1
/
of
12
www.ChineseStandard.us -- Field Test Asia Pte. Ltd.
YY 0832.1-2011 English PDF
YY 0832.1-2011 English PDF
Regular price
$150.00
Regular price
Sale price
$150.00
Unit price
/
per
Shipping calculated at checkout.
Couldn't load pickup availability
YY 0832.1-2011: Stereotactic and Planning System for Radiotherapy with X-Radiation - Part 1: Stereotactic and Planning System for Radiotherapy with X-Radiation for Head lesion
Delivery: 9 seconds. Download (& Email) true-PDF + Invoice.
Get Quotation: Click YY 0832.1-2011 (Self-service in 1-minute)
Historical versions (Master-website): YY 0832.1-2011
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll-down if blank)
YY 0832.1-2011
YY
PHARMACEUTICAL INDUSTRY STANDARD
OF THE PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 11.040.50
C 43
Stereotactic and Planning System for Radiotherapy with
X-Radiation - Part 1. Stereotactic and Planning System
for Radiotherapy with X-Radiation for Head lesion
ISSUED ON. DECEMBER 31, 2011
IMPLEMENTED ON. JUNE 01, 2013
Issued by. China Food and Drug Administration
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
1 Scope ... 4
2 Normative References ... 4
3 Terms and Definitions ... 5
4 Requirements ... 5
5 Test Methods ... 7
Stereotactic and Planning System for Radiotherapy with
X-Radiation - Part 1. Stereotactic and Planning System
for Radiotherapy with X-Radiation for Head lesion
1 Scope
This Part of YY 0832 specifies the scope, terms, performance requirements of the
stereotactic and planning system for radiotherapy with X-radiation for head lesion.
This Part is applicable to the stereotactic and planning system for radiotherapy with X-
radiation for head lesion (hereinafter referred to as the system). Such system shall be
used in conjunction with a medical electron accelerator to perform stereotactic
radiotherapy for small lesions in the head and neck.
2 Normative References
The following documents are essential to the application of this document. For the
dated documents, only the versions with the dates indicated are applicable to this
document; for the undated documents, only the latest version (including all the
amendments) are applicable to this document.
GB 9706.5 Medical Electrical Equipment - Part 2. Particular Requirements for the
Safety of Electron Accelerators in the Range 1 MeV to 50 MeV
GB 15213 Medical Electron Accelerators – Functional Performance Characteristics
and Test Methods
GB/T 17857 Medical Radiology - Terminology (Equipment for Radiotherapy,
Nuclear Medicine and Radiation Dosimetry)
GB/T 18987 Radiotherapy Equipment – Coordinates, Movements and Scales
YY 0637 Medical Electrical Equipment—Requirements for the Safety of
Radiotherapy Treatment Planning Systems
3 Terms and Definitions
For the purposes of this document, the terms and definitions given in GB 9706.5, GB
15213, GB/T 17857 apply.
4 Requirements
4.1 Coordinates
The system shall adopt the requirements for coordinates, movements and scales in
GB/T 18987. If other coordinates are adopted, they shall be indicated in the random
file as required in 4.2a).
4.2 Random file
The random file shall include at least the following contents.
a) The coordinates adopted by the system; as well as the relationship between such
coordinates and the coordinates defined in GB/T 18987;
b) The medical electron accelerator (hereinafter referred to as the accelerator) used
in conjunction with shall meet the requirements of GB 15213 and GB 9706.5;
c) The energy range of the accelerator used in conjunction with;
d) The parameters of collimator, including the quantity, No., height, nominal
dimensions of the two end faces;
e) The size of the radiation filed for the accelerator used in conjunction with, after
assembly of the collimator;
f) The size of radiation field of each collimator along the direction of the two main
axes of the isocenter of accelerator used in conjunction with;
g) The value of penumbra of each collimator along the direction of the two main
axes of the isocenter of accelerator used in conjunction with;
h) The parameters, dimensions, and relevant information of the stereotactic device
used in conjunction with;
i) In order to meet the isocenter accuracy and other requirements of the accelerator
used in conjunction with as required in 4.6;
j) In order to meet the imaging parameters required in 4.8, as well as the test
methods whether the image satisfies the therapy plan.
The target reconstruction position error calculated by the therapy planning software
shall be no greater than 1.5mm.
4.8.3 Area coincidence rate
The coincidence rate BETWEEN the area enclosed by 80% isodose line calculated by
the therapy planning software AND the area enclosed by the film calculated under the
same conditions shall be greater than 90%.
4.9 Security requirements of the therapy planning software
The therapy planning software in the system shall meet the requirements of YY 0637.
5 Test Methods
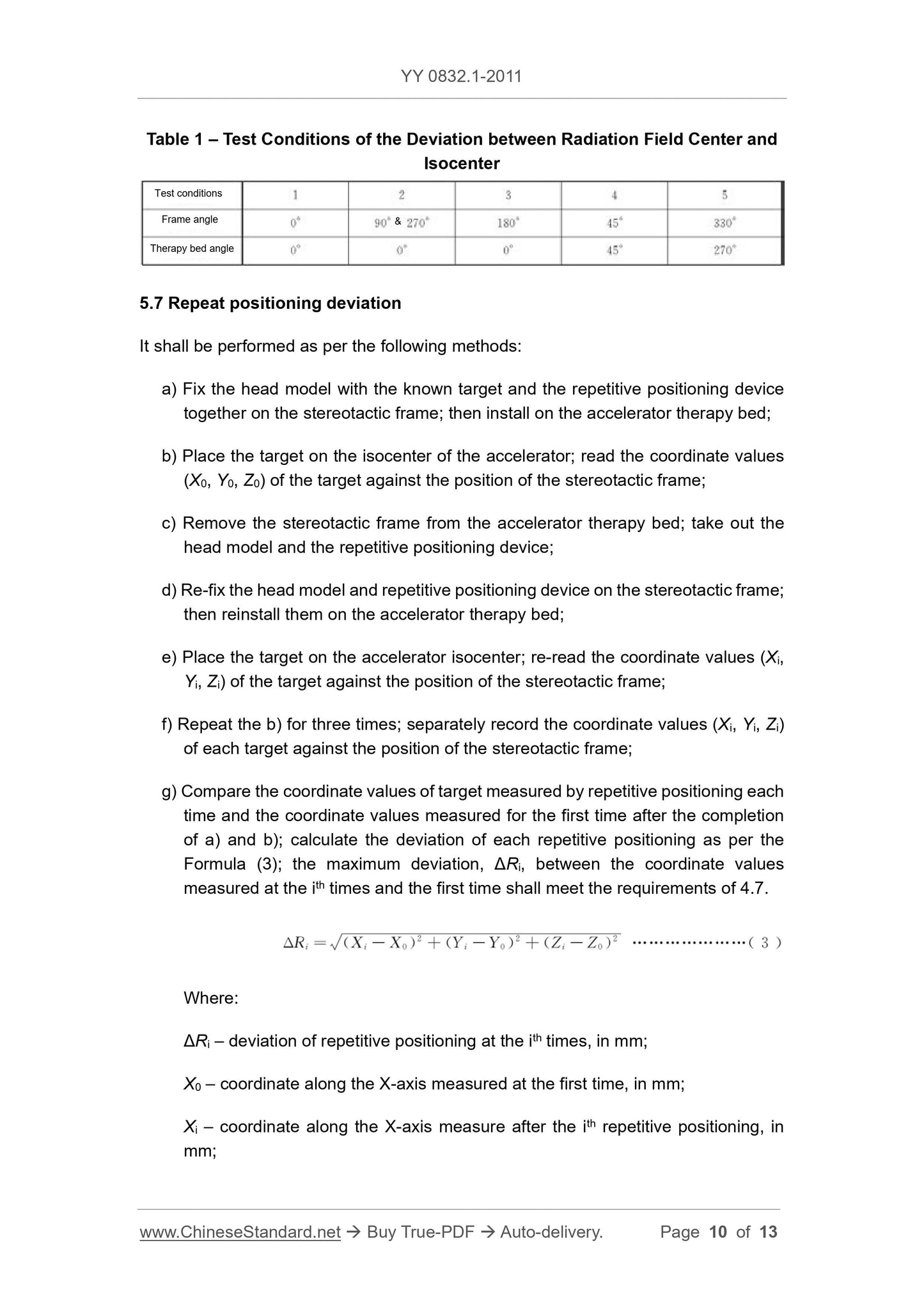
5.1 Coordinates
The inspection of the random file shall meet the requirements of 4.1.
5.2 Requirements for the random file
The inspection of random file shall meet the requirements of 4.2.
5.3 Size deviation of radiation field
It shall be performed by the following methods.
a) Select a collimator for therapy; place the film in a plane that is through the
isocenter and perpendicular to the radiation beam axis; the equivalent water
mold thickness on the film is at least 5cm; while the equivalent water mold
thickness below the film is 5cm. Set the angle between accelerator frame and
the speed-limiting system into 0°; select the appropriate energy and dose for the
accelerator used in conjunction with; sequentially expose the film from the lower
to the higher dose; so that calibrate the film gray scale value corresponding to
different absorbed dose.
b) Use the appropriate mathematical model according to the absorbed dose value
of the irradiation and the gray scale value of the corresponding film; draw a gray
scale-dose response curve of the used radiation film;
c) According to the conditions of a), select appropriate dose to sequentially expose
the collimator of each size; the irradiation dose shall be within the appropriate
response area of the gray scale-dose response curve of the used film; process
the film after exposure;
d) Input the processed film through the scanner into a computer; use the gray scale-
Y0 – coordinate along the Y-axis measured at the first time, in mm;
Yi – coordinate along the Y-axis measure after the ith repetitive positioning, in mm;
Z0 – coordinate along the Z-axis measured at the first time, in mm;
Yi – coordinate along the Z-axis measure after the ith repetitive positioning, in mm
5.8 Performance of therapy planning software
5.8.1 Dose calculation error of therapy planning software
It shall be performed as per the following methods.
a) The ionization chamber used for measurement shall meet the requirements of
the measuring conditions. Use head model, separately take the three references
points, i.e. model center and two isocenters as the targets to do three therapy
plans; set the radiation dose of the target within the high-dose and low-gradient
area; and finish the design of the therapy plan;
b) Insert the ionization chamber into the model; so that its effective measurement
points overlap with the target;
c) Separately place the three targets at the accelerator isocenters; use the
collimator adopted in the therapy planning and the radiation conditions to
irradiate; measure the absorbed dose of the three targets;
d) Calculate the error between the absorbed dose value calculated by the therapy
planning software as per the Formula (4) and the actually-measured absorbed
dose value; the maximum value shall meet the requirements of 4.8.1.
Where.
ΔP – the relative percentage error between he actually-measured absorbed dose
value and the absorbed dose value calculated by the therapy planning, in %;
P0 – absorbed dose value of target calculated by the therapy planning software,
in Gy;
Pi – actually-measured absorbed dose value (i=1~3) of target, in Gy.
5.8.2 Target position calculation error of the therapy planning software
It shall be performed as per the following methods.
YY 0832.1-2011
YY
PHARMACEUTICAL INDUSTRY STANDARD
OF THE PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 11.040.50
C 43
Stereotactic and Planning System for Radiotherapy with
X-Radiation - Part 1. Stereotactic and Planning System
for Radiotherapy with X-Radiation for Head lesion
ISSUED ON. DECEMBER 31, 2011
IMPLEMENTED ON. JUNE 01, 2013
Issued by. China Food and Drug Administration
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
1 Scope ... 4
2 Normative References ... 4
3 Terms and Definitions ... 5
4 Requirements ... 5
5 Test Methods ... 7
Stereotactic and Planning System for Radiotherapy with
X-Radiation - Part 1. Stereotactic and Planning System
for Radiotherapy with X-Radiation for Head lesion
1 Scope
This Part of YY 0832 specifies the scope, terms, performance requirements of the
stereotactic and planning system for radiotherapy with X-radiation for head lesion.
This Part is applicable to the stereotactic and planning system for radiotherapy with X-
radiation for head lesion (hereinafter referred to as the system). Such system shall be
used in conjunction with a medical electron accelerator to perform stereotactic
radiotherapy for small lesions in the head and neck.
2 Normative References
The following documents are essential to the application of this document. For the
dated documents, only the versions with the dates indicated are applicable to this
document; for the undated documents, only the latest version (including all the
amendments) are applicable to this document.
GB 9706.5 Medical Electrical Equipment - Part 2. Particular Requirements for the
Safety of Electron Accelerators in the Range 1 MeV to 50 MeV
GB 15213 Medical Electron Accelerators – Functional Performance Characteristics
and Test Methods
GB/T 17857 Medical Radiology - Terminology (Equipment for Radiotherapy,
Nuclear Medicine and Radiation Dosimetry)
GB/T 18987 Radiotherapy Equipment – Coordinates, Movements and Scales
YY 0637 Medical Electrical Equipment—Requirements for the Safety of
Radiotherapy Treatment Planning Systems
3 Terms and Definitions
For the purposes of this document, the terms and definitions given in GB 9706.5, GB
15213, GB/T 17857 apply.
4 Requirements
4.1 Coordinates
The system shall adopt the requirements for coordinates, movements and scales in
GB/T 18987. If other coordinates are adopted, they shall be indicated in the random
file as required in 4.2a).
4.2 Random file
The random file shall include at least the following contents.
a) The coordinates adopted by the system; as well as the relationship between such
coordinates and the coordinates defined in GB/T 18987;
b) The medical electron accelerator (hereinafter referred to as the accelerator) used
in conjunction with shall meet the requirements of GB 15213 and GB 9706.5;
c) The energy range of the accelerator used in conjunction with;
d) The parameters of collimator, including the quantity, No., height, nominal
dimensions of the two end faces;
e) The size of the radiation filed for the accelerator used in conjunction with, after
assembly of the collimator;
f) The size of radiation field of each collimator along the direction of the two main
axes of the isocenter of accelerator used in conjunction with;
g) The value of penumbra of each collimator along the direction of the two main
axes of the isocenter of accelerator used in conjunction with;
h) The parameters, dimensions, and relevant information of the stereotactic device
used in conjunction with;
i) In order to meet the isocenter accuracy and other requirements of the accelerator
used in conjunction with as required in 4.6;
j) In order to meet the imaging parameters required in 4.8, as well as the test
methods whether the image satisfies the therapy plan.
The target reconstruction position error calculated by the therapy planning software
shall be no greater than 1.5mm.
4.8.3 Area coincidence rate
The coincidence rate BETWEEN the area enclosed by 80% isodose line calculated by
the therapy planning software AND the area enclosed by the film calculated under the
same conditions shall be greater than 90%.
4.9 Security requirements of the therapy planning software
The therapy planning software in the system shall meet the requirements of YY 0637.
5 Test Methods
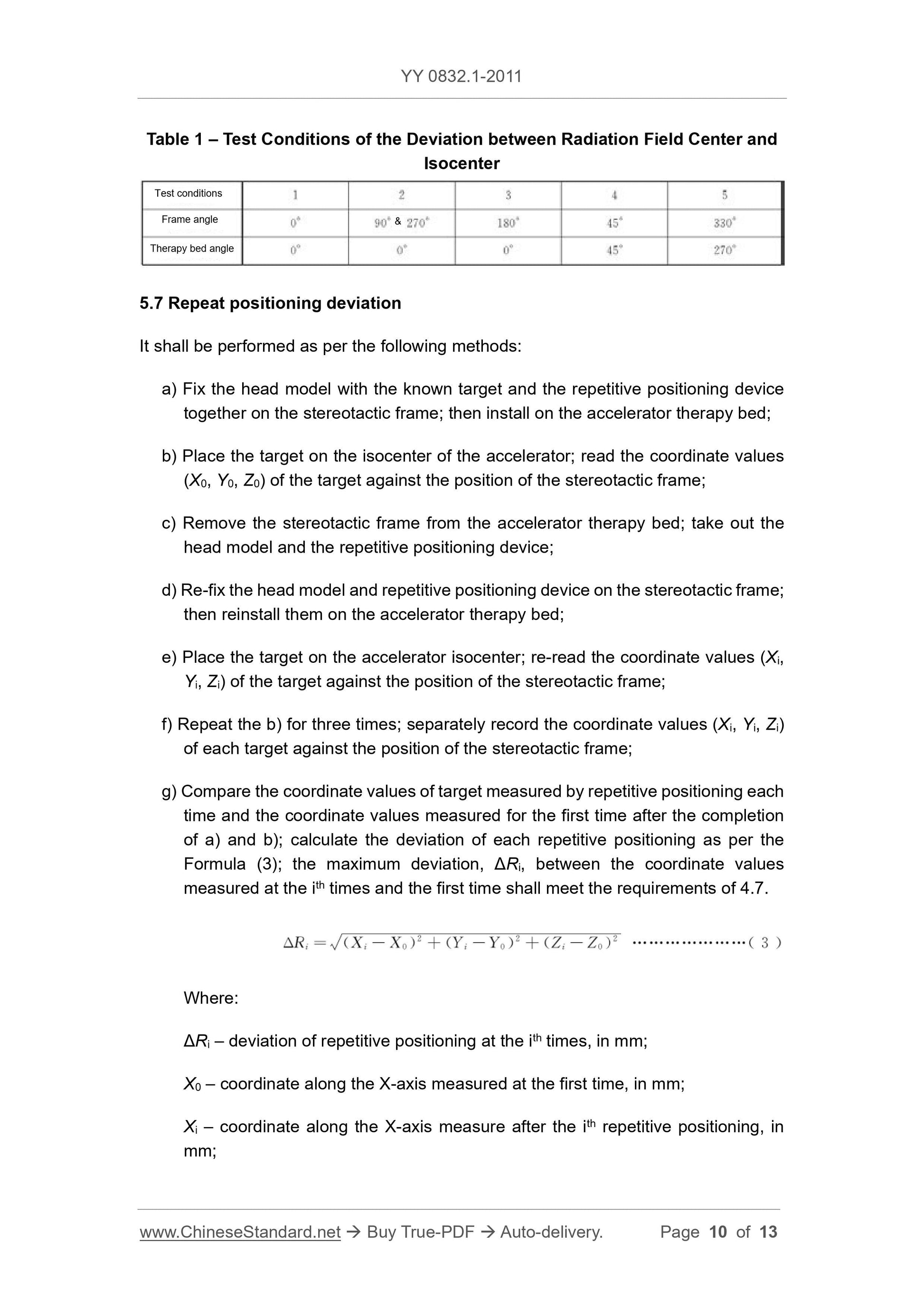
5.1 Coordinates
The inspection of the random file shall meet the requirements of 4.1.
5.2 Requirements for the random file
The inspection of random file shall meet the requirements of 4.2.
5.3 Size deviation of radiation field
It shall be performed by the following methods.
a) Select a collimator for therapy; place the film in a plane that is through the
isocenter and perpendicular to the radiation beam axis; the equivalent water
mold thickness on the film is at least 5cm; while the equivalent water mold
thickness below the film is 5cm. Set the angle between accelerator frame and
the speed-limiting system into 0°; select the appropriate energy and dose for the
accelerator used in conjunction with; sequentially expose the film from the lower
to the higher dose; so that calibrate the film gray scale value corresponding to
different absorbed dose.
b) Use the appropriate mathematical model according to the absorbed dose value
of the irradiation and the gray scale value of the corresponding film; draw a gray
scale-dose response curve of the used radiation film;
c) According to the conditions of a), select appropriate dose to sequentially expose
the collimator of each size; the irradiation dose shall be within the appropriate
response area of the gray scale-dose response curve of the used film; process
the film after exposure;
d) Input the processed film through the scanner into a computer; use the gray scale-
Y0 – coordinate along the Y-axis measured at the first time, in mm;
Yi – coordinate along the Y-axis measure after the ith repetitive positioning, in mm;
Z0 – coordinate along the Z-axis measured at the first time, in mm;
Yi – coordinate along the Z-axis measure after the ith repetitive positioning, in mm
5.8 Performance of therapy planning software
5.8.1 Dose calculation error of therapy planning software
It shall be performed as per the following methods.
a) The ionization chamber used for measurement shall meet the requirements of
the measuring conditions. Use head model, separately take the three references
points, i.e. model center and two isocenters as the targets to do three t...
Delivery: 9 seconds. Download (& Email) true-PDF + Invoice.
Get Quotation: Click YY 0832.1-2011 (Self-service in 1-minute)
Historical versions (Master-website): YY 0832.1-2011
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll-down if blank)
YY 0832.1-2011
YY
PHARMACEUTICAL INDUSTRY STANDARD
OF THE PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 11.040.50
C 43
Stereotactic and Planning System for Radiotherapy with
X-Radiation - Part 1. Stereotactic and Planning System
for Radiotherapy with X-Radiation for Head lesion
ISSUED ON. DECEMBER 31, 2011
IMPLEMENTED ON. JUNE 01, 2013
Issued by. China Food and Drug Administration
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
1 Scope ... 4
2 Normative References ... 4
3 Terms and Definitions ... 5
4 Requirements ... 5
5 Test Methods ... 7
Stereotactic and Planning System for Radiotherapy with
X-Radiation - Part 1. Stereotactic and Planning System
for Radiotherapy with X-Radiation for Head lesion
1 Scope
This Part of YY 0832 specifies the scope, terms, performance requirements of the
stereotactic and planning system for radiotherapy with X-radiation for head lesion.
This Part is applicable to the stereotactic and planning system for radiotherapy with X-
radiation for head lesion (hereinafter referred to as the system). Such system shall be
used in conjunction with a medical electron accelerator to perform stereotactic
radiotherapy for small lesions in the head and neck.
2 Normative References
The following documents are essential to the application of this document. For the
dated documents, only the versions with the dates indicated are applicable to this
document; for the undated documents, only the latest version (including all the
amendments) are applicable to this document.
GB 9706.5 Medical Electrical Equipment - Part 2. Particular Requirements for the
Safety of Electron Accelerators in the Range 1 MeV to 50 MeV
GB 15213 Medical Electron Accelerators – Functional Performance Characteristics
and Test Methods
GB/T 17857 Medical Radiology - Terminology (Equipment for Radiotherapy,
Nuclear Medicine and Radiation Dosimetry)
GB/T 18987 Radiotherapy Equipment – Coordinates, Movements and Scales
YY 0637 Medical Electrical Equipment—Requirements for the Safety of
Radiotherapy Treatment Planning Systems
3 Terms and Definitions
For the purposes of this document, the terms and definitions given in GB 9706.5, GB
15213, GB/T 17857 apply.
4 Requirements
4.1 Coordinates
The system shall adopt the requirements for coordinates, movements and scales in
GB/T 18987. If other coordinates are adopted, they shall be indicated in the random
file as required in 4.2a).
4.2 Random file
The random file shall include at least the following contents.
a) The coordinates adopted by the system; as well as the relationship between such
coordinates and the coordinates defined in GB/T 18987;
b) The medical electron accelerator (hereinafter referred to as the accelerator) used
in conjunction with shall meet the requirements of GB 15213 and GB 9706.5;
c) The energy range of the accelerator used in conjunction with;
d) The parameters of collimator, including the quantity, No., height, nominal
dimensions of the two end faces;
e) The size of the radiation filed for the accelerator used in conjunction with, after
assembly of the collimator;
f) The size of radiation field of each collimator along the direction of the two main
axes of the isocenter of accelerator used in conjunction with;
g) The value of penumbra of each collimator along the direction of the two main
axes of the isocenter of accelerator used in conjunction with;
h) The parameters, dimensions, and relevant information of the stereotactic device
used in conjunction with;
i) In order to meet the isocenter accuracy and other requirements of the accelerator
used in conjunction with as required in 4.6;
j) In order to meet the imaging parameters required in 4.8, as well as the test
methods whether the image satisfies the therapy plan.
The target reconstruction position error calculated by the therapy planning software
shall be no greater than 1.5mm.
4.8.3 Area coincidence rate
The coincidence rate BETWEEN the area enclosed by 80% isodose line calculated by
the therapy planning software AND the area enclosed by the film calculated under the
same conditions shall be greater than 90%.
4.9 Security requirements of the therapy planning software
The therapy planning software in the system shall meet the requirements of YY 0637.
5 Test Methods
5.1 Coordinates
The inspection of the random file shall meet the requirements of 4.1.
5.2 Requirements for the random file
The inspection of random file shall meet the requirements of 4.2.
5.3 Size deviation of radiation field
It shall be performed by the following methods.
a) Select a collimator for therapy; place the film in a plane that is through the
isocenter and perpendicular to the radiation beam axis; the equivalent water
mold thickness on the film is at least 5cm; while the equivalent water mold
thickness below the film is 5cm. Set the angle between accelerator frame and
the speed-limiting system into 0°; select the appropriate energy and dose for the
accelerator used in conjunction with; sequentially expose the film from the lower
to the higher dose; so that calibrate the film gray scale value corresponding to
different absorbed dose.
b) Use the appropriate mathematical model according to the absorbed dose value
of the irradiation and the gray scale value of the corresponding film; draw a gray
scale-dose response curve of the used radiation film;
c) According to the conditions of a), select appropriate dose to sequentially expose
the collimator of each size; the irradiation dose shall be within the appropriate
response area of the gray scale-dose response curve of the used film; process
the film after exposure;
d) Input the processed film through the scanner into a computer; use the gray scale-
Y0 – coordinate along the Y-axis measured at the first time, in mm;
Yi – coordinate along the Y-axis measure after the ith repetitive positioning, in mm;
Z0 – coordinate along the Z-axis measured at the first time, in mm;
Yi – coordinate along the Z-axis measure after the ith repetitive positioning, in mm
5.8 Performance of therapy planning software
5.8.1 Dose calculation error of therapy planning software
It shall be performed as per the following methods.
a) The ionization chamber used for measurement shall meet the requirements of
the measuring conditions. Use head model, separately take the three references
points, i.e. model center and two isocenters as the targets to do three therapy
plans; set the radiation dose of the target within the high-dose and low-gradient
area; and finish the design of the therapy plan;
b) Insert the ionization chamber into the model; so that its effective measurement
points overlap with the target;
c) Separately place the three targets at the accelerator isocenters; use the
collimator adopted in the therapy planning and the radiation conditions to
irradiate; measure the absorbed dose of the three targets;
d) Calculate the error between the absorbed dose value calculated by the therapy
planning software as per the Formula (4) and the actually-measured absorbed
dose value; the maximum value shall meet the requirements of 4.8.1.
Where.
ΔP – the relative percentage error between he actually-measured absorbed dose
value and the absorbed dose value calculated by the therapy planning, in %;
P0 – absorbed dose value of target calculated by the therapy planning software,
in Gy;
Pi – actually-measured absorbed dose value (i=1~3) of target, in Gy.
5.8.2 Target position calculation error of the therapy planning software
It shall be performed as per the following methods.
YY 0832.1-2011
YY
PHARMACEUTICAL INDUSTRY STANDARD
OF THE PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
ICS 11.040.50
C 43
Stereotactic and Planning System for Radiotherapy with
X-Radiation - Part 1. Stereotactic and Planning System
for Radiotherapy with X-Radiation for Head lesion
ISSUED ON. DECEMBER 31, 2011
IMPLEMENTED ON. JUNE 01, 2013
Issued by. China Food and Drug Administration
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
1 Scope ... 4
2 Normative References ... 4
3 Terms and Definitions ... 5
4 Requirements ... 5
5 Test Methods ... 7
Stereotactic and Planning System for Radiotherapy with
X-Radiation - Part 1. Stereotactic and Planning System
for Radiotherapy with X-Radiation for Head lesion
1 Scope
This Part of YY 0832 specifies the scope, terms, performance requirements of the
stereotactic and planning system for radiotherapy with X-radiation for head lesion.
This Part is applicable to the stereotactic and planning system for radiotherapy with X-
radiation for head lesion (hereinafter referred to as the system). Such system shall be
used in conjunction with a medical electron accelerator to perform stereotactic
radiotherapy for small lesions in the head and neck.
2 Normative References
The following documents are essential to the application of this document. For the
dated documents, only the versions with the dates indicated are applicable to this
document; for the undated documents, only the latest version (including all the
amendments) are applicable to this document.
GB 9706.5 Medical Electrical Equipment - Part 2. Particular Requirements for the
Safety of Electron Accelerators in the Range 1 MeV to 50 MeV
GB 15213 Medical Electron Accelerators – Functional Performance Characteristics
and Test Methods
GB/T 17857 Medical Radiology - Terminology (Equipment for Radiotherapy,
Nuclear Medicine and Radiation Dosimetry)
GB/T 18987 Radiotherapy Equipment – Coordinates, Movements and Scales
YY 0637 Medical Electrical Equipment—Requirements for the Safety of
Radiotherapy Treatment Planning Systems
3 Terms and Definitions
For the purposes of this document, the terms and definitions given in GB 9706.5, GB
15213, GB/T 17857 apply.
4 Requirements
4.1 Coordinates
The system shall adopt the requirements for coordinates, movements and scales in
GB/T 18987. If other coordinates are adopted, they shall be indicated in the random
file as required in 4.2a).
4.2 Random file
The random file shall include at least the following contents.
a) The coordinates adopted by the system; as well as the relationship between such
coordinates and the coordinates defined in GB/T 18987;
b) The medical electron accelerator (hereinafter referred to as the accelerator) used
in conjunction with shall meet the requirements of GB 15213 and GB 9706.5;
c) The energy range of the accelerator used in conjunction with;
d) The parameters of collimator, including the quantity, No., height, nominal
dimensions of the two end faces;
e) The size of the radiation filed for the accelerator used in conjunction with, after
assembly of the collimator;
f) The size of radiation field of each collimator along the direction of the two main
axes of the isocenter of accelerator used in conjunction with;
g) The value of penumbra of each collimator along the direction of the two main
axes of the isocenter of accelerator used in conjunction with;
h) The parameters, dimensions, and relevant information of the stereotactic device
used in conjunction with;
i) In order to meet the isocenter accuracy and other requirements of the accelerator
used in conjunction with as required in 4.6;
j) In order to meet the imaging parameters required in 4.8, as well as the test
methods whether the image satisfies the therapy plan.
The target reconstruction position error calculated by the therapy planning software
shall be no greater than 1.5mm.
4.8.3 Area coincidence rate
The coincidence rate BETWEEN the area enclosed by 80% isodose line calculated by
the therapy planning software AND the area enclosed by the film calculated under the
same conditions shall be greater than 90%.
4.9 Security requirements of the therapy planning software
The therapy planning software in the system shall meet the requirements of YY 0637.
5 Test Methods
5.1 Coordinates
The inspection of the random file shall meet the requirements of 4.1.
5.2 Requirements for the random file
The inspection of random file shall meet the requirements of 4.2.
5.3 Size deviation of radiation field
It shall be performed by the following methods.
a) Select a collimator for therapy; place the film in a plane that is through the
isocenter and perpendicular to the radiation beam axis; the equivalent water
mold thickness on the film is at least 5cm; while the equivalent water mold
thickness below the film is 5cm. Set the angle between accelerator frame and
the speed-limiting system into 0°; select the appropriate energy and dose for the
accelerator used in conjunction with; sequentially expose the film from the lower
to the higher dose; so that calibrate the film gray scale value corresponding to
different absorbed dose.
b) Use the appropriate mathematical model according to the absorbed dose value
of the irradiation and the gray scale value of the corresponding film; draw a gray
scale-dose response curve of the used radiation film;
c) According to the conditions of a), select appropriate dose to sequentially expose
the collimator of each size; the irradiation dose shall be within the appropriate
response area of the gray scale-dose response curve of the used film; process
the film after exposure;
d) Input the processed film through the scanner into a computer; use the gray scale-
Y0 – coordinate along the Y-axis measured at the first time, in mm;
Yi – coordinate along the Y-axis measure after the ith repetitive positioning, in mm;
Z0 – coordinate along the Z-axis measured at the first time, in mm;
Yi – coordinate along the Z-axis measure after the ith repetitive positioning, in mm
5.8 Performance of therapy planning software
5.8.1 Dose calculation error of therapy planning software
It shall be performed as per the following methods.
a) The ionization chamber used for measurement shall meet the requirements of
the measuring conditions. Use head model, separately take the three references
points, i.e. model center and two isocenters as the targets to do three t...
Share