JB/T 5000.11 Heavy mechanical general techniques and standards - Part 11.
Attached piping
JB/T 5000.12 Heavy mechanical general techniques and standards - Part 12.
Paint
JB/T 5926 Vibrating stress relief effect - Evaluation methods
JB/T 6046 Welding assembly for carbon steel and low alloy steel - Post-
welding heat treatment method
JB/T 6061 Non-destructive testing - Magnetic particle testing of welds
JB/T 7949 Weld outer dimensions for steel construction
3 General requirements
3.1 Welded parts shall be manufactured in accordance with the design drawings,
process documents, and this Part.
3.2 The steel grade, specifications, and dimensions of the raw materials (steel
sheets, section steel, and steel pipes, etc.) used to manufacture the welded
parts shall comply with the requirements of design drawings. For material
substitution, substitution sheet shall be handled in accordance with relevant
regulations.
3.3 Raw materials and welding materials (welding rods, welding wire, flux,
shield gas, etc.) used to manufacture welded parts shall, when entering the
factory, based on the certificate of compliance provided by the supplier,
5 Forming bending of steel
5.1 For the rolling bending of steel, when the bending radius (inner radius) is
greater than the following values, cold bending can be carried out (SEE Figure
1). However, regardless of cold bending or hot bending, the edges and corners
of the steel sheet near the bent part shall be chamfered.
5.1.1 Steel sheet. For low alloy steel, R≥25δ;
For low carbon steel, R≥20δ.
R - Bending radius; δ - Thickness of steel sheet.
5.1.2 I-beam. R≥25H or R≥25B (depending on the direction of bending);
H - I-beam’s height; B - I-beam’s width.
5.1.3 Channel steel. R≥45B or R≥25H (depending on the direction of bending);
H - Channel steel’s height; B - Channel steel’s width.
5.1.4 Angle steel. R≥45B;
B - Angle steel’s edge-width (for unequal angle steel,
depending on the direction of bending).
5.2 For the rolling bending of steel, when the bending radius (inner radius) is
less than the values specified in 5.1, according to the specific situation, the
technician shall determine whether to perform annealing heat treatment after
hot bending or cold bending.
5.3 The tolerances for the dimensions of bend formed cylinder shall be in
accordance with Figure 2 and Table 3.
5.4 The unfitness of butt joint e for the butt joint between cylinders or for the
longitudinal joint of cylinder shall not exceed 20% of thickness and no more
than 4mm (SEE Figure 3 and Figure 4).
5.5 For the bend forming of the pipe, during hot bending, the heating
temperature is 900°C~1000°C. During bending, the temperature shall not be
lower than 700°C. Cold bending shall be carried out on a special pipe bender.
5.6 The bending radius R of the pipe (SEE Figure 5) shall comply with the
provisions of JB/T 5000.11.
7.1.1 Welders shall be specially trained and qualified before they can perform
welding work.
7.1.2 If the steel is not pretreated, before welding, the surface dirt of welding
area shall be removed, such as rust scale, oil stain, paint, and other impurities
which affect the quality of weld. The cleaning area is not less than 20mm from
the edge of the weld.
7.1.3 During open-air welding, in case of rain, snow, heavy fog, and strong wind,
if no protective measures are taken, welding shall not be carried out.
7.2 Preheating before welding.
7.2.1 Welded parts of low carbon stee...
Get QUOTATION in 1-minute: Click JB/T 5000.3-2007
Historical versions: JB/T 5000.3-2007
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll if blank)
JB/T 5000.3-2007: Heavy mechanical general techniques - Part 3: And standards welding
JB/T 5000.3-2007
JB
NATIONAL MACHINERY INDUSTRY STANDARD
OF THE PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 25.160
J 33
Record number. 21697-2007
Replacing JB/T 5000.3-1998
Heavy mechanical general techniques
- Part 3. And standards welding
ISSUED ON. AUGUST 28, 2007
IMPLEMENTED ON. FEBRUARY 1, 2008
Issued by. National Development and Reform Commission, People’s
Republic of China
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
1 Scope ... 5
2 Normative references ... 5
3 General requirements ... 6
4 Preliminary straightening of steel ... 7
5 Forming bending of steel ... 8
6 Welding assembly ... 11
7 Welding ... 12
8 Machining allowance of welded structural parts ... 18
9 Welded joints and grooves ... 19
10 Inspection ... 19
11 Drawing indications ... 20
Foreword
JB/T 5000 “Heavy mechanical general techniques and standards” is divided
into 15 parts.
- Part 1. Check of product;
- Part 2. Oxygen cutting workpiece;
- Part 3. And standards welding [Translator note. should be “Welding”];
- Part 4. Iron Casting;
- Part 5. Non-ferrous casting;
- Part 6. Steel Castings;
- Part 7. Repair welding for steel castings;
- Part 8. Forging;
- Part 9. Cutting;
- Part 10. Assembly;
- Part 11. Attached piping;
- Part 12. Paint;
- Part 13. Packing;
- Part 14. Non-destructive inspection of cast steel;
- Part 15. Non-destructive inspection of forged steel.
This Part is Part 3 of JB/T 5000.
This Part replaces JB/T 5000.3-1998 “The heavy mechanical general
techniques and standards - Welding”.
As compared with JB/T 5000.3-1998, the main changes of this Part are as
follows.
- ADD the requirement for chamfering the edges and corners of the bent steel
part when the steel is rolled.
- ADD length, weld angle, and quality requirements for tack weld.
Heavy mechanical general techniques
- Part 3. And standards welding
1 Scope
This Part of JB/T 5000 specifies the technical requirements, inspection methods,
and drawing indications of steel welded parts.
This Part applies to steel welded parts by shielded metal arc welding, gas
shielded welding, and submerged arc welding in heavy machinery and
components.
Where there are no special requirements in product drawings, technical
documents, and ordering technical conditions, the provisions of this Part shall
be complied with.
2 Normative references
The clauses in the following documents, by reference in this Part of JB/T 5000,
constitute the clauses of this Part. For the dated references, the subsequent
amendments (not including errata content) or revisions do not apply to this Part.
However, parties which have reached an agreement according to this Part are
encouraged to study whether the latest edition of these documents can be used.
For the undated references, the latest edition is applicable to this Part.
GB/T 324 Welds - symbolic representation on drawings (GB/T 324-1988, eqv
ISO 2553.1989)
GB/T 985 Basic forms and sizes of weld grooves for gas welding, manual
arc welding and gas-shielded welding
GB/T 986 Basic forms and sizes of weld grooves for submerged arc welding
GB/T 2649 Methods of sampling for mechanical properties tests of welded
joint
GB/T 2650 Impact test methods on welded joints
GB/T 2651 Tensile test method on welded joints
GB/T 2652 Tensile test methods on weld and deposited metal
GB/T 2653 Methods of bend and compression tests for welded joint
GB/T 2654 Methods of hardness tests for welded joint and surfacing metal
GB/T 3323 Radiographic examination of fusion welded joints in metallic
materials (GB/T 3323-2005, EN 135.1997, MOD)
GB/T 11345 Non-destructive testing of welds - Ultrasonic testing -
Techniques, testing levels, and assessment
JB/T 3223 Welding material quality management procedures
JB/T 4735 Steel welded atmospheric pressure vessels
JB/T 5000.2 Heavy mechanical general techniques and standards - Part 2.
Oxygen cutting workpiece
JB/T 5000.11 Heavy mechanical general techniques and standards - Part 11.
Attached piping
JB/T 5000.12 Heavy mechanical general techniques and standards - Part 12.
Paint
JB/T 5926 Vibrating stress relief effect - Evaluation methods
JB/T 6046 Welding assembly for carbon steel and low alloy steel - Post-
welding heat treatment method
JB/T 6061 Non-destructive testing - Magnetic particle testing of welds
JB/T 7949 Weld outer dimensions for steel construction
3 General requirements
3.1 Welded parts shall be manufactured in accordance with the design drawings,
process documents, and this Part.
3.2 The steel grade, specifications, and dimensions of the raw materials (steel
sheets, section steel, and steel pipes, etc.) used to manufacture the welded
parts shall comply with the requirements of design drawings. For material
substitution, substitution sheet shall be handled in accordance with relevant
regulations.
3.3 Raw materials and welding materials (welding rods, welding wire, flux,
shield gas, etc.) used to manufacture welded parts shall, when entering the
factory, based on the certificate of compliance provided by the supplier,
5 Forming bending of steel
5.1 For the rolling bending of steel, when the bending radius (inner radius) is
greater than the following values, cold bending can be carried out (SEE Figure
1). However, regardless of cold bending or hot bending, the edges and corners
of the steel sheet near the bent part shall be chamfered.
5.1.1 Steel sheet. For low alloy steel, R≥25δ;
For low carbon steel, R≥20δ.
R - Bending radius; δ - Thickness of steel sheet.
5.1.2 I-beam. R≥25H or R≥25B (depending on the direction of bending);
H - I-beam’s height; B - I-beam’s width.
5.1.3 Channel steel. R≥45B or R≥25H (depending on the direction of bending);
H - Channel steel’s height; B - Channel steel’s width.
5.1.4 Angle steel. R≥45B;
B - Angle steel’s edge-width (for unequal angle steel,
depending on the direction of bending).
5.2 For the rolling bending of steel, when the bending radius (inner radius) is
less than the values specified in 5.1, according to the specific situation, the
technician shall determine whether to perform annealing heat treatment after
hot bending or cold bending.
5.3 The tolerances for the dimensions of bend formed cylinder shall be in
accordance with Figure 2 and Table 3.
5.4 The unfitness of butt joint e for the butt joint between cylinders or for the
longitudinal joint of cylinder shall not exceed 20% of thickness and no more
than 4mm (SEE Figure 3 and Figure 4).
5.5 For the bend forming of the pipe, during hot bending, the heating
temperature is 900°C~1000°C. During bending, the temperature shall not be
lower than 700°C. Cold bending shall be carried out on a special pipe bender.
5.6 The bending radius R of the pipe (SEE Figure 5) shall comply with the
provisions of JB/T 5000.11.
7.1.1 Welders shall be specially trained and qualified before they can perform
welding work.
7.1.2 If the steel is not pretreated, before welding, the surface dirt of welding
area shall be removed, such as rust scale, oil stain, paint, and other impurities
which affect the quality of weld. The cleaning area is not less than 20mm from
the edge of the weld.
7.1.3 During open-air welding, in case of rain, snow, heavy fog, and strong wind,
if no protective measures are taken, welding shall not be carried out.
7.2 Preheating before welding.
7.2.1 Welded parts of low carbon stee...
Share