1
/
of
12
PayPal, credit cards. Download editable-PDF & invoice in 1 second!
YY/T 0589-2016 English PDF (YYT0589-2016)
YY/T 0589-2016 English PDF (YYT0589-2016)
Regular price
$180.00 USD
Regular price
Sale price
$180.00 USD
Unit price
/
per
Shipping calculated at checkout.
Couldn't load pickup availability
Delivery: 3 seconds. Download true-PDF + Invoice.
Get Quotation: Click YY/T 0589-2016 (Self-service in 1-minute)
Historical versions (Master-website): YY/T 0589-2016
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll-down if blank)
YY/T 0589-2016: Electrolyte analyzer
YY/T 0589-2016
ICS11.100
C44
People's Republic of China Pharmaceutical Industry Standard
Replace YY/T 0589-2005
Electrolyte analyzer
2016-03-23 released
2017-01-01 Implementation
Issued by the State Food and Drug Administration
Foreword
This standard was drafted in accordance with the rules given in GB/T 1.1-2009.
This standard replaces YY/T 0589-2005 "Electrolyte Analyzer". Compared with YY/T 0589-2005, the main changes are as follows.
--- Added supplementary description of the scope of application;
--- Removed terms and definitions;
--- Performance indicators have added "Li, iCa2" performance requirements;
--- Absolute deviation is added to the accuracy requirements, and the absolute deviation calculation method is added to the test method;
--- Increase the absolute deviation and linear correlation coefficient in the linear requirement, and add the calculation method of absolute deviation and linear correlation coefficient in the test method
Calculation method;
--- Stability experiment method changed the method of testing a total of 6 times in 10min to 0h, 4h, 8h for each time point;
--- Changed the preparation method of the fixed value quality control test solution used in the performance test of K, Na, Cl- test items in Appendix A
The amount of each chemical reagent in
--- Appendix A adds the preparation method of the fixed value quality control test solution used in the performance test of the "iCa2, Li" test item.
Please note that some content of this document may involve patents. The issuing authority of this document does not assume responsibility for identifying these patents.
This standard was proposed by the State Food and Drug Administration.
This standard is under the jurisdiction of the National Medical Clinical Laboratory and the In vitro Diagnostic System Standardization Technical Committee (SAC/TC136).
This standard was drafted by. Beijing Medical Device Inspection Institute, Shenzhen Kate Biomedical Electronic Technology Co., Ltd., Guilin Youlit Medical
Therapy Electronics Co., Ltd., Hitachi High-Tech (Shanghai) International Trade Co., Ltd. Beijing Branch, Beckman Coulter Trading (China) Co., Ltd.
the company.
The main drafters of this standard. Zhao Bingfeng, Wu Guoqiang, Lv Zhenxing, Du Haiou, Cheng Qing, Liu Qiuyue.
The previous versions of the standard replaced by this standard are as follows.
--- YY/T 0589-2005.
Electrolyte analyzer
1 Scope
This standard specifies the classification and basic parameters of the electrolyte analyzer, requirements, test methods, signs, labels, instructions for use and packaging, transportation
Lose, store.
This standard applies to electrolyte analyzers using ion selective electrodes as sensors (hereinafter referred to as instruments).
Detection of degraded items. The electrolyte module on the biochemical analyzer can refer to this standard.
2 Normative references
The following documents are indispensable for the application of this document. For dated references, only the dated versions apply to this article
For the cited documents without date, the latest version (including all amendments) applies to this document.
GB/T 191 Icon mark for packaging, storage and transportation
GB 4793.1 Safety Requirements for Electrical Equipment for Measurement, Control, and Laboratory Part 1. General Requirements
GB/T 14710 Medical appliance environment and test methods
GB/T 18268.1 Requirements for electromagnetic compatibility of electrical equipment for measurement, control, and laboratory use. Part 1. General requirements
GB/T 18268.26 Requirements for electromagnetic compatibility of electrical equipment for measurement, control, and laboratory use. Part 26. Special requirements
Diagnostic (IVD) medical equipment
YY/T 0466.1 Medical devices used in medical device labels, marking and information provided symbols Part 1. General requirements
YY 0648 Safety Requirements for Electrical Equipment for Measurement, Control, and Laboratory Part 2-101. In Vitro Diagnostic (IVD) Medical Equipment
Specific requirements
3 Classification and basic parameters
3.1 Classification
3.1.1 According to the structure type. it can be divided into desktop and portable.
3.1.2 According to measurement method. it can be divided into direct measurement method and indirect measurement method.
3.1.3 According to the degree of operation automation. it can be divided into fully automatic, semi-automatic and manual.
3.2 Measurement parameters
Applicable items of the instrument should meet the following requirements.
3.2.1 The reference range of electrode slope value is shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Reference range of electrode slope value
Name slope value reference range/mV
K 40 ~ 70
Na 40 ~ 70
Table 1 (continued)
Name slope value reference range/mV
Cl-> 35
Li 40 ~ 70
iCa2 20 ~ 40
3.2.2 Types of samples. serum, plasma (whole blood) or other body fluids.
3.2.3 Analysis speed. The analysis speed parameters of the instrument should be provided.
3.2.4 Minimum sample size. The minimum sample size parameter of the instrument should be provided.
3.2.5 Data storage capacity. The data storage parameter of the instrument should be provided.
3.3 Naming
It should be named according to the type of ion selective electrode configured by the instrument or uniformly named after the electrolyte instrument.
4 Requirements
4.1 Performance requirements
Applicable items of the instrument should meet the following requirements.
4.1.1 Accuracy
The accuracy of the instrument should meet the requirements of Table 2.
4.1.2 Precision
The precision of the instrument should meet the requirements of Table 2.
4.1.3 Linear
The linear deviation of the instrument should meet the requirements of Table 2.
4.1.4 Stability
The stability of the instrument should meet the requirements of Table 2.
4.1.5 Carrying pollution rate
The pollution rate of the instrument should meet the requirements of Table 2.
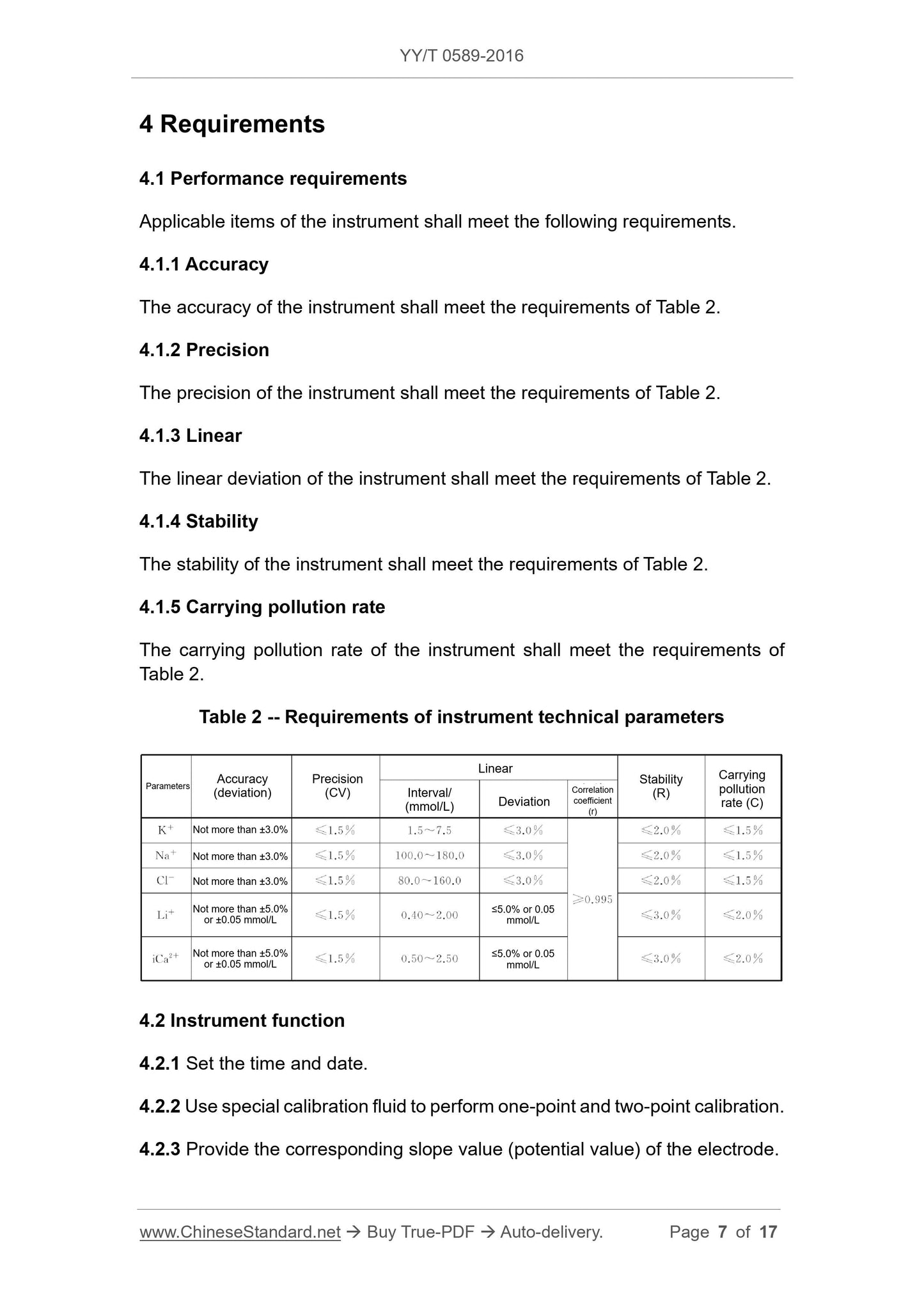
Table 2 Requirements for instrument technical parameters
Parameter accuracy (deviation) precision (CV)
Linear
Interval/(mmol/L) deviation
Related
Coefficient (r)
stability
(R)
Carrying pollution rate
(C)
K does not exceed ± 3.0% ≤1.5% 1.5 ~ 7.5 ≤3.0%
Na does not exceed ± 3.0% ≤1.5% 100.0 ~ 180.0 ≤3.0%
Cl- not more than ± 3.0% ≤1.5% 80.0 ~ 160.0 ≤3.0%
Li
Not more than ± 5.0% or
± 0.05mmol/L
≤1.5% 0.40 ~ 2.00
≤5.0% or
0.05mmol/L
iCa2
Not more than ± 5.0% or
± 0.05mmol/L
≤1.5% 0.50 ~ 2.50
≤5.0% or
0.05mmol/L
≥0.995
≤2.0% ≤1.5%
≤2.0% ≤1.5%
≤2.0% ≤1.5%
≤3.0% ≤2.0%
≤3.0% ≤2.0%
4.2 Instrument function
4.2.1 Set the time and date.
4.2.2 Perform one-point and two-point calibration with special calibration solution.
4.2.3 Provide the corresponding slope value (potential value) of the electrode.
4.2.4 Save and print the measurement data of the instrument.
4.3 Appearance
The appearance should meet the following requirements.
a) The whole machine should be complete without scratches and cracks;
b) Fastener connection should be firm and reliable, without loosening;
c) There should be no obvious defects on the surface of metal parts.
4.4 Security
It shall meet the requirements of the applicable clauses in GB 4793.1 and YY 0648.
4.5 Environmental test
It shall meet the requirements of the applicable clauses in GB/T 14710.
4.6 Electromagnetic compatibility
It shall meet the requirements of the applicable clauses in GB/T 18268.1 and GB/T 18268.26.
5 Test method
5.1 Test conditions
Normal working conditions of the instrument.
--- Power supply. AC 220V ± 22V, 50Hz ± 1Hz; or other suitable power supply;
--- Ambient temperature. 15 ℃ ~ 30 ℃;
--- Relative humidity. not more than 85%;
--- Far away from strong electromagnetic field interference sources.
Note. When the conditions in 5.1 are inconsistent with the manufacturer's product regulations, the product regulations shall prevail. The manufacturer shall state in the product standard.
5.2 Accuracy
The sample uses a reference substance with fixed value data based on serum.
Under normal working conditions, the instrument shall be calibrated in accordance with the conventional test procedures, and then the reference value of the fixed value shall be continuously measured 3 times, according to formula (1)
Calculate the relative deviation (Br) or calculate the absolute deviation (Ba) according to formula (2).
If the result equal to 2 times does not meet, it is judged as unqualified. If there is one time the result does not meet the requirements, you should re-test 20 times in succession, and divide
Do not calculate the relative deviation (Br) according to equation (1), and calculate the absolute deviation (Ba) according to equation (2), if the results of 19 tests are greater than or equal to 4.1.1
, The accuracy meets the requirements of 4.1.1.
Br = (M -T)/T × 100% (1)
Ba = (M -T) (2)
In the formula.
Br --- relative deviation;
Ba --- absolute deviation;
M --- test results;
T --- Certified reference material label value.
5.3 Precision
The sample was selected as the No. 3 K, Na, Cl-valued quality control test solution prepared in Table A.1 in Appendix A.
For the sample, use the No. 3 iCa2 and Li fixed value quality control test solution prepared in Table A.2 in Appendix A.
Under normal working conditions, the instrument is calibrated according to conventional test procedures, and then the No. 3 fixed value quality control test solution is continuously measured 10 times.
Obtain the average value (x) and standard deviation (SD) of the measured values of the output of each analytical element in the test solution, and calculate the variation of each analytical element according to equation (3)
The coefficient (CV) shall meet the requirements of 4.1.2.
CV =
SD
x × 100%
(3)
In the formula.
CV --- coefficient of variation;
SD --- standard deviation;
x --- 10 times the average value of the measured value is output continuously.
5.4 Linear
The samples were selected No. 1, No. 2, No. 3, No. 4 and No. 5 K, Na, Cl-prepared quality control test solution prepared in Table A.1 in Appendix A.
The samples were selected No.1, No.2, No.3, No.4 and No.5 iCa2 and Li fixed value quality control test solutions prepared in Table A.2 in Appendix A.
Under normal working conditions, the instrument should be calibrated according to the conventional test procedures, and then each of the certain value of the quality control test solution should be continuously measured in sequence.
Set 3 times, take the average value as the measured value, and each analyzed element will get a set of measured values Y of different concentrations.
Between the set of measured values of different concentrations Yn of each analyzed element and the corresponding set of nominal values of different concentrations X, the first
First use the linear regression analysis method to calculate the linear regression parameters a (slope) and b (intercept) of each analyzed element, and derive each analyzed
Linear regression equation of elements Y = a · X b.
For each analyzed element, a known set of nominal values X of different concentrations are substituted into their corresponding linear regression equations
Find the corresponding set of linear regression values Y.
Calculate the absolute value or relative deviation of the measured value Yn of each analyzed element at different concentrations relative to the linear regression value Y
The absolute value of the difference and the calculation of the correlation coefficient of linear regression ︱r︱ should all comply with the provisions of 4.1.3.
5.5 Stability
The sample was selected as the No. 3 K, Na, Cl-valued quality control test solution prepared in Table A.1 in Appendix A.
For the sample, use the No. 3 iCa2 and Li fixed value quality control test solution prepared in Table A.2 in Appendix A.
Under normal working conditions, the instrument should be calibrated according to the conventional test procedures, and then test the No. 3 fixed value quality control test solution.
0h, 4h, 8h, test once and record the measured value of each analytical element, each analytical element gets 3 measured values respectively, and select the most
The maximum value Xmax and the minimum value Xmin, and then calculate the fluctuation percentage R of each analysis element according to equation (4), should meet the requirements of 4.1.4.
R =
Xmax-Xmin
T × 100%
(4)
In the formula.
R --- fluctuation percentage;
T --- nominal reference value;
Xmax --- the maximum measured value;
Xmin --- minimum measured value.
Note. Under normal operating conditions, the instrument is in standby or working state.
5.6 Carrying pollution rate
The samples were selected No. 1 and No. 5 K, Na, Cl-prepared quality control test solution prepared in Table A.1 in Appendix A.
The samples were selected No. 1 and No. 5 Ca2 and Li fixed value quality control test solutions prepared in Table A.2 in Appendix A.
Under normal working conditions, the instrument should be calibrated according to the conventional test procedures, and then the quality control test liquids of No. 1 and No. 5 should be alternately fed.
The test is performed. First, the No. 1 fixed value quality control test solution is continuously measured 4 times, then the No. 5 fixed value quality control test solution is continuously measured 4 times, and finally the
No. 1 fixed value quality control test solution was measured 4 times in succession, and each analyzed element in the test solution obtained 3 sets of measured values
1 set of high concentration values), and then calculate the values of each adjacent two groups according to formula (5) and formula (6) to obtain a carry from low concentration to high concentration
The pollution rate CLH and a carrying pollution rate CHL from high concentration to low concentration should meet the requirements of 4.1.5.
CLH =
(H2 H3 H4)/3-H1
(H2 H3 H4)/3- (L2 L3 L4)/3 ×
100% (5)
CHL =
L1- (L2 L3 L4)/3
(H2 H3 H4)/3- (L2 L3 L4)/3 ×
100% (6)
In the formula.
CHL --- carry pollution rate;
L1 ~ L4 --- the first to fourth measurement value of ...
Get Quotation: Click YY/T 0589-2016 (Self-service in 1-minute)
Historical versions (Master-website): YY/T 0589-2016
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll-down if blank)
YY/T 0589-2016: Electrolyte analyzer
YY/T 0589-2016
ICS11.100
C44
People's Republic of China Pharmaceutical Industry Standard
Replace YY/T 0589-2005
Electrolyte analyzer
2016-03-23 released
2017-01-01 Implementation
Issued by the State Food and Drug Administration
Foreword
This standard was drafted in accordance with the rules given in GB/T 1.1-2009.
This standard replaces YY/T 0589-2005 "Electrolyte Analyzer". Compared with YY/T 0589-2005, the main changes are as follows.
--- Added supplementary description of the scope of application;
--- Removed terms and definitions;
--- Performance indicators have added "Li, iCa2" performance requirements;
--- Absolute deviation is added to the accuracy requirements, and the absolute deviation calculation method is added to the test method;
--- Increase the absolute deviation and linear correlation coefficient in the linear requirement, and add the calculation method of absolute deviation and linear correlation coefficient in the test method
Calculation method;
--- Stability experiment method changed the method of testing a total of 6 times in 10min to 0h, 4h, 8h for each time point;
--- Changed the preparation method of the fixed value quality control test solution used in the performance test of K, Na, Cl- test items in Appendix A
The amount of each chemical reagent in
--- Appendix A adds the preparation method of the fixed value quality control test solution used in the performance test of the "iCa2, Li" test item.
Please note that some content of this document may involve patents. The issuing authority of this document does not assume responsibility for identifying these patents.
This standard was proposed by the State Food and Drug Administration.
This standard is under the jurisdiction of the National Medical Clinical Laboratory and the In vitro Diagnostic System Standardization Technical Committee (SAC/TC136).
This standard was drafted by. Beijing Medical Device Inspection Institute, Shenzhen Kate Biomedical Electronic Technology Co., Ltd., Guilin Youlit Medical
Therapy Electronics Co., Ltd., Hitachi High-Tech (Shanghai) International Trade Co., Ltd. Beijing Branch, Beckman Coulter Trading (China) Co., Ltd.
the company.
The main drafters of this standard. Zhao Bingfeng, Wu Guoqiang, Lv Zhenxing, Du Haiou, Cheng Qing, Liu Qiuyue.
The previous versions of the standard replaced by this standard are as follows.
--- YY/T 0589-2005.
Electrolyte analyzer
1 Scope
This standard specifies the classification and basic parameters of the electrolyte analyzer, requirements, test methods, signs, labels, instructions for use and packaging, transportation
Lose, store.
This standard applies to electrolyte analyzers using ion selective electrodes as sensors (hereinafter referred to as instruments).
Detection of degraded items. The electrolyte module on the biochemical analyzer can refer to this standard.
2 Normative references
The following documents are indispensable for the application of this document. For dated references, only the dated versions apply to this article
For the cited documents without date, the latest version (including all amendments) applies to this document.
GB/T 191 Icon mark for packaging, storage and transportation
GB 4793.1 Safety Requirements for Electrical Equipment for Measurement, Control, and Laboratory Part 1. General Requirements
GB/T 14710 Medical appliance environment and test methods
GB/T 18268.1 Requirements for electromagnetic compatibility of electrical equipment for measurement, control, and laboratory use. Part 1. General requirements
GB/T 18268.26 Requirements for electromagnetic compatibility of electrical equipment for measurement, control, and laboratory use. Part 26. Special requirements
Diagnostic (IVD) medical equipment
YY/T 0466.1 Medical devices used in medical device labels, marking and information provided symbols Part 1. General requirements
YY 0648 Safety Requirements for Electrical Equipment for Measurement, Control, and Laboratory Part 2-101. In Vitro Diagnostic (IVD) Medical Equipment
Specific requirements
3 Classification and basic parameters
3.1 Classification
3.1.1 According to the structure type. it can be divided into desktop and portable.
3.1.2 According to measurement method. it can be divided into direct measurement method and indirect measurement method.
3.1.3 According to the degree of operation automation. it can be divided into fully automatic, semi-automatic and manual.
3.2 Measurement parameters
Applicable items of the instrument should meet the following requirements.
3.2.1 The reference range of electrode slope value is shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Reference range of electrode slope value
Name slope value reference range/mV
K 40 ~ 70
Na 40 ~ 70
Table 1 (continued)
Name slope value reference range/mV
Cl-> 35
Li 40 ~ 70
iCa2 20 ~ 40
3.2.2 Types of samples. serum, plasma (whole blood) or other body fluids.
3.2.3 Analysis speed. The analysis speed parameters of the instrument should be provided.
3.2.4 Minimum sample size. The minimum sample size parameter of the instrument should be provided.
3.2.5 Data storage capacity. The data storage parameter of the instrument should be provided.
3.3 Naming
It should be named according to the type of ion selective electrode configured by the instrument or uniformly named after the electrolyte instrument.
4 Requirements
4.1 Performance requirements
Applicable items of the instrument should meet the following requirements.
4.1.1 Accuracy
The accuracy of the instrument should meet the requirements of Table 2.
4.1.2 Precision
The precision of the instrument should meet the requirements of Table 2.
4.1.3 Linear
The linear deviation of the instrument should meet the requirements of Table 2.
4.1.4 Stability
The stability of the instrument should meet the requirements of Table 2.
4.1.5 Carrying pollution rate
The pollution rate of the instrument should meet the requirements of Table 2.
Table 2 Requirements for instrument technical parameters
Parameter accuracy (deviation) precision (CV)
Linear
Interval/(mmol/L) deviation
Related
Coefficient (r)
stability
(R)
Carrying pollution rate
(C)
K does not exceed ± 3.0% ≤1.5% 1.5 ~ 7.5 ≤3.0%
Na does not exceed ± 3.0% ≤1.5% 100.0 ~ 180.0 ≤3.0%
Cl- not more than ± 3.0% ≤1.5% 80.0 ~ 160.0 ≤3.0%
Li
Not more than ± 5.0% or
± 0.05mmol/L
≤1.5% 0.40 ~ 2.00
≤5.0% or
0.05mmol/L
iCa2
Not more than ± 5.0% or
± 0.05mmol/L
≤1.5% 0.50 ~ 2.50
≤5.0% or
0.05mmol/L
≥0.995
≤2.0% ≤1.5%
≤2.0% ≤1.5%
≤2.0% ≤1.5%
≤3.0% ≤2.0%
≤3.0% ≤2.0%
4.2 Instrument function
4.2.1 Set the time and date.
4.2.2 Perform one-point and two-point calibration with special calibration solution.
4.2.3 Provide the corresponding slope value (potential value) of the electrode.
4.2.4 Save and print the measurement data of the instrument.
4.3 Appearance
The appearance should meet the following requirements.
a) The whole machine should be complete without scratches and cracks;
b) Fastener connection should be firm and reliable, without loosening;
c) There should be no obvious defects on the surface of metal parts.
4.4 Security
It shall meet the requirements of the applicable clauses in GB 4793.1 and YY 0648.
4.5 Environmental test
It shall meet the requirements of the applicable clauses in GB/T 14710.
4.6 Electromagnetic compatibility
It shall meet the requirements of the applicable clauses in GB/T 18268.1 and GB/T 18268.26.
5 Test method
5.1 Test conditions
Normal working conditions of the instrument.
--- Power supply. AC 220V ± 22V, 50Hz ± 1Hz; or other suitable power supply;
--- Ambient temperature. 15 ℃ ~ 30 ℃;
--- Relative humidity. not more than 85%;
--- Far away from strong electromagnetic field interference sources.
Note. When the conditions in 5.1 are inconsistent with the manufacturer's product regulations, the product regulations shall prevail. The manufacturer shall state in the product standard.
5.2 Accuracy
The sample uses a reference substance with fixed value data based on serum.
Under normal working conditions, the instrument shall be calibrated in accordance with the conventional test procedures, and then the reference value of the fixed value shall be continuously measured 3 times, according to formula (1)
Calculate the relative deviation (Br) or calculate the absolute deviation (Ba) according to formula (2).
If the result equal to 2 times does not meet, it is judged as unqualified. If there is one time the result does not meet the requirements, you should re-test 20 times in succession, and divide
Do not calculate the relative deviation (Br) according to equation (1), and calculate the absolute deviation (Ba) according to equation (2), if the results of 19 tests are greater than or equal to 4.1.1
, The accuracy meets the requirements of 4.1.1.
Br = (M -T)/T × 100% (1)
Ba = (M -T) (2)
In the formula.
Br --- relative deviation;
Ba --- absolute deviation;
M --- test results;
T --- Certified reference material label value.
5.3 Precision
The sample was selected as the No. 3 K, Na, Cl-valued quality control test solution prepared in Table A.1 in Appendix A.
For the sample, use the No. 3 iCa2 and Li fixed value quality control test solution prepared in Table A.2 in Appendix A.
Under normal working conditions, the instrument is calibrated according to conventional test procedures, and then the No. 3 fixed value quality control test solution is continuously measured 10 times.
Obtain the average value (x) and standard deviation (SD) of the measured values of the output of each analytical element in the test solution, and calculate the variation of each analytical element according to equation (3)
The coefficient (CV) shall meet the requirements of 4.1.2.
CV =
SD
x × 100%
(3)
In the formula.
CV --- coefficient of variation;
SD --- standard deviation;
x --- 10 times the average value of the measured value is output continuously.
5.4 Linear
The samples were selected No. 1, No. 2, No. 3, No. 4 and No. 5 K, Na, Cl-prepared quality control test solution prepared in Table A.1 in Appendix A.
The samples were selected No.1, No.2, No.3, No.4 and No.5 iCa2 and Li fixed value quality control test solutions prepared in Table A.2 in Appendix A.
Under normal working conditions, the instrument should be calibrated according to the conventional test procedures, and then each of the certain value of the quality control test solution should be continuously measured in sequence.
Set 3 times, take the average value as the measured value, and each analyzed element will get a set of measured values Y of different concentrations.
Between the set of measured values of different concentrations Yn of each analyzed element and the corresponding set of nominal values of different concentrations X, the first
First use the linear regression analysis method to calculate the linear regression parameters a (slope) and b (intercept) of each analyzed element, and derive each analyzed
Linear regression equation of elements Y = a · X b.
For each analyzed element, a known set of nominal values X of different concentrations are substituted into their corresponding linear regression equations
Find the corresponding set of linear regression values Y.
Calculate the absolute value or relative deviation of the measured value Yn of each analyzed element at different concentrations relative to the linear regression value Y
The absolute value of the difference and the calculation of the correlation coefficient of linear regression ︱r︱ should all comply with the provisions of 4.1.3.
5.5 Stability
The sample was selected as the No. 3 K, Na, Cl-valued quality control test solution prepared in Table A.1 in Appendix A.
For the sample, use the No. 3 iCa2 and Li fixed value quality control test solution prepared in Table A.2 in Appendix A.
Under normal working conditions, the instrument should be calibrated according to the conventional test procedures, and then test the No. 3 fixed value quality control test solution.
0h, 4h, 8h, test once and record the measured value of each analytical element, each analytical element gets 3 measured values respectively, and select the most
The maximum value Xmax and the minimum value Xmin, and then calculate the fluctuation percentage R of each analysis element according to equation (4), should meet the requirements of 4.1.4.
R =
Xmax-Xmin
T × 100%
(4)
In the formula.
R --- fluctuation percentage;
T --- nominal reference value;
Xmax --- the maximum measured value;
Xmin --- minimum measured value.
Note. Under normal operating conditions, the instrument is in standby or working state.
5.6 Carrying pollution rate
The samples were selected No. 1 and No. 5 K, Na, Cl-prepared quality control test solution prepared in Table A.1 in Appendix A.
The samples were selected No. 1 and No. 5 Ca2 and Li fixed value quality control test solutions prepared in Table A.2 in Appendix A.
Under normal working conditions, the instrument should be calibrated according to the conventional test procedures, and then the quality control test liquids of No. 1 and No. 5 should be alternately fed.
The test is performed. First, the No. 1 fixed value quality control test solution is continuously measured 4 times, then the No. 5 fixed value quality control test solution is continuously measured 4 times, and finally the
No. 1 fixed value quality control test solution was measured 4 times in succession, and each analyzed element in the test solution obtained 3 sets of measured values
1 set of high concentration values), and then calculate the values of each adjacent two groups according to formula (5) and formula (6) to obtain a carry from low concentration to high concentration
The pollution rate CLH and a carrying pollution rate CHL from high concentration to low concentration should meet the requirements of 4.1.5.
CLH =
(H2 H3 H4)/3-H1
(H2 H3 H4)/3- (L2 L3 L4)/3 ×
100% (5)
CHL =
L1- (L2 L3 L4)/3
(H2 H3 H4)/3- (L2 L3 L4)/3 ×
100% (6)
In the formula.
CHL --- carry pollution rate;
L1 ~ L4 --- the first to fourth measurement value of ...
Share