1
/
of
10
PayPal, credit cards. Download editable-PDF & invoice in 1 second!
YY/T 0719.8-2019 English PDF (YY/T0719.8-2019)
YY/T 0719.8-2019 English PDF (YY/T0719.8-2019)
Regular price
$190.00 USD
Regular price
Sale price
$190.00 USD
Unit price
/
per
Shipping calculated at checkout.
Couldn't load pickup availability
Delivery: 3 seconds. Download true-PDF + Invoice.
Get Quotation: Click YY/T 0719.8-2019 (Self-service in 1-minute)
Historical versions (Master-website): YY/T 0719.8-2019
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll-down if blank)
YY/T 0719.8-2019: Ophthalmic optics - Contact lens care products - Part 8: Test method for detergent
YY/T 0719.8-2019
Ophthalmic optics - Contact lens care products - Prat 8.Test method for detergent
ICS 11.040.70
C40
People's Republic of China Pharmaceutical Industry Standard
Ophthalmic optical contact lens care products
Part 8.Detergent determination method
2019-10-23 released
2020-10-01 implementation
Issued by the State Drug Administration
Preface
"Ophthalmic Optical Contact Lens Care Products" is divided into 11 parts.
---Part 1.Terminology
---Part 2.Basic requirements
---Part 3.Microbiological requirements and test methods and contact lens care system
---Part 4.Antimicrobial Preservative Effectiveness Test and Guidelines for Determination of Abandonment Date
---Part 5.Determination of the physical compatibility of contact lenses and contact lens care products
---Part 6.Guidelines for determination of expiry date
---Part 7.Biological Evaluation Guidelines
---Part 8.Determination method of detergent
---Part 9.Determination method of chelating agent
---Part 10.Determination of disinfectants
---Part 11.Determination method of moisturizing lubricant
This part is Part 8 of "Ophthalmic Optical Contact Lens Care Products".
This section was drafted in accordance with the rules given in GB/T 1.1-2009.
Please note that certain contents of this document may involve patents. The issuing agency of this document is not responsible for identifying these patents.
This part was proposed by the State Drug Administration.
This part is under the jurisdiction of the National Medical Optics and Instrument Standardization Sub-Technical Committee (SAC/TC103/SC1).
Drafting unit of this section. Zhejiang Medical Device Inspection and Research Institute.
The main drafters of this standard. Zhang Li, Han Yin, Xu Pinghua, Zheng Jian, Xia Zhongcheng, Chen Jingyun, Zhou Jun.
Ophthalmic optical contact lens care products
Part 8.Detergent determination method
1 Scope
This part of YY/T 0719 specifies that the active ingredient cleaning agent in contact lens care products (referred to as care products) is poloxamer or ring
Test method for determination of oxyethylene hydrogenated castor oil content.
This section applies to care products containing poloxamer or epoxy ethylene hydrogenated castor oil as the active ingredient of the detergent.
2 Normative references
The following documents are indispensable for the application of this document. For dated reference documents, only the dated version applies to this document.
For undated references, the latest version (including all amendments) applies to this document.
GB/T 6682 Analytical laboratory water specifications and test methods
3 General
The test methods specified in this section should be carried out at room temperature, namely 10 ℃ ~ 30 ℃. Unless otherwise specified, the reagents used are of analytical grade.
The experimental water should meet the requirements of secondary water specified in GB/T 6682.
4 Test method
4.1 Poloxamer
4.1.1 Gel chromatography
4.1.1.1 Test principle
Poloxamer is a polyoxyethylene polyoxypropylene ether block copolymer. It is a class of polymer nonionic surfactants.
The commonly used models in management products are Poloxamer 188 and Poloxamer 407.This method uses a hydrophilic gel chromatography column and a refractive index detector to measure
Determine the concentration of poloxamer in the care solution, which can eliminate the functional component hydroxypropylmethylcelulose (hydroxypropylmethylcelulose,
HPMC) interference.
The determination of poloxamer content is based on gel chromatography.
4.1.1.2 Instruments and reagents
4.1.1.2.1 Reagents. acetonitrile (chromatographically pure), sodium dihydrogen phosphate (chromatographically pure).
4.1.1.2.2 Reference substance. Poloxamer.
4.1.1.2.3 Instruments and equipment. high performance liquid chromatograph, refractive index detector; analytical balance with an accuracy of 0.1 mg.
4.1.1.3 Solution preparation
Poloxamer standard stock solution. Weigh 1g of the poloxamer reference substance dried to constant weight, accurate to 0.1mg, dissolve it with mobile phase and dilute to volume
To 100mL, shake well, make a 10mg/mL standard stock solution, store in refrigerator, valid for 1 month.
Blank solution. Prepare a poloxamer-free excipient solution according to the formula of the care product.
4.1.1.4 Sample processing
Dilute the contact lens care products containing poloxamer ingredients and the blank solution with mobile phase to a suitable concentration, shake well, and pass through 0.45μm
After the filter membrane is filtered, the filtrate is collected for testing.
If feasible, pure water can also be used directly as a blank control.
4.1.1.5 Standard solution preparation
Respectively accurately pipet the poloxamer stock solution (10mg/mL) 0.2mL~3.0mL to a 10mL volumetric flask, dilute to the mark, and shake
Evenly, a series of standard solutions with a concentration of 0.2mg/mL~3.0mg/mL are obtained.
4.1.1.6 Chromatographic conditions (recommended)
Liquid chromatography conditions.
a) Chromatographic column. TSKgelG3000SW, or equivalent;
b) Column temperature. 30℃;
c) Differential refractive index detector, temperature 30℃;
d) Mobile phase. sodium dihydrogen phosphate solution (0.02mol/L). acetonitrile=7.3;
e) Flow rate. 0.7mL/min;
f) Injection volume. 50μL.
4.1.1.7 Determination and result analysis
Analyze and determine the standard solution and sample respectively, establish a standard working curve and regression equation, and calculate the poloxamer content in the sample
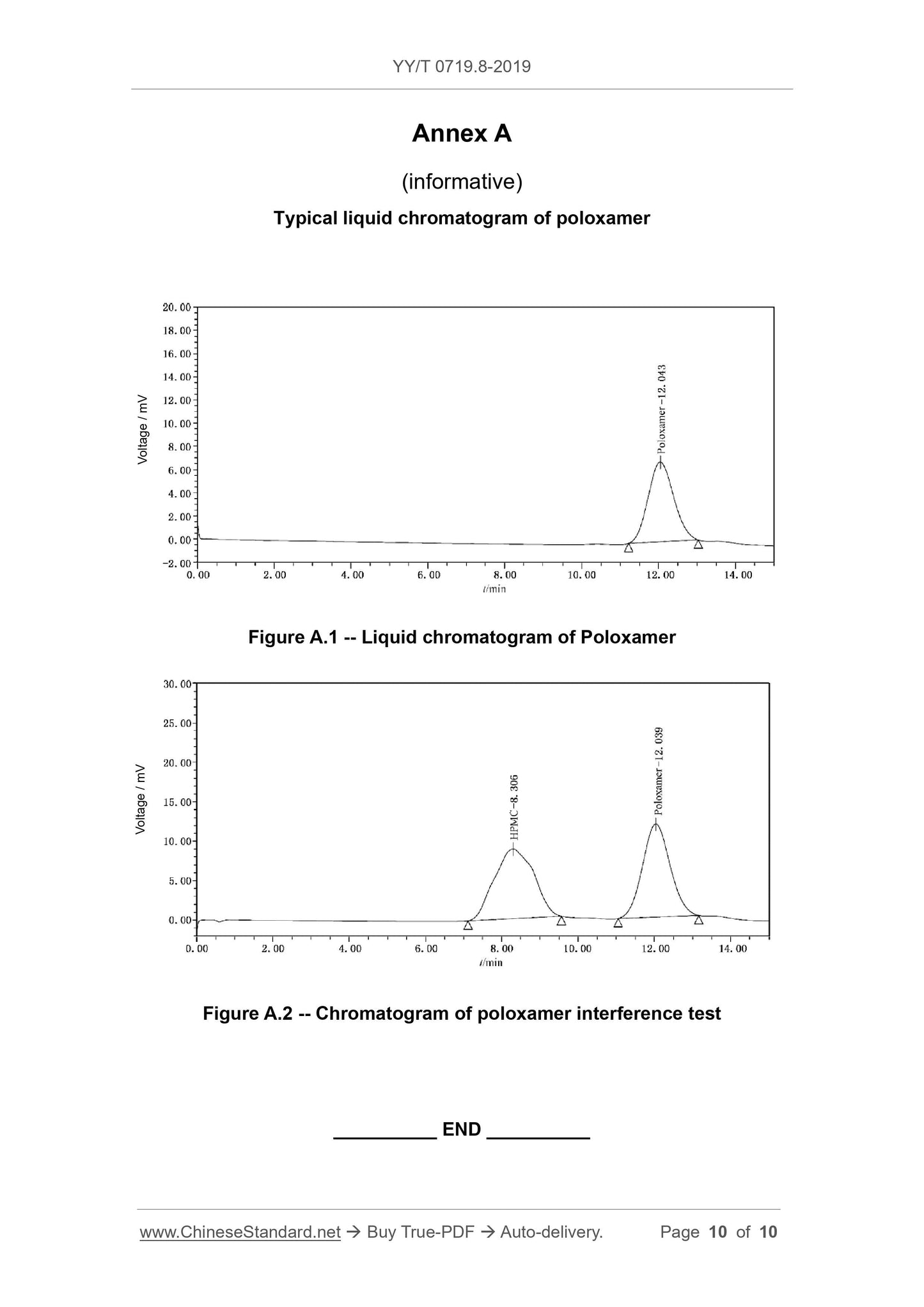
the amount. See Appendix A for a typical chromatogram.
4.1.2 Ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry
4.1.2.1 Test principle
According to the characteristics of hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose that forms a gel after heating in an aqueous solution, and then dissolves after cooling, the care solution
After removing HPMC in the pretreatment, use the ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry with iodine-potassium iodide solution as the developer to determine the poloxa in the nursing solution
姆 content.
4.1.2.2 Instruments and reagents
4.1.2.2.1 Reagents. iodine, potassium iodide.
4.1.2.2.2 Reference substance. Poloxamer.
4.1.2.2.3 Instruments and equipment. UV-visible spectrophotometer, 1cm quartz cuvette; analytical balance with an accuracy of 0.1mg.
4.1.2.3 Solution preparation
Poloxamer standard stock solution (0.1mg/mL). accurately weigh 0.5g of the control poloxamer that is dried to a constant weight, accurate to 0.1mg,
Dissolve in pure water ultrasonically and dilute to a 50mL volumetric flask. Shake well, then accurately pipette 1mL of the above solution to a 100mL volumetric flask.
Dilute the volume of pure water to the mark, shake well, and get it.
Iodine-potassium iodide color developing solution. Weigh 2.0g of potassium iodide, add an appropriate amount of water to dissolve, and then accurately add 1.0g of iodine to dissolve, and transfer to
In a 100mL volumetric flask, add water to dilute to the mark, shake well, and get it (this product needs to be stored in the dark).
4.1.2.4 Preparation of standard solution
Respectively accurately pipet the poloxamer standard solution (0.1mg/mL) 0.2mL~1.4mL into a 10mL volumetric flask, and dilute to the mark.
Shake well, then accurately add 0.25 mL of iodine-potassium iodide color developing solution, shake well, and obtain a series of standard solvents with concentrations of 2×10-6~14×10-6.
Solution, at least 5 concentration points should be selected, the same method with pure water as a blank control.
4.1.2.5 Sample processing
Take an appropriate amount of the care product, and after boiling the water for 15 minutes, quickly filter to remove the flocculent precipitate while it is hot. Repeat the above operation until the filtrate is clear. Such as
The sample does not contain the interference of HPMC components, so this step is not necessary.
Accurately pipette the filtrate, dilute it to a concentration of about 5×10-6, and then accurately add 0.25 mL of iodine-potassium iodide color solution, and shake it well.
4.1.2.6 Determination and result analysis
After the standard and sample are placed for 2h, the absorbance is measured at 500nm, and 3 sets of data are measured in parallel for the sample. Establish a standard working curve and
Regression equation is used to calculate the poloxamer content in the sample according to the standard curve.
4.2 Epoxyethylene hydrogenated castor oil
4.2.1 Test principle
Epoxy ethylene hydrogenated castor oil, also known as polyoxyethylene hydrogenated castor oil, is a class of non-ionic surfactants. Iodine-iodination
The ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometric method with potassium solution as the developer is used to determine the content of epoxy ethylene hydrogenated castor oil in the nursing solution. You should consider this method when using this method
Consider the interference of propylene glycol and other ingredients.
4.2.2 Reagents and instruments
4.2.2.1 Reagents. iodine, potassium iodide.
4.2.2.2 Reference substance. epoxy ethylene hydrogenated castor oil.
4.2.2.3 Instruments and equipment. UV-Visible spectrophotometer, 1cm quartz cuvette; analytical balance with accuracy of 0.1mg.
4.2.3 Solution preparation
Epoxyethylene hydrogenated castor oil standard stock solution (0.2mg/mL). Weigh 0.1g RH40 reference substance, accurate to 0.1mg, and use pure water
Dissolve, dilute to a 50mL volumetric flask, shake well, then accurately pipette the above solution 1mL to a 10mL volumetric flask, and dilute to a minute with pure water.
Shake well to get 0.2mg/mL standard stock solution.
Iodine-potassium iodide color developing solution. Weigh 2.0g of potassium iodide, add an appropriate amount of water to dissolve, and then accurately add 1.0g of iodine to dissolve, and transfer to
In a 100mL volumetric flask, add water to dilute to the mark, shake well, and get it (this product needs to be stored in the dark).
4.2.4 Preparation of standard solution
Pipette ethylene oxide hydrogenated castor oil standard stock solution 1.0mL~3.0mL to a 10mL volumetric flask, dilute to volume and shake well, add and mix to show
Color solution 0.25mL, shake well. To obtain a series of standard solutions with a concentration of 20×10-6~60×10-6, at least 5 concentration points should be selected, and the same method
Use pure water as a blank.
4.2.5 Sample processing
Precisely pipette an appropriate amount of the sample, dilute it to a concentration of about 40×10-6, and then accurately add 0.25 mL of iodine-potassium iodide color solution, and shake it well.
4.2.6 Determination and result analysis
After the standard and sample are placed for 2h, the absorbance is measured at 500nm, and 3 sets of data are measured in parallel. Establish working standard curve and regression
Equation, calculate the content of epoxy ethylene hydrogenated castor oil in the sample according to the standard curve.
5 Test report
The test report should include at least the following.
a) Test sample information;
b) The standard number of this part;
c) test results;
d) Test date;
e) Test personnel.
Get Quotation: Click YY/T 0719.8-2019 (Self-service in 1-minute)
Historical versions (Master-website): YY/T 0719.8-2019
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll-down if blank)
YY/T 0719.8-2019: Ophthalmic optics - Contact lens care products - Part 8: Test method for detergent
YY/T 0719.8-2019
Ophthalmic optics - Contact lens care products - Prat 8.Test method for detergent
ICS 11.040.70
C40
People's Republic of China Pharmaceutical Industry Standard
Ophthalmic optical contact lens care products
Part 8.Detergent determination method
2019-10-23 released
2020-10-01 implementation
Issued by the State Drug Administration
Preface
"Ophthalmic Optical Contact Lens Care Products" is divided into 11 parts.
---Part 1.Terminology
---Part 2.Basic requirements
---Part 3.Microbiological requirements and test methods and contact lens care system
---Part 4.Antimicrobial Preservative Effectiveness Test and Guidelines for Determination of Abandonment Date
---Part 5.Determination of the physical compatibility of contact lenses and contact lens care products
---Part 6.Guidelines for determination of expiry date
---Part 7.Biological Evaluation Guidelines
---Part 8.Determination method of detergent
---Part 9.Determination method of chelating agent
---Part 10.Determination of disinfectants
---Part 11.Determination method of moisturizing lubricant
This part is Part 8 of "Ophthalmic Optical Contact Lens Care Products".
This section was drafted in accordance with the rules given in GB/T 1.1-2009.
Please note that certain contents of this document may involve patents. The issuing agency of this document is not responsible for identifying these patents.
This part was proposed by the State Drug Administration.
This part is under the jurisdiction of the National Medical Optics and Instrument Standardization Sub-Technical Committee (SAC/TC103/SC1).
Drafting unit of this section. Zhejiang Medical Device Inspection and Research Institute.
The main drafters of this standard. Zhang Li, Han Yin, Xu Pinghua, Zheng Jian, Xia Zhongcheng, Chen Jingyun, Zhou Jun.
Ophthalmic optical contact lens care products
Part 8.Detergent determination method
1 Scope
This part of YY/T 0719 specifies that the active ingredient cleaning agent in contact lens care products (referred to as care products) is poloxamer or ring
Test method for determination of oxyethylene hydrogenated castor oil content.
This section applies to care products containing poloxamer or epoxy ethylene hydrogenated castor oil as the active ingredient of the detergent.
2 Normative references
The following documents are indispensable for the application of this document. For dated reference documents, only the dated version applies to this document.
For undated references, the latest version (including all amendments) applies to this document.
GB/T 6682 Analytical laboratory water specifications and test methods
3 General
The test methods specified in this section should be carried out at room temperature, namely 10 ℃ ~ 30 ℃. Unless otherwise specified, the reagents used are of analytical grade.
The experimental water should meet the requirements of secondary water specified in GB/T 6682.
4 Test method
4.1 Poloxamer
4.1.1 Gel chromatography
4.1.1.1 Test principle
Poloxamer is a polyoxyethylene polyoxypropylene ether block copolymer. It is a class of polymer nonionic surfactants.
The commonly used models in management products are Poloxamer 188 and Poloxamer 407.This method uses a hydrophilic gel chromatography column and a refractive index detector to measure
Determine the concentration of poloxamer in the care solution, which can eliminate the functional component hydroxypropylmethylcelulose (hydroxypropylmethylcelulose,
HPMC) interference.
The determination of poloxamer content is based on gel chromatography.
4.1.1.2 Instruments and reagents
4.1.1.2.1 Reagents. acetonitrile (chromatographically pure), sodium dihydrogen phosphate (chromatographically pure).
4.1.1.2.2 Reference substance. Poloxamer.
4.1.1.2.3 Instruments and equipment. high performance liquid chromatograph, refractive index detector; analytical balance with an accuracy of 0.1 mg.
4.1.1.3 Solution preparation
Poloxamer standard stock solution. Weigh 1g of the poloxamer reference substance dried to constant weight, accurate to 0.1mg, dissolve it with mobile phase and dilute to volume
To 100mL, shake well, make a 10mg/mL standard stock solution, store in refrigerator, valid for 1 month.
Blank solution. Prepare a poloxamer-free excipient solution according to the formula of the care product.
4.1.1.4 Sample processing
Dilute the contact lens care products containing poloxamer ingredients and the blank solution with mobile phase to a suitable concentration, shake well, and pass through 0.45μm
After the filter membrane is filtered, the filtrate is collected for testing.
If feasible, pure water can also be used directly as a blank control.
4.1.1.5 Standard solution preparation
Respectively accurately pipet the poloxamer stock solution (10mg/mL) 0.2mL~3.0mL to a 10mL volumetric flask, dilute to the mark, and shake
Evenly, a series of standard solutions with a concentration of 0.2mg/mL~3.0mg/mL are obtained.
4.1.1.6 Chromatographic conditions (recommended)
Liquid chromatography conditions.
a) Chromatographic column. TSKgelG3000SW, or equivalent;
b) Column temperature. 30℃;
c) Differential refractive index detector, temperature 30℃;
d) Mobile phase. sodium dihydrogen phosphate solution (0.02mol/L). acetonitrile=7.3;
e) Flow rate. 0.7mL/min;
f) Injection volume. 50μL.
4.1.1.7 Determination and result analysis
Analyze and determine the standard solution and sample respectively, establish a standard working curve and regression equation, and calculate the poloxamer content in the sample
the amount. See Appendix A for a typical chromatogram.
4.1.2 Ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry
4.1.2.1 Test principle
According to the characteristics of hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose that forms a gel after heating in an aqueous solution, and then dissolves after cooling, the care solution
After removing HPMC in the pretreatment, use the ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry with iodine-potassium iodide solution as the developer to determine the poloxa in the nursing solution
姆 content.
4.1.2.2 Instruments and reagents
4.1.2.2.1 Reagents. iodine, potassium iodide.
4.1.2.2.2 Reference substance. Poloxamer.
4.1.2.2.3 Instruments and equipment. UV-visible spectrophotometer, 1cm quartz cuvette; analytical balance with an accuracy of 0.1mg.
4.1.2.3 Solution preparation
Poloxamer standard stock solution (0.1mg/mL). accurately weigh 0.5g of the control poloxamer that is dried to a constant weight, accurate to 0.1mg,
Dissolve in pure water ultrasonically and dilute to a 50mL volumetric flask. Shake well, then accurately pipette 1mL of the above solution to a 100mL volumetric flask.
Dilute the volume of pure water to the mark, shake well, and get it.
Iodine-potassium iodide color developing solution. Weigh 2.0g of potassium iodide, add an appropriate amount of water to dissolve, and then accurately add 1.0g of iodine to dissolve, and transfer to
In a 100mL volumetric flask, add water to dilute to the mark, shake well, and get it (this product needs to be stored in the dark).
4.1.2.4 Preparation of standard solution
Respectively accurately pipet the poloxamer standard solution (0.1mg/mL) 0.2mL~1.4mL into a 10mL volumetric flask, and dilute to the mark.
Shake well, then accurately add 0.25 mL of iodine-potassium iodide color developing solution, shake well, and obtain a series of standard solvents with concentrations of 2×10-6~14×10-6.
Solution, at least 5 concentration points should be selected, the same method with pure water as a blank control.
4.1.2.5 Sample processing
Take an appropriate amount of the care product, and after boiling the water for 15 minutes, quickly filter to remove the flocculent precipitate while it is hot. Repeat the above operation until the filtrate is clear. Such as
The sample does not contain the interference of HPMC components, so this step is not necessary.
Accurately pipette the filtrate, dilute it to a concentration of about 5×10-6, and then accurately add 0.25 mL of iodine-potassium iodide color solution, and shake it well.
4.1.2.6 Determination and result analysis
After the standard and sample are placed for 2h, the absorbance is measured at 500nm, and 3 sets of data are measured in parallel for the sample. Establish a standard working curve and
Regression equation is used to calculate the poloxamer content in the sample according to the standard curve.
4.2 Epoxyethylene hydrogenated castor oil
4.2.1 Test principle
Epoxy ethylene hydrogenated castor oil, also known as polyoxyethylene hydrogenated castor oil, is a class of non-ionic surfactants. Iodine-iodination
The ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometric method with potassium solution as the developer is used to determine the content of epoxy ethylene hydrogenated castor oil in the nursing solution. You should consider this method when using this method
Consider the interference of propylene glycol and other ingredients.
4.2.2 Reagents and instruments
4.2.2.1 Reagents. iodine, potassium iodide.
4.2.2.2 Reference substance. epoxy ethylene hydrogenated castor oil.
4.2.2.3 Instruments and equipment. UV-Visible spectrophotometer, 1cm quartz cuvette; analytical balance with accuracy of 0.1mg.
4.2.3 Solution preparation
Epoxyethylene hydrogenated castor oil standard stock solution (0.2mg/mL). Weigh 0.1g RH40 reference substance, accurate to 0.1mg, and use pure water
Dissolve, dilute to a 50mL volumetric flask, shake well, then accurately pipette the above solution 1mL to a 10mL volumetric flask, and dilute to a minute with pure water.
Shake well to get 0.2mg/mL standard stock solution.
Iodine-potassium iodide color developing solution. Weigh 2.0g of potassium iodide, add an appropriate amount of water to dissolve, and then accurately add 1.0g of iodine to dissolve, and transfer to
In a 100mL volumetric flask, add water to dilute to the mark, shake well, and get it (this product needs to be stored in the dark).
4.2.4 Preparation of standard solution
Pipette ethylene oxide hydrogenated castor oil standard stock solution 1.0mL~3.0mL to a 10mL volumetric flask, dilute to volume and shake well, add and mix to show
Color solution 0.25mL, shake well. To obtain a series of standard solutions with a concentration of 20×10-6~60×10-6, at least 5 concentration points should be selected, and the same method
Use pure water as a blank.
4.2.5 Sample processing
Precisely pipette an appropriate amount of the sample, dilute it to a concentration of about 40×10-6, and then accurately add 0.25 mL of iodine-potassium iodide color solution, and shake it well.
4.2.6 Determination and result analysis
After the standard and sample are placed for 2h, the absorbance is measured at 500nm, and 3 sets of data are measured in parallel. Establish working standard curve and regression
Equation, calculate the content of epoxy ethylene hydrogenated castor oil in the sample according to the standard curve.
5 Test report
The test report should include at least the following.
a) Test sample information;
b) The standard number of this part;
c) test results;
d) Test date;
e) Test personnel.
Share