1
/
of
12
PayPal, credit cards. Download editable-PDF & invoice in 1 second!
YY 1082-2007 English PDF
YY 1082-2007 English PDF
Regular price
$150.00 USD
Regular price
Sale price
$150.00 USD
Unit price
/
per
Shipping calculated at checkout.
Couldn't load pickup availability
Delivery: 3 seconds. Download true-PDF + Invoice.
Get Quotation: Click YY 1082-2007 (Self-service in 1-minute)
Historical versions (Master-website): YY 1082-2007
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll-down if blank)
YY 1082-2007: Rigid arthroscope
YY 1082-2007
Rigid arthroscope
ICS 11.040.70
C40
People's Republic of China Pharmaceutical Industry Standard
Replacing YY 91082-1999
Hard endoscope
Released on.2007-07-02
2008-03-01 implementation
State Food and Drug Administration released
Foreword
This standard is a revision of YY 91082-1999 "Knee Arthroscopy".
The main changes of this standard compared with YY 91082-1999 are as follows.
--- Standardized the standard name;
--- Added model mark and component code mark;
--- Increased the two main parameters of "viewing angle" and "clear observation range";
--- Added "funnel eyepiece cover", "temperature change, no fog layer", "illuminance uniformity" requirements;
--- Increased biocompatibility requirements.
The electrical connection part fully implements GB 9706.1-1995 "Medical Electrical Equipment Part 1. General Requirements for Safety" and
GB 9706.19-2000 "Medical Electrical Equipment Part 2. Special Requirements for Endoscope Equipment Safety", the specific content is attached
Record A (normative appendix) is given in the form.
Appendix A of this standard is a normative appendix.
This standard is approved by the State Food and Drug Administration.
This standard is proposed and managed by the National Technical Committee for Standardization of Medical Optical Instruments.
This standard was drafted by Shenyang Shenda Endoscope Co., Ltd.
The main drafters of this standard. Jiang Kerang, Gao Mingxian, Memorial Training, Zhang Changan.
The previous versions of this standard were released as follows.
---ZBC40003-1989;
---YY 91082-1999.
Hard endoscope
1 range
This standard specifies the classification and marking of rigid endoscopes, requirements, test methods, inspection rules, signs, labels and instructions for use,
Packaging, transportation and storage.
This standard is applicable to rigid arthroscopy (hereinafter referred to as arthroscopy). Arthroscopy is suitable for the examination of human joint diseases in medical clinic.
Diagnosis, diagnosis, and treatment with the relevant surgical system.
2 Normative references
The terms in the following documents become the terms of this standard by reference to this standard. All dated references, followed by all
Modifications (not including errata content) or revisions do not apply to this standard, however, parties to agreements based on this standard are encouraged to study
Is it possible to use the latest version of these files? For undated references, the latest edition applies to this standard.
GB/T 191-2000 packaging storage and transportation icon mark
GB/T 2829-2002 Periodic inspection count sampling procedures and tables (applicable to the inspection of process stability)
GB/T 6463-2005 Review of metal and other inorganic coating thickness measurement methods
GB 9706.1-1995 Medical electrical equipment Part 1. General requirements for safety (idt IEC 601-1.1988)
GB 9706.19-2000 Medical electrical equipment - Part 2. Particular requirements for safety of endoscope equipment (idt IEC 60601-2-18.
1996)
GB 11244-2005 General requirements for medical endoscopes and accessories
GB/T 14710-1993 Environmental requirements and test methods for medical electrical equipment
GB/T 16886.1-2001 Biological evaluation of medical devices - Part 1. Evaluation and testing (ISO 10993-1..1997, IDT)
GB/T 16886.5-2003 Biological evaluation of medical devices - Part 5. In vitro cytotoxicity test (ISO 10993-5..1999,
IDT)
GB/T 16886.10-2005 Biological evaluation of medical devices - Part 10. Stimulation and delayed hypersensitivity test
(ISO 10993-10.2002, IDT)
YY 0068 General technical conditions for medical rigid endoscopes
YY 0076-1992 Metal parts plating classification technical conditions
YY 0466-2003 Symbols for medical devices used for labeling, marking and providing information on medical devices (ISO 15223.2000, IDT)
3 composition
The arthroscope consists of an endoscope, a mirror sheath and a obturator, a puncture needle, a device puncture cannula, a instrument puncture needle, and a light guide beam.
4 requirements
4.1 Arthroscopy is a rigid endoscope product, in addition to the following requirements, it should also comply with the general requirements of YY 0068.
4.2 Surface and edge except for the puncture needle and the instrument needle. The components of the arthroscope should be designed so as not to cause any accidental injury to the human body.
Harm, all surfaces must be free of pores, cracks and burrs.
4.3 The basic dimensions of the arthroscope should meet the requirements of Table 1.
Table 1 The basic dimensions of arthroscopy are in millimeters
Project name basic parameter limit deviation
Maximum insert outer diameter
Minimum instrument hole diameter
Insert working length
Nominal value
No more than the nominal value
Not less than the nominal value
±3%
Guide beam length >1500 -
Note. When the insertion part is a circular tube, it is represented by a diameter (mm), and when it is a non-circular tube, it is represented by an equivalent circumference Fr.
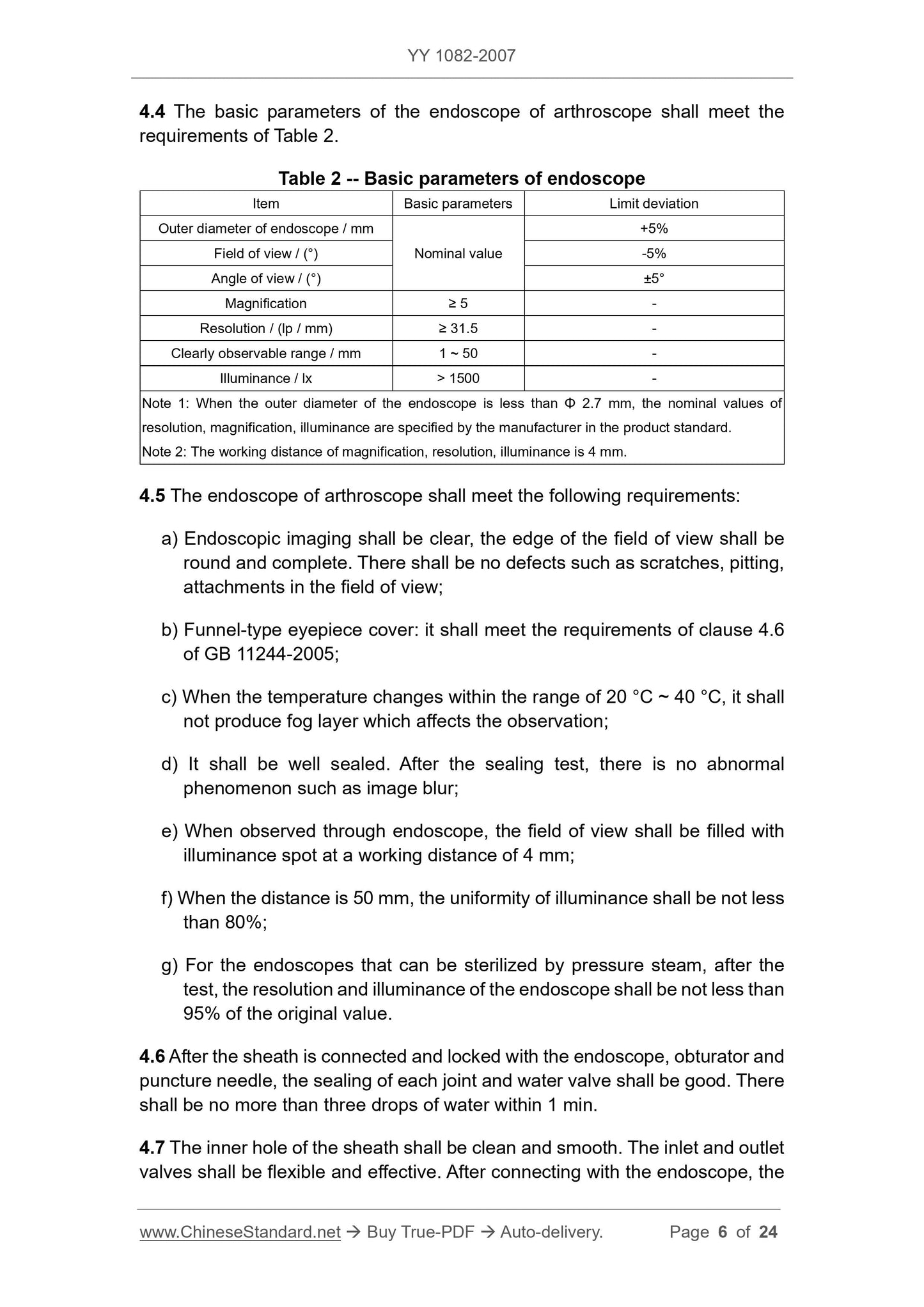
4.4 The basic parameters of the arthroscopy endoscope should meet the requirements of Table 2.
Table 2 Basic parameters of the endoscope
Project name basic parameter limit deviation
Mirror outer diameter/mm
Field of view/(°)
Viewing angle/(°)
Nominal value
+5%
-5%
±5°
Magnification ≥ 5 -
Resolution/(lp/mm) ≥ 31.5 -
Can clearly observe the range/mm 1 ~ 50 -
Illuminance/lx >1500 -
Note 1. When the outer diameter of the mirror body is less than 2.7mm, the resolution, magnification, and illuminance are specified by the manufacturer in the product standard.
Note 2. The working distance of magnification, resolution and illuminance is 4mm.
4.5 Arthroscopy endoscopes should meet the following requirements.
a) Endoscopic imaging should be clear, the edge of the field of view should be rounded, and there should be no defects such as scratches, pitting and attachments that affect the observation;
b) Funnel type eyepiece cover. it should meet the requirements of 4.6 of GB 11244-2005;
c) When the temperature changes within the range of 20 °C ~ 40 °C, no fog layer affecting the observation shall be produced;
d) The seal should be good, after the seal test, there is no image blurring phenomenon;
e) through the endoscope observation, the illumination spot should be filled with the field of view at a working distance of 4 mm;
f) When the distance is 50mm, the uniformity of illumination should be no less than 80%;
g) An endoscope that can be sterilized by pressure steam. After the test, the resolution and illuminance of the endoscope are not less than 95% of the original value.
4.6 After the mirror sheath is connected with the endoscope, the obturator and the puncture needle, the sealing of each joint and the water valve should be good, and the water seepage should be within 1 min.
No more than three drops.
4.7 The inner hole of the mirror sheath should be clean and smooth. The opening and closing of the inlet and outlet valves should be flexible and effective. After connecting with the endoscope, the flow rate of the water should be not less than
200 mL/min.
4.8 The head of the puncture needle should be smooth and sharp, the head of the blunt obturator should be smooth and round, and the handle of the needle of the instrument should be smooth and smooth.
4.9 The inner hole of the instrument puncture cannula should be clean and smooth, and can smoothly pass the instrument puncture needle and the supporting surgical instruments.
4.10 The hardness of the needle of the puncture needle and the instrument needle should be HRC36~46.
4.11 The welded parts of the arthroscope should be firm and reliable, smooth and smooth, and there is no welding or surfacing.
4.12 The plating of electroplated parts of arthroscopy shall comply with the Class V Class 2 requirements of YY 0076-1992.
4.13 Arthroscopy is a medical device that is short-term contact with the damaged surface. The outer surface material of the insertion portion should be certified to conform to the biological phase.
Capacitive material manufacturing, otherwise the following tests should be passed.
a) the cytotoxicity score should be no more than 1;
b) the type of stimulus should be no more than mild;
c) There should be no sensitization.
4.14 Safety requirements for interconnection with medical electrical equipment.
Arthroscopy should meet the requirements of GB 9706.1-1995 and GB 9706.19-2000. See Appendix A for specific requirements (normative
appendix).
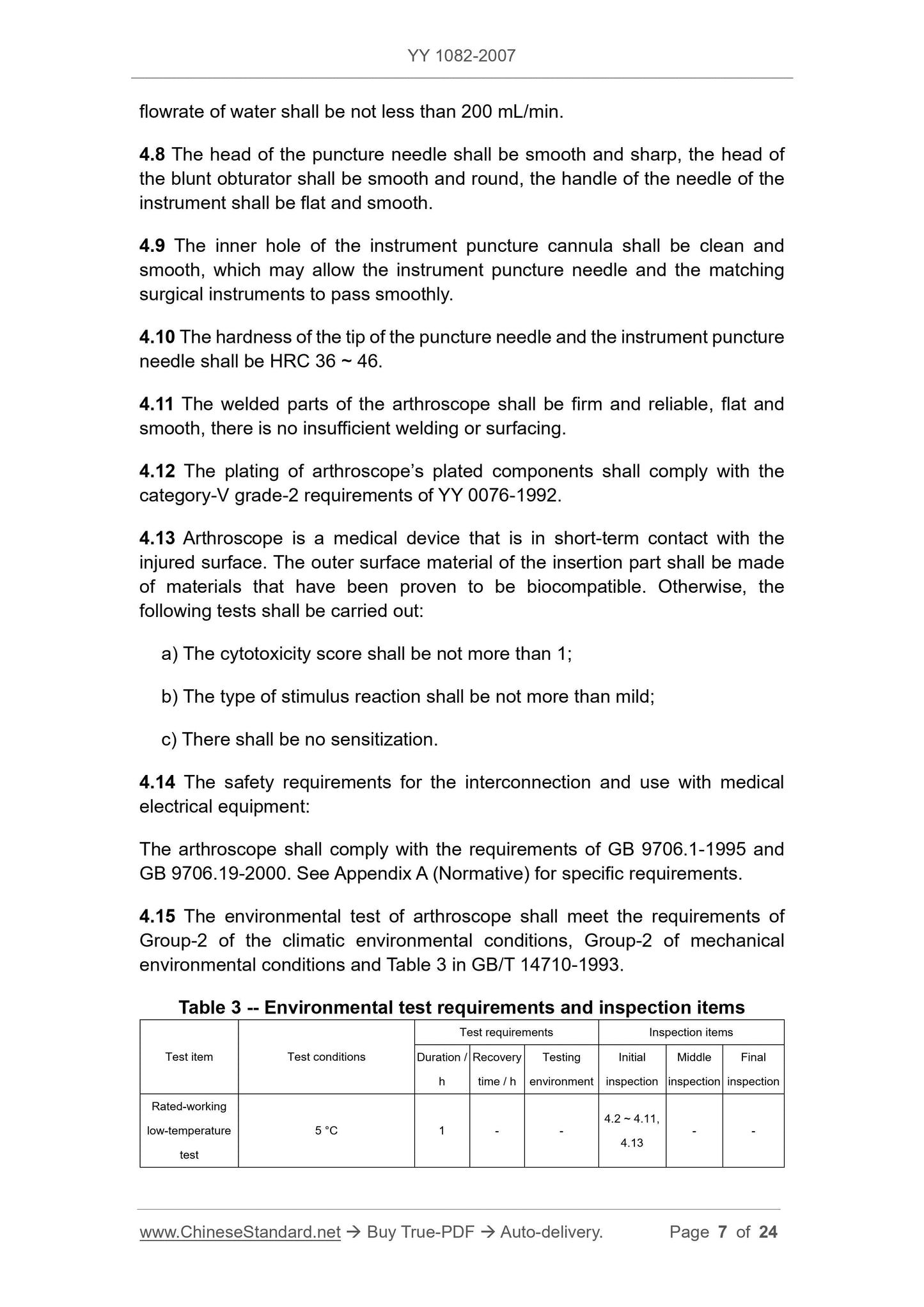
4.15 The environmental test of arthroscopy should meet the climatic and environmental conditions of Group II in GB/T 14710-1993, the mechanical environmental conditions II group and Table 3
Requirements.
Table 3 Environmental test requirements and inspection items
Test item test conditions
Test requirements inspection project
Ongoing
/h
Recovery time
/h
Detection
surroundings
initial
test
intermediate
test
At last
test
Rated work
Low temperature test
5°C 1 - -
4.2~4.11
4.13
Low temperature storage
test
-40°C 4 5
Normal test
Test condition
Rated work
High temperature test
40°C 1 - - -
High temperature storage
test
55°C 4 5
Normal test
Test condition
Rated work
Damp heat test
40°C 80+2-3% 4 - - -
Wet heat storage
test
40°C 93+2-3% 48 24
Normal test
Test condition
Vibration test
Frequency cycle range. 5Hz-35Hz-5Hz
Amplitude. 0.35mm
Number of scan cycles. 15 times
Scan rate ≤ 1 octave/min
Working status. non-working status
With packaging
Normal test
Test condition
Table 2 can be
Clear observation
range
Crash test
Acceleration. 50m/s2
Pulse duration. 11ms ± 3ms
Number of collisions. 1000 times ± 10 times
Pulse repetition frequency. 1.0Hz ~ 1.7Hz
Pulse waveform. half sine wave
Working status. non-working status
With packaging
Normal test
Test condition
- -
4.2~
4.11,
4.13
5 Test methods
5.1 Surface and edge
Under sufficient illumination, the visual and hand test shall meet the requirements of 4.2, 4.8 and 4.11.
5.2 Dimensional inspection
Verification with general purpose and special gages shall be in accordance with the dimensions in 4.3 and 4.4. If the cross section of the insert is non-circular, measure the outer cut
The minimum length U of the curve, and then use the formula (1) to calculate the value of Fr, should meet the requirements of 4.3.
Fr=3U/π (1)
In the formula.
Fr---equal circumference, in millimeters (mm);
U---The minimum length of the external curve, in millimeters (mm).
5.3 Basic parameters of the endoscope
5.3.1 Field of view and viewing angle
5.3.1.1 Method 1
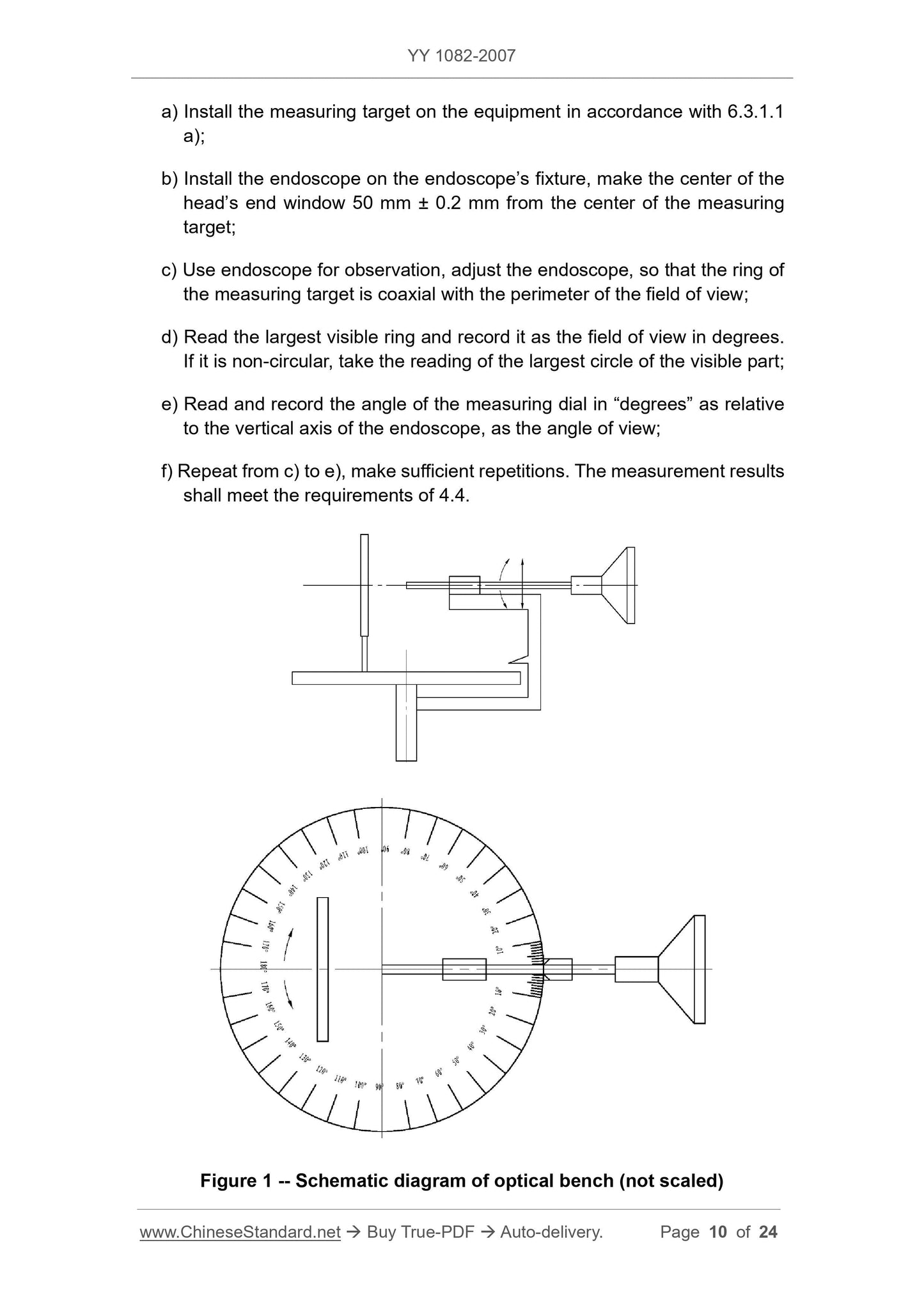
5.3.1.1.1 The measuring instrument consists of the following parts.
a) Optical bench or similar device that supports the endoscope for testing and adjusts the optical axis of the endoscope to coincide with the center of the measurement, endoscope
Measuring the field of view of the head end face at a distance of 50 mm from the center point of the concentric circle of the marked angle in the vertical direction;
b) the target holder and the dial divided by “degrees” (see Figure 1);
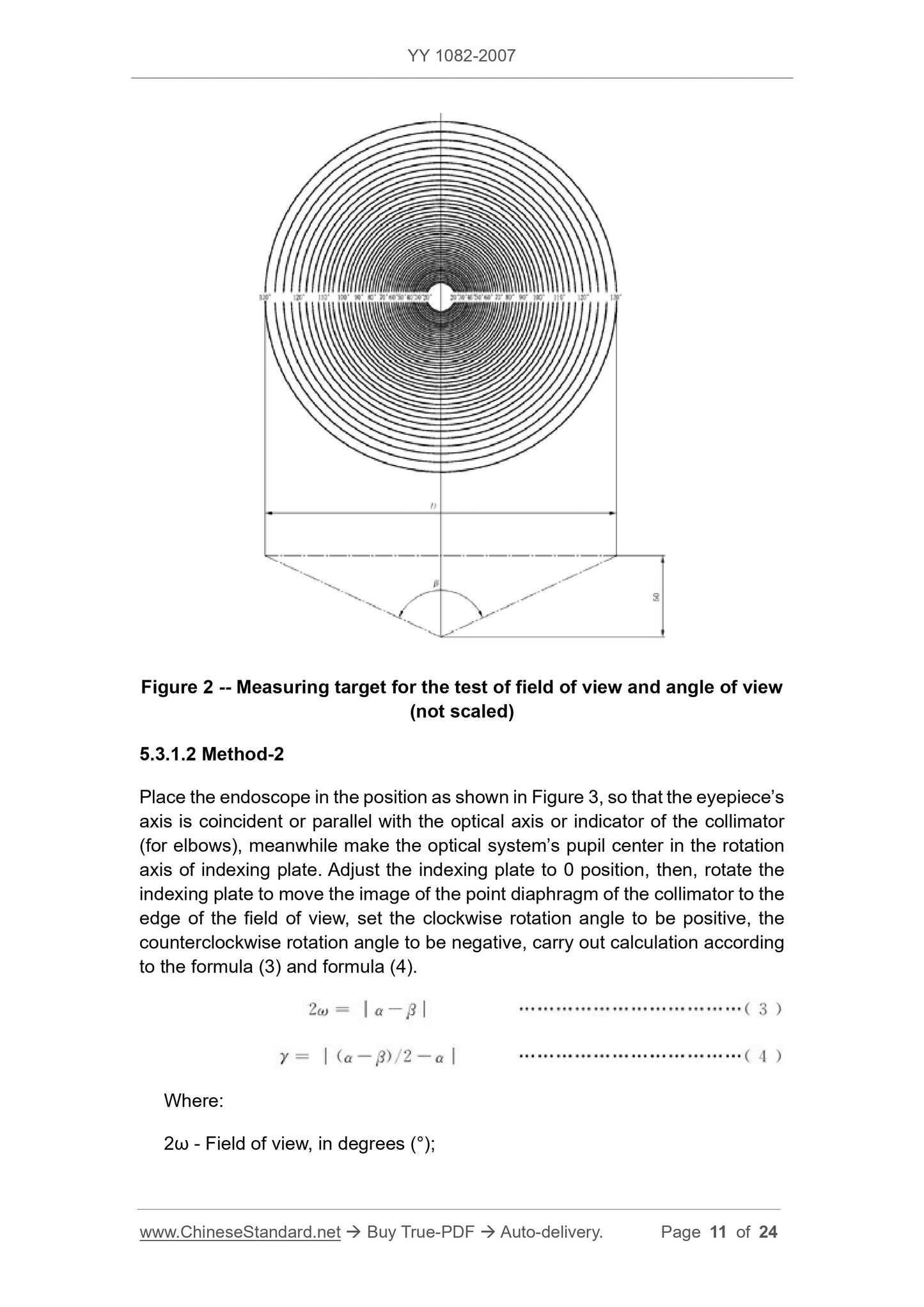
c) Measurement of field of view and viewing angle measurements (see Figure 2). Round, with a set of measurements in degrees of "degree", measured at 50 mm.
The ring of the measurement can be calculated by equation (2).
D=100tan(β/2)(2)
In the formula.
D---the diameter of the measuring ring corresponding to different angles of view, in millimeters (mm);
β---field angle, in degrees (°).
The calibration is fixed on the instrument;
There should be a main marking line every 10°, and the corresponding degree is indicated;
Marking lines should be marked every 2° between each main marking line, for a total of four;
d) Lighting should be measured by white light illumination, the minimum illumination is not less than 500lx, and an endoscope or external light source can be used.
5.3.1.1.2 Test methods, the following test methods are only recommended.
a) Mount the test mark on the equipment in accordance with 6.3.1.1 a);
b) Mount the endoscope on the endoscope fixture and make the center of the head end window 50 mm ± 0.2 mm from the center of the measurement;
c) observe with the endoscope and adjust the endoscope so that the ring of the measurement is coaxial with the perimeter of the field of view;
d) Read the largest visible ring and record it as the field of view in degrees. If it is non-circular, the largest part of the visible part can be read.
Reading
e) reading and recording the angle of the measuring dial in "degrees" relative to the vertical axis of the endoscope as the viewing angle;
f) Repeat from c) to e), repeat the number of times, the measurement results should meet the requirements of 4.4.
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of the optical bench (not to scale)
Figure 2 Measurement of field of view and viewing angle test (not to scale)
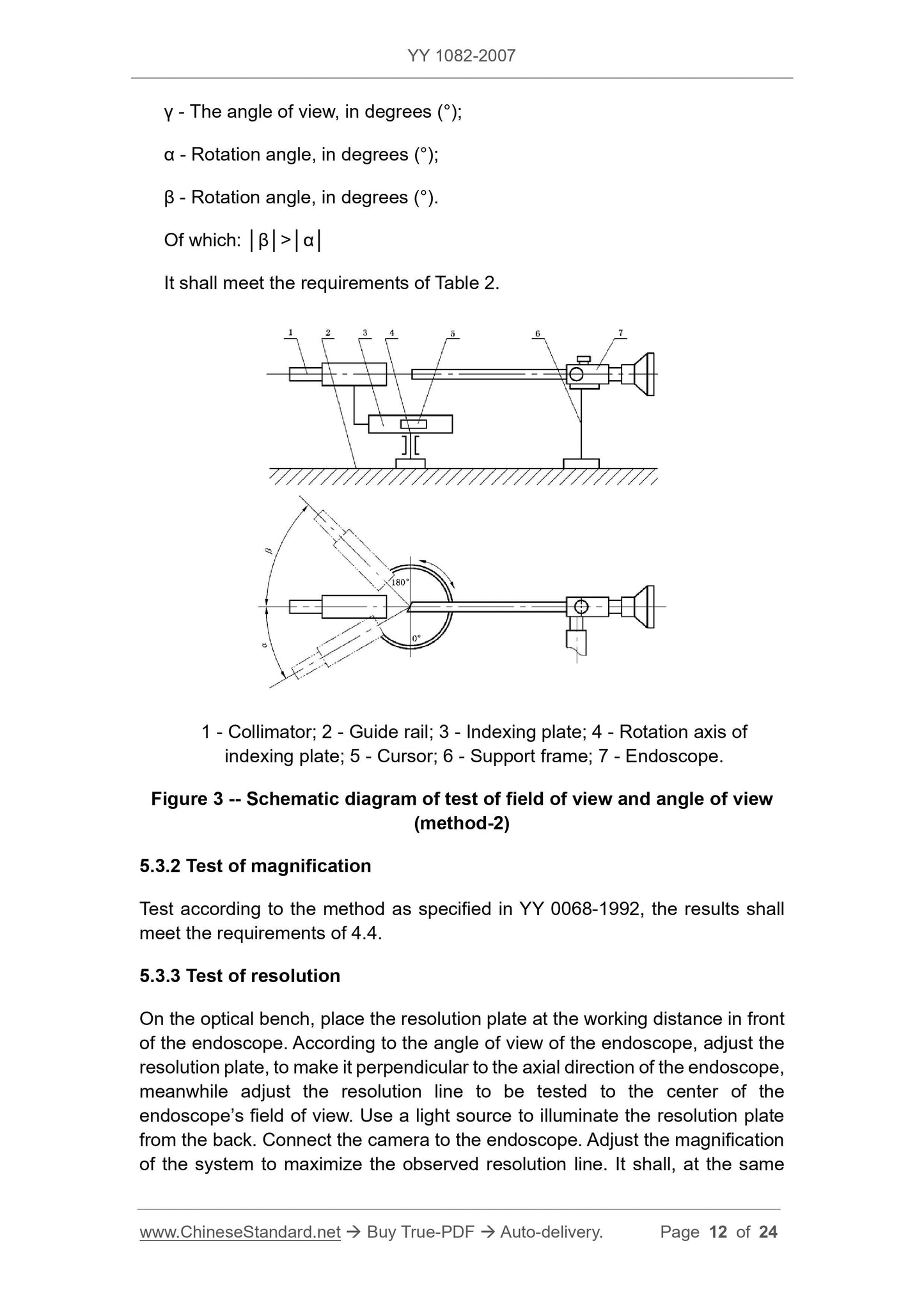
5.3.1.2 Method 2
Place the endoscope in the position shown in Figure 3 so that the eyepiece shaft is coincident or parallel with the collimator's optical axis or indicator (for elbows) and light is applied
The center of the system is located on the rotation axis of the indexing plate, adjust the indexing plate to the 0 position, and then rotate the indexing plate to make the image of the parallel light pipe
Move to the edge of the field of view, set the clockwise rotation angle to be positive, and the counterclockwise rotation angle to negative, according to equations (3) and (4).
2ω= │α-β│ (3)
γ= │(α-β)/2-α│ (4)
In the formula.
2ω---field angle, in degrees (°);
γ---angle of view, the unit is degree (°);
----rotation angle in degrees (°);
β---rotation angle in degrees (°).
Of which. │β│>│α│
Should meet the requirements of Table 2.
1---parallel light pipe;
2---rail;
3---indexing plate;
4---index dial rotation axis;
5---cursor;
6---support frame;
7---Endoscope.
Figure 3 Schematic diagram of field of view and viewing angle test (method 2)
5.3.2 Magnification test
Test accordi...
Get Quotation: Click YY 1082-2007 (Self-service in 1-minute)
Historical versions (Master-website): YY 1082-2007
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll-down if blank)
YY 1082-2007: Rigid arthroscope
YY 1082-2007
Rigid arthroscope
ICS 11.040.70
C40
People's Republic of China Pharmaceutical Industry Standard
Replacing YY 91082-1999
Hard endoscope
Released on.2007-07-02
2008-03-01 implementation
State Food and Drug Administration released
Foreword
This standard is a revision of YY 91082-1999 "Knee Arthroscopy".
The main changes of this standard compared with YY 91082-1999 are as follows.
--- Standardized the standard name;
--- Added model mark and component code mark;
--- Increased the two main parameters of "viewing angle" and "clear observation range";
--- Added "funnel eyepiece cover", "temperature change, no fog layer", "illuminance uniformity" requirements;
--- Increased biocompatibility requirements.
The electrical connection part fully implements GB 9706.1-1995 "Medical Electrical Equipment Part 1. General Requirements for Safety" and
GB 9706.19-2000 "Medical Electrical Equipment Part 2. Special Requirements for Endoscope Equipment Safety", the specific content is attached
Record A (normative appendix) is given in the form.
Appendix A of this standard is a normative appendix.
This standard is approved by the State Food and Drug Administration.
This standard is proposed and managed by the National Technical Committee for Standardization of Medical Optical Instruments.
This standard was drafted by Shenyang Shenda Endoscope Co., Ltd.
The main drafters of this standard. Jiang Kerang, Gao Mingxian, Memorial Training, Zhang Changan.
The previous versions of this standard were released as follows.
---ZBC40003-1989;
---YY 91082-1999.
Hard endoscope
1 range
This standard specifies the classification and marking of rigid endoscopes, requirements, test methods, inspection rules, signs, labels and instructions for use,
Packaging, transportation and storage.
This standard is applicable to rigid arthroscopy (hereinafter referred to as arthroscopy). Arthroscopy is suitable for the examination of human joint diseases in medical clinic.
Diagnosis, diagnosis, and treatment with the relevant surgical system.
2 Normative references
The terms in the following documents become the terms of this standard by reference to this standard. All dated references, followed by all
Modifications (not including errata content) or revisions do not apply to this standard, however, parties to agreements based on this standard are encouraged to study
Is it possible to use the latest version of these files? For undated references, the latest edition applies to this standard.
GB/T 191-2000 packaging storage and transportation icon mark
GB/T 2829-2002 Periodic inspection count sampling procedures and tables (applicable to the inspection of process stability)
GB/T 6463-2005 Review of metal and other inorganic coating thickness measurement methods
GB 9706.1-1995 Medical electrical equipment Part 1. General requirements for safety (idt IEC 601-1.1988)
GB 9706.19-2000 Medical electrical equipment - Part 2. Particular requirements for safety of endoscope equipment (idt IEC 60601-2-18.
1996)
GB 11244-2005 General requirements for medical endoscopes and accessories
GB/T 14710-1993 Environmental requirements and test methods for medical electrical equipment
GB/T 16886.1-2001 Biological evaluation of medical devices - Part 1. Evaluation and testing (ISO 10993-1..1997, IDT)
GB/T 16886.5-2003 Biological evaluation of medical devices - Part 5. In vitro cytotoxicity test (ISO 10993-5..1999,
IDT)
GB/T 16886.10-2005 Biological evaluation of medical devices - Part 10. Stimulation and delayed hypersensitivity test
(ISO 10993-10.2002, IDT)
YY 0068 General technical conditions for medical rigid endoscopes
YY 0076-1992 Metal parts plating classification technical conditions
YY 0466-2003 Symbols for medical devices used for labeling, marking and providing information on medical devices (ISO 15223.2000, IDT)
3 composition
The arthroscope consists of an endoscope, a mirror sheath and a obturator, a puncture needle, a device puncture cannula, a instrument puncture needle, and a light guide beam.
4 requirements
4.1 Arthroscopy is a rigid endoscope product, in addition to the following requirements, it should also comply with the general requirements of YY 0068.
4.2 Surface and edge except for the puncture needle and the instrument needle. The components of the arthroscope should be designed so as not to cause any accidental injury to the human body.
Harm, all surfaces must be free of pores, cracks and burrs.
4.3 The basic dimensions of the arthroscope should meet the requirements of Table 1.
Table 1 The basic dimensions of arthroscopy are in millimeters
Project name basic parameter limit deviation
Maximum insert outer diameter
Minimum instrument hole diameter
Insert working length
Nominal value
No more than the nominal value
Not less than the nominal value
±3%
Guide beam length >1500 -
Note. When the insertion part is a circular tube, it is represented by a diameter (mm), and when it is a non-circular tube, it is represented by an equivalent circumference Fr.
4.4 The basic parameters of the arthroscopy endoscope should meet the requirements of Table 2.
Table 2 Basic parameters of the endoscope
Project name basic parameter limit deviation
Mirror outer diameter/mm
Field of view/(°)
Viewing angle/(°)
Nominal value
+5%
-5%
±5°
Magnification ≥ 5 -
Resolution/(lp/mm) ≥ 31.5 -
Can clearly observe the range/mm 1 ~ 50 -
Illuminance/lx >1500 -
Note 1. When the outer diameter of the mirror body is less than 2.7mm, the resolution, magnification, and illuminance are specified by the manufacturer in the product standard.
Note 2. The working distance of magnification, resolution and illuminance is 4mm.
4.5 Arthroscopy endoscopes should meet the following requirements.
a) Endoscopic imaging should be clear, the edge of the field of view should be rounded, and there should be no defects such as scratches, pitting and attachments that affect the observation;
b) Funnel type eyepiece cover. it should meet the requirements of 4.6 of GB 11244-2005;
c) When the temperature changes within the range of 20 °C ~ 40 °C, no fog layer affecting the observation shall be produced;
d) The seal should be good, after the seal test, there is no image blurring phenomenon;
e) through the endoscope observation, the illumination spot should be filled with the field of view at a working distance of 4 mm;
f) When the distance is 50mm, the uniformity of illumination should be no less than 80%;
g) An endoscope that can be sterilized by pressure steam. After the test, the resolution and illuminance of the endoscope are not less than 95% of the original value.
4.6 After the mirror sheath is connected with the endoscope, the obturator and the puncture needle, the sealing of each joint and the water valve should be good, and the water seepage should be within 1 min.
No more than three drops.
4.7 The inner hole of the mirror sheath should be clean and smooth. The opening and closing of the inlet and outlet valves should be flexible and effective. After connecting with the endoscope, the flow rate of the water should be not less than
200 mL/min.
4.8 The head of the puncture needle should be smooth and sharp, the head of the blunt obturator should be smooth and round, and the handle of the needle of the instrument should be smooth and smooth.
4.9 The inner hole of the instrument puncture cannula should be clean and smooth, and can smoothly pass the instrument puncture needle and the supporting surgical instruments.
4.10 The hardness of the needle of the puncture needle and the instrument needle should be HRC36~46.
4.11 The welded parts of the arthroscope should be firm and reliable, smooth and smooth, and there is no welding or surfacing.
4.12 The plating of electroplated parts of arthroscopy shall comply with the Class V Class 2 requirements of YY 0076-1992.
4.13 Arthroscopy is a medical device that is short-term contact with the damaged surface. The outer surface material of the insertion portion should be certified to conform to the biological phase.
Capacitive material manufacturing, otherwise the following tests should be passed.
a) the cytotoxicity score should be no more than 1;
b) the type of stimulus should be no more than mild;
c) There should be no sensitization.
4.14 Safety requirements for interconnection with medical electrical equipment.
Arthroscopy should meet the requirements of GB 9706.1-1995 and GB 9706.19-2000. See Appendix A for specific requirements (normative
appendix).
4.15 The environmental test of arthroscopy should meet the climatic and environmental conditions of Group II in GB/T 14710-1993, the mechanical environmental conditions II group and Table 3
Requirements.
Table 3 Environmental test requirements and inspection items
Test item test conditions
Test requirements inspection project
Ongoing
/h
Recovery time
/h
Detection
surroundings
initial
test
intermediate
test
At last
test
Rated work
Low temperature test
5°C 1 - -
4.2~4.11
4.13
Low temperature storage
test
-40°C 4 5
Normal test
Test condition
Rated work
High temperature test
40°C 1 - - -
High temperature storage
test
55°C 4 5
Normal test
Test condition
Rated work
Damp heat test
40°C 80+2-3% 4 - - -
Wet heat storage
test
40°C 93+2-3% 48 24
Normal test
Test condition
Vibration test
Frequency cycle range. 5Hz-35Hz-5Hz
Amplitude. 0.35mm
Number of scan cycles. 15 times
Scan rate ≤ 1 octave/min
Working status. non-working status
With packaging
Normal test
Test condition
Table 2 can be
Clear observation
range
Crash test
Acceleration. 50m/s2
Pulse duration. 11ms ± 3ms
Number of collisions. 1000 times ± 10 times
Pulse repetition frequency. 1.0Hz ~ 1.7Hz
Pulse waveform. half sine wave
Working status. non-working status
With packaging
Normal test
Test condition
- -
4.2~
4.11,
4.13
5 Test methods
5.1 Surface and edge
Under sufficient illumination, the visual and hand test shall meet the requirements of 4.2, 4.8 and 4.11.
5.2 Dimensional inspection
Verification with general purpose and special gages shall be in accordance with the dimensions in 4.3 and 4.4. If the cross section of the insert is non-circular, measure the outer cut
The minimum length U of the curve, and then use the formula (1) to calculate the value of Fr, should meet the requirements of 4.3.
Fr=3U/π (1)
In the formula.
Fr---equal circumference, in millimeters (mm);
U---The minimum length of the external curve, in millimeters (mm).
5.3 Basic parameters of the endoscope
5.3.1 Field of view and viewing angle
5.3.1.1 Method 1
5.3.1.1.1 The measuring instrument consists of the following parts.
a) Optical bench or similar device that supports the endoscope for testing and adjusts the optical axis of the endoscope to coincide with the center of the measurement, endoscope
Measuring the field of view of the head end face at a distance of 50 mm from the center point of the concentric circle of the marked angle in the vertical direction;
b) the target holder and the dial divided by “degrees” (see Figure 1);
c) Measurement of field of view and viewing angle measurements (see Figure 2). Round, with a set of measurements in degrees of "degree", measured at 50 mm.
The ring of the measurement can be calculated by equation (2).
D=100tan(β/2)(2)
In the formula.
D---the diameter of the measuring ring corresponding to different angles of view, in millimeters (mm);
β---field angle, in degrees (°).
The calibration is fixed on the instrument;
There should be a main marking line every 10°, and the corresponding degree is indicated;
Marking lines should be marked every 2° between each main marking line, for a total of four;
d) Lighting should be measured by white light illumination, the minimum illumination is not less than 500lx, and an endoscope or external light source can be used.
5.3.1.1.2 Test methods, the following test methods are only recommended.
a) Mount the test mark on the equipment in accordance with 6.3.1.1 a);
b) Mount the endoscope on the endoscope fixture and make the center of the head end window 50 mm ± 0.2 mm from the center of the measurement;
c) observe with the endoscope and adjust the endoscope so that the ring of the measurement is coaxial with the perimeter of the field of view;
d) Read the largest visible ring and record it as the field of view in degrees. If it is non-circular, the largest part of the visible part can be read.
Reading
e) reading and recording the angle of the measuring dial in "degrees" relative to the vertical axis of the endoscope as the viewing angle;
f) Repeat from c) to e), repeat the number of times, the measurement results should meet the requirements of 4.4.
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of the optical bench (not to scale)
Figure 2 Measurement of field of view and viewing angle test (not to scale)
5.3.1.2 Method 2
Place the endoscope in the position shown in Figure 3 so that the eyepiece shaft is coincident or parallel with the collimator's optical axis or indicator (for elbows) and light is applied
The center of the system is located on the rotation axis of the indexing plate, adjust the indexing plate to the 0 position, and then rotate the indexing plate to make the image of the parallel light pipe
Move to the edge of the field of view, set the clockwise rotation angle to be positive, and the counterclockwise rotation angle to negative, according to equations (3) and (4).
2ω= │α-β│ (3)
γ= │(α-β)/2-α│ (4)
In the formula.
2ω---field angle, in degrees (°);
γ---angle of view, the unit is degree (°);
----rotation angle in degrees (°);
β---rotation angle in degrees (°).
Of which. │β│>│α│
Should meet the requirements of Table 2.
1---parallel light pipe;
2---rail;
3---indexing plate;
4---index dial rotation axis;
5---cursor;
6---support frame;
7---Endoscope.
Figure 3 Schematic diagram of field of view and viewing angle test (method 2)
5.3.2 Magnification test
Test accordi...
Share