1
/
of
12
PayPal, credit cards. Download editable-PDF & invoice in 1 second!
YY/T 0471.5-2017 English PDF (YYT0471.5-2017)
YY/T 0471.5-2017 English PDF (YYT0471.5-2017)
Regular price
$170.00 USD
Regular price
Sale price
$170.00 USD
Unit price
/
per
Shipping calculated at checkout.
Couldn't load pickup availability
Delivery: 3 seconds. Download true-PDF + Invoice.
Get Quotation: Click YY/T 0471.5-2017 (Self-service in 1-minute)
Historical versions (Master-website): YY/T 0471.5-2017
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll-down if blank)
YY/T 0471.5-2017: Test Methods for Primary Wound Dressings - Part 5: Bacterial Barrier Properties
YY/T 0471.5-2017
Test methods for primary wound dressings—Part 5. Bacterial barrier properties
ICS 11.120.20
C48
People's Republic of China Pharmaceutical Industry Standard
Replacing YY/T 0471.5-2004
Contact wound dressing test method
Part 5. Resilience
Part 5. Bacterialbarrierproperties
Published on.2017-02-28
2018-01-01 implementation
State Food and Drug Administration issued
Foreword
YY/T 0471 "Test Method for Contact Wound Dressing" is divided into six parts.
---Part 1. Liquid absorption;
--- Part 2. Water vapor transmission rate of breathable film dressings;
--- Part 3. Water repellency;
--- Part 4. Comfort;
---Part 5. Resilience;
--- Part 6. Odour control.
This part is part 5 of YY/T 0471.
This part is drafted in accordance with the rules given in GB/T 1.1-2009.
This part replaces YY/T 0471.5-2004 "Test methods for contact wound dressings - Part 5. bacteriostatic", and YY/T 0471.5-
Compared with.2004, the main technical changes are as follows.
--- Added "external dry internal wet" inhibition test method;
---Modified each test method;
--- Added informational appendix;
---Other editorial changes.
Please note that some of the contents of this document may involve patents. The issuing organization of this document is not responsible for identifying these patents.
This part is proposed by the State Food and Drug Administration.
This part is under the jurisdiction of Jinan Medical Device Quality Supervision and Inspection Center of the State Food and Drug Administration.
This section drafted by. Shandong Medical Device Product Quality Inspection Center, Shandong Sikesisi Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd., Minnesota
Mining Manufacturing Medical Equipment (Shanghai) Co., Ltd., Leisure Health (China) Medical Products Co., Ltd.
Drafters of this section. Wang Wenqing, Hao Dali, Zheng Yang, Hao Jianxin, Lu Jinrong, Li Yu.
The previous versions of this part of YY/T 0471 are released as follows.
YY/T 0471.5-2004 was first released on March 23,.2004.
Contact wound dressing test method
Part 5. Resilience
1 Scope
This part of YY/T 0471 specifies tests for the evaluation of the bacteriostatic properties of contact wound dressings that claim to have bacteriostatic properties.
method 1).
This test method involves microbiological testing and should be tested by trained personnel in a biosafety laboratory.
2 Terms and definitions
The following terms and definitions apply to this document.
2.1
Dry lowmoisturecondition
The two sides of the dressing are not wet. The dressing in this state, the wound surface has no exudate or a very small amount of exudate, and the outer surface of the dressing is at
Dry state.
Note. If the dressing does not claim to block water, it is considered that the outer surface is dry.
2.2
Semi-wet semiwetcondition
One side of the dressing is in a wet state. In the dressing in this state, the exudate leaks out of the wound surface, and the outer surface of the dressing is in a dry state, that is, "outside
Dry internal wetness; or, the wound surface has no exudate or a very small amount of exudate, and the outer surface of the dressing is expected to be in a wet state, that is, "dry outside."
Note. If the dressing does not claim to block water, it is considered that the outer surface is in a dry state; if the dressing claims to block water, it is considered that the outer surface is in a damp state.
2.3
Wet state
Both sides of the dressing are wet. The dressing in this state, the exudate oozes out on the wound surface, and the outer surface of the dressing is expected to be wet
status.
Note. If the dressing claims to block water, it is considered that the outer surface is in a damp state.
3 reagents and materials
3.1 Serratia marcescens 2);
3.2 nutrient broth medium;
3.3 nutrient agar medium;
3.4 sterile saline;
3.5 Sterile swabs.
1) Antibacterial ingredients in the dressing may have an effect on the test results in this section. Appendix A gives the application notes for this section.
2) Standard strains of approved strain collection institutions at home and abroad, such as ATCC8100, CICC10187, etc. Some Serratia marcescens can be presented on the surface of agar
Red colonies, such as CICC10187, are available, and this feature can be used to check for the growth of Serratia marcescens. This information is given for the convenience of this
Part of the user.
4 Challenge microbial preparation
4.1 Challenge inoculum preparation
Picking up Serratia marcescens colonies from the slant surface of Serratia marcescens working strain, streaked on the nutrient agar medium plate, 26 ° C
The challenge inoculum was prepared by overnight culture for dry inhibition and semi-wet (outer dry) wet inhibition test. Prepared tablet
It should be used on the same day.
4.2 Challenge bacterial preparation
A single colony of Serratia marcescens was picked from the challenge inoculum plate prepared in 4.1 and inoculated into the nutrient broth medium at 26 °C.
Night culture was carried out to obtain a challenge bacterial solution having a concentration of about 109 CFU/mL, which was used for the semi-wet state (outer wet dryness) and the wet state inhibition test. Prepared well
The challenge bacteria solution should be used on the same day.
5 dry inhibition
5.1 Test device
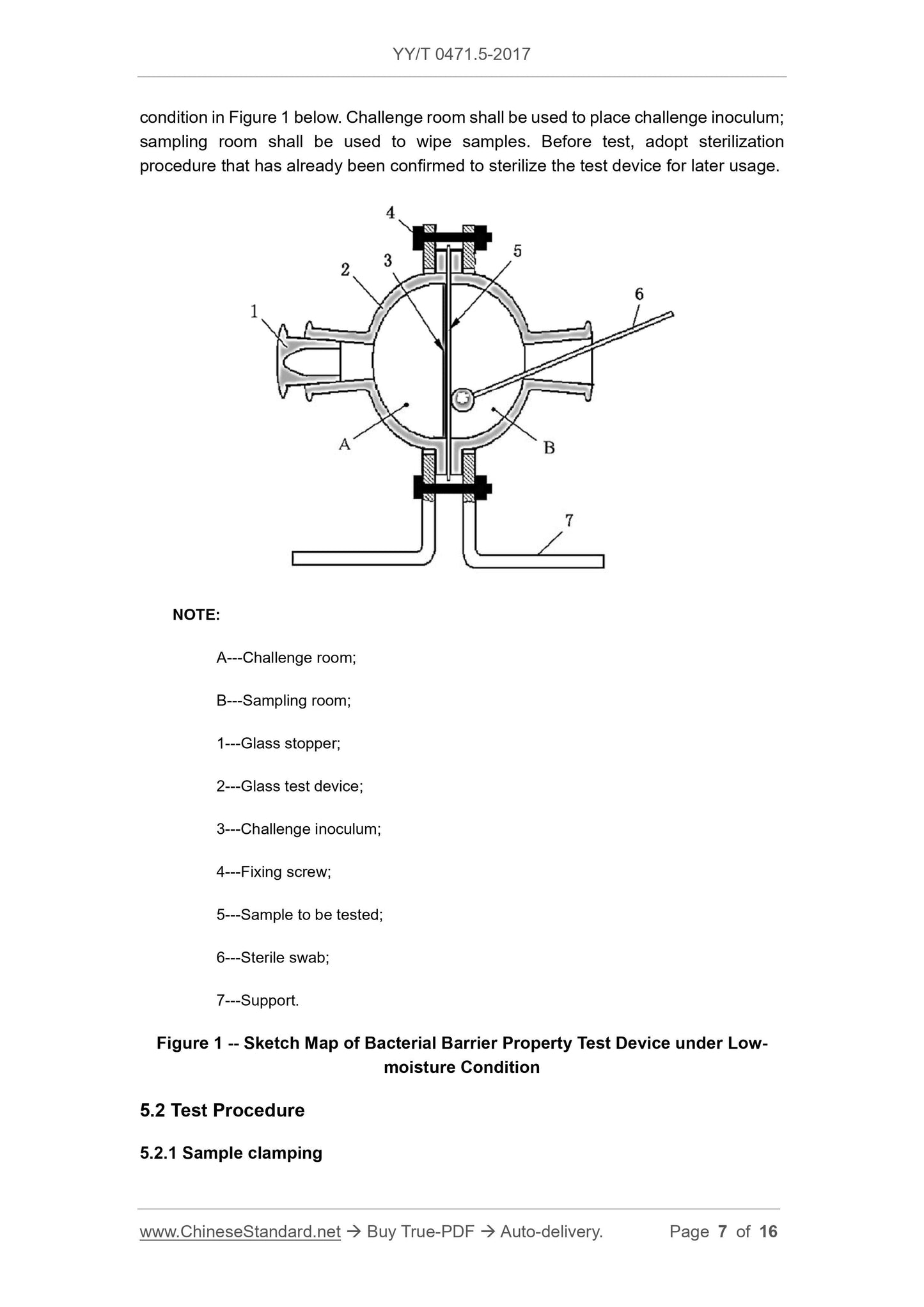
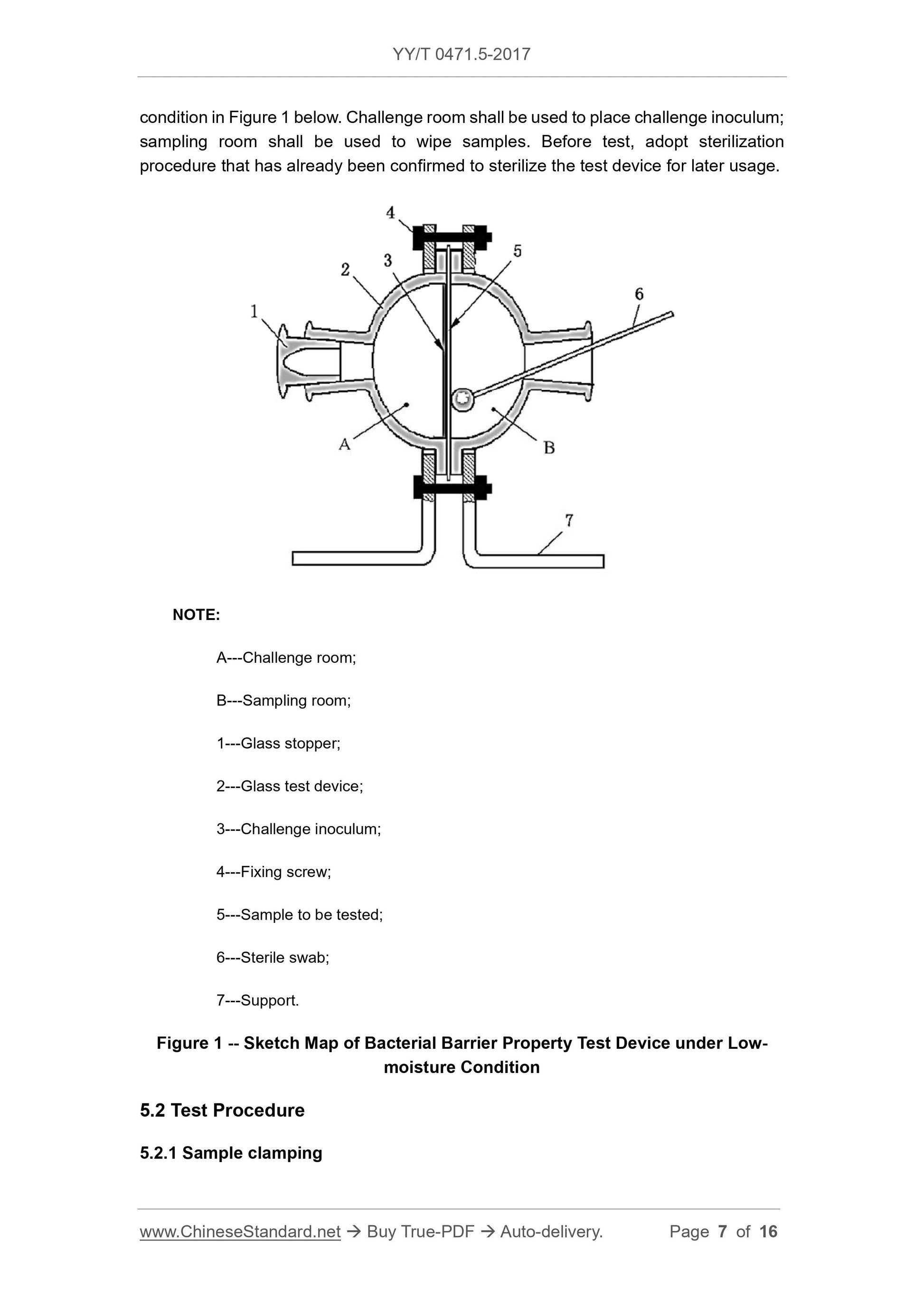
Figure 1 is a schematic diagram of a dry bacteriostatic test device. The challenge room is used to hold the challenge inoculum and the sampling chamber is used to wipe the sample. Before the test,
The test device is sterilized using a confirmed sterilization procedure.
Description.
A---Challenge room;
B---sampling room;
1 --- glass stopper;
2 --- glass test device;
3 --- challenge inoculum;
4 --- fixing screws;
5 --- test sample;
6 --- sterile swab;
7 --- bracket.
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of the dry bacteriostatic test device
5.2 Test procedure
5.2.1 Sample clamping
Take three samples separately so that the inner surface of the sample faces the sampling chamber and clamp the sample between the challenge chamber and the sampling chamber. The clamping method should go through
Confirm to ensure that no leakage of challenging microorganisms occurs. For larger samples, the remainder can be cut or wrapped around the experimental device
For small samples, it can be tested with larger sample materials, or can be filled in a suitable way.
Partially used for testing.
5.2.2 Adding challenged microorganisms
Wipe the challenge inoculum with a sterile swab and inoculate it onto the outer surface of the sample through the challenge chamber and spread as evenly as possible.
5.2.3 Sample Challenge
Close the challenge chamber and sampling chamber of the test device in a suitable manner to ensure that no external contamination will occur and place the test device
In a 26 ° C incubator for 24 h.
5.2.4 Penetration microbiological examination
After the specified time, pre-wet the sterile swab in sterile physiological saline and squeeze out the excess water, and wipe the sample as much as possible through the sampling chamber.
All inner surfaces were inoculated and then inoculated by wiping the surface of the nutrient agar plate. Wipe the sample with three sterile swabs per sample.
Inoculation was performed on three nutrient agar plates, respectively, during which the swab should be rotated multiple times. The nutrient agar plates were incubated at 26 ° C for 24 h.
5.2.5 Challenge Microbial Vitality Check
After the specified time, refer to 5.2.4 and wipe the outer surface of the sample through the challenge chamber to check for the challenge of microbial activity.
5.3 Result judgment
The nutrient agar medium plate used for vitality examination should have Serratia marcescens growth, otherwise the test is invalid. If used in the sample table
No microbial growth was observed on the nutrient agar plates analyzed by surface sampling, which was judged to be in compliance with the dry bacteriostatic requirements. If used for sample surface sampling
Microbial growth was observed on the nutrient agar plates analyzed, and appropriate microbiological methods should be used to check whether it is Serratia marcescens. If it is sticky
Serratia marcescens is judged to be inconsistent with the requirements of dry bacteriostasis; if it is not Serratia marcescens, it indicates that there is external pollution and the test is invalid.
6 semi-wet state (outer dry internal wet) bacteriostatic
6.1 Test device
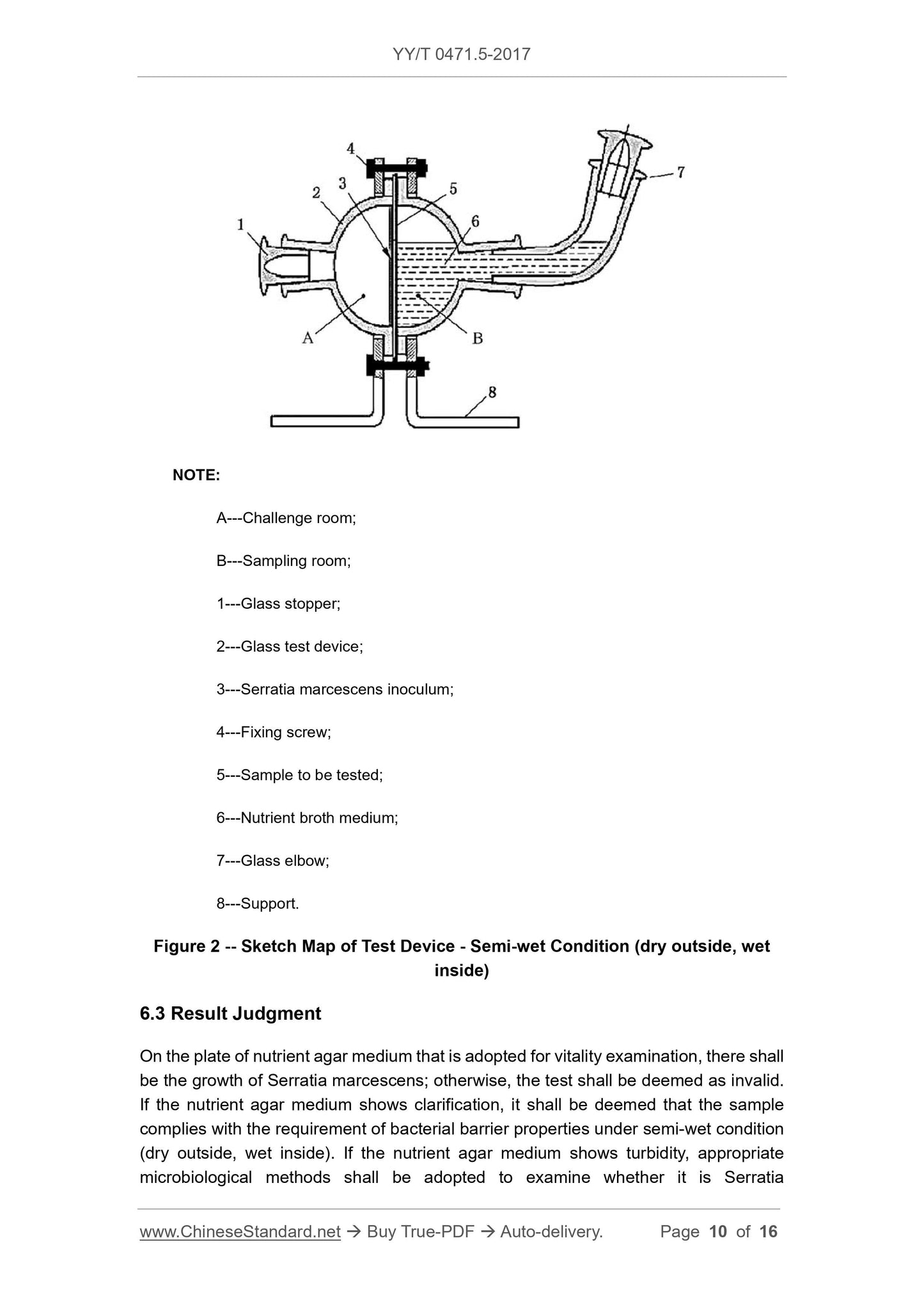
Figure 2 is a schematic diagram of a semi-wet (outer dry internal wet) bacteriostatic test device. The challenge room is used to hold the challenge inoculum, and the sampling room is used for holding
Nutritional broth medium. Prior to testing, the test device was sterilized using a validated sterilization procedure.
6.2 Test methods
6.2.1 Sample clamping
Follow the instructions in 5.2.1.
6.2.2 Adding challenged microorganisms
Follow the instructions in 5.2.2.
6.2.3 Add nutrient broth culture medium
Fill the sampling chamber with a nutrient broth medium in an aseptically operated manner.
6.2.4 Sample Challenge
Follow the instructions in 5.2.3.
6.2.5 Penetration microbiological examination
After the specified time, the microbial growth in the nutrient broth medium was visually observed.
6.2.6 Challenge Microbial Vitality Check
Follow the instructions in 5.2.5.
Description.
A---Challenge room;
B---sampling room;
1 --- glass stopper;
2 --- glass test device;
3 --- Serratia marcescens inoculum;
4 --- fixing screws;
5 --- test sample;
6 --- nutrient broth medium;
7 --- glass elbow;
8 --- bracket.
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of the test device --- semi-wet state (outer dry internal wet)
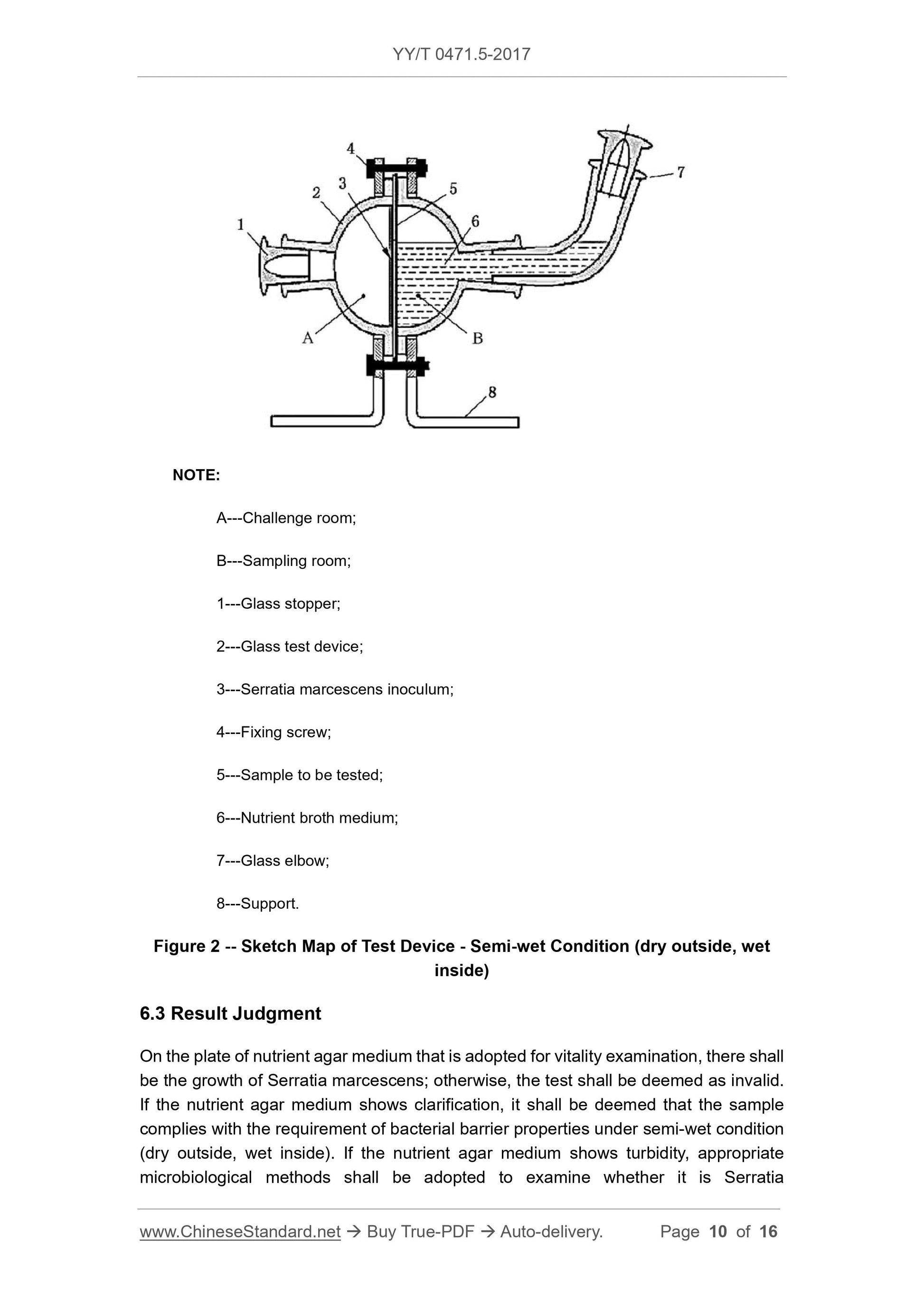
6.3 Result judgment
The nutrient agar medium plate used for vitality examination should have Serratia marcescens growth, otherwise the test is invalid. If nutrient broth culture
The base shows clarification and is judged to meet the requirements of the semi-wet state (external dry internal wetness). If the nutrient broth medium shows turbidity, the appropriate micro should be used.
Biological methods to check whether it is Serratia marcescens. If it is Serratia marcescens, it is judged to be inconsistent with the semi-wet state (external dry internal wetness) resistance requirement;
If it is not Serratia marcescens, it indicates that there is external pollution and the test is invalid.
Note. If necessary, sterile nutrient broth medium can be set as a negative control (showing clarification) and nutrient broth cultured with Serratia marcescens as
A positive control (showing turbidity) to avoid visual observation of possible subjective errors of clarification or turbidity.
7 semi-wet state (outer wet internal dry) bacteriostatic
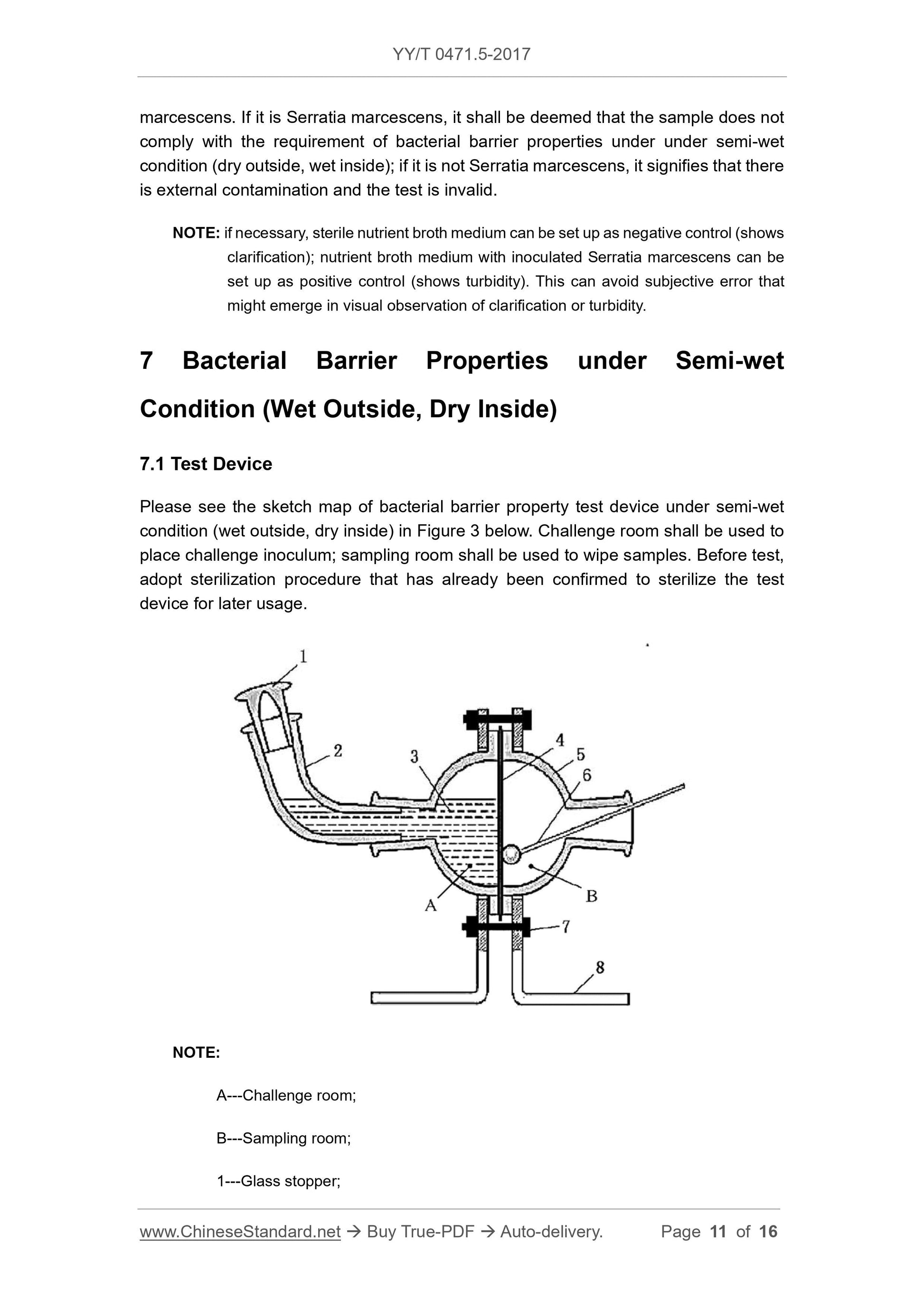
7.1 Test device
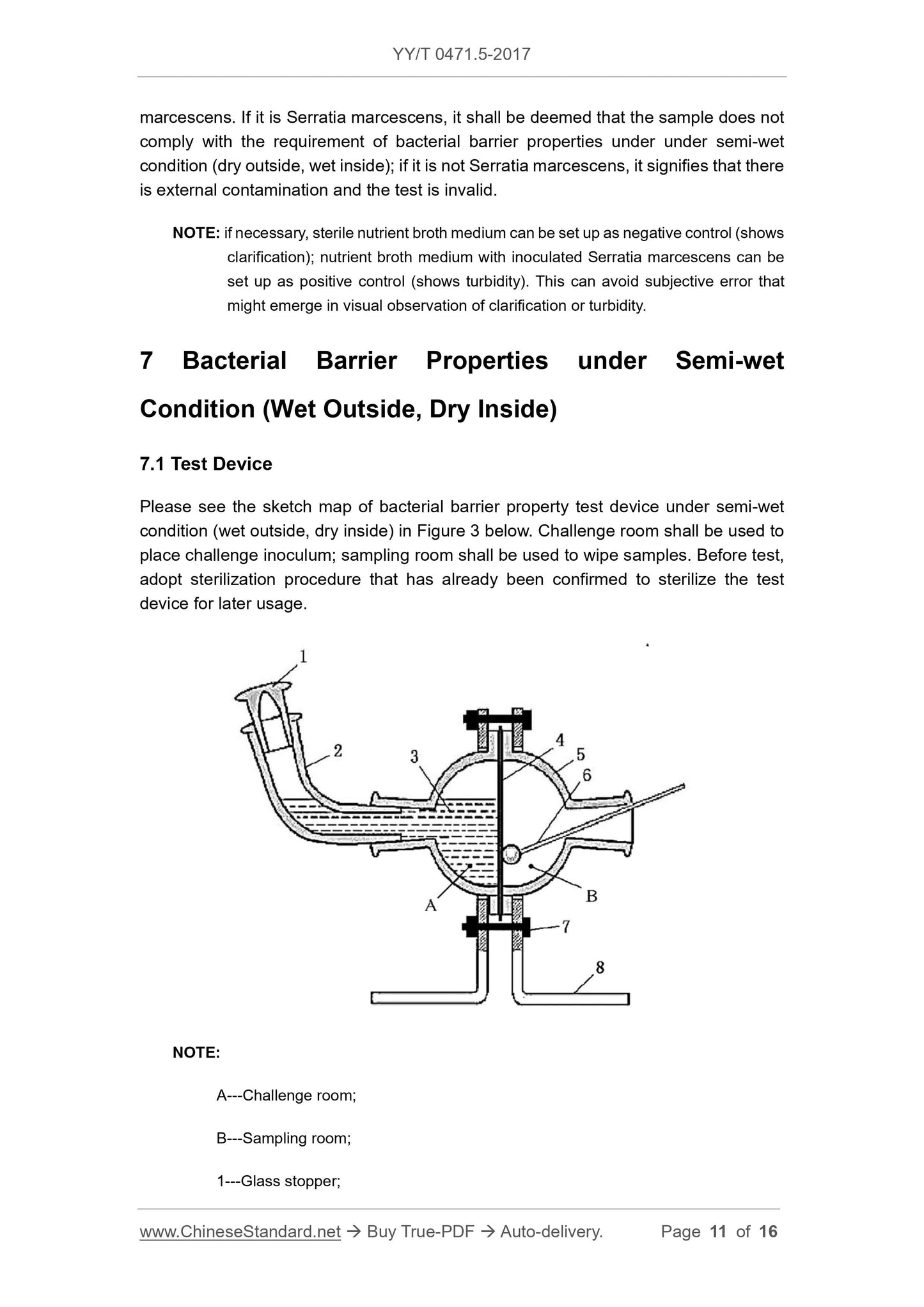
Fig. 3 is a schematic view of a semi-wet state (outer wet internal dry) bacteriostatic test device. The challenge room is used to hold the challenge liquid, and the sampling room is used for wiping
kind. Prior to testing, the test device was sterilized using a validated sterilization procedure.
Description.
A---Challenge room;
B---sampling room;
1 --- glass stopper;
2 --- glass elbow;
3 --- challenge bacterial liquid;
4 --- test sample;
5 --- glass test device;
6 --- sterile swab;
7 --- fixing screws;
8 --- bracket.
Figure 3 Schematic diagram of the test device --- semi-wet state (outer wet internal dry)
7.2 Test methods
7.2.1 Sample clamping
Follow the instructions in 5.2.1.
7.2.2 Adding challenged microorganisms
Fill the challenge room with the challenge liquid.
7.2.3 Sample Challenge
Follow the instructions in 5.2.3.
7.2.4 Penetration microbiological examination
Follow the instructions in 5.2.4.
7.2.5 Challenge microbial activity check
After the specified time, the sterile agar medium plate was swabbed with a sterile swab to collect the challenge bacteria solution to check for the challenge of microbial activity.
Three sterile swabs were used for each sample, and were applied to three nutrient agar plates for inoculation, and the plates were placed at 26 °C.
Raise for 24 hours.
7.3 Judgment of results
The nutrient agar medium plate used for vitality examination should have Serratia marcescens growth, otherwise the test is invalid. If used in the sample table
No microbial growth was observed on the nutrient agar medium plate of the surface sampling analysis, which was judged to be in compliance with the semi-wet state (external wet internal dryness). in case
Microbial growth on nutrient agar medium plates for sample surface analysis of samples, which should be examined by appropriate microbiological methods.
Whether it is a sticky Serratia. If it is Serratia marcescens, it is judged to be inconsistent with the semi-wet state (external wet internal dry) resistance; if it is not sticky saras
Bacteria, indicating that there is external pollution, the test is invalid.
8 wet state inhibition
8.1 Test device
Figure 4 is a schematic view of a wet bacteriostatic test device. The challenge room is used to hold the challenge bacteria solution, and the sampling room is used to hold the nutrient broth medium.
Prior to testing, the test device was sterilized using a validated sterilization procedure.
Description.
A---Challenge room;
B---sampling room;
1 --- glass stopper;
2 --- glass elbow;
3 --- challenge bacterial liquid;
4 --- test sample;
5 --- glass test device;
6 ---TSB medium;
7 --- fixing screws;
8 --- bracket.
Figure 4 Schematic diagram of the test device --- wet state
8.2 Test methods
8.2.1 Sample clamping
Follow the instructions in 5.2.1.
8.2.2 Adding challenged microorganisms
Follow the instructions in 7.2.2.
8.2.3 Adding nutrient broth culture medium
Follow the instructions in 6.2.3.
8.2.4 Sample Challenge
Follow the instructions in 5.2.3.
8.2.5 Penetration microbiological examination
Follow the instructions in 6.2.5.
8.2.6 Challenge Microbial Vitality Check
Follow the instructions in 7.2.5.
8.3 Result judgment
The nutrient agar medium plate used for vitality examination should have Serratia marcescens growth, otherwise the te...
Get Quotation: Click YY/T 0471.5-2017 (Self-service in 1-minute)
Historical versions (Master-website): YY/T 0471.5-2017
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll-down if blank)
YY/T 0471.5-2017: Test Methods for Primary Wound Dressings - Part 5: Bacterial Barrier Properties
YY/T 0471.5-2017
Test methods for primary wound dressings—Part 5. Bacterial barrier properties
ICS 11.120.20
C48
People's Republic of China Pharmaceutical Industry Standard
Replacing YY/T 0471.5-2004
Contact wound dressing test method
Part 5. Resilience
Part 5. Bacterialbarrierproperties
Published on.2017-02-28
2018-01-01 implementation
State Food and Drug Administration issued
Foreword
YY/T 0471 "Test Method for Contact Wound Dressing" is divided into six parts.
---Part 1. Liquid absorption;
--- Part 2. Water vapor transmission rate of breathable film dressings;
--- Part 3. Water repellency;
--- Part 4. Comfort;
---Part 5. Resilience;
--- Part 6. Odour control.
This part is part 5 of YY/T 0471.
This part is drafted in accordance with the rules given in GB/T 1.1-2009.
This part replaces YY/T 0471.5-2004 "Test methods for contact wound dressings - Part 5. bacteriostatic", and YY/T 0471.5-
Compared with.2004, the main technical changes are as follows.
--- Added "external dry internal wet" inhibition test method;
---Modified each test method;
--- Added informational appendix;
---Other editorial changes.
Please note that some of the contents of this document may involve patents. The issuing organization of this document is not responsible for identifying these patents.
This part is proposed by the State Food and Drug Administration.
This part is under the jurisdiction of Jinan Medical Device Quality Supervision and Inspection Center of the State Food and Drug Administration.
This section drafted by. Shandong Medical Device Product Quality Inspection Center, Shandong Sikesisi Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd., Minnesota
Mining Manufacturing Medical Equipment (Shanghai) Co., Ltd., Leisure Health (China) Medical Products Co., Ltd.
Drafters of this section. Wang Wenqing, Hao Dali, Zheng Yang, Hao Jianxin, Lu Jinrong, Li Yu.
The previous versions of this part of YY/T 0471 are released as follows.
YY/T 0471.5-2004 was first released on March 23,.2004.
Contact wound dressing test method
Part 5. Resilience
1 Scope
This part of YY/T 0471 specifies tests for the evaluation of the bacteriostatic properties of contact wound dressings that claim to have bacteriostatic properties.
method 1).
This test method involves microbiological testing and should be tested by trained personnel in a biosafety laboratory.
2 Terms and definitions
The following terms and definitions apply to this document.
2.1
Dry lowmoisturecondition
The two sides of the dressing are not wet. The dressing in this state, the wound surface has no exudate or a very small amount of exudate, and the outer surface of the dressing is at
Dry state.
Note. If the dressing does not claim to block water, it is considered that the outer surface is dry.
2.2
Semi-wet semiwetcondition
One side of the dressing is in a wet state. In the dressing in this state, the exudate leaks out of the wound surface, and the outer surface of the dressing is in a dry state, that is, "outside
Dry internal wetness; or, the wound surface has no exudate or a very small amount of exudate, and the outer surface of the dressing is expected to be in a wet state, that is, "dry outside."
Note. If the dressing does not claim to block water, it is considered that the outer surface is in a dry state; if the dressing claims to block water, it is considered that the outer surface is in a damp state.
2.3
Wet state
Both sides of the dressing are wet. The dressing in this state, the exudate oozes out on the wound surface, and the outer surface of the dressing is expected to be wet
status.
Note. If the dressing claims to block water, it is considered that the outer surface is in a damp state.
3 reagents and materials
3.1 Serratia marcescens 2);
3.2 nutrient broth medium;
3.3 nutrient agar medium;
3.4 sterile saline;
3.5 Sterile swabs.
1) Antibacterial ingredients in the dressing may have an effect on the test results in this section. Appendix A gives the application notes for this section.
2) Standard strains of approved strain collection institutions at home and abroad, such as ATCC8100, CICC10187, etc. Some Serratia marcescens can be presented on the surface of agar
Red colonies, such as CICC10187, are available, and this feature can be used to check for the growth of Serratia marcescens. This information is given for the convenience of this
Part of the user.
4 Challenge microbial preparation
4.1 Challenge inoculum preparation
Picking up Serratia marcescens colonies from the slant surface of Serratia marcescens working strain, streaked on the nutrient agar medium plate, 26 ° C
The challenge inoculum was prepared by overnight culture for dry inhibition and semi-wet (outer dry) wet inhibition test. Prepared tablet
It should be used on the same day.
4.2 Challenge bacterial preparation
A single colony of Serratia marcescens was picked from the challenge inoculum plate prepared in 4.1 and inoculated into the nutrient broth medium at 26 °C.
Night culture was carried out to obtain a challenge bacterial solution having a concentration of about 109 CFU/mL, which was used for the semi-wet state (outer wet dryness) and the wet state inhibition test. Prepared well
The challenge bacteria solution should be used on the same day.
5 dry inhibition
5.1 Test device
Figure 1 is a schematic diagram of a dry bacteriostatic test device. The challenge room is used to hold the challenge inoculum and the sampling chamber is used to wipe the sample. Before the test,
The test device is sterilized using a confirmed sterilization procedure.
Description.
A---Challenge room;
B---sampling room;
1 --- glass stopper;
2 --- glass test device;
3 --- challenge inoculum;
4 --- fixing screws;
5 --- test sample;
6 --- sterile swab;
7 --- bracket.
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of the dry bacteriostatic test device
5.2 Test procedure
5.2.1 Sample clamping
Take three samples separately so that the inner surface of the sample faces the sampling chamber and clamp the sample between the challenge chamber and the sampling chamber. The clamping method should go through
Confirm to ensure that no leakage of challenging microorganisms occurs. For larger samples, the remainder can be cut or wrapped around the experimental device
For small samples, it can be tested with larger sample materials, or can be filled in a suitable way.
Partially used for testing.
5.2.2 Adding challenged microorganisms
Wipe the challenge inoculum with a sterile swab and inoculate it onto the outer surface of the sample through the challenge chamber and spread as evenly as possible.
5.2.3 Sample Challenge
Close the challenge chamber and sampling chamber of the test device in a suitable manner to ensure that no external contamination will occur and place the test device
In a 26 ° C incubator for 24 h.
5.2.4 Penetration microbiological examination
After the specified time, pre-wet the sterile swab in sterile physiological saline and squeeze out the excess water, and wipe the sample as much as possible through the sampling chamber.
All inner surfaces were inoculated and then inoculated by wiping the surface of the nutrient agar plate. Wipe the sample with three sterile swabs per sample.
Inoculation was performed on three nutrient agar plates, respectively, during which the swab should be rotated multiple times. The nutrient agar plates were incubated at 26 ° C for 24 h.
5.2.5 Challenge Microbial Vitality Check
After the specified time, refer to 5.2.4 and wipe the outer surface of the sample through the challenge chamber to check for the challenge of microbial activity.
5.3 Result judgment
The nutrient agar medium plate used for vitality examination should have Serratia marcescens growth, otherwise the test is invalid. If used in the sample table
No microbial growth was observed on the nutrient agar plates analyzed by surface sampling, which was judged to be in compliance with the dry bacteriostatic requirements. If used for sample surface sampling
Microbial growth was observed on the nutrient agar plates analyzed, and appropriate microbiological methods should be used to check whether it is Serratia marcescens. If it is sticky
Serratia marcescens is judged to be inconsistent with the requirements of dry bacteriostasis; if it is not Serratia marcescens, it indicates that there is external pollution and the test is invalid.
6 semi-wet state (outer dry internal wet) bacteriostatic
6.1 Test device
Figure 2 is a schematic diagram of a semi-wet (outer dry internal wet) bacteriostatic test device. The challenge room is used to hold the challenge inoculum, and the sampling room is used for holding
Nutritional broth medium. Prior to testing, the test device was sterilized using a validated sterilization procedure.
6.2 Test methods
6.2.1 Sample clamping
Follow the instructions in 5.2.1.
6.2.2 Adding challenged microorganisms
Follow the instructions in 5.2.2.
6.2.3 Add nutrient broth culture medium
Fill the sampling chamber with a nutrient broth medium in an aseptically operated manner.
6.2.4 Sample Challenge
Follow the instructions in 5.2.3.
6.2.5 Penetration microbiological examination
After the specified time, the microbial growth in the nutrient broth medium was visually observed.
6.2.6 Challenge Microbial Vitality Check
Follow the instructions in 5.2.5.
Description.
A---Challenge room;
B---sampling room;
1 --- glass stopper;
2 --- glass test device;
3 --- Serratia marcescens inoculum;
4 --- fixing screws;
5 --- test sample;
6 --- nutrient broth medium;
7 --- glass elbow;
8 --- bracket.
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of the test device --- semi-wet state (outer dry internal wet)
6.3 Result judgment
The nutrient agar medium plate used for vitality examination should have Serratia marcescens growth, otherwise the test is invalid. If nutrient broth culture
The base shows clarification and is judged to meet the requirements of the semi-wet state (external dry internal wetness). If the nutrient broth medium shows turbidity, the appropriate micro should be used.
Biological methods to check whether it is Serratia marcescens. If it is Serratia marcescens, it is judged to be inconsistent with the semi-wet state (external dry internal wetness) resistance requirement;
If it is not Serratia marcescens, it indicates that there is external pollution and the test is invalid.
Note. If necessary, sterile nutrient broth medium can be set as a negative control (showing clarification) and nutrient broth cultured with Serratia marcescens as
A positive control (showing turbidity) to avoid visual observation of possible subjective errors of clarification or turbidity.
7 semi-wet state (outer wet internal dry) bacteriostatic
7.1 Test device
Fig. 3 is a schematic view of a semi-wet state (outer wet internal dry) bacteriostatic test device. The challenge room is used to hold the challenge liquid, and the sampling room is used for wiping
kind. Prior to testing, the test device was sterilized using a validated sterilization procedure.
Description.
A---Challenge room;
B---sampling room;
1 --- glass stopper;
2 --- glass elbow;
3 --- challenge bacterial liquid;
4 --- test sample;
5 --- glass test device;
6 --- sterile swab;
7 --- fixing screws;
8 --- bracket.
Figure 3 Schematic diagram of the test device --- semi-wet state (outer wet internal dry)
7.2 Test methods
7.2.1 Sample clamping
Follow the instructions in 5.2.1.
7.2.2 Adding challenged microorganisms
Fill the challenge room with the challenge liquid.
7.2.3 Sample Challenge
Follow the instructions in 5.2.3.
7.2.4 Penetration microbiological examination
Follow the instructions in 5.2.4.
7.2.5 Challenge microbial activity check
After the specified time, the sterile agar medium plate was swabbed with a sterile swab to collect the challenge bacteria solution to check for the challenge of microbial activity.
Three sterile swabs were used for each sample, and were applied to three nutrient agar plates for inoculation, and the plates were placed at 26 °C.
Raise for 24 hours.
7.3 Judgment of results
The nutrient agar medium plate used for vitality examination should have Serratia marcescens growth, otherwise the test is invalid. If used in the sample table
No microbial growth was observed on the nutrient agar medium plate of the surface sampling analysis, which was judged to be in compliance with the semi-wet state (external wet internal dryness). in case
Microbial growth on nutrient agar medium plates for sample surface analysis of samples, which should be examined by appropriate microbiological methods.
Whether it is a sticky Serratia. If it is Serratia marcescens, it is judged to be inconsistent with the semi-wet state (external wet internal dry) resistance; if it is not sticky saras
Bacteria, indicating that there is external pollution, the test is invalid.
8 wet state inhibition
8.1 Test device
Figure 4 is a schematic view of a wet bacteriostatic test device. The challenge room is used to hold the challenge bacteria solution, and the sampling room is used to hold the nutrient broth medium.
Prior to testing, the test device was sterilized using a validated sterilization procedure.
Description.
A---Challenge room;
B---sampling room;
1 --- glass stopper;
2 --- glass elbow;
3 --- challenge bacterial liquid;
4 --- test sample;
5 --- glass test device;
6 ---TSB medium;
7 --- fixing screws;
8 --- bracket.
Figure 4 Schematic diagram of the test device --- wet state
8.2 Test methods
8.2.1 Sample clamping
Follow the instructions in 5.2.1.
8.2.2 Adding challenged microorganisms
Follow the instructions in 7.2.2.
8.2.3 Adding nutrient broth culture medium
Follow the instructions in 6.2.3.
8.2.4 Sample Challenge
Follow the instructions in 5.2.3.
8.2.5 Penetration microbiological examination
Follow the instructions in 6.2.5.
8.2.6 Challenge Microbial Vitality Check
Follow the instructions in 7.2.5.
8.3 Result judgment
The nutrient agar medium plate used for vitality examination should have Serratia marcescens growth, otherwise the te...
Share