1
/
of
6
PayPal, credit cards. Download editable-PDF and invoice in 1 second!
Q/BQB 401-2014 English PDF (QBQB401-2014)
Q/BQB 401-2014 English PDF (QBQB401-2014)
Regular price
$225.00 USD
Regular price
Sale price
$225.00 USD
Unit price
/
per
Shipping calculated at checkout.
Couldn't load pickup availability
Delivery: 3 seconds. Download true-PDF + Invoice.Newer version: (Replacing this standard) QBQB401-2019
Get QUOTATION in 1-minute: Click Q/BQB 401-2014
Historical versions: Q/BQB 401-2014
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll if blank)
Q/BQB 401-2014: Cold rolled steel sheet and strip - Size, shape, weight and permissible deviations
Q/BQB 401-2014
TECHNICAL SUPPLY CONDITION OF
BAOSTEEL GROUP CORPORATION
Replacing Q/BQB 401-2009
Dimension, shape, weight and tolerance for
cold-rolled steel plates and strips
ISSUED ON. OCTOBER 18, 2014
IMPLEMENTED ON. MARCH 31, 2015
Issued by. Baosteel Group Corporation
Table of Contents
1 Scope ... 3
2 Normative references ... 3
3 Classification and codes ... 3
4 Dimensions ... 4
5 Dimensional tolerances ... 4
6 Shape ... 7
7 Dimension and shape measurement ... 9
8 Weight ... 10
9 [No Title] ... 10
10 Rules of rounding off for numerical values ... 10
Appendix A (Normative) Method for calculating the theoretical weight ... 12
Additional information... 13
Dimension, shape, weight and tolerance for
cold-rolled steel plates and strips
1 Scope
This Standard specifies the requirements for the classification and code,
dimension, shape, weight and tolerance of cold-rolled steel plates and strips.
This Standard is applicable to the cold-rolled steel strips with the thickness of
0.17mm to 3.50mm and the width of 400mm to 1,850mm, and the steel plates
cut from the above-mentioned steel strips (hereinafter referred to as “steel
plates and strips”), which are produced by Baosteel Group Corporation.
2 Normative references
The following documents are essential to the application of this document. For
dated references, only the editions with the dates indicated are applicable to
this document. For undated references, only the latest editions (including all the
amendments) are applicable to this document.
GB/T 8170-2008 Rules of rounding off for numerical values and expression and
judgement of limiting values
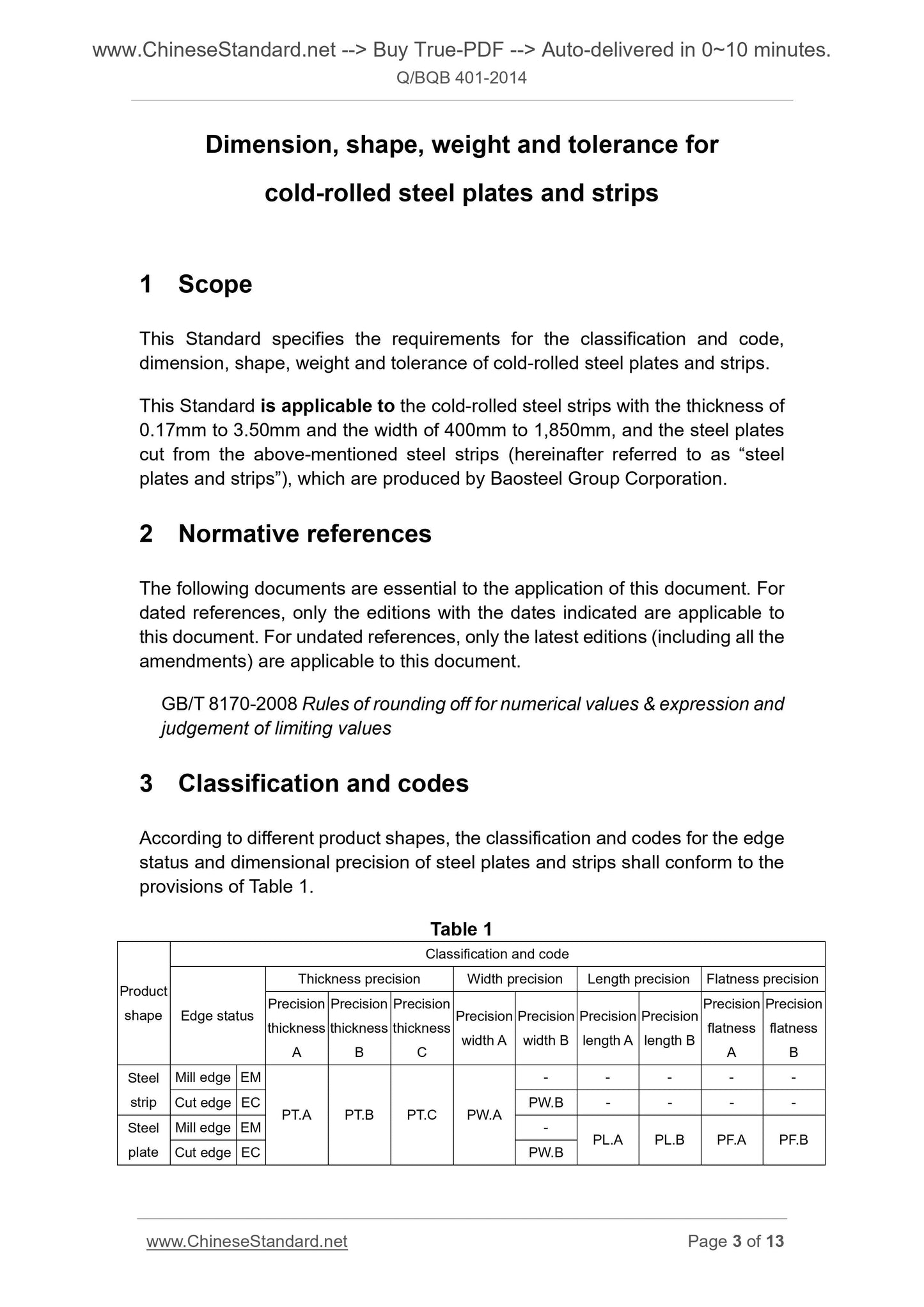
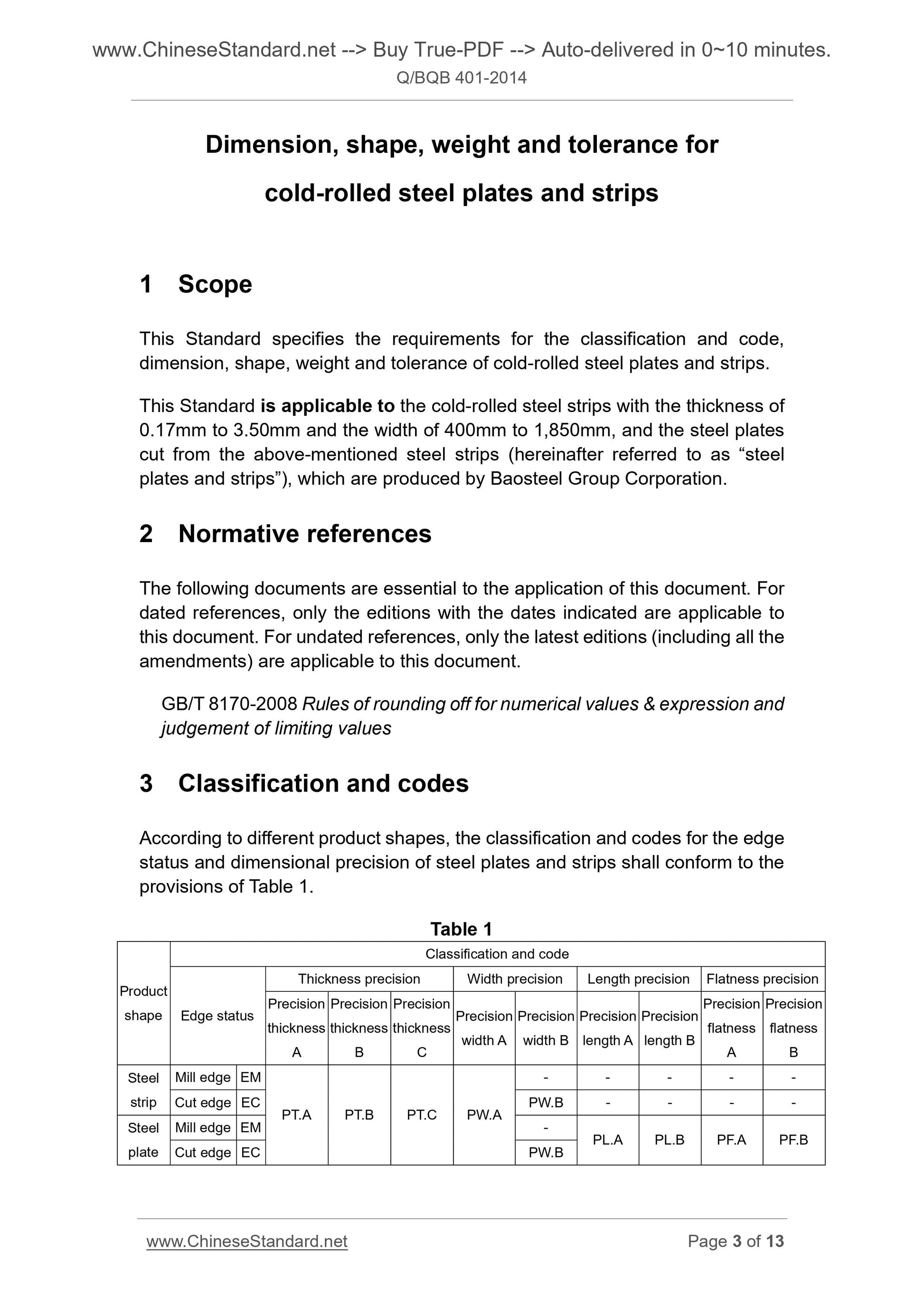
3 Classification and codes
According to different product shapes, the classification and codes for the edge
status and dimensional precision of steel plates and strips shall conform to the
provisions of Table 1.
Table 1
Product
shape
Classification and code
Edge status
Thickness precision Width precision Length precision Flatness precision
Precision
thickness
Precision
thickness
Precision
thickness
Precision
width A
Precision
width B
Precision
length A
Precision
length B
Precision
flatness
Precision
flatness
Steel
strip
Mill edge EM
PT.A PT.B PT.C PW.A
- - - - -
Cut edge EC PW.B - - - -
Steel
plate
Mill edge EM - PL.A PL.B PF.A PF.B Cut edge EC PW.B
Note. According to the shapes and the positions where the steel plates show up, the strain
types of steel plates can be divided into the following categories.
Bow
It refers to the residual curving along various directions of the steel plate, which can be
in longitudinal direction (along the rolling direction) and in transverse direction
(perpendicular to the rolling direction);
Wave
The waves refer to the waves and rippling along the longitudinal direction of the steel
plate;
Edge wave
The edge waves refer to the waves along the edges of the steel plate;
Center buckle, centre fullness, full centre
It refers to the waves appearing in the middle of the steel plate, which is also known as
central fold.
6.3.4 For the steel plates with the minimum yield strength of less than 260MPa,
during the supply in accordance with the precision flatness B, it is necessary to
conduct further inspection to the edge waves in the case of arbitration. The
edge waves shall conform to the following provisions.
— When the edge wave’s length is not less than 200mm, for the steel plate
whose nominal width is less than 1,500mm, the wave height shall be less
than 1% of the edge wave’s length;
— When the edge wave’s length is not less than 200mm, for the steel plate
whose nominal width is not less than 1,500mm, the wave height shall be
less than 1.5% of the edge wave’s length;
— When the edge wave’s length is less than 200mm, the wave height shall
not be greater than 2mm.
6.3.5 For the steel plates with the specified minimum yield strength of not less
than 340MPa, the flatness shall be negotiated by the supply and requisitioning
parties, and shall also be indicated in the contract.
6.3.6 If the requisitioning party makes no provisions on the flatness of steel
plates, the supply party shall meet the end-use requirements of the product to
the greatest extent.
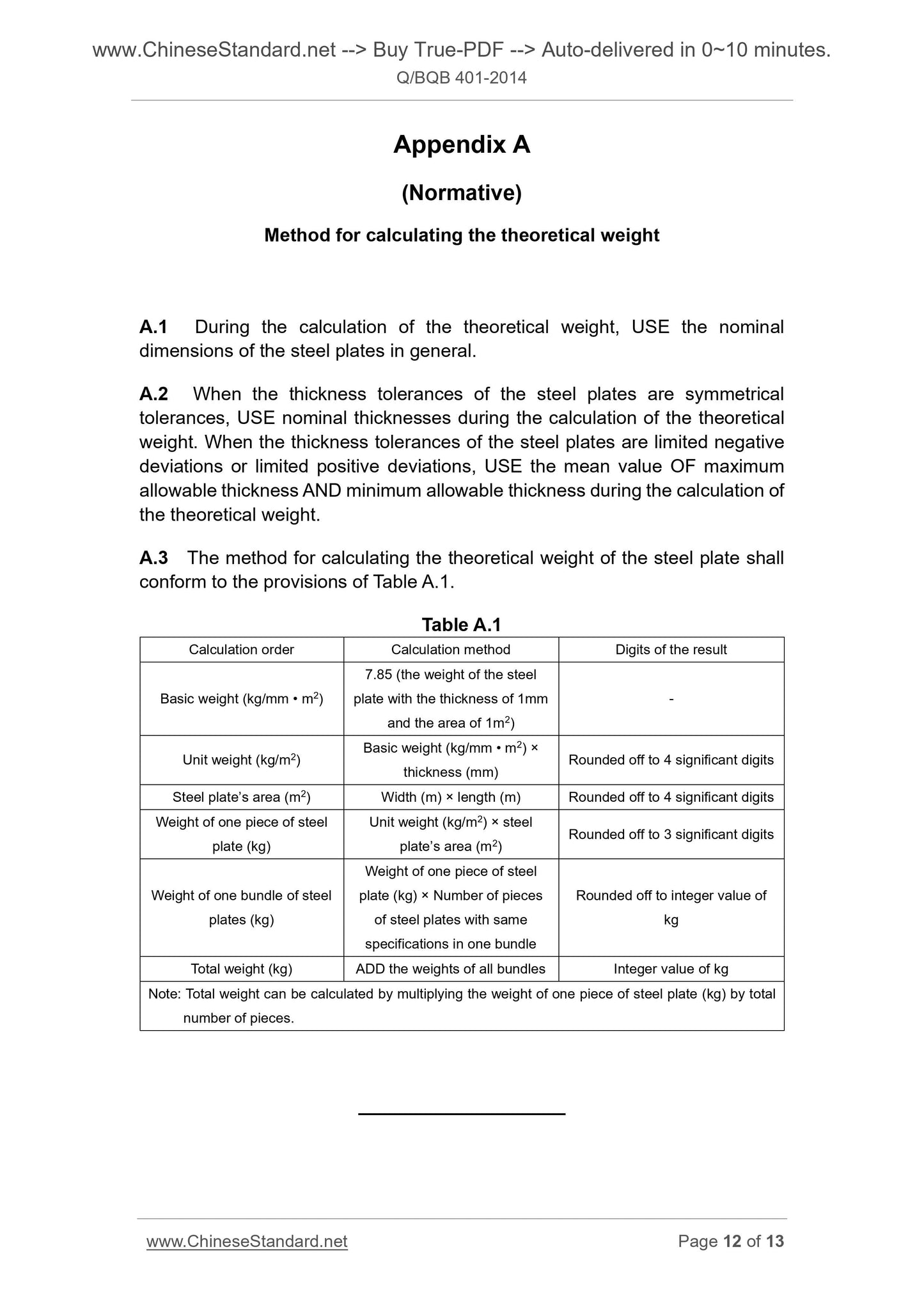
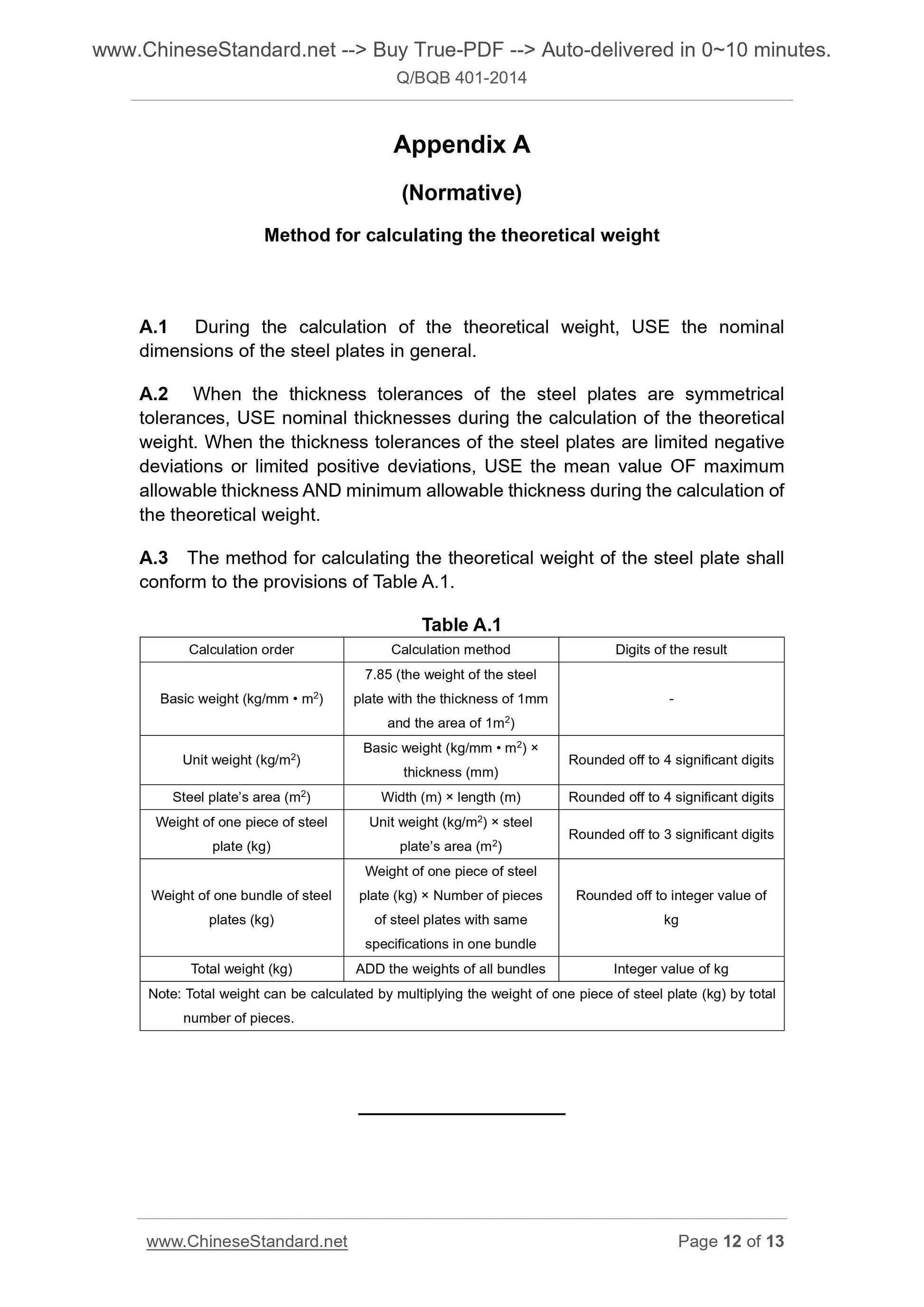
Appendix A
(Normative)
Method for calculating the theoretical weight
A.1 During the calculation of the theoretical weight, USE the nominal
dimensions of the steel plates in general.
A.2 When the thickness tolerances of the steel plates are symmetrical
tolerances, USE nominal thicknesses during the calculation of the theoretical
weight. When the thickness tolerances of the steel plates are limited negative
deviations or limited positive deviations, USE the mean value OF maximum
allowable thickness AND minimum allowable thickness during the calculation of
the theoretical weight.
A.3 The method for calculating the theoretical weight of the steel plate shall
conform to the provisions of Table A.1.
Table A.1
Calculation order Calculation method Digits of the result
Basic weight (kg/mm • m2)
7.85 (the weight of the steel
plate with the thickness of 1mm
and the area of 1m2)
Unit weight (kg/m2) Basic weight (kg/mm • m
2) ×
thickness (mm) Rounded off to 4 significant digits
Steel plate’s area (m2) Width (m) × length (m) Rounded off to 4 significant digits
Weight of one piece of steel
plate (kg)
Unit weight (kg/m2) × steel
plate’s area (m2) Rounded off to 3 significant digits
Weight of one bundle of steel
plates (kg)
Weight of one piece of steel
plate (kg) × Number of pieces
of steel plates with same
specifications in one bundle
Rounded off to integer value of
kg
Total weight (kg) ADD the weights of all bundles Integer value of kg
Note. Total weight can be calculated by multiplying the weight of one piece of steel plate (kg) by total
number of pieces.
Additional information.
This Technical Condition was drafted by reference to EN 10131.2006, JIS
G3141.2011 and GMW 3224-2012.
This Technical Condition replaces Q/BQB 401-2009.
Compared with Q/BQB 401-2009, the major modifications in this Technical
Condition are as follows.
— DELETE the provisions on the original slitting steel strips;
— ADD the provisions on the precision thickness C;
— ADD the provisions on using the diagonal method for measuring the out
of squareness.
The Appendix A of this Technical Condition is normative appendix.
This Technical Condition was proposed by the Manufacturing Management
Department of Baosteel Group Corporation.
This Technical Condition was drafted by the Manufacturing Management
Department of Baosteel Group Corporation.
Drafter of this Technical Condition. Sun Zhongming.
This Technical Condition was first released in 1988. The first revision was
released in 1994. The second revision was released in 1999. The third revision
was released in 2003. The fourth revision was released in 2009. This is the fifth
revision.
Get QUOTATION in 1-minute: Click Q/BQB 401-2014
Historical versions: Q/BQB 401-2014
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll if blank)
Q/BQB 401-2014: Cold rolled steel sheet and strip - Size, shape, weight and permissible deviations
Q/BQB 401-2014
TECHNICAL SUPPLY CONDITION OF
BAOSTEEL GROUP CORPORATION
Replacing Q/BQB 401-2009
Dimension, shape, weight and tolerance for
cold-rolled steel plates and strips
ISSUED ON. OCTOBER 18, 2014
IMPLEMENTED ON. MARCH 31, 2015
Issued by. Baosteel Group Corporation
Table of Contents
1 Scope ... 3
2 Normative references ... 3
3 Classification and codes ... 3
4 Dimensions ... 4
5 Dimensional tolerances ... 4
6 Shape ... 7
7 Dimension and shape measurement ... 9
8 Weight ... 10
9 [No Title] ... 10
10 Rules of rounding off for numerical values ... 10
Appendix A (Normative) Method for calculating the theoretical weight ... 12
Additional information... 13
Dimension, shape, weight and tolerance for
cold-rolled steel plates and strips
1 Scope
This Standard specifies the requirements for the classification and code,
dimension, shape, weight and tolerance of cold-rolled steel plates and strips.
This Standard is applicable to the cold-rolled steel strips with the thickness of
0.17mm to 3.50mm and the width of 400mm to 1,850mm, and the steel plates
cut from the above-mentioned steel strips (hereinafter referred to as “steel
plates and strips”), which are produced by Baosteel Group Corporation.
2 Normative references
The following documents are essential to the application of this document. For
dated references, only the editions with the dates indicated are applicable to
this document. For undated references, only the latest editions (including all the
amendments) are applicable to this document.
GB/T 8170-2008 Rules of rounding off for numerical values and expression and
judgement of limiting values
3 Classification and codes
According to different product shapes, the classification and codes for the edge
status and dimensional precision of steel plates and strips shall conform to the
provisions of Table 1.
Table 1
Product
shape
Classification and code
Edge status
Thickness precision Width precision Length precision Flatness precision
Precision
thickness
Precision
thickness
Precision
thickness
Precision
width A
Precision
width B
Precision
length A
Precision
length B
Precision
flatness
Precision
flatness
Steel
strip
Mill edge EM
PT.A PT.B PT.C PW.A
- - - - -
Cut edge EC PW.B - - - -
Steel
plate
Mill edge EM - PL.A PL.B PF.A PF.B Cut edge EC PW.B
Note. According to the shapes and the positions where the steel plates show up, the strain
types of steel plates can be divided into the following categories.
Bow
It refers to the residual curving along various directions of the steel plate, which can be
in longitudinal direction (along the rolling direction) and in transverse direction
(perpendicular to the rolling direction);
Wave
The waves refer to the waves and rippling along the longitudinal direction of the steel
plate;
Edge wave
The edge waves refer to the waves along the edges of the steel plate;
Center buckle, centre fullness, full centre
It refers to the waves appearing in the middle of the steel plate, which is also known as
central fold.
6.3.4 For the steel plates with the minimum yield strength of less than 260MPa,
during the supply in accordance with the precision flatness B, it is necessary to
conduct further inspection to the edge waves in the case of arbitration. The
edge waves shall conform to the following provisions.
— When the edge wave’s length is not less than 200mm, for the steel plate
whose nominal width is less than 1,500mm, the wave height shall be less
than 1% of the edge wave’s length;
— When the edge wave’s length is not less than 200mm, for the steel plate
whose nominal width is not less than 1,500mm, the wave height shall be
less than 1.5% of the edge wave’s length;
— When the edge wave’s length is less than 200mm, the wave height shall
not be greater than 2mm.
6.3.5 For the steel plates with the specified minimum yield strength of not less
than 340MPa, the flatness shall be negotiated by the supply and requisitioning
parties, and shall also be indicated in the contract.
6.3.6 If the requisitioning party makes no provisions on the flatness of steel
plates, the supply party shall meet the end-use requirements of the product to
the greatest extent.
Appendix A
(Normative)
Method for calculating the theoretical weight
A.1 During the calculation of the theoretical weight, USE the nominal
dimensions of the steel plates in general.
A.2 When the thickness tolerances of the steel plates are symmetrical
tolerances, USE nominal thicknesses during the calculation of the theoretical
weight. When the thickness tolerances of the steel plates are limited negative
deviations or limited positive deviations, USE the mean value OF maximum
allowable thickness AND minimum allowable thickness during the calculation of
the theoretical weight.
A.3 The method for calculating the theoretical weight of the steel plate shall
conform to the provisions of Table A.1.
Table A.1
Calculation order Calculation method Digits of the result
Basic weight (kg/mm • m2)
7.85 (the weight of the steel
plate with the thickness of 1mm
and the area of 1m2)
Unit weight (kg/m2) Basic weight (kg/mm • m
2) ×
thickness (mm) Rounded off to 4 significant digits
Steel plate’s area (m2) Width (m) × length (m) Rounded off to 4 significant digits
Weight of one piece of steel
plate (kg)
Unit weight (kg/m2) × steel
plate’s area (m2) Rounded off to 3 significant digits
Weight of one bundle of steel
plates (kg)
Weight of one piece of steel
plate (kg) × Number of pieces
of steel plates with same
specifications in one bundle
Rounded off to integer value of
kg
Total weight (kg) ADD the weights of all bundles Integer value of kg
Note. Total weight can be calculated by multiplying the weight of one piece of steel plate (kg) by total
number of pieces.
Additional information.
This Technical Condition was drafted by reference to EN 10131.2006, JIS
G3141.2011 and GMW 3224-2012.
This Technical Condition replaces Q/BQB 401-2009.
Compared with Q/BQB 401-2009, the major modifications in this Technical
Condition are as follows.
— DELETE the provisions on the original slitting steel strips;
— ADD the provisions on the precision thickness C;
— ADD the provisions on using the diagonal method for measuring the out
of squareness.
The Appendix A of this Technical Condition is normative appendix.
This Technical Condition was proposed by the Manufacturing Management
Department of Baosteel Group Corporation.
This Technical Condition was drafted by the Manufacturing Management
Department of Baosteel Group Corporation.
Drafter of this Technical Condition. Sun Zhongming.
This Technical Condition was first released in 1988. The first revision was
released in 1994. The second revision was released in 1999. The third revision
was released in 2003. The fourth revision was released in 2009. This is the fifth
revision.
Share