1
/
of
12
PayPal, credit cards. Download editable-PDF & invoice in 1 second!
YY/T 0654-2017 English PDF (YY/T0654-2017)
YY/T 0654-2017 English PDF (YY/T0654-2017)
Regular price
$145.00 USD
Regular price
Sale price
$145.00 USD
Unit price
/
per
Shipping calculated at checkout.
Couldn't load pickup availability
Delivery: 3 seconds. Download true-PDF + Invoice.
Get Quotation: Click YY/T 0654-2017 (Self-service in 1-minute)
Historical versions (Master-website): YY/T 0654-2017
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll-down if blank)
YY/T 0654-2017: Automatic chemistry analyzer
YY/T 0654-2017
Automatic chemistry analyzer
ICS 11.100
C44
People's Republic of China Pharmaceutical Industry Standard
Replacing YY/T 0654-2008
Automatic biochemical analyzer
Released on.2017-03-28
2018-04-01 implementation
State Food and Drug Administration issued
Foreword
This standard was drafted in accordance with the rules given in GB/T 1.1-2009.
This standard has been revised on the basis of YY/T 0654-2008, compared with YY/T 0654-2008, except for editorial changes.
The technical changes are as follows.
--- The scope of application is changed to an automatic biochemical analyzer for quantitative analysis of various samples by ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry;
---In the normative reference document, change the environmental requirements and test methods of GB/T 14710 medical electrical equipment to GB/T 14710
Use electrical environment requirements and test methods;
---In the normative reference file, delete the GB/T 2829 cycle check counting sampling program and sampling table (suitable for stable production process)
Sexual inspection);
--- Remove the YY 0466 medical device for medical device labeling, marking and providing information symbols in the canonical reference document
(ISO 15233.2000, IDT);
--- The sample carrying contamination rate should be changed to no more than 0.1% and the test method is changed (see 5.8, 6.7);
--- The calibration range of the UREA (urea) in the intra-assay precision of clinical projects was adjusted to 7.0mmol/L~11.0mmol/L (see
5.10);
--- Add requirements and test methods for the applicable provisions of GB 4793.9 and YY 0648 in the safety requirements (see 5.13, 6.12);
--- Increase GB/T 18268.1, GB/T 18268.26 electromagnetic compatibility requirements and test methods (see 5.14, 6.13);
--- Absorbance stability test method used in the potassium dichromate solution at 340nm wavelength changed to orange yellow G solution (see 6.4);
--- Absorbance repeatability test method in the potassium chromite solution used at 340nm wavelength changed to orange yellow G solution (see 6.5);
--- Adding accuracy and repeatability in the experimental method modified to the manufacturer can choose one of two methods (see 6.8);
--- Logo and instructions for use should be in accordance with the requirements of GB/T 29791.3 (see 7);
--- Appendix B to refer to the.1990 international temperature standard pure water density table.
Please note that some of the contents of this document may involve patents. The issuing organization of this document is not responsible for identifying these patents.
This standard was proposed by the State Food and Drug Administration.
This standard is under the jurisdiction of the National Medical Clinical Laboratory and the In vitro Diagnostic System Standardization Technical Committee (SAC/TC136).
This standard was drafted. Beijing Medical Device Inspection Institute, Hitachi High-Tech (Shanghai) International Trade Co., Ltd. Beijing Branch, on
Haikehua Experimental System Co., Ltd., Beijing Songshang Technology Co., Ltd., Roche Diagnostics (Shanghai) Co., Ltd., Beckman Coulter Trade
(China) Co., Ltd.
The main drafters of this standard. Zhao Bingfeng, Cheng Qing, Su Tao, Fu Yuguang, Tian Wei, Bi Wei.
Automatic biochemical analyzer
1 Scope
This standard specifies the terms and definitions, classifications, requirements, test methods, signs and causes of the automatic biochemical analyzer (hereinafter referred to as the analyzer).
Instructions, packaging, transportation and storage.
This standard applies to automatic biochemical analyzers for quantitative analysis of various samples by UV-visible spectrophotometry.
2 Normative references
The following documents are indispensable for the application of this document. For dated references, only dated versions apply to this article.
Pieces. For undated references, the latest edition (including all amendments) applies to this document.
GB/T 191 packaging storage and transportation icon
Safety of electrical equipment for measurement, control and laboratory use - Part 1. General requirements
GB 4793.9 Safety requirements for electrical equipment for measurement, control and laboratory use - Part 9. Laboratory analysis and other purposes
Special requirements for moving and semi-automatic equipment
GB/T 14710 Medical electrical requirements and test methods
GB/T 18268.1 Electromagnetic compatibility requirements for electrical equipment - Part 1 . General requirements
GB/T 18268.26 Electromagnetic compatibility requirements for electrical equipment for measurement, control and laboratory - Part 26. Particular requirements
External diagnostic (IVD) medical equipment
GB/T 29791.3 Information provided by in vitro diagnostic medical device manufacturers (labeling) Part 3. Professional in vitro diagnostic equipment
Safety of electrical equipment for measurement, control and laboratory use - Part 2-101. In vitro diagnostic (IVD) medical equipment
Special requirements
3 Terms and definitions
The following terms and definitions apply to this document.
3.1
Absorbance absorbance
The ratio of the transmitted light intensity to the incident light intensity is the transmittance; the common logarithm of the reciprocal of the transmittance is called the absorbance.
Note. In this document, all absorbance values refer to values when the light path is 10 mm.
3.2
All analytical procedures (including filling of samples and reagents, mutual reactions, chemical and biological analysis, calculation of results, and reading of results) are implemented
An automated biochemical analyzer.
3.3
Carrying pollution carry-over
The measurement system carries a test sample reaction to another analyte discontinuity that detects the sample reaction, thereby erroneously affecting
Another test sample was expressed.
3.4
Stray light
Light other than the wavelength that deviates from the normal optical path and reaches the detector is measured.
4 classification
4.1 Instrument type
Discrete, mobile.
4.2 Monochrome device
Filter, grating or other means.
4.3 Optical path form
Front split or post split.
4.4 Colorimetric Container Type
Recycling or single use.
5 requirements
5.1 Normal working environment conditions
5.1.1 Power supply voltage. 220V±22V, 50Hz±1Hz.
5.1.2 Ambient temperature. 15 ° C ~ 30 ° C.
5.1.3 Relative humidity. 40%~85%.
5.1.4 Atmospheric pressure. 86.0kPa~106.0kPa.
Note. When the conditions in 5.1.2~5.1.4 are inconsistent with the conditions stated in the manufacturing mark, the conditions specified in the product shall prevail.
5.2 stray light
The absorbance is not less than 2.3.
5.3 absorbance linear range
The maximum absorbance in the range of ±5% relative bias should be no less than 2.0.
5.4 Absorbance accuracy
Should comply with the provisions of Table 1.
Table 1 Absorbance accuracy requirements
Absorbance value tolerance
0.5 ±0.025
1.0 ±0.07
5.5 Stability of absorbance
The change in absorbance should not be greater than 0.01.
5.6 Repeatability of absorbance
Expressed by the coefficient of variation, it should not be greater than 1.5%.
5.7 Temperature accuracy and volatility
The temperature value is within ±0.3 °C of the set value, and the fluctuation is not more than ±0.2 °C.
5.8 Sample carrying pollution rate
The sample carrying contamination rate should not exceed 0.1%.
5.9 Loading accuracy and repeatability
The minimum and maximum sample loading of the nominal sample of the instrument, and the amount of sample loading near 5 μL, for detection, accuracy of loading accuracy
Not more than ± 5%, the coefficient of variation does not exceed 2%.
The minimum and maximum sample loading amount of the instrument is tested, and the accuracy of the sample loading is not more than ± 5%, and the coefficient of variation is not exceeded.
Over 2%.
5.10 Intra-assay precision of clinical projects
The coefficient of variation (CV) should meet the requirements of Table 2.
Table 2 Clinical project approval accuracy requirements
Project name concentration range variation coefficient requirement /%
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) 30U/L~50U/L CV≤5
Urea (UREA) 7.0mmol/L~11.0mmol/L CV≤2.5
Total protein (TP) 50.0g/L~70.0g/L CV≤2.5
5.11 Appearance requirements
The appearance should meet the following requirements.
a) The graphic symbols and text on the panel should be accurate, clear, uniform and free of scratches;
b) The fastener connection shall be firm and reliable and shall not be loose;
c) The moving parts should be stable, should not be stuck, sudden jump and significant empty return, the key group should be flexible.
5.12 Environmental test requirements
Should meet the requirements of the applicable provisions of GB/T 14710.
5.13 Safety requirements
Should comply with the requirements of the applicable provisions of GB 4793.1, 4793.9, YY 0648.
5.14 Electromagnetic Compatibility Requirements
It shall comply with the requirements of the applicable provisions of GB/T 18268.1 and GB/T 18268.26.
6 Test methods
6.1 stray light
Using deionized water as a reference, determine 50g/L sodium nitrite standard solution at 340nm (see Appendix A for preparation method); or use air
For reference, the absorbance of the JB400 cut-off filter is measured at 340 nm and should meet the requirements of 5.2.
Note. The two methods are equivalent and the manufacturer can choose one.
6.2 absorbance linear range
Linear range determination of any wavelength in the range of 340 nm and 450 nm to 520 nm of the analyzer, the pigment solution of each wavelength
The preparation method is shown in Table 3. The absorbance of the pigment stock solution should be about 5% higher than the upper limit of the absorbance specified by the analyzer.
Table 3 Preparation method of pigment stock solution
Wavelength/nm solute solvent (diluent)
340 potassium dichromate 0.05mol/L sulfuric acid
Orange wavelength G (OrangeG) deionized water at any wavelength between 450 and 520
Note. Surfactants may be added to the solvent (such as Triton X-100).
The pigment stock solution is 0/10, 1/10, 2/10, 3/10, 4/10, 5/10, 6/10, 7/10, 8/10, 9/10, 10 with the corresponding diluent /10
Proportionally diluted to obtain a total of 11 concentration gradients. On the analyzer, the absorbance of the above solution was measured, and each concentration was measured 5 times, and the average was calculated.
value. The relative concentration is the abscissa, the average value of the absorbance is the ordinate, and the least squares method is used for the 4 points of 0/10, 1/10, 2/10 and 3/10.
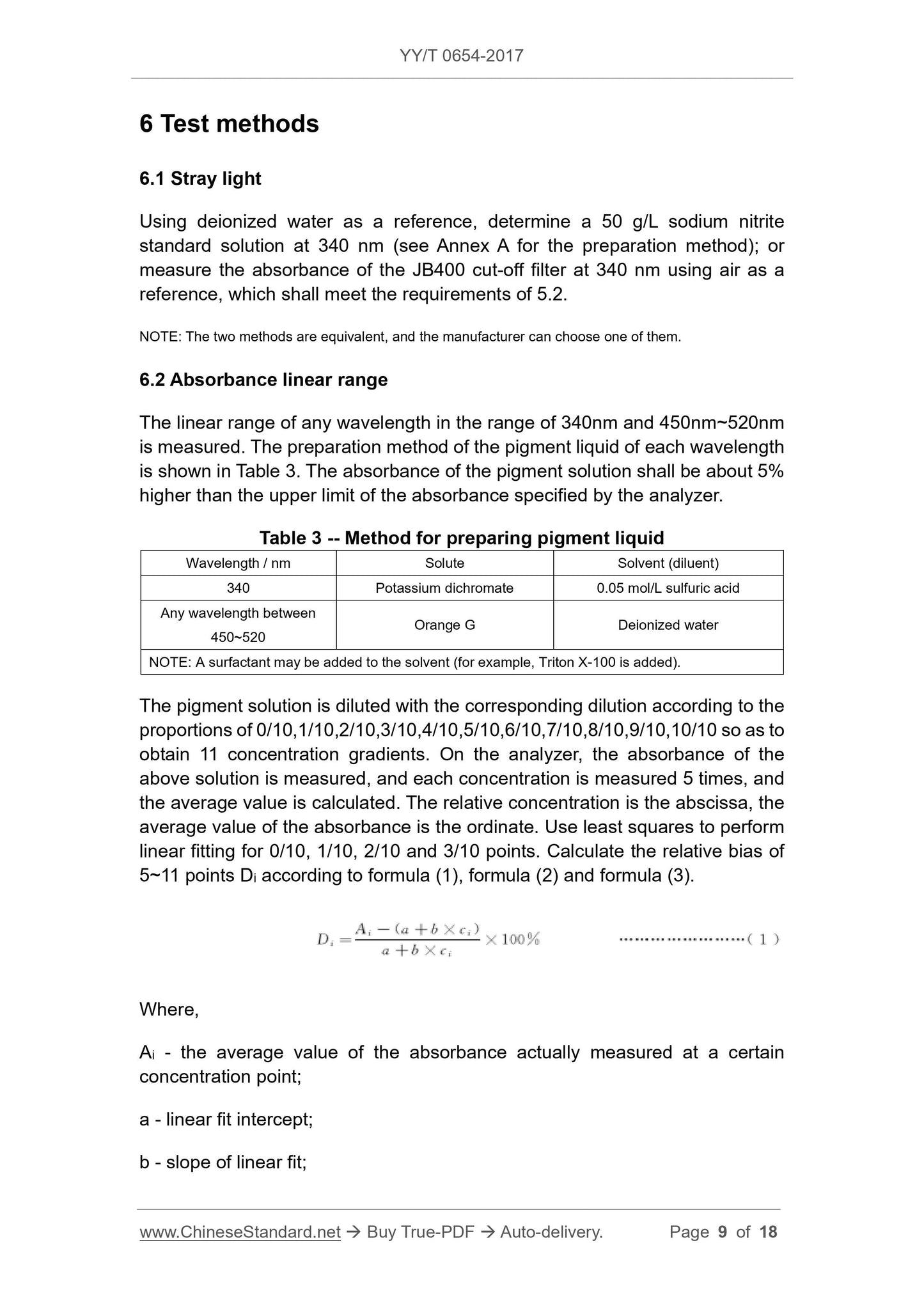
Perform a linear fit and calculate the relative bias Di from 5 to 11 points according to equations (1), (2) and (3).
Di=
Ai-(ab×ci)
Ab×ci ×
100% (1)
In the formula.
Ai --- the average of the absorbance actually measured at a certain concentration point;
a --- the intercept of the linear fit;
b --- the slope of the linear fit;
Ci --- relative concentration;
i --- concentration serial number, the range is 5~11.
b=
N∑
i=1
Aici-∑
i=1
Ai∑
i=1
Ci
N∑
i=1
C2i-(∑
i=1
Ci)2
(2)
a=
i=1
Ai
n -b×
i=1
Ci
(3)
In the formula.
Ai --- the average of the absorbance actually measured at a certain concentration point;
Ci --- relative concentration;
n --- the number of selected concentrations;
i --- concentration serial number, the range is 1~4.
The absorbance range of relative bias less than ± 5% is the linear range of absorbance and should meet the requirements of 5.3.
6.3 Absorbance accuracy
Using deionized water as a reference, the absorbance at 340 nm was determined to be about 0.5 on the analyzer (with deionized water as a blank, tolerance allowed)
The absorbance of potassium dichromate standard solution of ± 5%) and 1.0 (with deionized water as a blank with a tolerance of ± 5%). Repeat the test 3 times,
Calculate the difference between the arithmetic mean of the three measurements and the standard value, which should meet the requirements of Table 1.
6.4 absorbance stability
The absorbance stability of the analyzer was measured at any wavelength in the wavelength range of 340 nm and 600 nm to 700 nm. 340nm
The measurement solution is a yellow orange G (OrangeG) standard solution having an absorbance of 0.5 (with deionized water as a blank and an allowable deviation of ±5%).
The measurement solution of any wavelength in the wavelength range of 600 nm to 700 nm has an absorbance of 0.5 (with deionized water as a blank, the allowable deviation is
±5%) copper sulfate standard solution.
According to the following setting conditions a) and b), the absorbance of the above solution is measured on the analyzer, and the difference between the maximum value and the minimum value is calculated.
Should meet the requirements of 5.5.
a) The measurement time is the longest reaction time of the instrument nominal or 10 min;
b) The measurement interval is the reading interval of the instrument or 30 s.
6.5 absorbance repeatability
The absorbance repeatability of the analyzer was measured at a wavelength of 340 nm. The 340 nm wavelength measurement solution has an absorbance of 1.0 (deionized)
The water is blank, allowing a deviation of ± 5%) of the orange G (OrangeG) standard solution.
According to the following setting conditions a) and b), the absorbance of the above solution was measured on an analyzer, and the measurement was repeated 20 times, and the change was calculated according to the formula (4).
The coefficient of variation CV shall comply with the requirements of 5.6.
a) the amount of solution added is the nominal minimum reaction volume of the analyzer;
b) The reaction time is the analyzer's nominal maximum reaction time or 10 min.
CV=
×100% (4)
In the formula.
S=
i=1
(Xi-X) 2
N-1
The arithmetic mean of X ---1~20 times;
Xi---the measured value of each time;
n --- the number of measurements;
i --- The serial number of the measurement, i = 1 to 20.
6.6 Temperature accuracy and fluctuations
Probes of temperature detectors with an accuracy of not less than 0.1 ° C, or the same precision and calibrated special t...
Get Quotation: Click YY/T 0654-2017 (Self-service in 1-minute)
Historical versions (Master-website): YY/T 0654-2017
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll-down if blank)
YY/T 0654-2017: Automatic chemistry analyzer
YY/T 0654-2017
Automatic chemistry analyzer
ICS 11.100
C44
People's Republic of China Pharmaceutical Industry Standard
Replacing YY/T 0654-2008
Automatic biochemical analyzer
Released on.2017-03-28
2018-04-01 implementation
State Food and Drug Administration issued
Foreword
This standard was drafted in accordance with the rules given in GB/T 1.1-2009.
This standard has been revised on the basis of YY/T 0654-2008, compared with YY/T 0654-2008, except for editorial changes.
The technical changes are as follows.
--- The scope of application is changed to an automatic biochemical analyzer for quantitative analysis of various samples by ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry;
---In the normative reference document, change the environmental requirements and test methods of GB/T 14710 medical electrical equipment to GB/T 14710
Use electrical environment requirements and test methods;
---In the normative reference file, delete the GB/T 2829 cycle check counting sampling program and sampling table (suitable for stable production process)
Sexual inspection);
--- Remove the YY 0466 medical device for medical device labeling, marking and providing information symbols in the canonical reference document
(ISO 15233.2000, IDT);
--- The sample carrying contamination rate should be changed to no more than 0.1% and the test method is changed (see 5.8, 6.7);
--- The calibration range of the UREA (urea) in the intra-assay precision of clinical projects was adjusted to 7.0mmol/L~11.0mmol/L (see
5.10);
--- Add requirements and test methods for the applicable provisions of GB 4793.9 and YY 0648 in the safety requirements (see 5.13, 6.12);
--- Increase GB/T 18268.1, GB/T 18268.26 electromagnetic compatibility requirements and test methods (see 5.14, 6.13);
--- Absorbance stability test method used in the potassium dichromate solution at 340nm wavelength changed to orange yellow G solution (see 6.4);
--- Absorbance repeatability test method in the potassium chromite solution used at 340nm wavelength changed to orange yellow G solution (see 6.5);
--- Adding accuracy and repeatability in the experimental method modified to the manufacturer can choose one of two methods (see 6.8);
--- Logo and instructions for use should be in accordance with the requirements of GB/T 29791.3 (see 7);
--- Appendix B to refer to the.1990 international temperature standard pure water density table.
Please note that some of the contents of this document may involve patents. The issuing organization of this document is not responsible for identifying these patents.
This standard was proposed by the State Food and Drug Administration.
This standard is under the jurisdiction of the National Medical Clinical Laboratory and the In vitro Diagnostic System Standardization Technical Committee (SAC/TC136).
This standard was drafted. Beijing Medical Device Inspection Institute, Hitachi High-Tech (Shanghai) International Trade Co., Ltd. Beijing Branch, on
Haikehua Experimental System Co., Ltd., Beijing Songshang Technology Co., Ltd., Roche Diagnostics (Shanghai) Co., Ltd., Beckman Coulter Trade
(China) Co., Ltd.
The main drafters of this standard. Zhao Bingfeng, Cheng Qing, Su Tao, Fu Yuguang, Tian Wei, Bi Wei.
Automatic biochemical analyzer
1 Scope
This standard specifies the terms and definitions, classifications, requirements, test methods, signs and causes of the automatic biochemical analyzer (hereinafter referred to as the analyzer).
Instructions, packaging, transportation and storage.
This standard applies to automatic biochemical analyzers for quantitative analysis of various samples by UV-visible spectrophotometry.
2 Normative references
The following documents are indispensable for the application of this document. For dated references, only dated versions apply to this article.
Pieces. For undated references, the latest edition (including all amendments) applies to this document.
GB/T 191 packaging storage and transportation icon
Safety of electrical equipment for measurement, control and laboratory use - Part 1. General requirements
GB 4793.9 Safety requirements for electrical equipment for measurement, control and laboratory use - Part 9. Laboratory analysis and other purposes
Special requirements for moving and semi-automatic equipment
GB/T 14710 Medical electrical requirements and test methods
GB/T 18268.1 Electromagnetic compatibility requirements for electrical equipment - Part 1 . General requirements
GB/T 18268.26 Electromagnetic compatibility requirements for electrical equipment for measurement, control and laboratory - Part 26. Particular requirements
External diagnostic (IVD) medical equipment
GB/T 29791.3 Information provided by in vitro diagnostic medical device manufacturers (labeling) Part 3. Professional in vitro diagnostic equipment
Safety of electrical equipment for measurement, control and laboratory use - Part 2-101. In vitro diagnostic (IVD) medical equipment
Special requirements
3 Terms and definitions
The following terms and definitions apply to this document.
3.1
Absorbance absorbance
The ratio of the transmitted light intensity to the incident light intensity is the transmittance; the common logarithm of the reciprocal of the transmittance is called the absorbance.
Note. In this document, all absorbance values refer to values when the light path is 10 mm.
3.2
All analytical procedures (including filling of samples and reagents, mutual reactions, chemical and biological analysis, calculation of results, and reading of results) are implemented
An automated biochemical analyzer.
3.3
Carrying pollution carry-over
The measurement system carries a test sample reaction to another analyte discontinuity that detects the sample reaction, thereby erroneously affecting
Another test sample was expressed.
3.4
Stray light
Light other than the wavelength that deviates from the normal optical path and reaches the detector is measured.
4 classification
4.1 Instrument type
Discrete, mobile.
4.2 Monochrome device
Filter, grating or other means.
4.3 Optical path form
Front split or post split.
4.4 Colorimetric Container Type
Recycling or single use.
5 requirements
5.1 Normal working environment conditions
5.1.1 Power supply voltage. 220V±22V, 50Hz±1Hz.
5.1.2 Ambient temperature. 15 ° C ~ 30 ° C.
5.1.3 Relative humidity. 40%~85%.
5.1.4 Atmospheric pressure. 86.0kPa~106.0kPa.
Note. When the conditions in 5.1.2~5.1.4 are inconsistent with the conditions stated in the manufacturing mark, the conditions specified in the product shall prevail.
5.2 stray light
The absorbance is not less than 2.3.
5.3 absorbance linear range
The maximum absorbance in the range of ±5% relative bias should be no less than 2.0.
5.4 Absorbance accuracy
Should comply with the provisions of Table 1.
Table 1 Absorbance accuracy requirements
Absorbance value tolerance
0.5 ±0.025
1.0 ±0.07
5.5 Stability of absorbance
The change in absorbance should not be greater than 0.01.
5.6 Repeatability of absorbance
Expressed by the coefficient of variation, it should not be greater than 1.5%.
5.7 Temperature accuracy and volatility
The temperature value is within ±0.3 °C of the set value, and the fluctuation is not more than ±0.2 °C.
5.8 Sample carrying pollution rate
The sample carrying contamination rate should not exceed 0.1%.
5.9 Loading accuracy and repeatability
The minimum and maximum sample loading of the nominal sample of the instrument, and the amount of sample loading near 5 μL, for detection, accuracy of loading accuracy
Not more than ± 5%, the coefficient of variation does not exceed 2%.
The minimum and maximum sample loading amount of the instrument is tested, and the accuracy of the sample loading is not more than ± 5%, and the coefficient of variation is not exceeded.
Over 2%.
5.10 Intra-assay precision of clinical projects
The coefficient of variation (CV) should meet the requirements of Table 2.
Table 2 Clinical project approval accuracy requirements
Project name concentration range variation coefficient requirement /%
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) 30U/L~50U/L CV≤5
Urea (UREA) 7.0mmol/L~11.0mmol/L CV≤2.5
Total protein (TP) 50.0g/L~70.0g/L CV≤2.5
5.11 Appearance requirements
The appearance should meet the following requirements.
a) The graphic symbols and text on the panel should be accurate, clear, uniform and free of scratches;
b) The fastener connection shall be firm and reliable and shall not be loose;
c) The moving parts should be stable, should not be stuck, sudden jump and significant empty return, the key group should be flexible.
5.12 Environmental test requirements
Should meet the requirements of the applicable provisions of GB/T 14710.
5.13 Safety requirements
Should comply with the requirements of the applicable provisions of GB 4793.1, 4793.9, YY 0648.
5.14 Electromagnetic Compatibility Requirements
It shall comply with the requirements of the applicable provisions of GB/T 18268.1 and GB/T 18268.26.
6 Test methods
6.1 stray light
Using deionized water as a reference, determine 50g/L sodium nitrite standard solution at 340nm (see Appendix A for preparation method); or use air
For reference, the absorbance of the JB400 cut-off filter is measured at 340 nm and should meet the requirements of 5.2.
Note. The two methods are equivalent and the manufacturer can choose one.
6.2 absorbance linear range
Linear range determination of any wavelength in the range of 340 nm and 450 nm to 520 nm of the analyzer, the pigment solution of each wavelength
The preparation method is shown in Table 3. The absorbance of the pigment stock solution should be about 5% higher than the upper limit of the absorbance specified by the analyzer.
Table 3 Preparation method of pigment stock solution
Wavelength/nm solute solvent (diluent)
340 potassium dichromate 0.05mol/L sulfuric acid
Orange wavelength G (OrangeG) deionized water at any wavelength between 450 and 520
Note. Surfactants may be added to the solvent (such as Triton X-100).
The pigment stock solution is 0/10, 1/10, 2/10, 3/10, 4/10, 5/10, 6/10, 7/10, 8/10, 9/10, 10 with the corresponding diluent /10
Proportionally diluted to obtain a total of 11 concentration gradients. On the analyzer, the absorbance of the above solution was measured, and each concentration was measured 5 times, and the average was calculated.
value. The relative concentration is the abscissa, the average value of the absorbance is the ordinate, and the least squares method is used for the 4 points of 0/10, 1/10, 2/10 and 3/10.
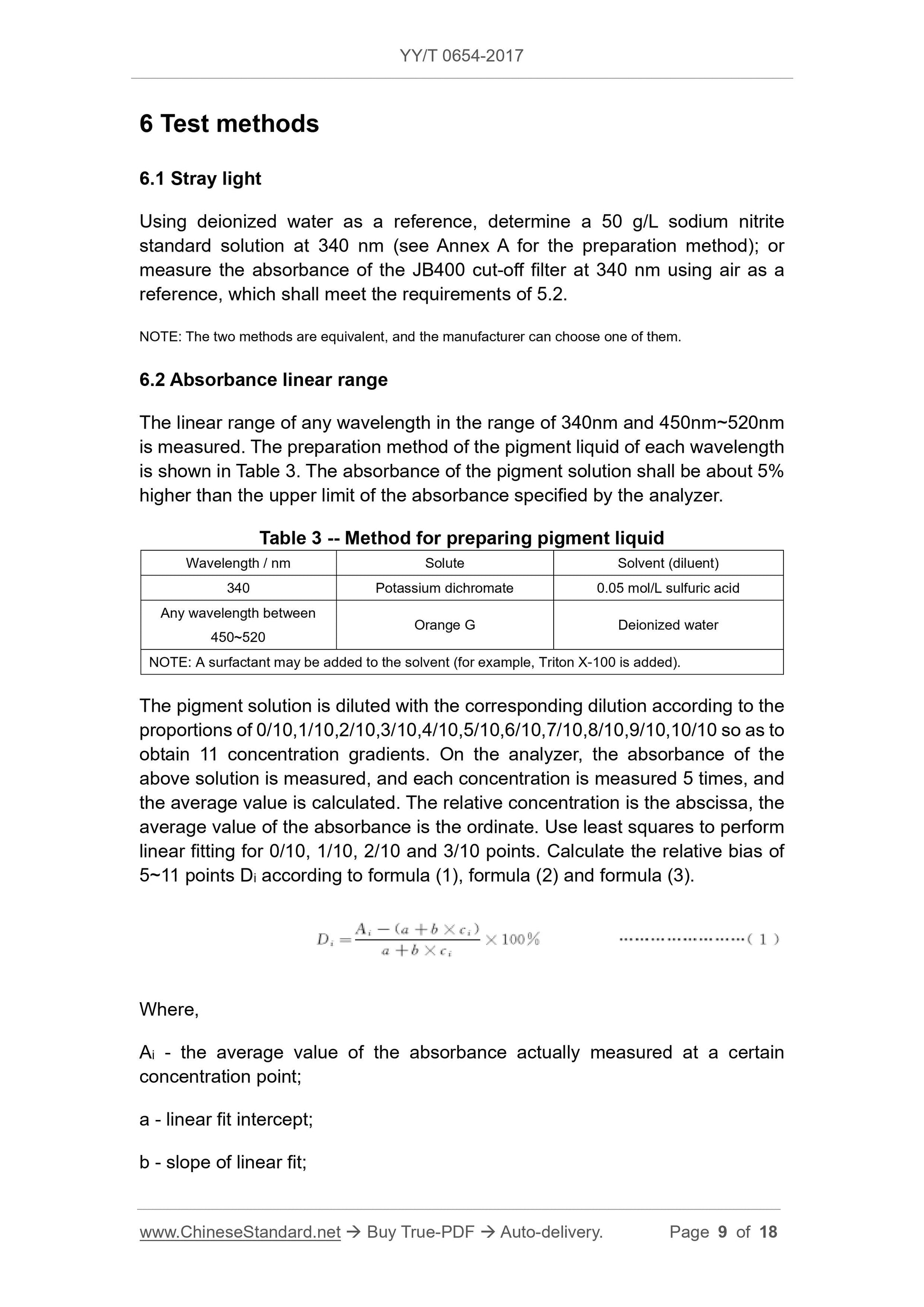
Perform a linear fit and calculate the relative bias Di from 5 to 11 points according to equations (1), (2) and (3).
Di=
Ai-(ab×ci)
Ab×ci ×
100% (1)
In the formula.
Ai --- the average of the absorbance actually measured at a certain concentration point;
a --- the intercept of the linear fit;
b --- the slope of the linear fit;
Ci --- relative concentration;
i --- concentration serial number, the range is 5~11.
b=
N∑
i=1
Aici-∑
i=1
Ai∑
i=1
Ci
N∑
i=1
C2i-(∑
i=1
Ci)2
(2)
a=
i=1
Ai
n -b×
i=1
Ci
(3)
In the formula.
Ai --- the average of the absorbance actually measured at a certain concentration point;
Ci --- relative concentration;
n --- the number of selected concentrations;
i --- concentration serial number, the range is 1~4.
The absorbance range of relative bias less than ± 5% is the linear range of absorbance and should meet the requirements of 5.3.
6.3 Absorbance accuracy
Using deionized water as a reference, the absorbance at 340 nm was determined to be about 0.5 on the analyzer (with deionized water as a blank, tolerance allowed)
The absorbance of potassium dichromate standard solution of ± 5%) and 1.0 (with deionized water as a blank with a tolerance of ± 5%). Repeat the test 3 times,
Calculate the difference between the arithmetic mean of the three measurements and the standard value, which should meet the requirements of Table 1.
6.4 absorbance stability
The absorbance stability of the analyzer was measured at any wavelength in the wavelength range of 340 nm and 600 nm to 700 nm. 340nm
The measurement solution is a yellow orange G (OrangeG) standard solution having an absorbance of 0.5 (with deionized water as a blank and an allowable deviation of ±5%).
The measurement solution of any wavelength in the wavelength range of 600 nm to 700 nm has an absorbance of 0.5 (with deionized water as a blank, the allowable deviation is
±5%) copper sulfate standard solution.
According to the following setting conditions a) and b), the absorbance of the above solution is measured on the analyzer, and the difference between the maximum value and the minimum value is calculated.
Should meet the requirements of 5.5.
a) The measurement time is the longest reaction time of the instrument nominal or 10 min;
b) The measurement interval is the reading interval of the instrument or 30 s.
6.5 absorbance repeatability
The absorbance repeatability of the analyzer was measured at a wavelength of 340 nm. The 340 nm wavelength measurement solution has an absorbance of 1.0 (deionized)
The water is blank, allowing a deviation of ± 5%) of the orange G (OrangeG) standard solution.
According to the following setting conditions a) and b), the absorbance of the above solution was measured on an analyzer, and the measurement was repeated 20 times, and the change was calculated according to the formula (4).
The coefficient of variation CV shall comply with the requirements of 5.6.
a) the amount of solution added is the nominal minimum reaction volume of the analyzer;
b) The reaction time is the analyzer's nominal maximum reaction time or 10 min.
CV=
×100% (4)
In the formula.
S=
i=1
(Xi-X) 2
N-1
The arithmetic mean of X ---1~20 times;
Xi---the measured value of each time;
n --- the number of measurements;
i --- The serial number of the measurement, i = 1 to 20.
6.6 Temperature accuracy and fluctuations
Probes of temperature detectors with an accuracy of not less than 0.1 ° C, or the same precision and calibrated special t...
Share