1
/
/
12
PayPal, credit cards. Download editable-PDF & invoice in 1 second!
GB 1886.184-2016 English PDF (GB1886.184-2016)
GB 1886.184-2016 English PDF (GB1886.184-2016)
Normal fiyat
$90.00 USD
Normal fiyat
İndirimli fiyat
$90.00 USD
Birim fiyat
/
/
Kargo, ödeme sayfasında hesaplanır.
Teslim alım stok durumu yüklenemedi
Delivery: 3 seconds. Download true-PDF + Invoice.
Get QUOTATION in 1-minute: Click GB 1886.184-2016
Historical versions: GB 1886.184-2016
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll if blank)
GB 1886.184-2016: Food additive -- Sodium benzoate
GB 1886.184-2016
GB
NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE
PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
National Food Safety Standard –
Food Additive – Sodium Benzoate
食品添加剂 苯甲酸钠
ISSUED ON. AUGUST 31, 2016
IMPLEMENTED ON. JANUARY 1, 2017
Issued by. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the
People’s Republic of China
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
1 Application Scope ... 4
2 Structural Formula, Molecular Formula and Relative Molecular Mass ... 4
3 Technical Requirements ... 4
Annex A Test Methods ... 6
Foreword
This Standard replaces GB 1902-2005, Food Additive – Sodium Benzoate.
Compared with GB 1902-2005, the major changes of this Standard are as follows.
-- it changes the standard name into “National Food Safety Standard – Food
Additive – Sodium Benzoate”;
-- it deletes the item of arsenic;
-- it adds the item of phthalic acid;
-- it modifies the indexes of chlorides;
-- it adds the test method for heavy metals.
National Food Safety Standard –
Food Additive – Sodium Benzoate
1 Application Scope
This Standard applies to food additive sodium benzoate; the food additive is made
from benzoic acid which is reacted with sodium hydroxide or sodium bicarbonate.
Benzoic acid is made by catalytic oxidation of petroleum toluene; sodium hydroxide or
sodium bicarbonate is made with the method of ion exchange membrane.
2 Structural Formula, Molecular Formula and Relative
Molecular Mass
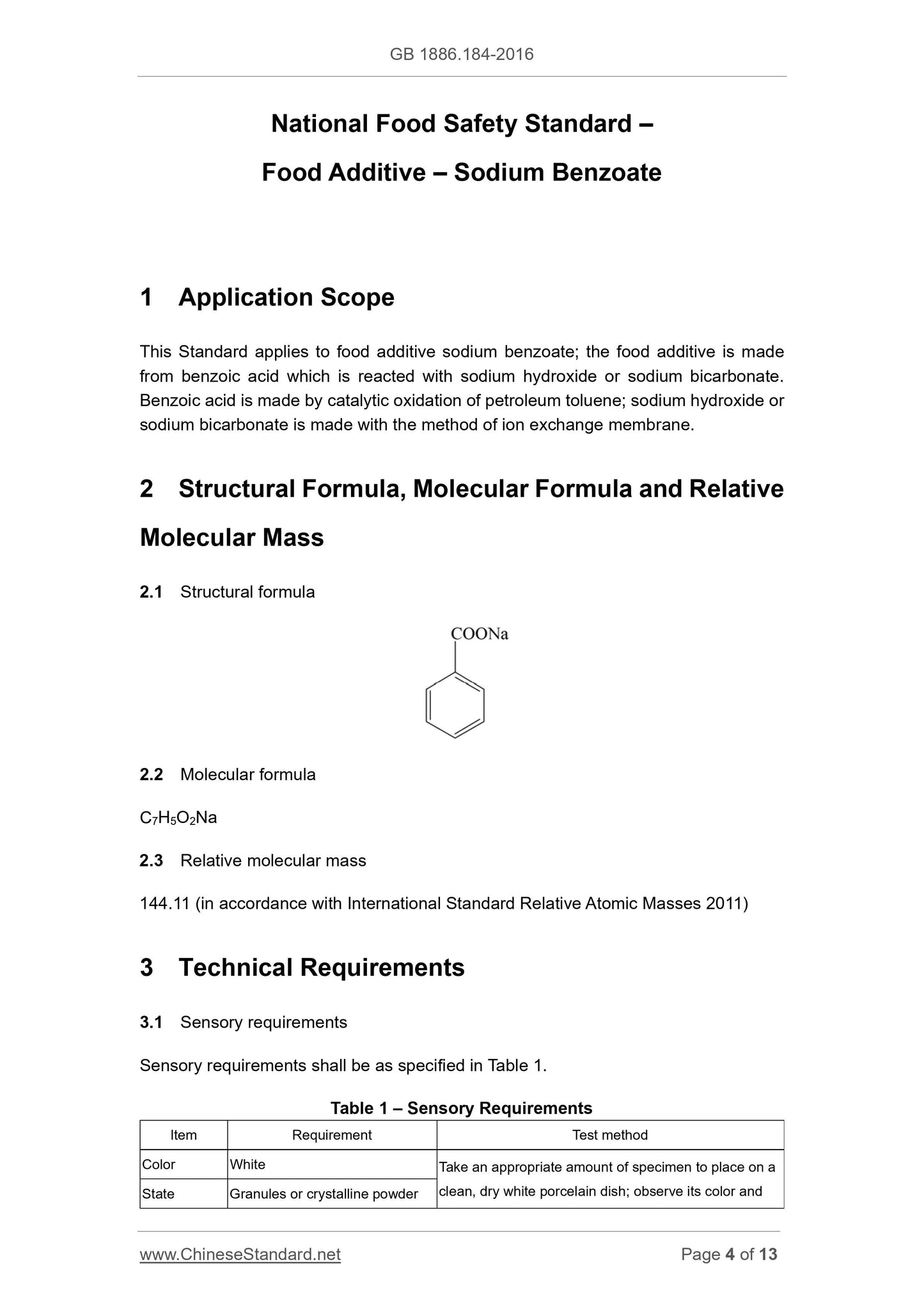
2.1 Structural formula
2.2 Molecular formula
C7H5O2Na
2.3 Relative molecular mass
144.11 (in accordance with International Standard Relative Atomic Masses 2011)
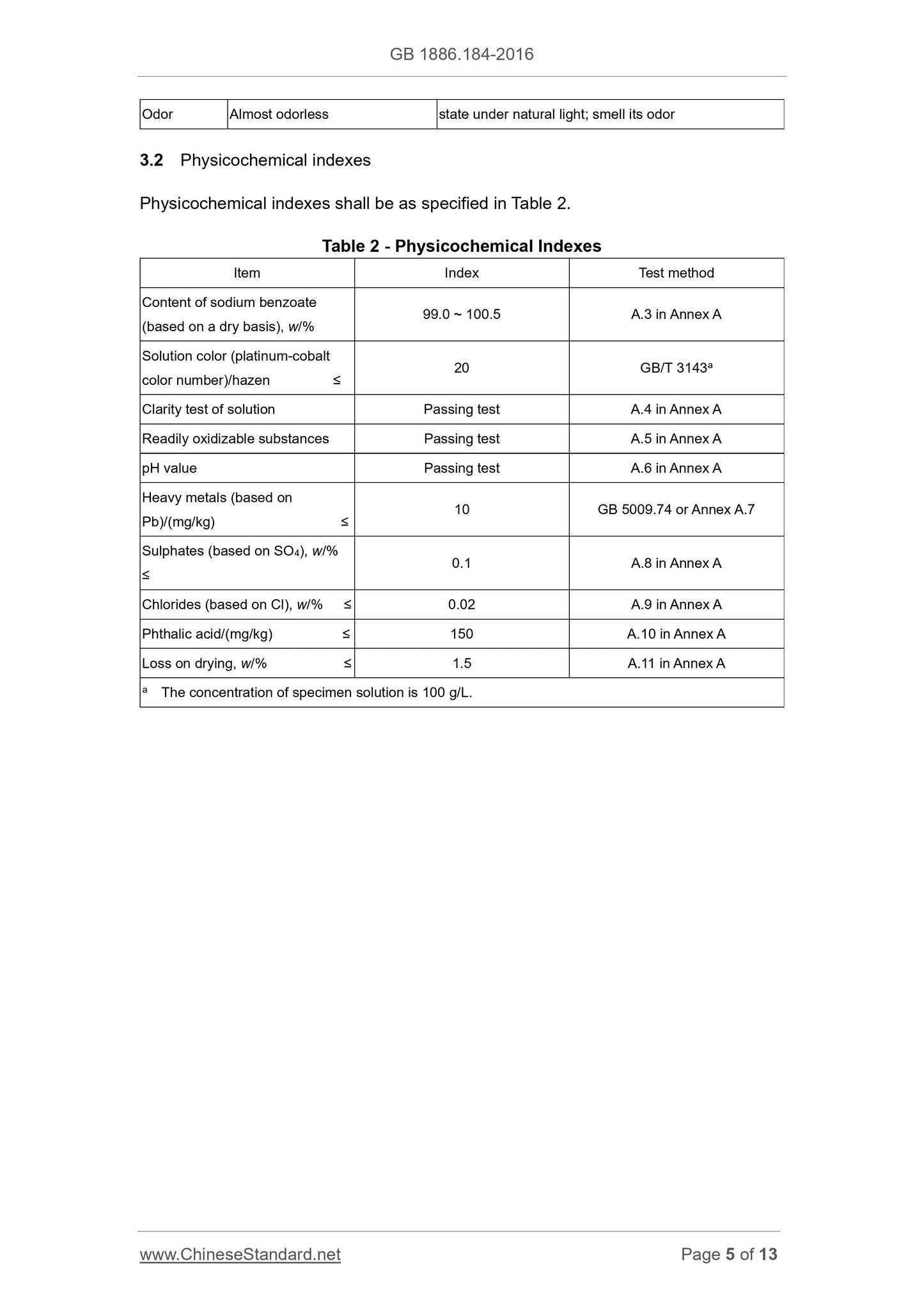
3 Technical Requirements
3.1 Sensory requirements
Sensory requirements shall be as specified in Table 1.
Table 1 – Sensory Requirements
Item Requirement Test method
Color White Take an appropriate amount of specimen to place on a
clean, dry white porcelain dish; observe its color and State Granules or crystalline powder
Annex A
Test Methods
A.1 General
Unless specified otherwise, all reagents and water used in this Standard are
analytically pure reagents and grade 3 water specified in GB/T 6682. Unless specified
otherwise, all standard solutions used in tests, standard solutions used for the
determination of impurities, preparations and products are prepared as specified in
GB/T 601, GB/T 602, GB/T 603. A solution used in test refers to an aqueous solution
if the solvents used for its preparation are not specified.
A.2 Identification test
A.2.1 Reagents and materials
A.2.1.1 Hydrochloric acid solution. 1 + 2.
A.2.1.2 Ferric chloride solution. 100 g/L.
A.2.2 Identification of benzoate anion
Add 1 drop of ferric trichloride solution in specimen solution (100 g/L) to generate
ochreous precipitates; add hydrochloric acid for acidification to separate white
precipitates.
A.2.3 Identification of sodium element
Weigh about 0.2 g of specimen to dissolve in 10 mL of water; use platinum wire to dip
hydrochloric acid solution to burn on a colorless flame until colorless; then dip a small
amount of test solution to burn on a colorless flame. The flame shall appear bright
yellow.
A.3 Determination of sodium benzoate content (based on a dry basis)
A.3.1 Method summary
Neutral reaction occurs between hydrochloric acid and sodium benzoate. Use benzoic
acid generated from ether extraction; then calculate the content of benzoic acid in
accordance with the consumption of hydrochloric acid standard titration solution.
A.3.2 Reagents and materials
A.3.2.1 Diethyl ether.
A.3.2.2 Hydrochloric acid standard titration solution. c(HCl) = 0.5 mol/L.
Weigh 1.0 g of specimen, accurate to 0.000 1 g; add 20 mL of water free of carbon
dioxide to dissolve; add 2 drops of phenolphthalein indicator solution. If the test solution
appears colorless, add 0.20 mL of sodium hydroxide standard titration solution and
then the test solution appears light red; if the test solution appears light red, add 0.20
mL of hydrochloric acid standard titration solution and then the light red color shall
disappear.
A.7 Determination of heavy metals (based on Pb)
A.7.1 Reagents and materials
A.7.1.1 Hydrochloric acid solution. 234 → 1 000. The content of HCl in this solution
shall be 9.5% ~ 10.5%.
A.7.1.2 Thioacetamide solution. take 4 g of thioacetamide; add water to dissolve; add
dropwise to 100 mL; store in a refrigerator. Take 5.0 mL of mixture (composite of 15.0
mL of 40 g/L sodium hydroxide solution, 5.0 mL of water and 20.0 mL of glycerine);
add 1.0 mL of thioacetamide solution; heat on a water bath for 20 s immediately before
use.
A.7.1.3 pH 3.5 acetate buffer solution. prepared as specified in GB 5009.74.
A.7.1.4 Lead standard working solution (10 μg/mL). prepared as specified in GB
5009.74.
A.7.2 Apparatus
Nessler tube. 25 mL.
A.7.3 Analytical procedure
A.7.3.1 A tube. take a Nessler tube; add 1.0 mL of lead standard working solution
and 2 mL of pH 3.5 acetate buffer solution before adding water to dilute to 25 mL.
A.7.3.2 B tube. take 2.0 g of specimen to place in a beaker; add 45 mL of water; keep
stirring; add dropwise 5 mL of hydrochloric acid before filtering; separate 25 mL of
filtrate and store in a Nessler tube.
A.7.3.3 C tube. take 1.0 g of specimen to place into a Nessler tube; add an
appropriate amount of water to dissolve; then add 1.0 mL of lead standard working
solution (10 μg/mL) and 2.0 mL of pH 3.5 acetate buffer solution before using water to
dilute to 25 mL.
A.7.3.4 Add separately 2 mL of thioacetamide test solution into three tubes, A, B and
C; shake up; store for 2 min; observe longitudinally from top to bottom on a white
background. If the chromaticity of C tube is not lighter than that of A tube and the
chromaticity of B tube is not darker than that of A tube, then it can be decided that the
content of heavy metals (based on Pb) is lower than 10 mg/kg.
Get QUOTATION in 1-minute: Click GB 1886.184-2016
Historical versions: GB 1886.184-2016
Preview True-PDF (Reload/Scroll if blank)
GB 1886.184-2016: Food additive -- Sodium benzoate
GB 1886.184-2016
GB
NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE
PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA
National Food Safety Standard –
Food Additive – Sodium Benzoate
食品添加剂 苯甲酸钠
ISSUED ON. AUGUST 31, 2016
IMPLEMENTED ON. JANUARY 1, 2017
Issued by. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the
People’s Republic of China
Table of Contents
Foreword ... 3
1 Application Scope ... 4
2 Structural Formula, Molecular Formula and Relative Molecular Mass ... 4
3 Technical Requirements ... 4
Annex A Test Methods ... 6
Foreword
This Standard replaces GB 1902-2005, Food Additive – Sodium Benzoate.
Compared with GB 1902-2005, the major changes of this Standard are as follows.
-- it changes the standard name into “National Food Safety Standard – Food
Additive – Sodium Benzoate”;
-- it deletes the item of arsenic;
-- it adds the item of phthalic acid;
-- it modifies the indexes of chlorides;
-- it adds the test method for heavy metals.
National Food Safety Standard –
Food Additive – Sodium Benzoate
1 Application Scope
This Standard applies to food additive sodium benzoate; the food additive is made
from benzoic acid which is reacted with sodium hydroxide or sodium bicarbonate.
Benzoic acid is made by catalytic oxidation of petroleum toluene; sodium hydroxide or
sodium bicarbonate is made with the method of ion exchange membrane.
2 Structural Formula, Molecular Formula and Relative
Molecular Mass
2.1 Structural formula
2.2 Molecular formula
C7H5O2Na
2.3 Relative molecular mass
144.11 (in accordance with International Standard Relative Atomic Masses 2011)
3 Technical Requirements
3.1 Sensory requirements
Sensory requirements shall be as specified in Table 1.
Table 1 – Sensory Requirements
Item Requirement Test method
Color White Take an appropriate amount of specimen to place on a
clean, dry white porcelain dish; observe its color and State Granules or crystalline powder
Annex A
Test Methods
A.1 General
Unless specified otherwise, all reagents and water used in this Standard are
analytically pure reagents and grade 3 water specified in GB/T 6682. Unless specified
otherwise, all standard solutions used in tests, standard solutions used for the
determination of impurities, preparations and products are prepared as specified in
GB/T 601, GB/T 602, GB/T 603. A solution used in test refers to an aqueous solution
if the solvents used for its preparation are not specified.
A.2 Identification test
A.2.1 Reagents and materials
A.2.1.1 Hydrochloric acid solution. 1 + 2.
A.2.1.2 Ferric chloride solution. 100 g/L.
A.2.2 Identification of benzoate anion
Add 1 drop of ferric trichloride solution in specimen solution (100 g/L) to generate
ochreous precipitates; add hydrochloric acid for acidification to separate white
precipitates.
A.2.3 Identification of sodium element
Weigh about 0.2 g of specimen to dissolve in 10 mL of water; use platinum wire to dip
hydrochloric acid solution to burn on a colorless flame until colorless; then dip a small
amount of test solution to burn on a colorless flame. The flame shall appear bright
yellow.
A.3 Determination of sodium benzoate content (based on a dry basis)
A.3.1 Method summary
Neutral reaction occurs between hydrochloric acid and sodium benzoate. Use benzoic
acid generated from ether extraction; then calculate the content of benzoic acid in
accordance with the consumption of hydrochloric acid standard titration solution.
A.3.2 Reagents and materials
A.3.2.1 Diethyl ether.
A.3.2.2 Hydrochloric acid standard titration solution. c(HCl) = 0.5 mol/L.
Weigh 1.0 g of specimen, accurate to 0.000 1 g; add 20 mL of water free of carbon
dioxide to dissolve; add 2 drops of phenolphthalein indicator solution. If the test solution
appears colorless, add 0.20 mL of sodium hydroxide standard titration solution and
then the test solution appears light red; if the test solution appears light red, add 0.20
mL of hydrochloric acid standard titration solution and then the light red color shall
disappear.
A.7 Determination of heavy metals (based on Pb)
A.7.1 Reagents and materials
A.7.1.1 Hydrochloric acid solution. 234 → 1 000. The content of HCl in this solution
shall be 9.5% ~ 10.5%.
A.7.1.2 Thioacetamide solution. take 4 g of thioacetamide; add water to dissolve; add
dropwise to 100 mL; store in a refrigerator. Take 5.0 mL of mixture (composite of 15.0
mL of 40 g/L sodium hydroxide solution, 5.0 mL of water and 20.0 mL of glycerine);
add 1.0 mL of thioacetamide solution; heat on a water bath for 20 s immediately before
use.
A.7.1.3 pH 3.5 acetate buffer solution. prepared as specified in GB 5009.74.
A.7.1.4 Lead standard working solution (10 μg/mL). prepared as specified in GB
5009.74.
A.7.2 Apparatus
Nessler tube. 25 mL.
A.7.3 Analytical procedure
A.7.3.1 A tube. take a Nessler tube; add 1.0 mL of lead standard working solution
and 2 mL of pH 3.5 acetate buffer solution before adding water to dilute to 25 mL.
A.7.3.2 B tube. take 2.0 g of specimen to place in a beaker; add 45 mL of water; keep
stirring; add dropwise 5 mL of hydrochloric acid before filtering; separate 25 mL of
filtrate and store in a Nessler tube.
A.7.3.3 C tube. take 1.0 g of specimen to place into a Nessler tube; add an
appropriate amount of water to dissolve; then add 1.0 mL of lead standard working
solution (10 μg/mL) and 2.0 mL of pH 3.5 acetate buffer solution before using water to
dilute to 25 mL.
A.7.3.4 Add separately 2 mL of thioacetamide test solution into three tubes, A, B and
C; shake up; store for 2 min; observe longitudinally from top to bottom on a white
background. If the chromaticity of C tube is not lighter than that of A tube and the
chromaticity of B tube is not darker than that of A tube, then it can be decided that the
content of heavy metals (based on Pb) is lower than 10 mg/kg.
Share